UF MCB3020 EXAM 2 Bacusmo
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
What is the most common mechanism for bacterial cell division?
Binary Fission
List the four steps of the mechanism above.
1. Elongation of the cell
2. Replication of the chromosome
3. Separation of the chromosomes into the two parts of the cell
4. Formation of septum in the middle (Cytokinesis, or septation)
Define 'Origin of replication'.
Where replication begins
How many Origins of replication do bacterial chromosomes have?
One
What is Cytokinesis? Include a brief overview of its four steps.
The division of the cell into two via formation of a cross wall between the two daughter cells.
Define the following terms and their role in cell division:
Penicillin-binding protein (PBP):
Group of proteins that hydrolyze bonds in existing peptidoglycan strands and link together new strands.
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM):
Major components of peptidoglycan that bind to a membrane protein called bactoprenol.
Autolysins:
Degrade polypeptide where new units are to be added, and the new NAM-NAG units can then be inserted into the peptidoglycan layer.
What is crescentin?
A homologue of eukaryotic intermediate filaments
What are the other forms of asexual reproduction? Define each
-Budding: Budding off daughter cells; seen in Listeria monocytogenes
-Baeocyte formation (multiple fission): Multiple rounds of cell division; seen in Cyanobacteria
-Spore formation: Form multinucleoid filaments that ultimately divide to produce spores with a single nucleus.
Know the Bacterial Growth Curve
lag,log,stationary,dead
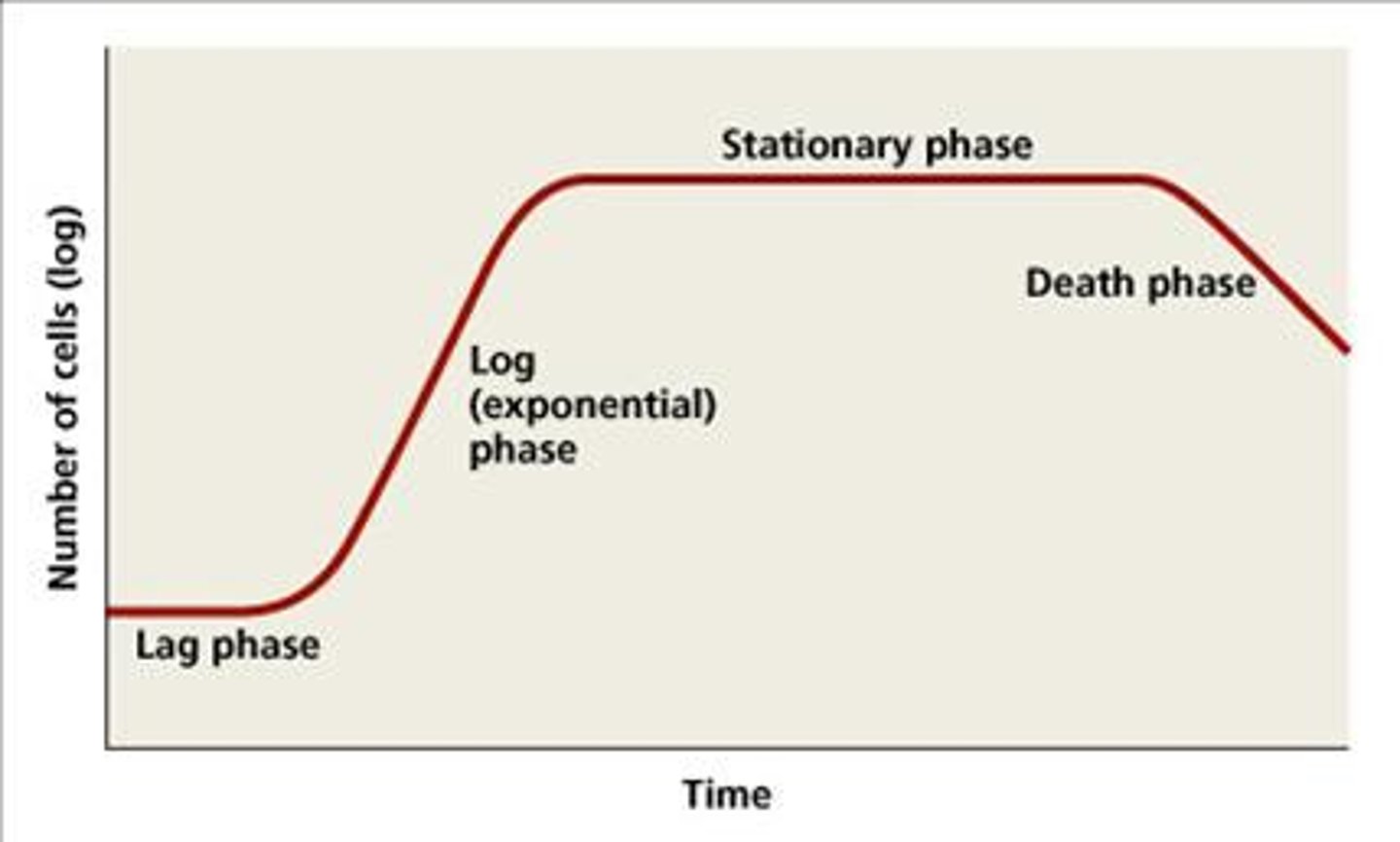
List and define each phase of the above curve.
-Lag Phase: No net growth because, although the nutrients are abundant, the bacteria are adjusting to new conditions.
-Log (Exponential) Phase: Nutrients are abundant, and bacteria divide at their highest rate.
-Stationary Phase: Number of viable microorganisms is stable because the nutrients level off and waste products accumulate
-Death Phase: Nutrients are depleted, and levels of waste products and toxins are high, so the number of viable microorganisms decreases
