Genetics Final Exam
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
reciprocal crosses
flip the sexes of the parents
particulate factors
determine phenotype
true or false: genetic traits can skip generations
true
Mendel’s 3 Postulates
1) particulate factors (alleles) exist in pairs
2) one allele is dominant, the other is recessive
3) alleles segregate independently during gamete formation
4) independent assortment (traits assort independently during gamete formation)

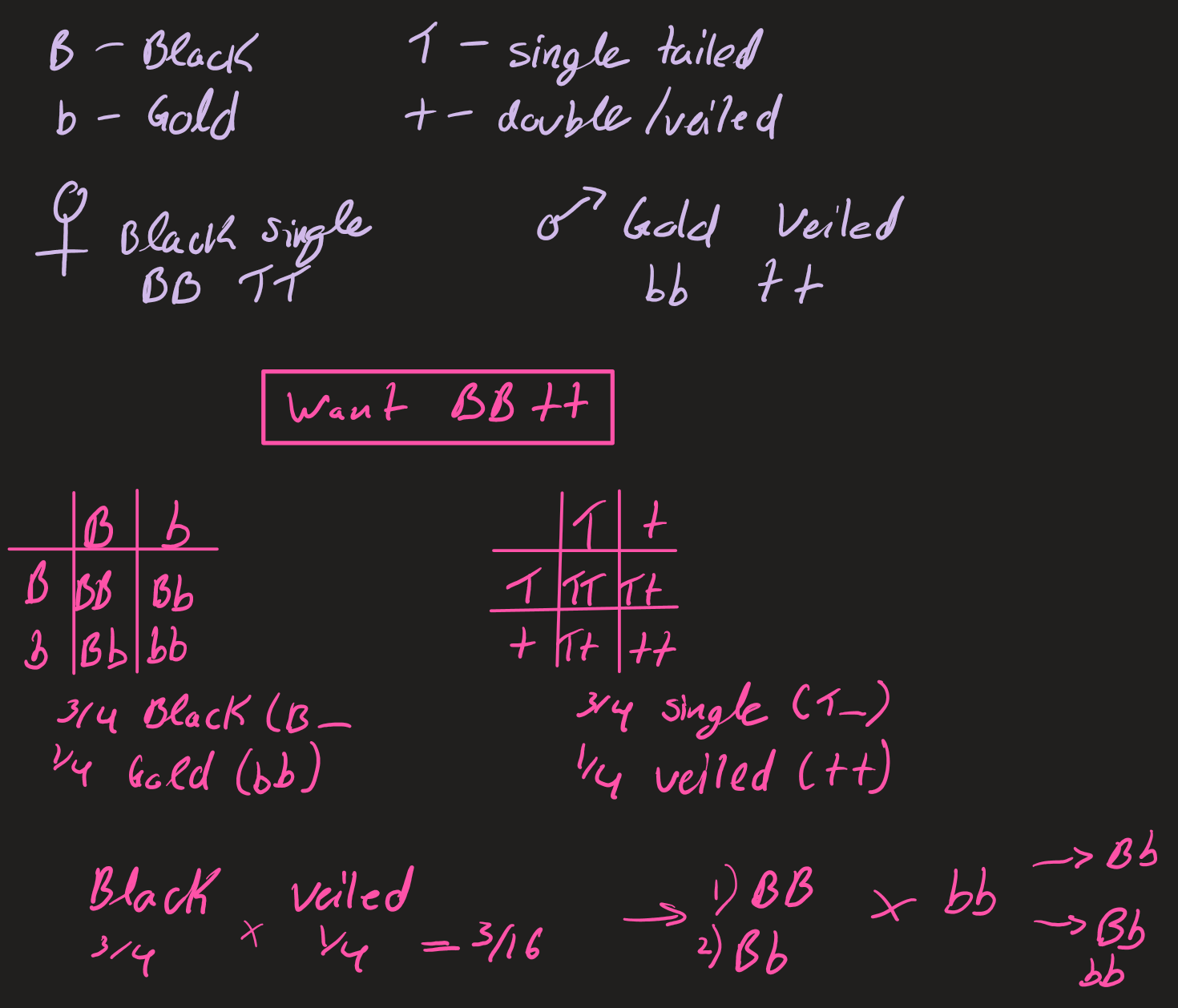

metaphase 1
