APES I Cycles and Chemical Equations
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
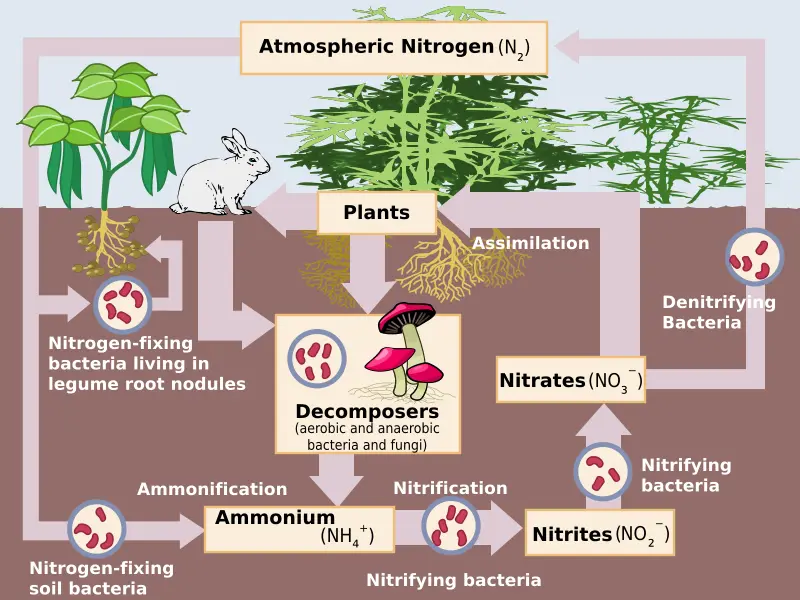
Describe the nitrogen cycle
Nitrogen fixation: converts nitrogen gas into a usable form
bacteria in plant roots (bush beans)
Nitrification: ammonia and other compounds become nitrite (NO2) and nitrate (NO3)
bacteria in soil and water
Assimilation: nitrogen is in a usable form and is incorporated into proteins, DNA, and other biomolecules
absorbed by plant tissues
synthesized by consumers
runoff into ocean
Denitrification: return nitrogen to the atmosphere
bacteria convert nitrate into nitrous oxide (N2O) and then into nitrogen gas (N2)
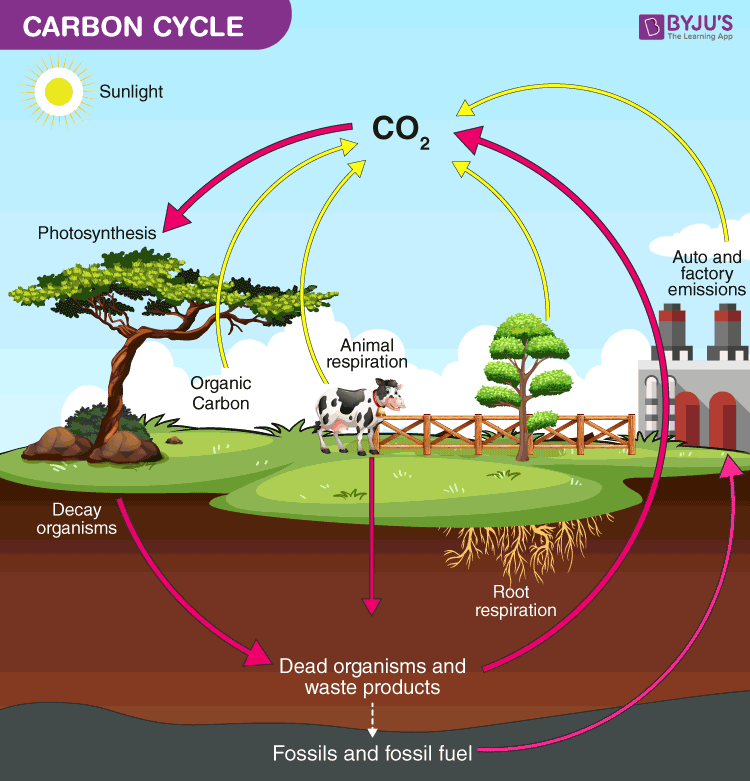
Describe the carbon cycle
Carbon in atmosphere is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis (carbon sequestration)
Plants eaten by animals and carbon is bioaccumulated into their bodies
Plants + animals die and decompose, releasing carbon into the atmosphere
Some carbon becomes fossil fuels
Burning fossil fuels adds more oxygen into the atmosphere
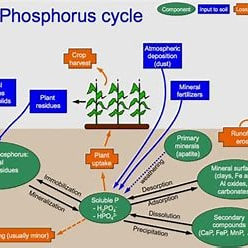
Describe the phosphorus cycle
Weathering
Absorption by plants
Animals eat plants and absorb the phosphorus
Decomposition releases phosphorus back into the soil
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Equations
CFC’s+UV = Cl-
Cl- + O3 = ClO + O2
ClO + O- = Cl- +O2
Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Explanation
CFCS are broken down by UV rays into Cl-. The free Chlorine bonds Ozone and makes ClO + O2. The cycle then repeats and chlorine doesn’t allow the free O2 molecule to bond another oxygen atom.
Stratospheric Ozone Formation Equations
O- + O2 =O3
O3+UV=O- +O2
Stratospheric Ozone Formation Explanation
A free O (oxygen) atom bonds with an O2 (oxygen molecule) and makes stratospheric ozone. The O3 is then broken apart by UV rays into O2 and O- and the free O- bonds to another O2 and creates more O3. The cycle Repeats.
Tropospheric ozone formation explanation
Ultraviolet sunlight breaks apart an oxygen molecule to form two separate oxygen atoms. In the second step, each atom then undergoes a binding collision with another oxygen molecule to form an ozone molecule.