Water Resources GWU Geog 2136 EXAM 1 pt.1
1/226
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
227 Terms
What is water important for?
60% of body weight, farmers/agriculture, engineers (predict flooding/bridges), transportation, governments, hydrologists.
Hydrology-Water Resources
Hydrology focuses on the global hydrologic cycle and the processes involved in the land phase of that cycle. Water resources refers to the water movement in the environment.
Who are the constituents of water?
intersection between government, scientists, conservationists, developers, and business interests
What percent of the total water in the hydrologic cycle is available to humans?
Less than 1%
What percent of the total water supply is freshwater?
2.5%
What percent of freshwater is accessible from lakes, rivers, soil moisture, and the atmosphere?
0.4%
Where are the other percentages of freshwater located?
74% in ice caps and glaciers, 25.6% in groundwater
What percent of the total water supply is sea water?
97.5%
How much of the world’s precipitation do oceans (79% of Earth’s surface) generate?
85%
Why is so much water being used for irrigation?
Crops are being forced to grow in areas where they would not traditionally grow/flourish.
Is the amount of precipitation evenly distributed throughout the world?
No
Where is precipitation the strongest?
Along the equator
Why is the population higher in areas with more precipitation?
Water is cycled and flows through rivers, so areas with more precipitation are easier to get to.
Why are EPA requirements on how much waste can be put into the river so important?
Cities take in water from rivers at the top of the city, and then release their wastewater back into the river at the bottom of the city. Then, the next city below that one will have to take in that wastewater because that water continues to flow downstream.
Where is the majority of water in a city?
It is cycling in and out through pipes because water is constantly needing to be available for washing hands, showering, etc.
How can you tell a change in water quality and ecology?
Change in water temperature
What is the most abundant molecule on Earth?
Water
What type of bond connects the atoms in a water molecule?
Covalent bond
What type of bond connects the water molecules together?
Hydrogen bond
How many electrons are present in an H2O molecule?
8
What are the atoms in a water molecule?
Two small hydrogen atoms, and one large oxygen atom
Which type of bond is stronger? By how much?
Covalent bond. 20x stronger than hydrogen bonds.
How does a hydrogen bond’s strength vary?
With temperature. Stronger when it is cold.
Which side of a H2O molecule has a positive charge?
Hydrogen side
Which side of a H2O molecule has a negative charge?
Oxygen side
What is cohesion?
Mutual attraction between water molecules, due to hydrogen bonds
What happens when a water molecule makes a physical phase change?
Its molecules arrange themselves in different patterns
What is the molecular structure in gases?
Random molecular structure
What is the molecular structure in liquids?
Semi-ordered molecular structure
What is the molecular structure in solids?
Ordered molecular structure
What happens to hydrogen bonds when the temperature is below 0 Celsius?
They lock in a hexagonal, lattice structure with air in the middle and expand.
How much does water expand when frozen?
15%
What percentage of hydrogen bonds break during melting?
15%
What happens to the lattice structure during melting?
The lattice partially collapses, and density increases because the liquid collapses and fills in the air pockets
Is water expanding when frozen an unusual property?
Yes - most solids are denser than liquids
What is density?
mass/volume
When does mass density in liquid form occur?
3.98 Celsius
Does sea level rise in frozen cold water as ice cubes/glaciers melt?
No, because the ice cubes/glaciers are already displacing the water
Does sea level rise in warmer water as ice cubes/glaciers melt?
Yes
How do temperature changes affect density in lakes?