-Long-term Stationary Phase: Nutrients are depleted, and waves of genetic variants come and go
True or False: When nutrient levels are low, the limitation of microbial growth occurs as a result of the saturation of transport proteins for nutrient uptake.
False; should be when levels are high
What is generation time (GT)?
The time it takes the population to double
What phase is it best to calculate GT?
Log Phase (aka Exponential Phase)
True or False: Cells typically exist in aqueous conditions.
true
Define hypertonic and hypotonic.
Hypertonic: One solution has higher concentration of solutes than another
Hypotonic: One solution has lower concentration of solutes than another
If a cell is in a hypertonic solution it will ____, while in a hypotonic solution it will ____.
Shrink; Burst
What are the three distinct cardinal growth temperatures for organisms?
1. Minimum growth temperature: Lowest temperature at which an organism can grow and survive
2. Maximum growth temperature: Highest temperature at which an organism can grow and survive
3. Optimal growth temperature: Most suitable temperature for bacterial growth
Know the following microbial adaptations. Define each.
Halophiles
Grow best in extremely salty environments
b. Xerophiles:
Grow best in dry conditions
c. Psychrophiles:
Grow between 0C and 20C - refrigeration temperatures
d. Mesophiles:
Grow between 20C and 45C
e. Thermophiles:
Grow between 55C and 85C
f. Hyperthermophiles:
Grow between 85C and 113C - usually archaens
g. Aerobe:
Grow in presence of atmospheric oxygen
h. Obligate Aerobes:
Require oxygen for growth and die without it
i. Anaerobe:
Grow in absence of oxygen
j. Obligate Anaerobes:
Cannot survive in presence of oxygen
k. Facultative Anaerobes:
Grow better with oxygen than without it (not needed)
l. Barotolerant:
Survive increased pressures
True or False: Most human pathogens are Mesophiles.
TRUE
When does food spoilage occur?
Occurs when nutritional value, texture, or flavor of food is changed due to presence of food spoilage organisms.
True or False: Only a select few of our foods contain food spoilage microorganisms.
False; All of our foods do
What are the three most common food spoilage organisms?
