Chemistry subtopic 3: R2.1 and S2.1 and Titration
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
process for when an ionic compound dissolves and the ions become surrounded by water molecules.
hydration
m
n
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is formed by the electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the positively charged nuclei.
Metallic bond
a bond formed between metal atoms due to the attraction of free-floating electrons to positively charged metal ions, allowing for conductivity and malleability.
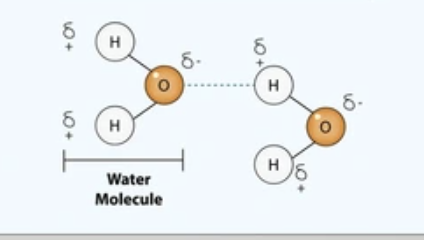
Hydrogen bond
Hydrogen from a molecule attracts an electronegative atom from another molecule electrostatically
Polyatomic ions
ions composed of more than one atom
m
n
Spectator ion
Found on both sides
Complete ionic equation
write as dissociated uibs (get rid of ionic bonds but leave covalent etc)
Net ionic equation
cancel out spectator ion on both sides
Limiting reactant
The substance which is completely consumed in a chemical reaction and determines the yield of the product formed
Excess reactant
The reactant which is still remaining after the reaction has taken place.
Metal physical state and exception
solid, Hg (l)
Non metals physical state and exception
Gases, C (s), S8(s), Br2 (l), I2 (s), P4(s), Clever Students Bring Ice Pops
Ionic compounds eg and physical state
NaCl, CaCO3, solids at room temperature, many dissolve in H20
Molecular compounds
CO2
STP
0 degrees, 273.15K, 100kPa
SAmbientTP
25 degrees, 100kPa
Reasons for lower experimental yield (4)
loss of product - evaporation and spillage
Incomplete reaction - impurities and not enough time
Side/Alternative reactions
Impure reactants
Reasons for greater experimental yield
Presence of moisture
Precipitate not dry
Precipitate
insoluble solid from a reaction in solution
Atom economy
Measure of reaction efficiency, compares to total mass of reactant atoms which end up as desired products
Titration
a technique used to determine the unknown concentration of a solution by reacting with solution of known concentrtion
Équivalence point
point at which reaction is complete
indicator
substance that changes colour at end point
ionic bond
electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions that holds its electrons in close proximatey
lattice
a 3D regular repeating arrangement of ions, atoms or molecules in a crystalline solid
Latice enthalpy IB def
endothermic process of turning a crystalline solid into its gaseous ions
Volatility
the ease at which a substance vaporizes or becomes a gas
what causes increasing ionic bond strength (3)
As the radius of the cation increases (bcs more energy levels are occupied), the lattice enthalpy decreases
the greater distance between two ions as radius increases, weakening electrostatic attraction
Group 2 chlorides have a higher lattice enthalpy then G1 and so on, bcs the greater distance between two ions as radius increases so electro static attraction is weakened
Physical properties of ionic compounds (6) and why see nb2
high melting/boiling pts
low volatility
many but not all are water soluble
not electrically conductive as a solid, only when dissolved in water or molten liquid
brittle
hard
Hydroxide ion
OH-
Phosphate ion
PO4 ,3-
Sulphate ion
SO4, 2-
Carbonate ion
CO3, 2-
Hydrogen carbonate ion
HCO3, -
Nitrate ion
NO3 -
Ammoniumm ion
NH4+
ionic bond
a type of chemical bond that involves the electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions,