[anat] e1 back muscles and vertebrae
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
compartmentalize (extrinsic and intrinsic) and function
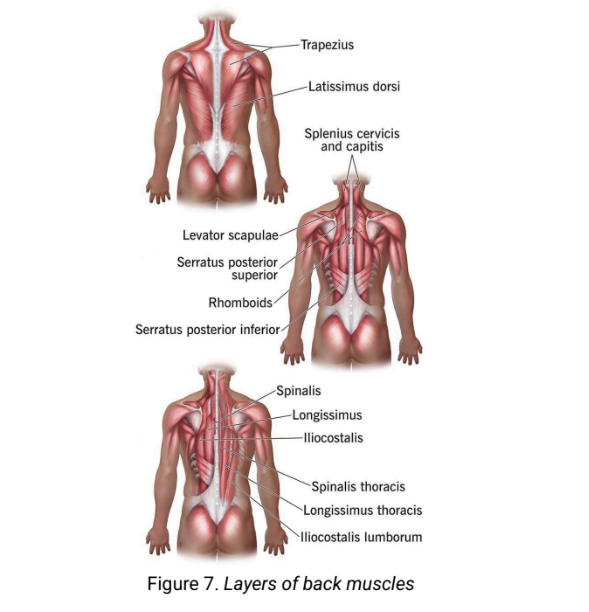
[muscles of the back] - back muscles are categorized into two layers.
extrinsic muscles
[muscles of the back] - these are muscles that are more external and the movements are noticeable.
superficial extrinsic back muscles
[muscles of the back] extrinsic muscles - they connect the upper limb to the trunk and facilitate its movement. it contains the trapezius, latissmus dorsi and levator scapulae.
intermediate extrinsic back muscles
[muscles of the back] extrinsic muscles - these are superficial respiratory muscles that are supploed by the intercostal nerves.
serratus posterior superior
[muscles of the back] extrinsic muscles - innervated by the 2nd to 5th intercostal nerves. helps you breathe in.
serratus posterior inferior
[muscles of the back] extrinsic muscles - innervated by the 9th to 12 intercostal nerves. it helps you breathe out.
superficial respiratory muscle
[muscles of the back] extrinsic muscles - assists in respiration.
diaphragm
it is the main muscle for respiration.
intrinsic muscle
[muscles of the back] these are deep muscles of the back proper. supplied by the posterior primary rami of spinal nerves. it maintains posture and control movement. thicker than extrinsic muscle.
anterior rami
[muscles of the back] intrinsic muscles - supplies all the nerve and sensory nerve of the front body.
posterior rami
[muscles of the back] intrinsic muscles - innervation of the skin of the back and back itself.
superficial intrinsic muscle
[muscles of the back] intrinsic muscles - includes splenius cervices and splenius capitis
intermediate intrinsic back muscle
[muscles of the back] intrinsic muscles - includes erector spinae (main back muscle). actions are bilateral (extend head and neck from flexion) and unilateral (laterally flex vertebral column).
erector spinae
[muscles of the back] intrinsic muscles - it is the main back muscle. it is also the MOST IMPORTANT. it is hard to see bc it is deep in the back.
(i love spine) iliocostalis (lateral column), longissimus (intermediate column), spinalis (medial column)
[muscles of the back] intrinsic muscles - the erector spinae is divided into three columns.
deep intrinsic back muscles
[muscles of the back] deep intrinsic muscles - these are group of muscles that lie deep to the erector spinae. this stabilizes the spine and for proprioception.
major deep layer and minor deep layer
[muscles of the back] deep intrinsic muscles - the deep intrinsic back muscle is divided into two layers which are ___ and ___.
semispinalis, multifidus, rotators
[muscles of the back] deep intrinsic muscles - the major deep layer group of the deep intrinsic back muscles includes the ____, ___ and ____.
interspinales, intertransversarii, levatores costarum
[muscles of the back] deep intrinsic muscles - the minor deep layer group of the deep intrinsic back muscles includes the ____, ___ and ____.
trapezius, latissimus dorsi, splenius cervicis and capitis, levator scapulae, serratus posterior superior, rhomboids, serratus posterior inferior, spinalis, longissimus, llicostalis, spinalis thoracis, llicostalis lumborum
label the layers of back muscles
spine/ vertebral column
[the spine / vertebral column] - most significant functional unit for general movement. these are complex structure of bones. also known as the spinal, vertebral column and backbone. (approx. 33 bones)
spinal cord
[the spine / vertebral column] - it is the extension of the brain, made of lengthy nerves and relays information to the muscle.
spinal/ vertebral column
[the spine / vertebral column] - connected and stacked column of bones from the base of the skull to lower back. it is made of vertebrates.
body structure and support, protects the spinal cord, allows to bend and flexibility
[the spine / vertebral column] - these are the functions of spine/ vertebral column.
7 cervical vertebrae
[the spine / vertebral column] composition - it develops when infant start to lift their heads (neck)
12 thoracic vertebrae
[the spine / vertebral column] composition - this articulates with the ribs (upper back).
5 lumbar vertebrae
[the spine / vertebral column] composition - this develops in response (lower back).
sacrum
[the spine / vertebral column] composition - it has five fused vertebrae. includes pelvis
coccyx
[the spine / vertebral column] composition - it has 4-5 fused vertebrae.
kyphosis (kuba)
[the spine / vertebral column] abnormal curvature of the spine - c1 is in front. excessive posterior curvature of the thoracic region.
lordosis
[the spine / vertebral column] abnormal curvature of the spine - c1 is at the back. excessive anterior curvature of lumbar region.
scoliosis
dextroscoliosis = right
levoscoliosis = left
[the spine / vertebral column] abnormal curvature of the spine - most common. lateral deviation of spinal column. this involves thocacic and/or lumbar regions. can be c or s shaped.
note:
extreme abnormal curvature may compromise lung expansion.
illiac crest
[the spine / vertebral column] abnormal curvature of the spine - this is where doctors insert needles for anesthesias for pregnant women.
1 spinous process (most prominent / easy to palpate), 2 transverse process, 4 articulating facets (2 interior and 2 superior)
[the spine / vertebral column] vertebral body projections - these are the seven projections.
rounded vertebral body (anteriorly)
[the spine / vertebral column] part of typical vertebra - mainly for weight bearing.
vertebral arch (posteriorly)
[the spine / vertebral column] part of typical vertebra - for protection. this includes the cylindrical pedicles or walls and lamina or roof.
vertebral foramen / spinal canal
[the spine / vertebral column] part of typical vertebra - this houses the spinal cord.
spinous process
[the spine / vertebral column] part of typical vertebra - this is for muscle attachment. this is also the midline structure and the important insertion point for the back muscles.
transverse process
[the spine / vertebral column] part of typical vertebra - this is the lateral structure. articulate with ribs for thoracic, and it contains the foramen transversarium.
articular process / facet joints
[the spine / vertebral column] part of typical vertebra - this arise from junctions of laminae and pedicles. interaction of vertebras.
intervertebral foramen
[the spine / vertebral column] part of typical vertebra - this transmits spinal nerves from spinal cord and blood vessels. in between 2 individual vertebra.
facet joints (synovial) and intervertebral disc (symphysis)
[the spine / vertebral column] joints - the vertebral bodies are joined together by ___and ___.
joint movement
[the spine / vertebral column] joints - this is constituted between two joints.
intervertebral foramen
[the spine / vertebral column] joints - opening located between two vertebrae. this is also where spinal nerves exit
pinched nerve
[the spine / vertebral column] joints - this occurs when too much pressure is applied to a nerve.
intervertebral discs
[the spine / vertebral column] intervertebral discs joints - these are pads of fibrocartilage. this is the shock absorbers of the spine. (1/4 length of vertebral column) this is also the thickest in cervical and lumbar regions.
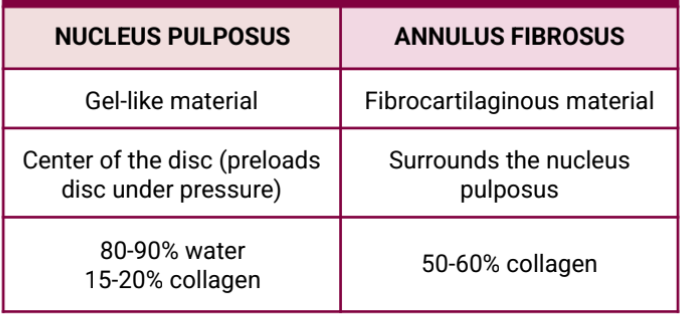
nucleus pulposus (gel-like) and annulus fibrosus (fibrocartilaginous)
[the spine / vertebral column] intervertebral discs joints - these are the two regions of vertebral disc.
anterior longitudinal ligament
[the spine / vertebral column] anterior portion motion ligaments - thicker than posterior longitudinal ligament. very dense and powerful. this attaches the anterior disc and vertebral body. this limits hypertension and vertebrae relative to each other.
posterior longitudinal ligament
[the spine / vertebral column] anterior portion motion ligaments - this travels inside the spinal canal. this connects to the posterior rim of vertebral bodies and disc. this also offers resistance to flexion.
ligamentum flavum
[the spine / vertebral column] posterior portion motion segments - this spans laminae to laminae. this is also very elastic thus aids in extension following trunk flexion.
supraspinous and interspinous
[the spine / vertebral column] posterior portion motion segments - this span spinous processes and resist shear and forward bending of the spine.
lumbar vertebra
[the spine / vertebral column] lumbar vertebra - largest vertebrae. oval-shaped. it has a total of (5).
superios articular process
[the spine / vertebral column] lumbar vertebra articular process - face up and down.
inferior articular process
[the spine / vertebral column] lumbar vertebra articular process - face down and out.
thoracic vertebra
[the spine / vertebral column] thoracic vertebra - it has a heart-shaped bodies. it has larger bodies but small vertebral foramen. it has ribs attached. and the transverse process is oriented outwards and upwards.
thoracic cage
[the spine / vertebral column] thoracic vertebra - this is one of the distinct feature of the thoracic vertebra.
cervical vertebra
[the spine / vertebral column] cervical vertebra - this consists of seven vertebrae. it forms the skeletal framework of the neck. situated between the skull and the thoracid vertebrae. SMALLEST.
jumped facets
[the spine / vertebral column] cervical vertebra -superior and inferior articular processes of the vertebrae becomes misaligned. this is often caused by trauma.
c1 vertebra: atlas
[the spine / vertebral column] cervical vertebra - this articulates with occipital condyles of the skull. it has no vertebral body.
c2 vertebra: axis
[the spine / vertebral column] cervical vertebra - this is the strongest cervical vertebra. this is larger and bulkier than c1.
c1-c2 complex
[the spine / vertebral column] cervical vertebra - atlas and axis fused together. blunt tooth-like projection.