Bacteria, yeasts, and molds
How is food spoilage controlled?
By manipulating temperature
Define the term sessile.
Microorganisms that grows attached to a surface rather than floating freely (planktonic growth).
What do sessile microorganisms form? Define this structure.
Biofilm: a complex of slime-enclosed colonies that stick to each other on a surface.
Why does Dr. Bacusmo describe the structure above as an "ecosystem on its own"?
Biofilm because a mature biofilm has a heterogenous community of microorganisms that differ in metabolic activity and physiology.
True or False: Biofilms form only on non-living surfaces, such as medical devices.
False: They can also form on living surfaces
What is Quorum Sensing?
A strategy in which bacteria coordinate the expression of certain genes based on their population density.
Define and rank these terms from most to least biocidal: Antisepsis, Disinfection, Sanitization, Sterilization
1) Sterilization: refers to the removal or destruction of all viable microorganisms in the medium
2) Disinfection: involves killing, removing, or inhibiting disease-causing organisms in medium.
3) Sanitization: involves removing microbial populations to "safe" levels, according to public health standards.
4) Antisepsis: involves preventing infection of living tissue from microorganisms
A -_____________ agent is one that kills microorganisms; for example, _______________ kill bacteria.
Cidal; Bactericidal
A -_______________ agent is one the inhibits the growth of microorganisms; for example, ___________________ inhibits the growth of bacteria.
Static; Bacteriostatic
____________ populations take longer to kill than ___________ populations when exposed to a lethal agent.
Larger; Smaller
True or False: Overall death rate decreases as the population gets smaller.
True
Filtration techniques allow scientists to selectively remove microbes based on their ___________.
Size
What microorganism are membrane filters not able to remove?
Viruses
Name an example of an air filter.
Surgical masks and cotton plugs on culture vesicles.
What two physical control methods that destroy microorganisms?
Heat and Radiation
*NOTE: Radiation is used for disinfecting items that are soft and/or plastic*
Define the following physical agents that are used to destroy microorganisms and provide one example:
Moist- heat sterilization:
Exposure to heat at temperatures above 100C destroys viruses, fungi, and bacteria; Autoclave
b.) Pasteurization:
Treating heat-sensitive beverages at controlled heating temperatures well below their boiling points; milk and beer
c.) Dry-heat sterilization:
Requires higher temperatures and longer exposure times to oxidize cell constituents and denture proteins; Bench top incinerators
d.) Ionizing radiation:
Gamma radiation penetrates deep into objects (remove atoms creating free radicals) destroying bacterial endospores; sterilization and pasteurization of antibiotics, hormones, sutures, plastic supplies, and food
e.) Ultraviolet radiation:
Causes thymine dimers to prevent replication and transcription; surface sterilization.
Pasteurization ________ spoilage by reducing total load of organisms' present, but does not sterilize.
slows
True or False: Ionizing radiation is effective against all microorganisms.
False; not always effective against viruses
What UV wavelength is the most bactericidal?
260 nm
What is chemotherapy?
The use of chemicals to kill microorganisms or inhibit their growth within host tissue.
1. Define the following disinfectants and antiseptics:
Phenolics:
Denature proteins and disrupt cell membranes, commonly used in labs and hospitals; example is Orthocresol.
b.) Alcohols:
Dissolve membrane lipids and denature proteins
c. Halogens:
Most important are Iodine and Chlorine. Iodine - skin antiseptic; Chlorine - municipal water supply
d.) Heavy metals:
Once used as germicides to inactivate proteins (includes ions of mercury, silver, arsenic, zinc, and copper)
e.) Quaternary ammonium compounds:
Antimicrobial detergents that have the ability to denature proteins and disrupt microbial membranes
f.) Sterilizing gases:
Ethylene oxide gas kills microbes and spores and it is primarily used to sterilize heat-sensitive materials
Why are heavy metals not used today?
Have a high degree of toxicity
What is an Antimicrobial detergent?