things line up randomly leading to independent assortment
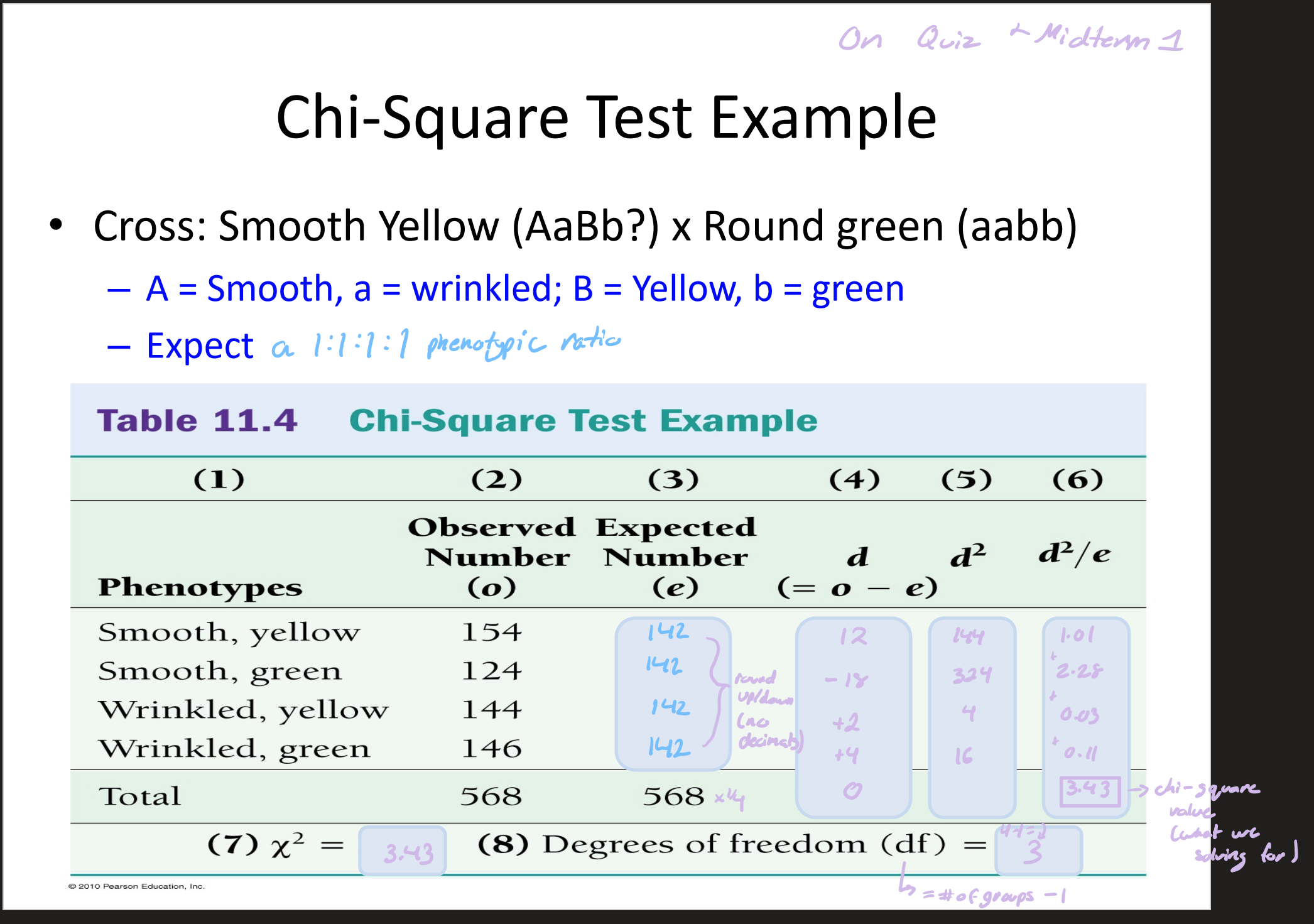
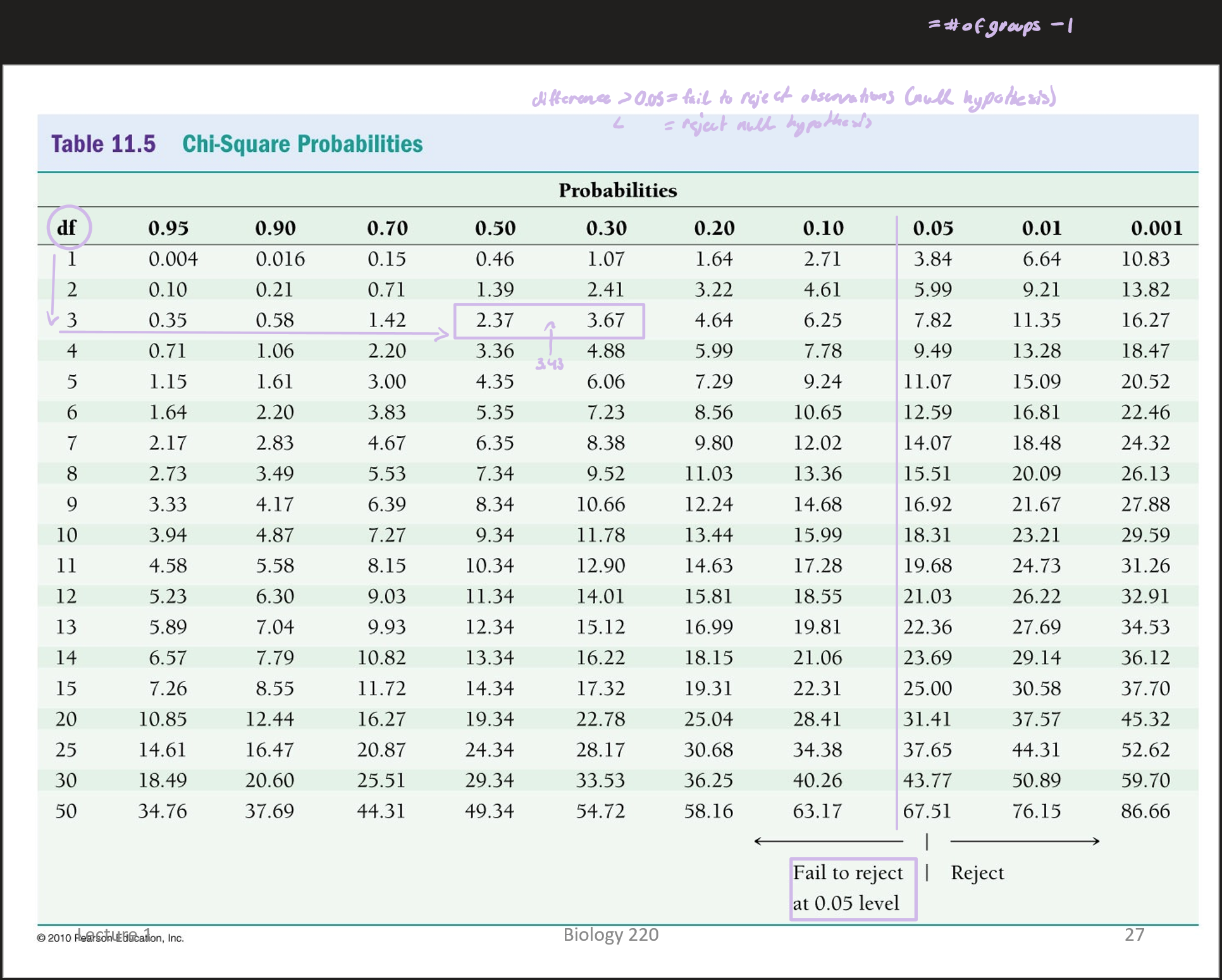
fail to reject
dominant autosomal traits
no generation skipping
both genders affected equally
both genders can pass on trait
ex. achondoplasia
recessive autosomal traits
can skip generations
both genders affected equally
ex: albinism
autosomal
genes/traits located on any numbered chromosomes (1-22) not sex (X or Y)
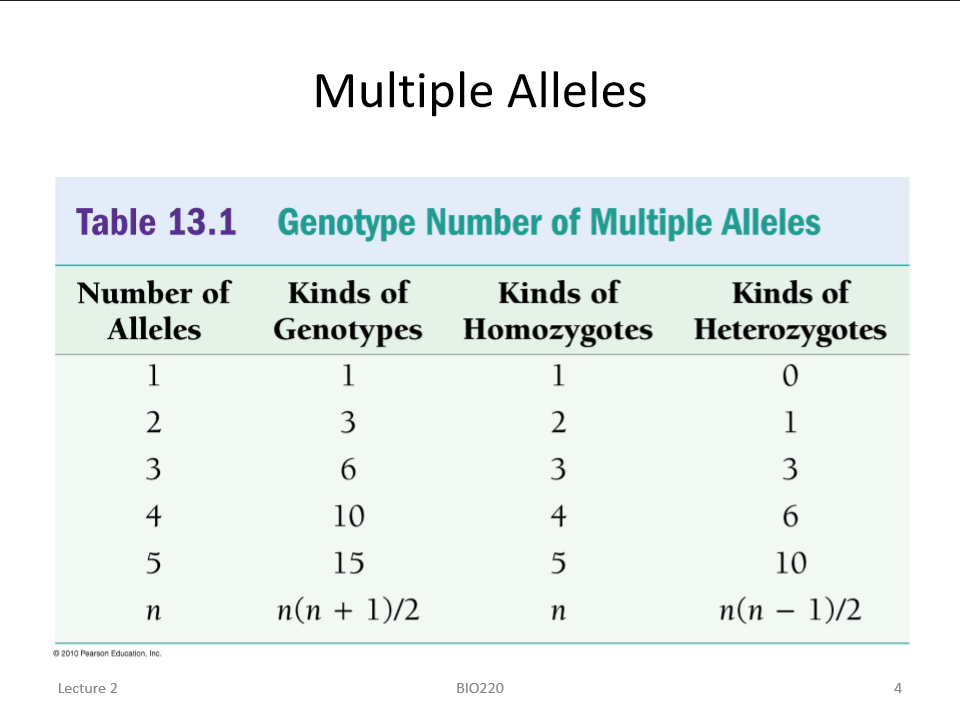
complete dominance
one allele is dominant to another
complete recessiveness
recessive allele is phenotypically only expressed when it is homozygous
codominance
two alleles at a locus produce different and detectable gene products in heterozygote
blood type AB is the universal…
acceptor
blood type O is the universal…
donor
ABO blood group gene encodes…
glycotransferases
H antigen encoded by dominant H allele
Bombay blood type (can’t accept other blood types, not even O b/c lack of H substance)
if a girl has blood type O, what are all possible genotypes of her parents?
