Neck: Thyroid, Parathyroid, Lymph Nodes, and Salivary Glands
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Where is the thyroid gland located in the neck?
Anterior and inferior to the larynx
How many lobes does the thyroid gland normally have?
Two lobes connected by an isthmus
Where does the thyroid originate before descending into the neck?
Tongue base
What is the thyroglossal duct?
Embryologic tract for thyroid descent
Failure of the thyroglossal duct to involute (meaning the duct remains patent) results in:
Thyroglossal duct cyst
Where is a thyroglossal duct cyst usually located?
Midline, superior to the thyroid
Which statement about the pyramidal lobe of the thyroid is correct?
It is a normal variant extending superiorly from the isthmus or adjacent lobe
What arteries supply the thyroid gland?
Superior and inferior thyroid arteries
The superior thyroid artery branches from which vessel?
External carotid artery
The inferior thyroid artery arises from which source?
Thyrocervical trunk of subclavian artery
Which hormones are secreted by the thyroid?
T3, T4, Calcitonin
What element is essential for thyroid hormone synthesis?
Iodine
What is the main function of T3 and T4?
Regulate metabolism and growth
What is the role of calcitonin?
Lowers blood calcium by inhibiting osteoclasts
Which gland secretes TSH?
Anterior pituitary
Which hormone from the hypothalamus stimulates TSH release?
TRH
Which muscles are located anterior to each thyroid lobe?
Strap muscles (sternohyoid, sternothyroid, omohyoid)
Which muscle lies anterior and lateral to each thyroid lobe?
Sternocleidomastoid
Which muscle lies posterior and lateral to each thyroid lobe?
Longus colli
Which structure order is correct from medial to lateral in the neck?
Thyroid lobe → Common carotid artery → Internal jugular vein
Where is the esophagus located in relation to the thyroid gland?
Posterior to the left thyroid lobe and lateral to the trachea
What are the functional units of the thyroid gland?
Follicles
What are the two main components of each thyroid follicle?
A single layer of follicular (epithelial) cells surrounding the colloid-filled lumen
What is the main function of colloid within the thyroid follicles?
Acts as a storage reservoir for thyroid hormones
Which component of the follicles of thyroid gland produce T3 and T4?
Follicular (thyroid epithelial) cells
Which sequence correctly describes the thyroid hormone regulatory pathway?
Hypothalamus releases TRH → Anterior pituitary releases TSH → Thyroid gland releases T3 and T4
Which hormone opposes the effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH) on calcium regulation?
Calcitonin
How do thyroid function test (TFT) levels relate to thyroid disease?
Elevated TFT = hyperthyroidism; Decreased TFT = hypothyroidism
Which term describes a thyroid gland that is functioning normally with normal hormone levels?
Euthyroid
What is the normal anteroposterior (AP) measurement range of the thyroid isthmus?
2–6 mm
Which of the following represents the normal dimensions of a thyroid lobe?
4–6 cm length, 1.5–2 cm width, 2–3 cm AP
If a patient’s serum calcium is low, which of the following best explains how the parathyroid glands respond?
Increase secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) to raise calcium levels
During a neck ultrasound, a small oval structure posterior to the thyroid lobe is found to be slightly hypoechoic to the thyroid. What characteristic supports that this is a normal parathyroid gland rather than a lymph node?
It is uniformly hypoechoic without a hilum
A cervical lymph node is visualized as round with loss of fatty hilum and increased cortical thickness. What should the sonographer consider first?
Malignant involvement
When imaging a patient with recurrent swelling under the mandible after meals, which sonographic finding most strongly suggests sialolithiasis (salivary stone) in the submandibular gland?
Echogenic focus with posterior acoustic shadowing in the duct
A young adult presents with a midline neck mass that moves with swallowing and tongue protrusion. Which of the following is most consistent with this finding?
Thyroglossal duct cyst
If TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) levels are decreased, what is the most likely state of thyroid hormone production?
Hyperthyroidism
During ultrasound, a thyroid lobe appears diffusely enlarged and hypoechoic with increased vascularity (“thyroid inferno”). Which condition is most consistent with this finding?
Graves’ disease
A patient with elevated serum calcium and a small hypoechoic oval structure posterior to the mid-thyroid lobe most likely has:
Parathyroid adenoma
Which feature would raise the greatest concern for malignant lymphadenopathy during neck sonography?
Round shape with loss of fatty hilum
Which of the following hormones are produced by the thyroid gland?
Triiodothyronine, thyroxine, thyrocalcitonin
All of the following are possible causes of hypothyroidism EXCEPT:
Graves’ disease
Which statement about Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is TRUE?
It is an autoimmune disease, also called chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, and leads to hypothyroidism
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States?
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
Which statement about the treatment of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is TRUE?
There is no cure, but thyroid hormone replacement can restore normal metabolism.
Which statement about the sonographic appearance of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is TRUE?