An organic cleansing agent that are amphipathic (meaning both hydrophilic and hydrophobic components).
What are the two most important alcohol germicides?
Ethanol and Isopropanol
What three factors influence the efficiency of antimicrobial agents?
Concentration of the agent, duration of exposure, and temperature
What is the genetic material?
DNA
Define a genome.
The entire set of DNA present in a cell or virus
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype: Specific sets of genes
Phenotype: Collection of observable characteristics
What are the three ways Frederick Griffith demonstrated transformation in his experiments?
1- Introduced living, encapsulated cells to mice and observed that the mice died
2- Introduced living, non-encapsulated cells and heat-killed encapsulated cell to mice and observed that the mice lived
3- Introduced both heat-killed encapsulated cells and living, non-encapsulated cells into mice and observed that the mice died. He was also able to isolate living, encapsulated cells from the dead mice.
What is transformation?
The ability of organisms to take up DNA from environment
True or False: DNA and RNA are nucleic acids.
true
What is the structure of a nucleotide vs nucleoside?
Nucleoside: A pentose sugar attached to a nitrogenous base.
Nucleotide: A pentose sugar attached to a nitrogenous base and phosphate group.
What bond binds nucleotides?
Phosphodiester bonds
What are the 4 differences between DNA and RNA?
1- DNA has a deoxyribose sugar, while RNA has a ribose sugar
2- DNA has a Thymine, while RNA has Uracil
3- DNA is usually double stranded, RNA is usually single stranded
4- RNA has a larger set of functions (i.e., mRNA, tRNA, & rRNA)
What is a Pyrimidine? Name them.
Pyrimidines are nitrogenous bases with one ring structures
These include Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil
What is a Purine? Name them.
Purines are nitrogenous bases with double-ring structures
These include Adenine and Guanine
** REMEMBER: Pure As Gold (Purine = Adenine and Guanine)
1. Describe the role of the following:
mRNA:
Carries genetic information to the ribosome, which is used to make proteins
b.) tRNA:
Binds to mRNA sequences to carry specific Amino Acids to growing polypeptide chain during translation
c.) rRNA:
Structural component of Ribosomes that sometimes acts as a catalyst
True or False: DNA strands run parallel to each other.
False; They run antiparallel
True or False: Covalent bonding is stronger than Hydrogen boding.
True; Hydrogen bonds are easily broken and made
A single turn of the helix stretches for about _____ nm and consists of _______ base pairs per helical period.
3.4nm; 10 base pairs
Major and minor grooves result from __________.
Asymmetrical spacing of the backbones of the DNA double helix
What is Chargaff's rule?
The amount of Guanine in DNA is equal to the amount of Cytosine and the amount of Adenine in DNA is equal to the amount of Thymine.
True or False: DNA sequences with more Adenine and Thymine bonds are more stable.
False, Adenine and Thymine are held by 2 hydrogen bonds, while Guanine and Cytosine is held together by 3 hydrogen bonds. Therefore, more G and C bonds make a more stable sequence.