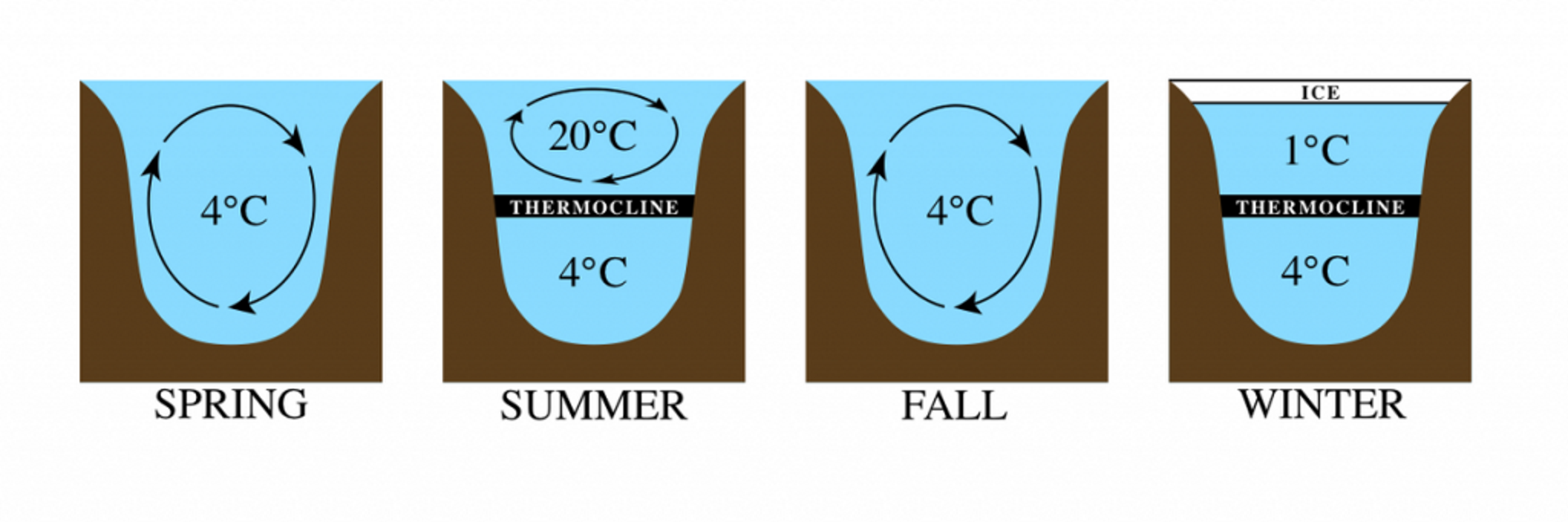
Changes in temperature cause a change in density, which causes lakes to turnover between seasons
What is lake turnover?
as ice melts, that water sinks to the bottom and allows the bottom water to come up, bringing up oxygen and nutrients.
How do lakes become oxygenated?
Lake turnover
Why can things still live below the ice level in a lake?
If ice was more dense than water, it would freeze at or to the bottom, which would crush everything below it after forming, and would never melt. Lake turnover and density changes prevent this.
Lake Turnover
What happens during evaporation at <100 Celsius?
Molecules at air-surface interface that have greater energy sever hydrogen bonds. These hydrogen bonds must break to convert from a liquid to a gas.
What happens when high energy molecules are removed?
The temperature is lowered. This is because the high energy (hotter) molecules are used to break the bonds, which escapes with it (known as latent heat).
What is temperature a measure of within a water structure?
The movement of the molecules
Does it take a lot of energy to move between states?
Yes, breaking all of the hydrogen bonds requires a lot of energy because the molecules want to stay together.
Sublimation
When a solid skips the liquid stage and transitions straight to a gas. Occurs at all temperatures and in ice.
What happens during evaporation at >100 Celsius?
Causes eventual break of all remaining bonds. Liquid to gas, mostly non-bonded individual molecules.
Condensation
Conversion of a gas to a liquid
Evaporation
Conversion of a liquid or solid state into a vapor
What happens during condensation?
As air gets close to the surface, the air gets colder and the water molecules will start to come together and form liquid on a surface. During this process, heat is released?
What does condensation form?
Clouds and dew on surfaces (particulates)
Surface tension
Unusual property of water. Molecules on the surface are subject to a net inward force. This is how water pulls itself together.
How does surface tension increase and decrease?
Surface tension decreases rapidly with an increase in temperature. Dissolved substances can increase or decrease surface tension.
When does surface tension have significant influence?
Water moving short distances
Capillary Rise
Caused by adhesion to the surfaces surrounding water. So strong, it overcomes gravity and atmospheric pressure.
Height of Capillary Rise Equation
Hcr = (2T cosθ) / (Wv R)
Where T = surface tension
Θ = contact angle
Wv = Density of water
R = radius of the tube
What is height of capillary rise a function of?
Radius of the tube. As radius increases, Hcr will decrease.
What is radius of a tube in a Hcr problem dictated by?
Soil properties. These tubes are a representation of tiny gaps within the soil, ranging around 2meters in height
What are the pressure relations in capillary rise?