AO + OO
BO + OO
OO + OO
AO + BO
AO + AO
BO + BO
incomplete dominance
one allele is not completely dominant to another allele of the same gene
the phenotype of heterozygote lies between…
either homozygote
codominance
results from both alleles (both alleles can be expressed, but only one observed)
incomplete dominance
only one allele product gets expressed
gene sufficiency
how many copies of a gene are required to give a normal phenotype
haplosufficent
only one gene copy is sufficient to give a normal phenotype
essential genes
genes that, when mutated, can results in a lethal phenotype (required for survival)
lethal allele
allele that results in the death of an organism
Tay-Sachs disease
lack of enzyme that breaks down lipids in lysosomes
results in excess lipids in CNS
huntington disease
huntington protein has too many glutamine amino acids leading to progressive degeneration of brain cells (onset between 30-40 years of age)
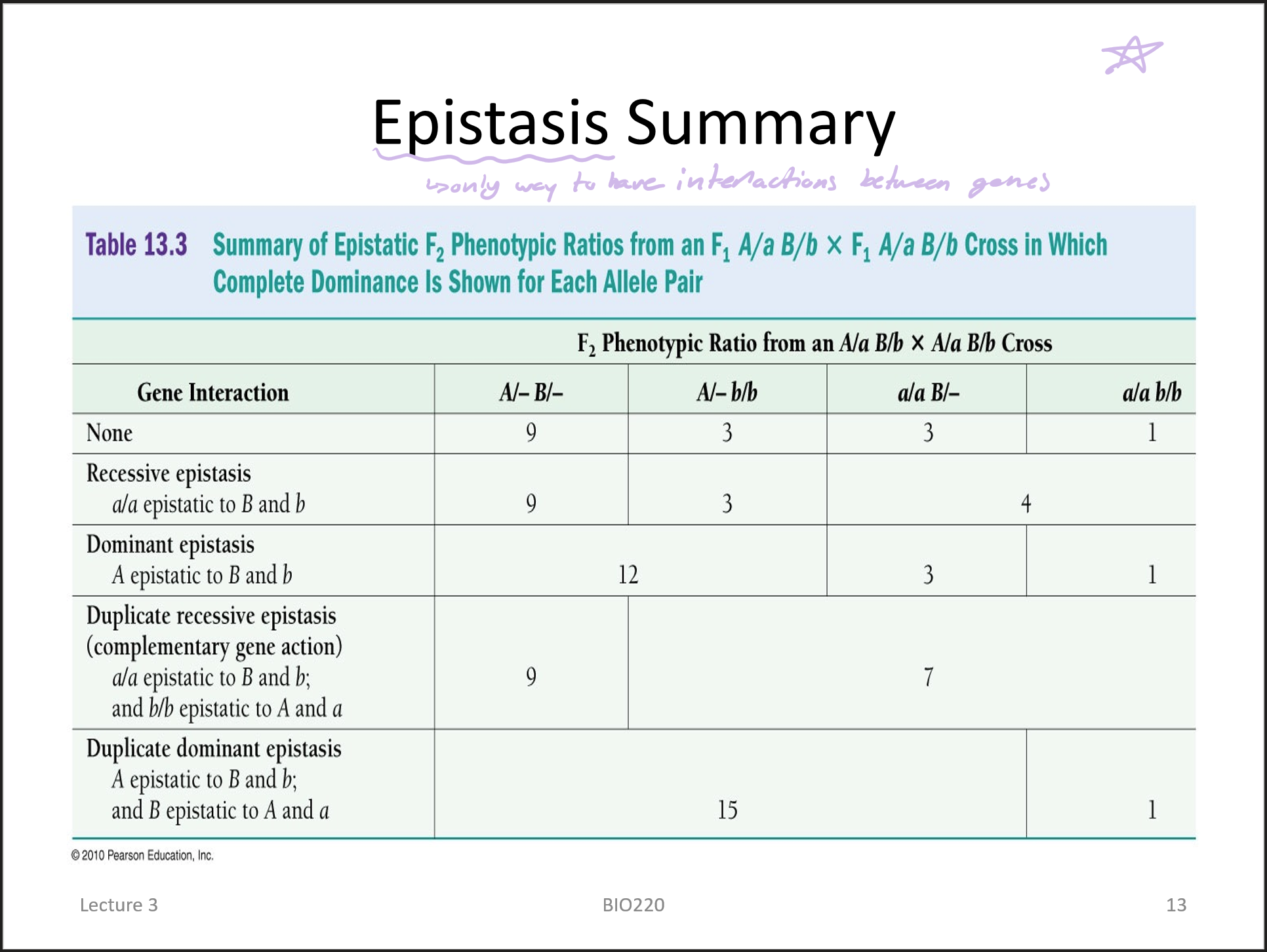
epistasis
genetic interaction where one gene pair masks the phenotype of another gene pair
epistatic
masking gee
hypostatic
masked gene
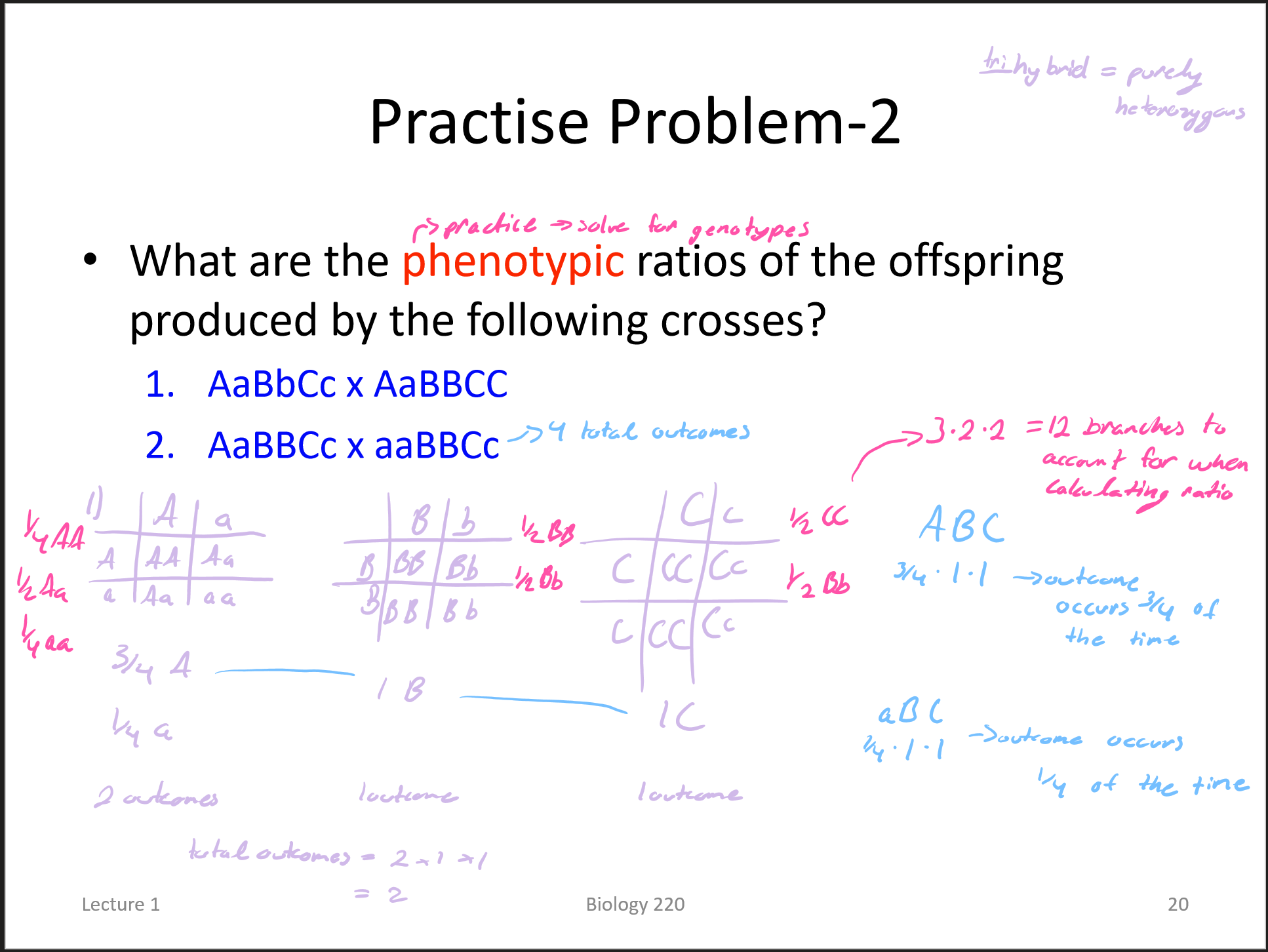
dihybrid crosses (4 phenotypes, 9 genotypes)
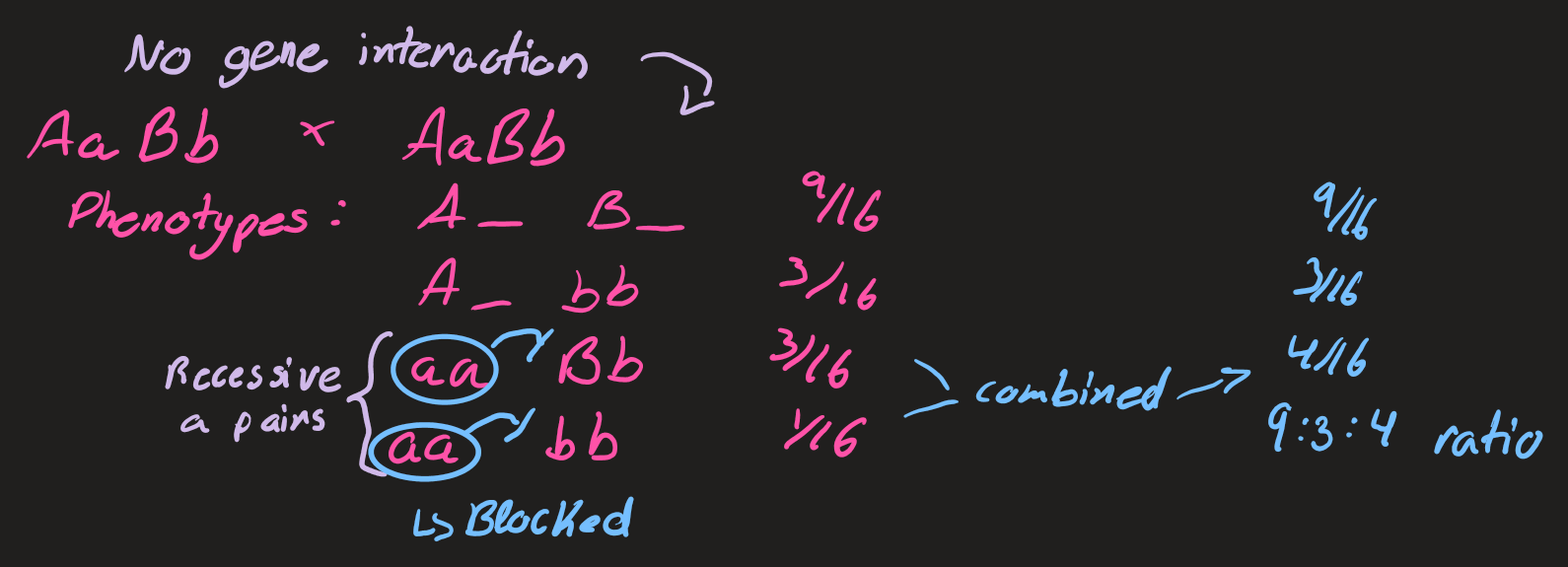
recessive epistasis

