Lesson 6: Frequency, Association, Impact, Significance, Hypothesis Testing
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the types of measures?
Frequencies (prevalence and incidence), association, impact
What is prevalence?
Prevalence (P) quantifies the proportion of individuals in a population who suffer from a disease at a given time or period of time.
Calculate prevalence

What is incidence?
Incidence is defined as the number of new cases of a disease that develop in a population during a given period of time.
What are the two types of incidence measures?
Cumulative incidence and incidence rate (incidence density).
What is cumulative incidence (CI)?
The proportion of healthy individuals who develop the disease over a specific period of time.
Probability to get the disease

What is incidence rate or incidence density (ID)?
ID = Number of new cases of disease / sum of individual observation times.
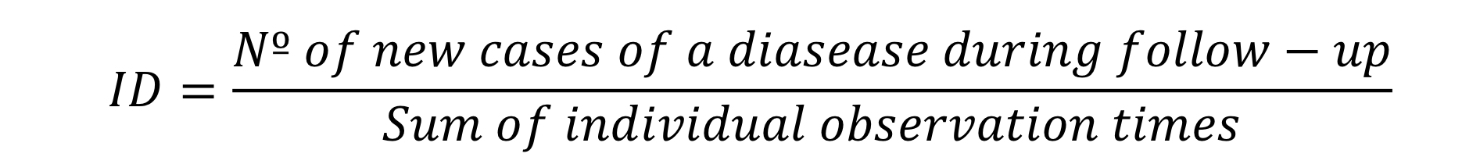
What is the purpose of a contingency (2×2) table?
To quantify how much and how a risk factor is associated with a disease, based on the frequency of the event in exposed vs. non-exposed groups.
RR calculation

What is Relative Risk (RR)?
RR reports how much higher the risk of the event is for the exposed compared to the unexposed. RR = incidence in the exposed / incidence in the non-exposed.
In which studies is RR used?
Cohort studies, clinical trials, cross-sectional studies.
What does RR = 1 mean?
The probability of getting sick is the same in both groups.
What does RR > 1 mean?
The exposed group has a higher affinity to become ill.
What does RR < 1 mean?
The exposure is a protective factor.
OR calculation
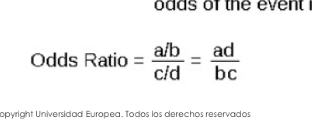
What is the Odds Ratio (OR)?
A measure comparable to RR, used when incidence cannot be calculated.
In which studies is OR used?
Case-control studies and cross-sectional studies.
What does the OR measure?
The odds of having an exposure in the group with the disease compared to those without the disease.
When is OR a good estimator of RR?
When the frequency of disease is Low.
How do you interpret results >1, =1, or <1?
>1 = exposure is a risk factor; =1 = no association; <1 = exposure is protective.
What is a hypothesis?
A hypothesis is not an assertion; it is subject to empirical testing to accept or reject it based on results.
What is a “Hypothesis test”?
Comparison of 2 hypothesis
p<0,05…. It means we are going to work with a level of preciseness of 95%
(probability of 95% of being right when we are accepting Ha)
What is the null hypothesis (H₀)?
There are no significant differences between groups; no association between exposure and disease.
What is the alternative hypothesis (H₁)?
It states that there is a difference between groups, i.e., an association between exposure and disease.
What is a Type I error?
Rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true.
What is a Type II error?
Accepting the null hypothesis when the alternative is true.