Know the structure of DNA
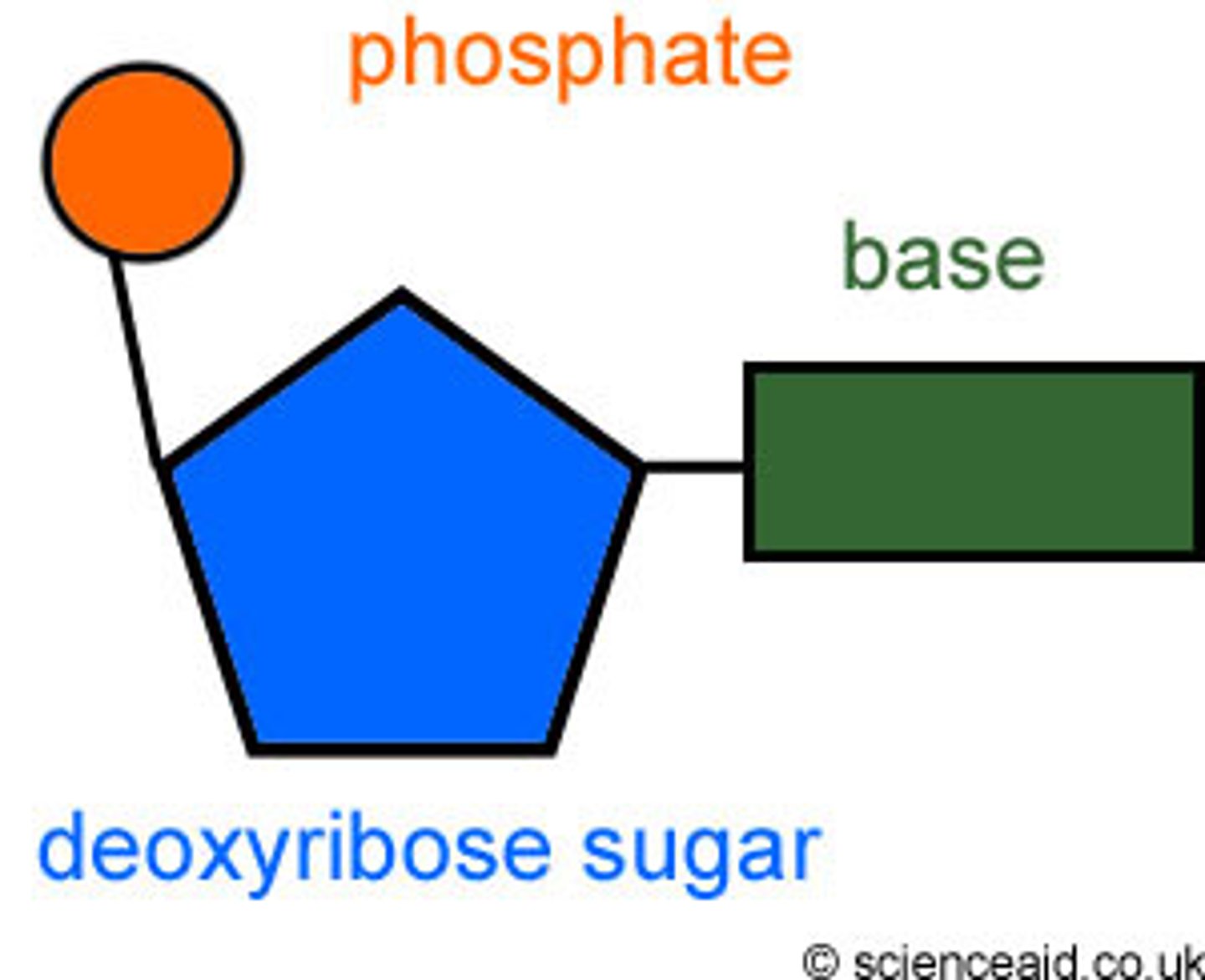
True or False: Proteins are polymers of nucleic acids.
False, Proteins are polymers of amino acids.
What is the structure of an amino acid?
Made up of a central alpha carbon surrounded by an amino group, a carboxyl group on the end, and a variable side group (R).
What is a peptide bond?
Covalent bonds between amino acids in proteins and are formed by a dehydration reaction
What direction does polymerization occur in?
Occurs from the N terminal to the C terminal
Define Transcription and Translation.
