2.6.3 Supply-side policies
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
SUPPLY-SIDE POLICIES
gov policies aimed at increasing productive potential of economy and moving supply curve to right
MARKET BASED POLICIES
policies which are designed to remove anything that prevents free market system working efficiently, causing lower output and higher prices
barriers include those which reduce willingness of workers to take jobs or lead to inefficient production, high prices or a lack of risk-taking
INTERVENTIONIST BASED POLICIES
policies designed to correct market failure
POLICIES
increase incentives
promote competition
reform labour market
improve skills and quality of labour force
improve infrastructure
INCREASE INCENTIVES
increasing incentive, will increase size of workforce, so more g and s would be produced
METHODS:
reduction in benefits will increase OC of being out of work so people will work (why gov introduced Universal Credit , which helps to ease transition into and out of work)
reduction in benefits and subsidising workers may prevent poverty/unemployment trap, where low income workers end up in same or lower position after a new job because of benefits received
could encourage parts of the workforce back to work, e.g. women offered free childcare
reducing taxes on firms would increase incentives to employ
reduction of min wage would increase incentive for firms to employ
INCREASE INCENTIVES- EVAL
many people argue small change in any tax will have little impact on people’s incentive to work
reductions of tax on high income earners and reducing benefits will lead to more income inequality
reduction of tax will mean govs have less revenue so have to decrease spending or borrow more
PROMOTE COMPETITION
privatisation- selling nationalised companies to private sectors
deregulation- reducing restriction on businesses which restrict entry to the market, makes firms more competitive
competition policy (e.g. CMA) used to prevent monopolies in market
competition necessary to make firms efficient as they have to offer a cheaper or better service
PROMOTE COMPETITION- EVAL
deregulation and privatisation may lead to a poorer quality service
could cause env issues if deregulation is seen in env regulations
REFORM LABOUR MARKET
will reduce unemployment- means that more g and s can be produced
METHODS:
increase retirement age-more working
labour market could become more flexible to make it more efficient as it can respond to external changes
weakening of unions- trade unions push up wages which can lead to firms laying off some workers and reducing production- limits AS
making it easier to change jobs, through higher mobility of labour: improved info about job vacancies and improved geographical mobility
to improve geographical mobility, gov has to improve house affordability
decrease min wage to prevent real-wage inflexibility unemployment
REFORM LABOUR MARKET- EVAL
trade unions already very weak so reducing their power further may have little effect
reducing benefits will lower AD-less profit, less employment + increased income inequality
making labour force more flexible will lead to low pay for some, which will increase income inequality and may reduce AD
IMPROVE SKILLS AND QUALITY OF LABOUR FORCE
means that workers are more efficient so can produce more g and s and be more skilled so can develop new tech etc.
METHODS:
increase spending on education and training to create a more educated workforce who will be more efficient and able to do more skilled jobs
could be in terms of academic education, or improving quality of on job training, such as apprenticeships
gov working w/ trade unions and firms to improve the skills of long term unemployed
increase in high skilled migrants would also improve quality of workforce
IMPROVE SKILLS AND QUALITY OF LABOUR FORCE- EVAL
improving education may have no effect if it’s in irrelevant skills to workforce
increasing education will create an OC
time lag of effects of increased education
IMPROVE INFRASTRUCTURE
METHODS:
could be done through offering tax incentives or subsidies on investment
Investment in UK is just 17% of GDP compared to 35% in South Korea- to improve this, gov planned to reduce corporation tax to 18% in 2020
gov could spend money to improve infrastructure-e.g. building new roads, HS2 and CrossRail
will mean new tech will be developed and more will be invested in buying new tech- improvement in efficiency
IMPROVE INFRASTRUCTURE- EVAL
offering tax breaks/subsidies will effect gov budget- lose tax revenue or create OC
some businesses may not actually invest this money and instead used it as a method of tax evasion
not all investment will be successful in improving supply as it may not achieve its aim or it may not be aimed at increasing supply
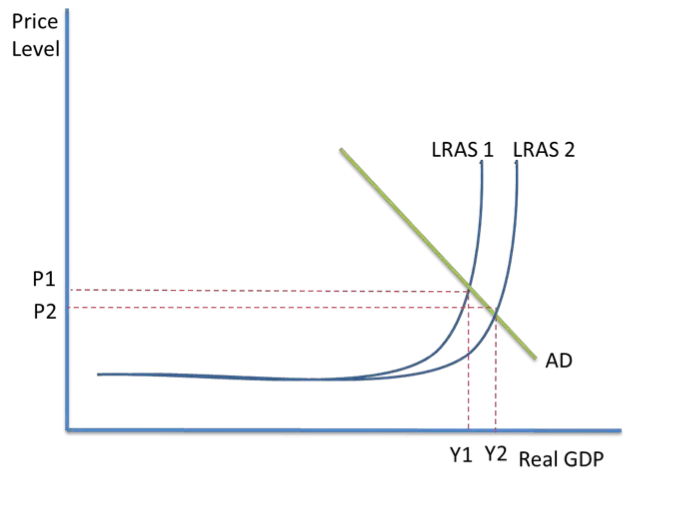
SS POLICY- KEYNESIAN DIAGRAM
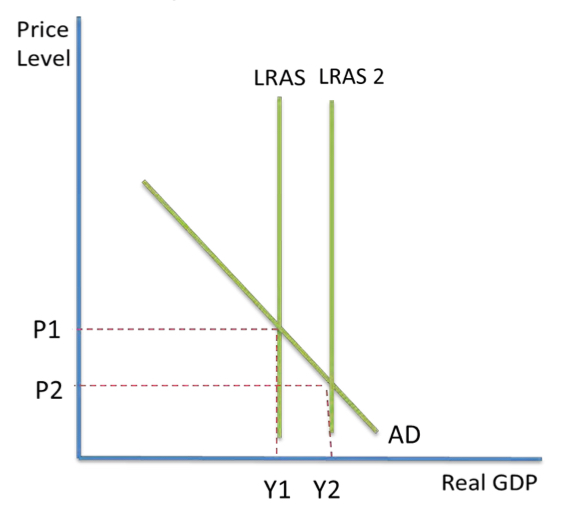
SS POLICY- CLASSICAL DIAGRAM
STRENGTHS
able to both increase output and decrease prices- no inflation
lead to long term economic growth, rather than small changes in economic growth following changes in AD
can be directed at increasing exports which will improve balance of payments
allow 2 diff approaches: market based and interventionist
means that both free market and interventionist economists will accept it
WEAKNESSES
Keynesian LRAS curve shows that they have no impact when LRAS is elastic, so demand-side policies needed to fix problem in short run
not all SS policies increase supply and others cause conflicts- issues vary depending on which policies used
often, gov has to spend more money or decrease taxes- will decrease revenue and lead to budget deficit
actions may also have undesirable impacts on AD and could cause higher inflation
time lag on effect on output