Tension, because it is < than atmospheric pressure.
Adhesion, which pushes the water up.
Atmospheric pressure and gravity pull the water down.
What is the importance of capillary rise?
It is how plants grow. Without it, water would never be pulled up in the soil, it would just go down deep into the ground.
What is the thermal capacity of water?
It relates temperature change of a substance to change in its heat energy content.
What is specific heat?
The amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for 1g of that substance to change its temperature by 1 Celsius.
Relative value
Refers to how water has the highest thermal capacity compared to commonly encountered substances.
Why is the relative thermal capacity of water high?
The intermolecular hydrogen bonds
Why is the relative thermal capacity of water important?
Ocean temperatures/energy and sea level. If you warm up the ocean, the surface tension will decrease because the surface temperature decreases and the volume of the ocean expands. So this is important because it causes changes in sea level!
Latent heat
Property of water. Energy released (during condensation) or absorbed (during evaporation) when a given mass of a substance undergoes a change in phase.
Is the latent heat of water high or low?
High due to the hydrogen bonds.
Latent heat of vaporization
The quantity of heat energy that is absorbed (/released) when a unit of mass substance vaporizes (/condenses)
Why is latent heat called “hidden heat”?
You can’t feel it
Why do you need so much energy to change states of water?
Tons of energy to break hydrogen bonds- it all comes back to their +- charges.
Solvent power of water
Almost every substance is soluble in water to some degree. Since water is a relatively small molecule, it acts as a universal solvent and melds with nearly any element.
Is water frequently found clean in nature?
Very rarely because of its solvent power. Will dissolve and meld with minerals, salts, calcium carbonate, etc.
How does water work as a universal solvent?
The water molecules surround the charged solute; + to - and - to +. This interaction suspends the solute molecule in a sea of water molecules, where it disperses and dissolves the material easily.
What is hydrology?
Focuses on the global hydrologic cycle and the processes involved in the land phase of that cycle. Considered in engineering problems and geosciences. Can be anything amt of space, ex. within a few meters or even globally.
What are computer simulation models of hydrology used for?
Future predictions, improve our understandings of the system, policy decisions, flood forecasting.
What is lambda?
The latent heat of vaporization
Vapor Pressure Deficit, aka Relative Humidity
Sink in the atmosphere to hold water
Turbulence
Causes mixing in the atmosphere
What causes aerodynamic resistance?
Wind speed, vegetation height (induces turbulence in the airstream), and stability of the atmosphere.
How is the amount of water in the air measured?
Vapor pressure
What is the saturation vapor pressure?
It is the max amount of water vapor that can be held in a parcel of air.
What is actual vapor pressure?
The actual amount of water being held in a parcel of air.
What is dew point temperature?
When the saturated vapor pressure is equal to the actual vapor pressure.
What is saturation vapor pressure a function of?
Temperature
What is the difference between saturation vapor pressure and a point on the curve?
Vapor pressure deficit (VPD)
What happens to the evaporation rate of water as wind speed increases?
As wind speed increases, resistance gets smaller, which makes it easier for water to evaporate.
What happens to evaporation rates as VPD increases?
The drier the atmosphere is (which is greater VPD), the more water can evaporate! This is because there is a greater capacity for it in the atmosphere
What happens to evaporation rates as wind speed increases?
The resistance goes down, so the amount of evaporation goes up
What happens to evaporation rates as vegetation gets taller?
It creates more turbulence, which causes resistance to go down, so the amount of evaporation goes up
Where are the highest evaporation rates?
In rainforests (and forests in general) because there is lots of water, lots of wind, lots of vegetation
Why is energy in area/time?
Because it is always happening
Why do you need water at the surface?
Because something has to be evaporated
What is the first factor for evaporating water at the surface?
The atmosphere needs to be able to hold H2O
What are the factors of evaporation from open water (like oceans)?
Energy availability, heat storage, wind speed, and a non-limited water supply
Why is water stored in the soil?
Capillary rise
What are the factors of evaporation from bare soil?
Albedo differences, texture, and water constraints
Why do albedo differences effect evaporation from bare soil?
It will impact energy because availability is dependent on incoming/outgoing solar radiation. Soil gets dark when its wet so more energy will be absorbed.