Transcription: Information from DNA is transferred to the mRNA in the nucleus
Translation: The process in which a ribosomal complex attaches to the mRNA to form a polypeptide
Recall central dogma
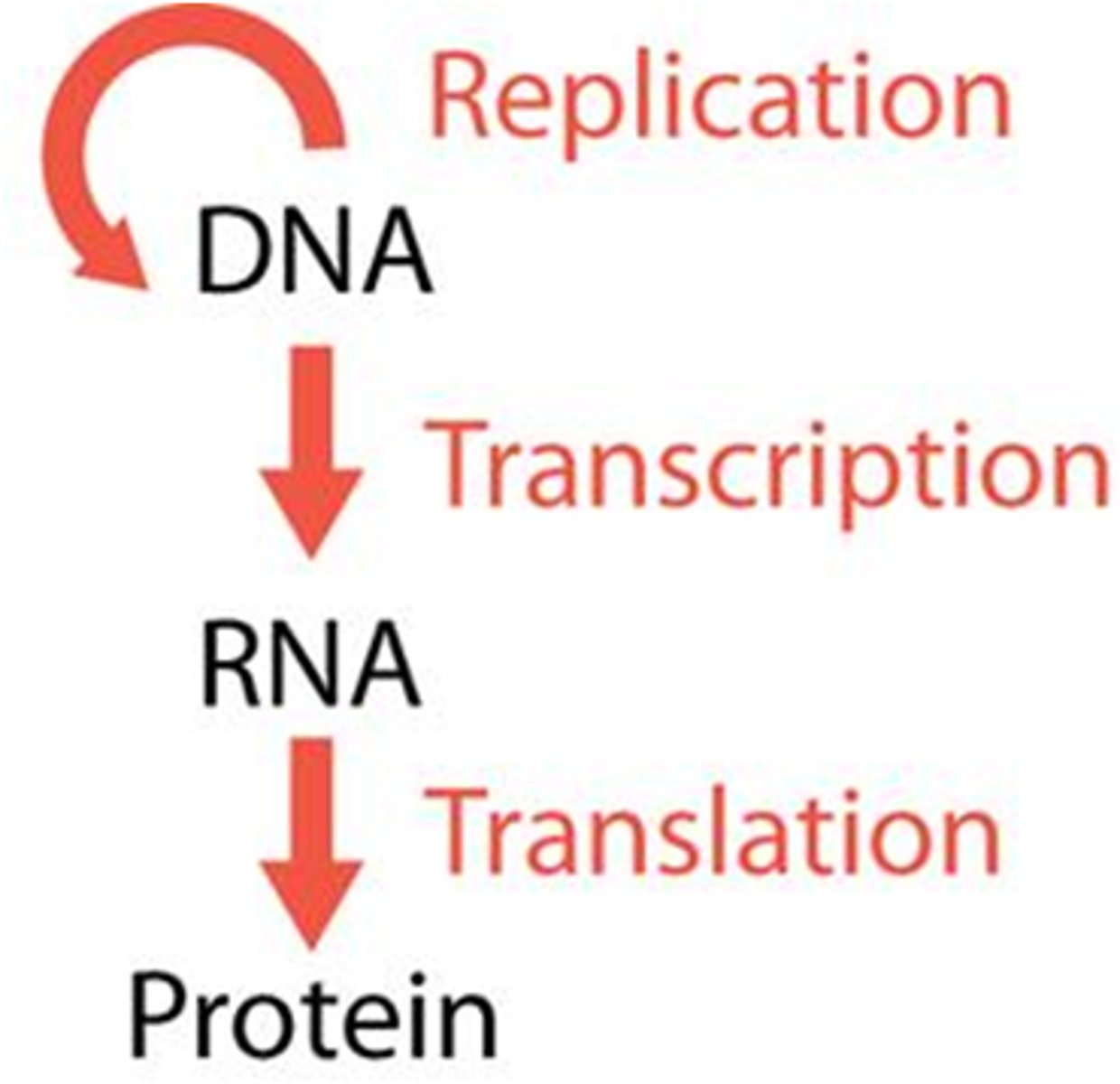
True or False: DNA replication is conservative.
False, DNA replication is Semi-conservative.
Describe the following types of replication:
Conservative model:
One daughter DNA molecule is all new and the other is all old DNA
b. Semi-conservative model
Each daughter DNA molecule contains one new strand and one old strand
c. Dispersive model
Each daughter DNA molecule contains a mixture of old and new DNA