01 - Tree of life pt 1
1/41
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
5 majors groups of plant
bryophytes
lycophytes
ferns
gymnosperms
angiosperms
which group of plants has the most species
angiosperms
what evolved first
bacteria aroun 3700 million years ago
major evolution or plants.
when green algae evolved in water
middle of proterozoic era
around 1200 miilion years ago
green algae
ancestors of plants
what did green algae give rise to
gave rise to bryophytes
types of bryophytes
liverworts
mosses
hornworts
smallest to biggest species of bryophytes
least - hornworts
liverworts
most - mosses
oldest to newest species of bryophytes
oldest - liverworts
mosses
newest - hornworts
how do liverworts look like
often flattened
when liverworts reproduce what are they knwon as
F - archegonia
M - antheridia
how do mosses look like
very diverse and heterogeneous
lots of different sizes and shape
how do hornworts look
simmilar to liver worts
“flattened body“
what happens when hornworts reproduce
when they reproduce they produce horns
characteristics of bryophytes
Lack vascular systems (no xylem or phloem)
No true roots, only rhizoids
Small in size
Limited or no cuticle
Dependence on wet environments for survival
different life cycles
consequences of no vascular system
no structural support or backbones
typically small
harder to move materials cuz no systems
Mosses and liverworts typically are small → cell-to-cell passive H2O diffusion
rhizoids
tiny filamentous ‘roots‘
pros and cons of rhizoids
• Good enough for anchoring
• Not great for uptake resources
• No vascular tissue, so nutrients move very slowly
pros and cons of No or very limited cuticle
cuticles usually seals cells and make sure water stays and doesn’t evaporate
• Quick loss & uptake of water along whole surface
• Adapted to survive total desiccation (very moist env)
what environment do bryophytes like
wet
imperfect adaptation of bryophytes
no cuticle → lose water very quickly