It shows hypoechoic micronodules with echogenic septations, creating a pseudonodular or “giraffe” pattern, and Doppler may show normal, decreased, or occasionally increased flow.
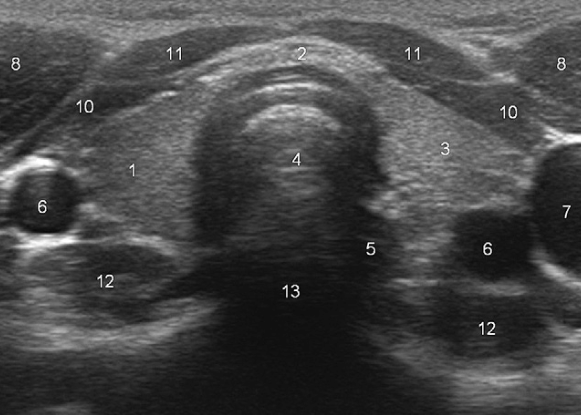
What does “5” represent?
Esophagus
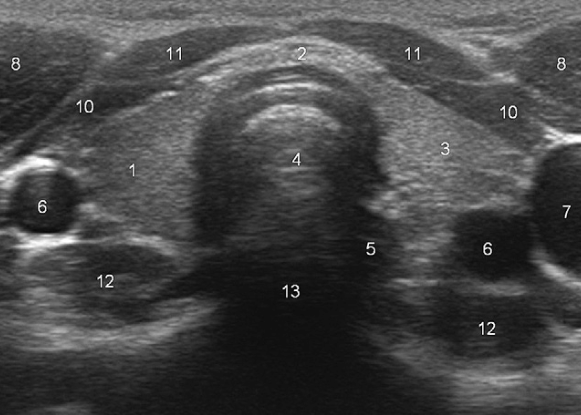
What does “8” represent?
Sternocleidomastoid muscles
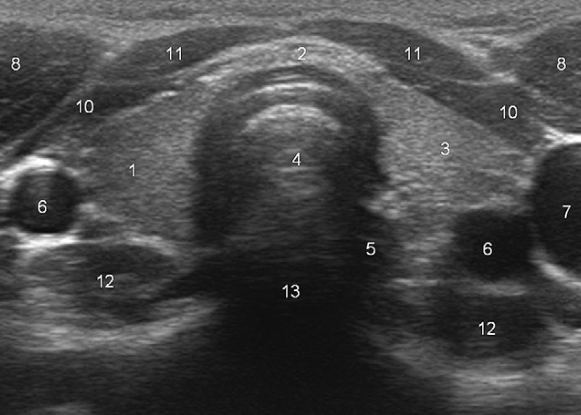
What do “10” and “11” represent?
Strap muscles (sternothyroid + sternohyoid)
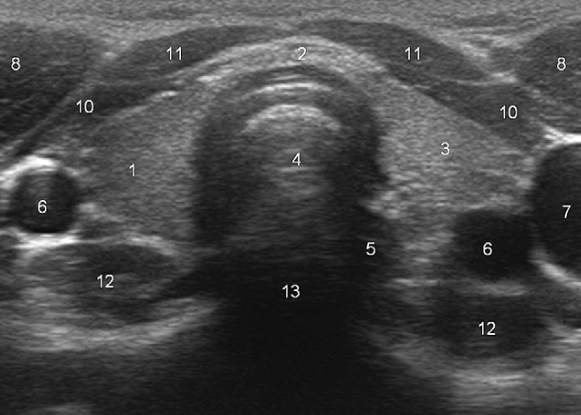
What does “12” represent?
Longus colli muscles
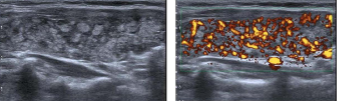
This pseudo-micronodular appearance of the thyroid is characteristic of:
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
All of the following statements about Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are correct EXCEPT
It decreases the patient’s risk for developing thyroid malignancy.
Which statement about iodine and thyroid function is TRUE?
Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of thyroid disorders worldwide and can lead to hypothyroidism.
All of the following are common clinical symptoms of hypothyroidism EXCEPT:
Heat intolerance and unintentional weight loss
All of the following are possible causes of hyperthyroidism EXCEPT:
Pituitary gland failure to produce TSH
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism?
Graves’ disease
Which statement about Graves’ disease is TRUE?
It is an autoimmune disease in which thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin causes the thyroid to overproduce hormones.
All of the following are common clinical symptoms of hyperthyroidism EXCEPT:
Weight gain and fatigue
Which Doppler finding is characteristic of active Graves’ disease?
Thyroid inferno” pattern
Which of the following best describes hypermetabolism in hyperthyroidism?
Abnormal increase in the body’s basal metabolic rate
Which statement about De Quervain’s thyroiditis is TRUE?
It is a subacute, painful thyroid inflammation often following a viral infection such as mumps or flu, most common in women aged 20–50.
