Maths - Statistics Y2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
2 possible log equations for exponential models
y = axb
y = abx
How do you measure the strength and type of linear correlation?
The product moment coefficient
What must you check when using the inverse normal function?
It is in the format P(Z<z) = …
It will NOT work if in the format P(Z>z) = …
What values can PMCC take?
Values between -1 and 1
What does the PMCC describe?
The linear correlation between 2 variables
What is the symbol for the PMCC of a sample?
r
What does it mean if r = 1?
There is perfect positive linear correlation
What does it mean if r = -1?
There is perfect negative linear correlation
What does it mean if r = 0?
There is no linear correlation
What is the symbol for the PMCC of a population?
ρ
When carrying out a hypothesis test for the PMCC, when do you use a one tailed test?
To test if there's a positive / negative correlation
When carrying out a hypothesis test for the PMCC, when do you use a two tailed test?
To test if there's a correlation
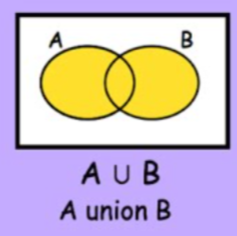
A ∪ B meaning
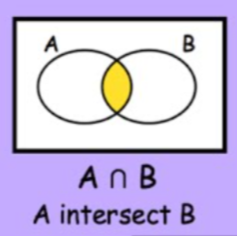
A ∩ B meaning
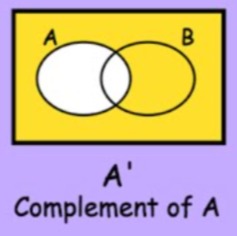
A’ meaning
(i.e. everything but A)
If A and B are mutually exclusive, what does P(A ∪ B) = ?
P(A) + P(B)
When does P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B)?
When A and B are mutually exclusive
If A and B are independent, what does P(A ∩ B) = ?
P(A) x P(B)
When does P(A ∩ B) = P(A) x P(B)?
When A and B are indepedent
Whole sample space symbol
ℰ
P(B|A)
The probability of B occurs given that A has already occurred
When A and B are independent, what does P(A|B) = ?
P(A|B’) and P(A)
The addition formula for 2 events, A aand B
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) − P(A ∩ B)
The multiplication formula for 2 events, A and B, to find P(B|A)
P(B|A) = P(B ∩ A) / P(A)
P(B ∩ A) = P(B|A) × P(A)
Continuous random variable
A variable that can take on one of infinitely many values
In a normal distribution, what is the probability that a continuous random variable takes any one specific value?
0
What is the area under a continuous probability distribution equal to?
1
5 features of the normal distribution curve
Has parameters μ for mean and σ2 for variance
Symmetrical - mean = mode = median
Bell-shaped curve with asymptotes at each end
points of inflection at ‘μ + σ’ and ‘μ - σ’
Total area under curve = 1
What is the significance of the normal distribution curve being symmetrical?
The mean = mode = median
How is a normal distribution represented?
X ~ N(μ,σ2)
For a normal distribution where you know p, how do you find the value of a in P(x<a) = p?
By using the inverse normal distribution
In a normal distribution, what proportion of data lie below Q1 and below Q3?
Below Q1 = 25%
Below Q3 = 75%
What is the mean and standard deviation of the standard normal distribution?
Mean = 0
Standard deviation = 1
How do you code the normal distribution to be the standard normal distribution?
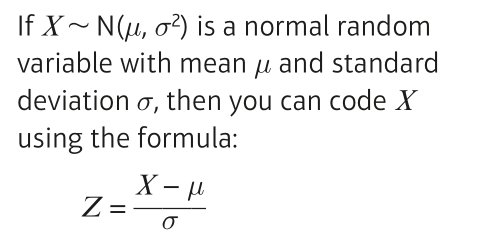
How is the standard normal distribution represented?
Z ~ N(μ,σ2) or Φ(a)
How do you find the mean or standard deviation of a normal distribution from the probability/area?
Code the values to be the standard normal distribution
Use the inverse normal distribution and solve
When can you approximate a binomial distribution to a normal distribution? (2)
If n is large
If p is close to 0.5
How do you approximate a binomial distribution to a normal distribution?
X ~ B(n,p) is approximately equal to N(μ,σ2) where
μ = np
σ = root of [np(1-p)] [so σ2 = np(1-p)]
What do you need to do when approximating a binomial distribution to a normal distribution?
Apply a continuity correction
When testing a hypotheses about the mean of a normally-distributed random variable, what is the distribution used?

When testing a hypothesis about the mean of a normally-distributed random variable, how do you find the critical region / value?
By using the inverse normal distribution or by standardising the test statistic then using the table

How do you carry out a hypothesis test for the mean of a normally-distributed random variable?
Write out H0 and H1
Assume H0 and write out the distribution
Write out the sample mean distribution
Find the critical value, x, when P(X<x) = a, where a is the level of significance for one-tailed / half the level of significance for two-tailed
Find the sample mean
When approximating a normal distribution from a binomial distribution, what would you calculate when:
i. X >/= 5
ii. X </= 6
iii. 5 </= X </= 6
i. Y > 4.5 (go for 0.5 below actual)
ii. Y < 6.5 (go for 0.5 above actual)
iii. 4.5 < Y < 6.5
After carrying out a hypothesis test on a normal distribution, how do you find the p-value?
Multiply your calculated value by 2
Why might a curve not be suitable for a normal distribution?
It is not symmetrical / bell-shaped
When testing a hypothesis about the mean of a normally-distributed random variable, how do you decide where the inequality sign faces?
If test statistic is greater than mean of H0, then >
If test statistic is less than mean of H0, then <
How do you carry out a hypothesis test for the PMCC? (4)
Write out H0 and H1
Calculate r for the data
Find critical value using the significance level of the test and the sample size
If testing for negative correlation and r is less than critical value: reject H0
If testing for positive correlation and r is more than critical value: accept H0
When adding new values to a data set closer to the mean than one standard deviation, what would happen to the standard deviation and why?
It would decrease because of the new values being closer than one standard deviation to the mean
How do you calculate P(A|B)?
Probability of A∩B / P(B)
When might a normal distribution not be a good model?
If it suggests that there is a non-negligible value for the probability of the variable being < 0 (in the cases where this is impossible e.g. time)
How do you calculate the percentage error when approximating a binomial distribution?
(binomial - normal approximation)/binomial
2 variables on LDS that would not be suitable for being modelled with a normal distribution
Daily Mean Windspeed (Beaufort) - qualitative data
Rainfall - not symmetric