no vascular system → do not transport water/nutrients very efficidnetly
generilized alternation of generation
haploid
meiosis
spores
mitosis
gametophytes
mitosis
gametes (egg and sperm)
fertilization
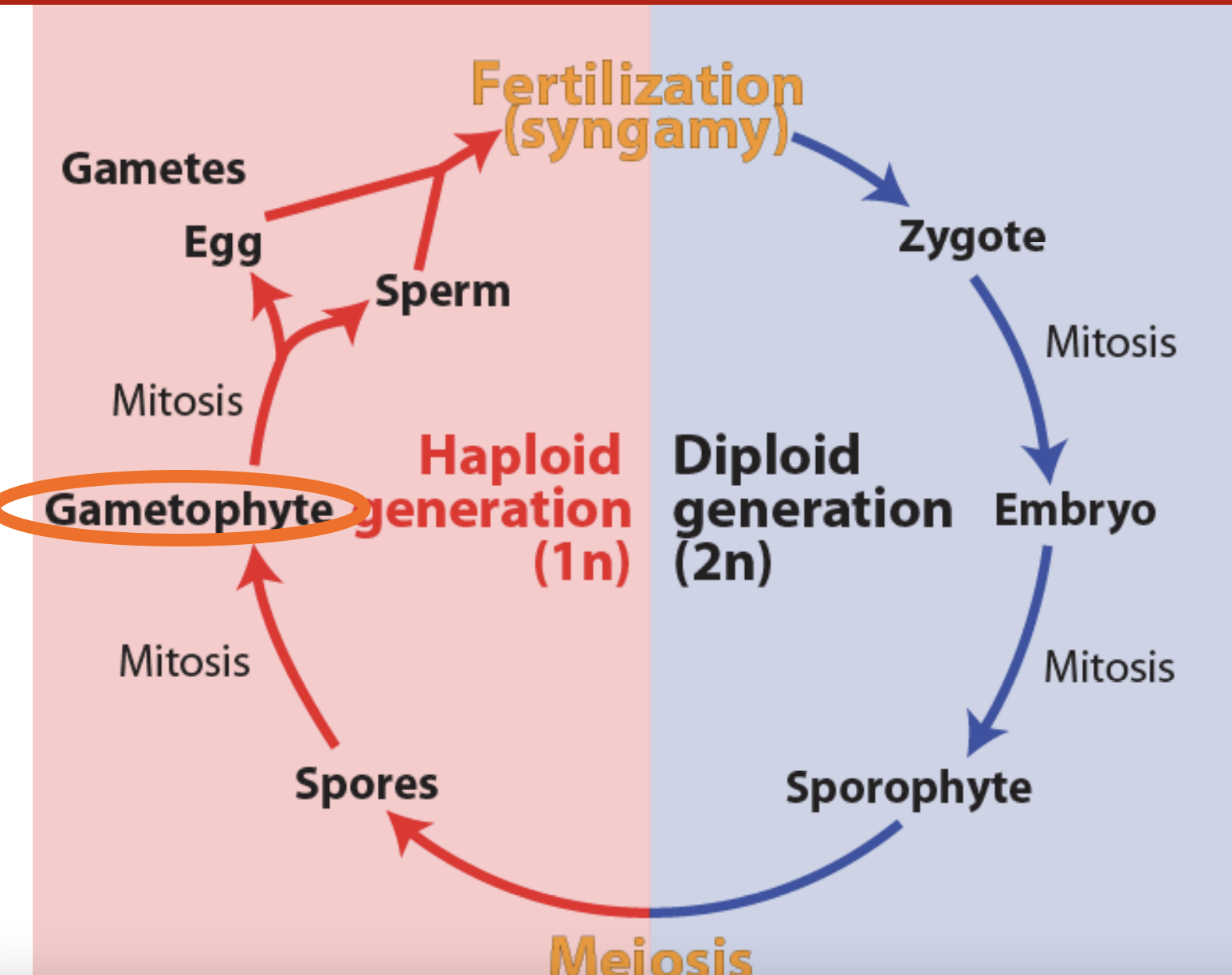
generilized alternation of generation
diploid
fertilization
zygote
mitosis
embryo
mitosis
sporophyte
meiosis
spermatozoids
Self-propelled in H2O (multiple flagellae)
how does fertilization work for bryophytes (mosses)
Spermatozoids: Typical swimming distance: 2m
Chemotaxis!
chemically smell and taist environemnet
How do bryophytes take up water?
Through their shoots, leaves and rhizoids
What is the name of the reproductive structure on a female gametophyte in bryophytes?
Archegonium
In bryophytes, spermatozoids are produced in the
Antheridium
What is the name of the structure supporting the spore capsule?
Seta
cuticle
This thin layer is used in the vast majority of plants to seal leaves against desiccation.
It is a hydrophobic layer.
What is the name of the reproductive structure on a male gametophyte in bryophytes?
Antheridium
what is diploid in the Life cycle of bryophytes (mosses)
Seta
Sporophyte
Wall of spore capsule
how do spores release
often explosive spore release
what is haploid in the Life cycle of bryophytes (mosses)
Antheridium
Archegonium
Egg cell
Gametophyte
Protonema
Spermatazoid
spore
Which generation is short-lived in bryophytes?
The diploid one
Sporophyte
Which generation is long-lived in bryophytes?
The haploid one
gametophyte
Which unit of the following life cycle is wind dispersed?
spores
Which unit of the following life cycle is self propelled ?
spermatozoid
Which of the following are photosynthetic in a moss?
Gametophyte
Protonema
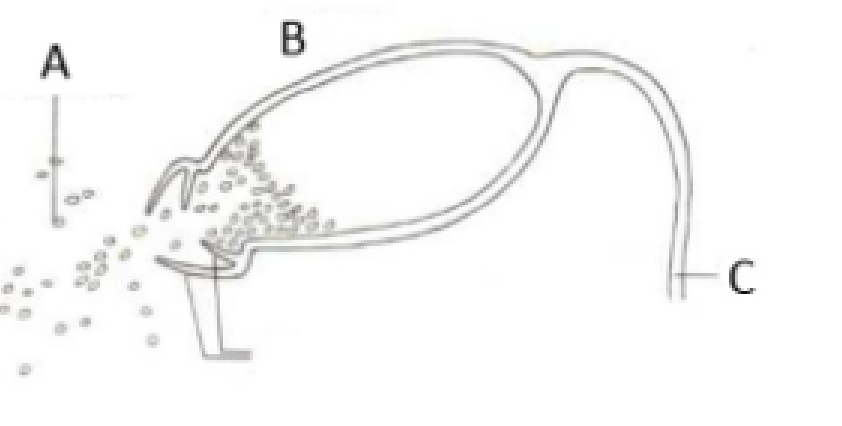
a = spores
b = capsule
c = seta
In bryophytes, the haploid egg cell is contained in the ...
Archegonium
What is the name of the structure from which female and male gametophytes grow in bryophytes?
Protonema