All of the following statements about thyroid nodules are correct EXCEPT
The majority are caused by metastatic disease
Which statement about a goiter is TRUE?
It is defined as an enlarged, hyperplastic thyroid gland.
All of the following are possible causes of goiter EXCEPT:
Parathyroid adenoma
What is the most common benign tumor of the thyroid?
Follicular adenoma
Which ultrasound finding is most characteristic of a follicular adenoma?
Hypoechoic peripheral halo caused by a complete fibrous capsule
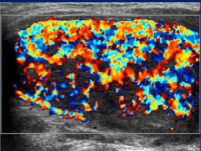
This “thyroid inferno” appearance is most characteristic of:
Grave’s Disease

This nodule within the right lobe of the thyroid most likely represents:
Follicular adenoma
This thyroid nodule appears more likely to be:
Malignant
What is the most common type of thyroid cancer?
Papillary carcinoma
All of the following are ultrasound characteristics of a malignant thyroid nodule EXCEPT:
Complete fibrous capsule
All of the following statements about follicular carcinoma are correct EXCEPT
It is less aggressive than papillary carcinoma.
Which statement about a nuclear medicine thyroid scan is TRUE?
It classifies nodules as hot, cold, or warm based on iodine uptake.
All of the following statements about hot thyroid nodules on nuclear medicine scans are correct EXCEPT:
They are more likely to be malignant than cold nodules.
Which statement about cold thyroid nodules on nuclear medicine scans is TRUE?
They are hypo- or non-functioning.
All of the following statements about warm thyroid nodules on nuclear medicine scans are correct EXCEPT:
They are hyperfunctioning and cause hyperthyroidism.
Which type of thyroid nodule is most likely to be malignant?
Cold nodule
All of the following statements about normal parathyroid glands are correct EXCEPT:
They produce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
Which hormone is secreted by the parathyroid glands to regulate blood calcium?
PTH
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) acts on all of the following organs to regulate serum calcium EXCEPT:
Liver
All of the following are true about PTH regulation EXCEPT:
PTH secretion is independent of blood calcium levels.
All of the following are true regarding calcitonin EXCEPT
It increases blood calcium levels.
All of the following are effects of parathyroid hormone (PTH) EXCEPT:
Increases bone mineralization
What is the most common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism?
Parathyroid adenoma
Which statement about hyperparathyroidism is TRUE?
It is caused by overactivity of one or more parathyroid glands and can be classified as primary or secondary.
All of the following are characteristic features of primary hyperparathyroidism EXCEPT:
Hypocalcemia (low blood calcium)
Which statement about secondary hyperparathyroidism is TRUE?
It results from abnormalities such as chronic hypocalcemia, vitamin D deficiency, or malabsorption, which stimulate excessive PTH secretion.
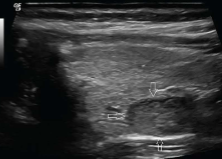
A 65-year-old woman presents with fatigue and mild bone pain. Laboratory tests reveal elevated serum calcium and elevated parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels. Based on the clinical presentation and ultrasound image, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Parathyroid adenoma
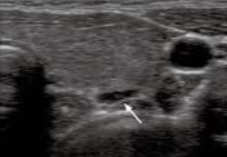
A 50-year-old patient undergoes neck ultrasound for unrelated reasons. A small, flat, ovoid structure is seen posterior and adjacent to the thyroid, and is hypoechoic compared to the thyroid tissue. What does this finding most likely represent?
Normal parathyroid gland
All of the following are common causes of abnormal lymph nodes EXCEPT:
Blunt force trauma
Which statement about localized vs. generalized lymphadenopathy is TRUE?
Localized lymphadenopathy involves only one area, while generalized involves two or more non-contiguous areas.
Which of the following is a sonographic feature of a normal lymph node?
Oval shape with vascularity at hilum
All of the following are features of malignant lymph nodes on ultrasound EXCEPT:
Oval shape with vascularity at hilum
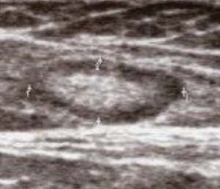
What does this ultrasound image most likely represent?
Normal lymph node
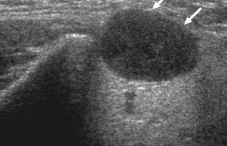
Based on the ultrasound appearance, this lymph node is most consistent with:
Malignant lymph node
Which statement about salivary glands is TRUE?
Their primary function is to produce saliva released into the oral cavity through ducts.
All of the following statements about the parotid glands are correct EXCEPT:
They are the smallest of the major salivary glands.
Which statement about the sublingual glands is TRUE?
They are located under the tongue and anterior to the submandibular glands.
The normal sonographic appearance of a salivary gland is:
Homogeneous and hyperechoic compared to adjacent muscle
Which statement about Sjogren syndrome is TRUE?
It is an autoimmune disease affecting moisture-producing glands, leading to severe dryness of the eyes, nose, skin, and mouth.