dominant epistasis

epistasis summary
modifier gene
alters the phenotype of another allelic gene
enhancers
intensify phenotype controlled by the other gene
reducers
decrease phenotypic expression of the other gene
suppressor gene
when modifier gene shifts phenotype associated with a mutant allele toward that of the wild-type
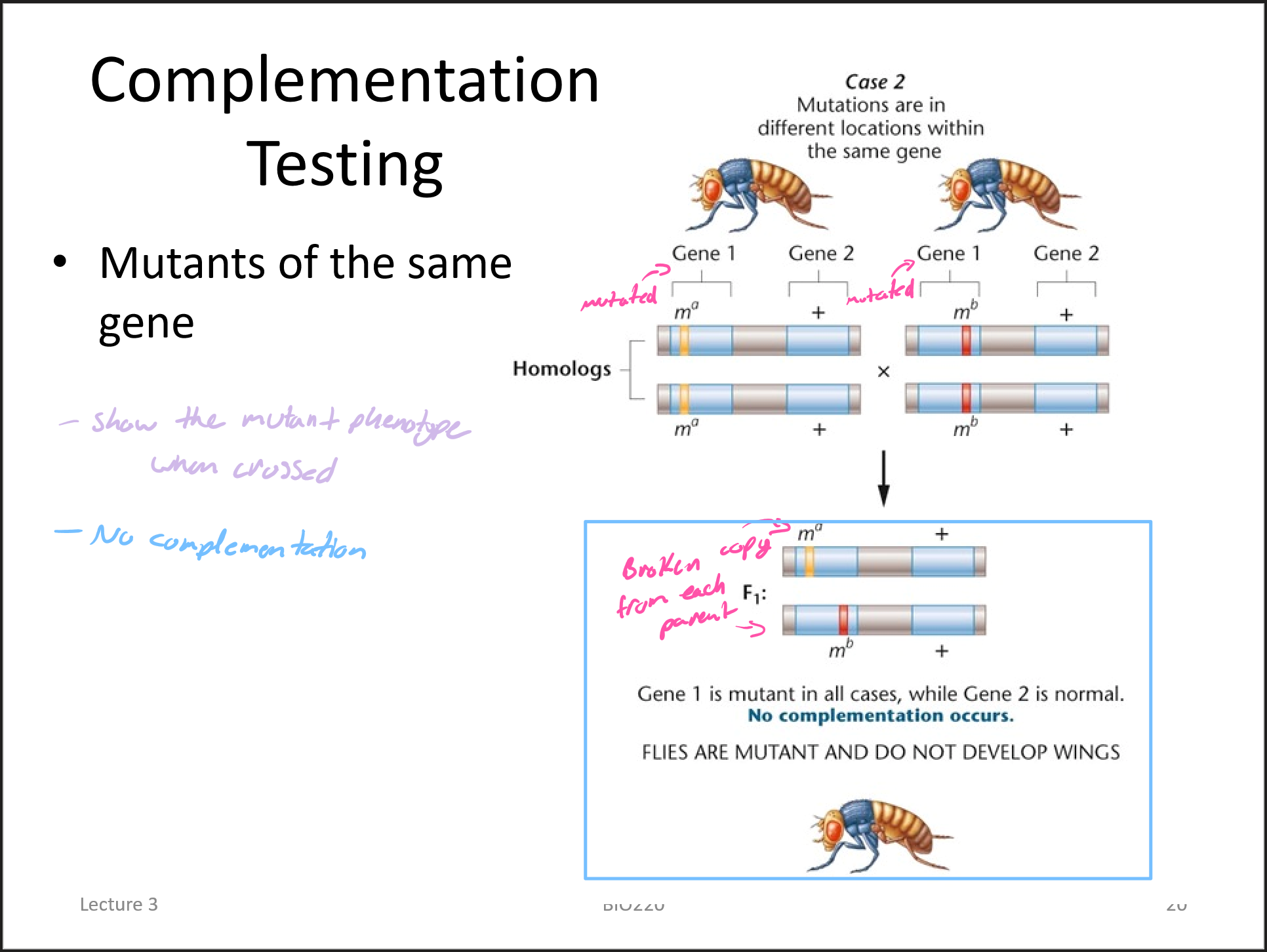
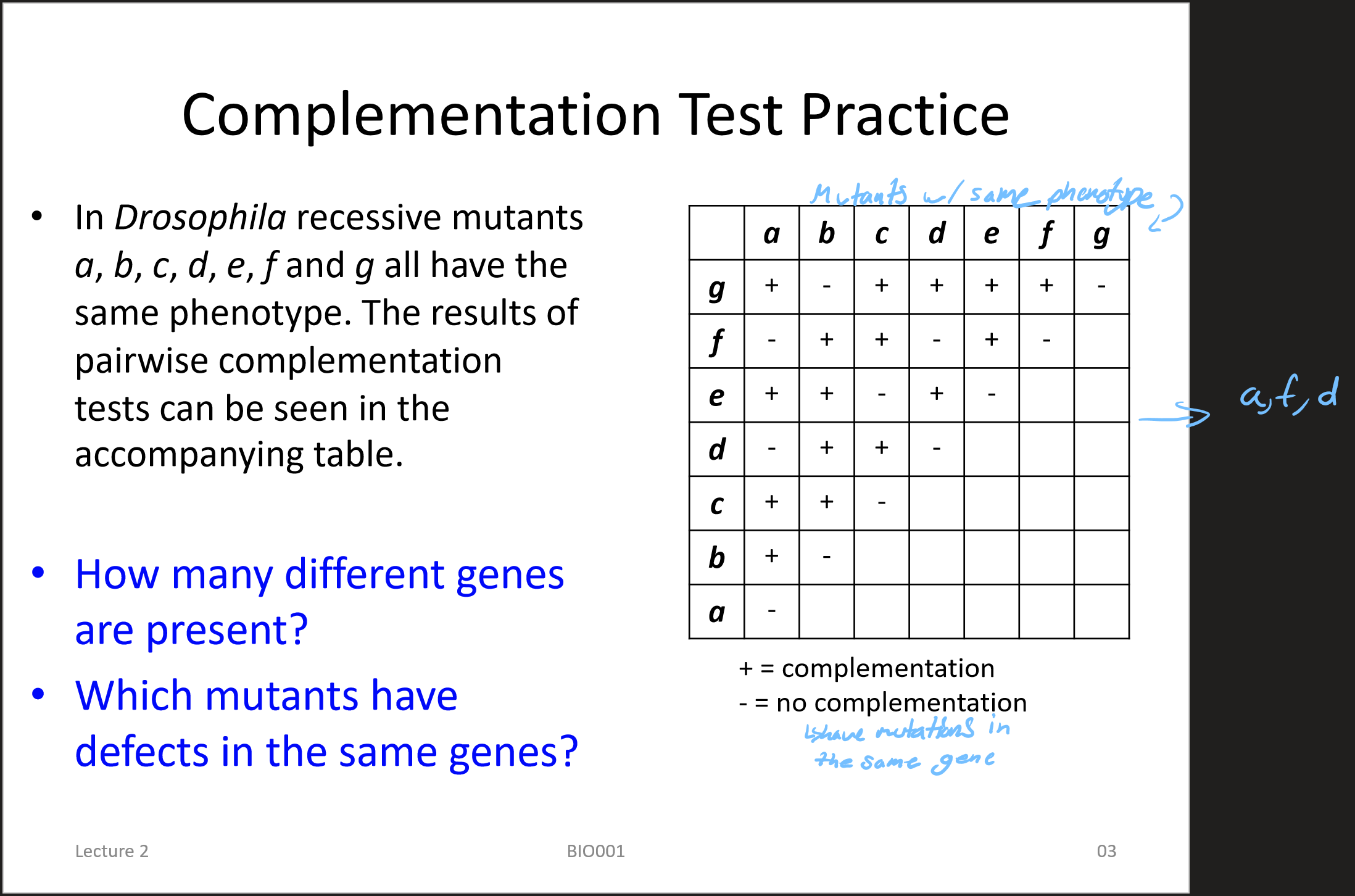
complementation test (also known as cis-trans test)
determines whether two independently isolated mutants have mutations in the same or different genes
complementation test example 1
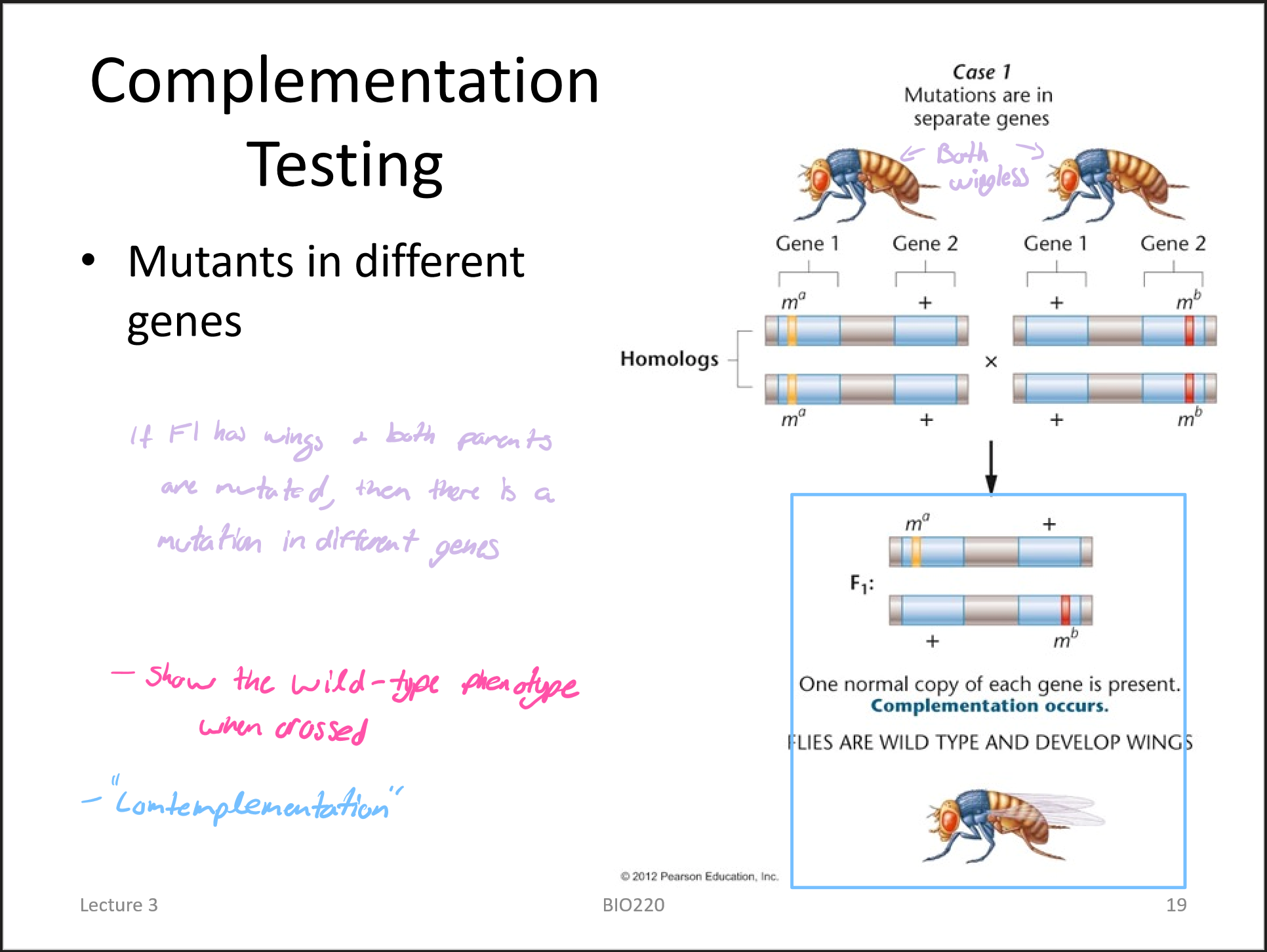
complementation test example 2
pleiotropy
when a gene influences many traits rather than just one
polygenic traits
where many genes contribute to producing a phenotype
usually multifactorial
influenced by genetics and environment
many show continuous variation
meristic traits described by whole numbers
threshold traits: small numbers of phenotypes
YOU EITHER ARE ____ OR ARE NOT ____
polygenic traits
grain colour in wheat
may be b/c of additive alleles
may show normal distribution within population
can estimate number of genes involved (n)

penetrance (on/off)
the phenotype of individuals with a given genotype that exhibits the associated phenotype
expressivity (dim/bright)
degree to which a penetrant gene of genotype is phenotypically expressed
factors that can alter the phenotype of a specific phenotype
age
sex
temperature
chemicals/nutrition
epigenetic modifications
phenotypic expression depends upon…
the parental origin of the chromosome carrying the particular allele
maternal/paternal imprinting
turning off the gene from mom/dad (respectively)
position effects
a change in the phenotypic expression of one or more genes (due to change in position of the genome)
genetic anticipation
when a genetic disease appears earlier with each succeeding generation