SL22107: Liposomes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What happens at low amphiphile concentration
The molecules disperse randomly with no order
What happens at high concentration of amphiphilic molecules
Surfactant concentration > CMC
Amphiphilic molecules spontaneously assemble into micelles or vesicles
Hiding the hydrophobic tail of the amphiphile
Describe the 2 transformative phases in micelles as amphiphile concentration increases
At high concentration micelles form hexagonal columnar phase/middle phase: amphiphiles form long cylinders
At higher concentration a lamellar/neat phase forms: amphiphiles seperated by thin layers of water
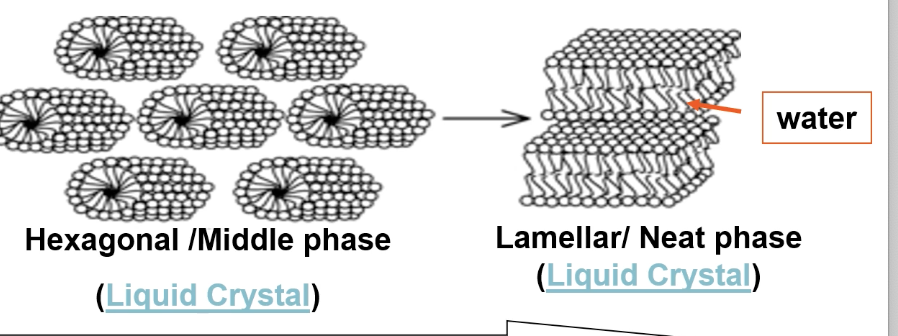
What is a liposome
A vesicular structure based on one or more lipid bilayer encapsulating an aqueous core
Amphipathic: hydrophilic head and 2 hydrophobic tails
A lipid crystal
How is a liposome formed
Phospholipid + water forms a phospholipid bilayer in neat phase
At a high concentration the bilayer self-assembles into spherical liposome with aqueous core and hydrophobic outer layer
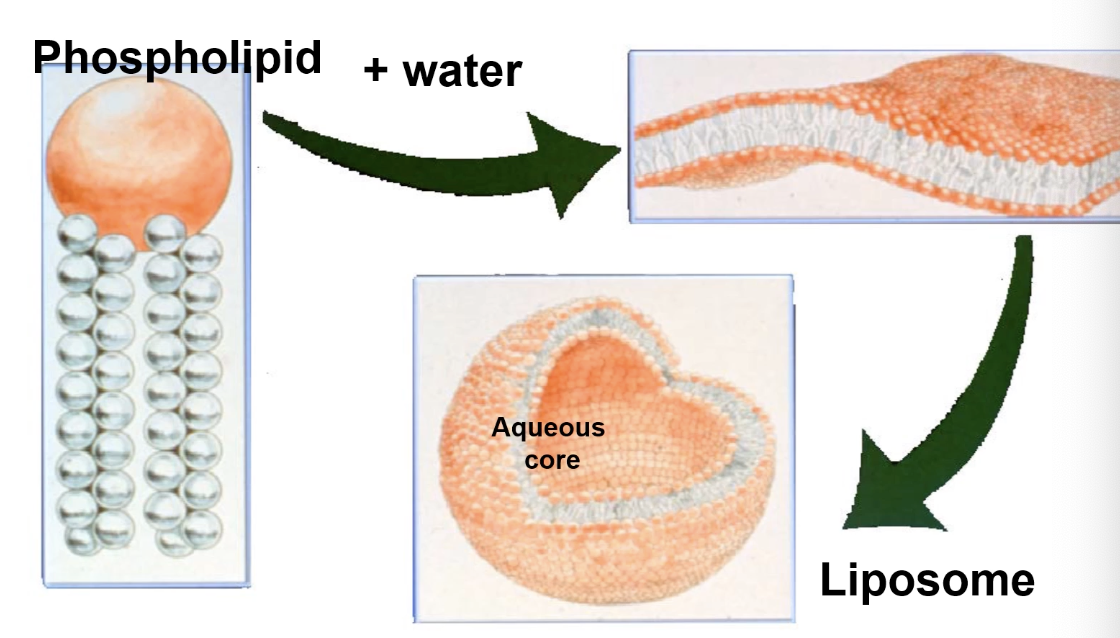
Why do liposomes form lipid bilayers
Spontaneously orientate in water to give the most THERMODYNAMICALLY STABLE conformation
Hydrophilic head faces out
Lipid chains faces in
Multilamellar or unilamellar
Several bimolecular lipid lamellae separated by aqueous layers = multilamellar liposome
Single lipid lamellae formed by sonification of units = unilamellar liposome
What are the functions of liposomes
Can carry lipophilic drugs fully buried in lipid bilayer
Can carry hydrophilic drugs sequestered in aqueous interior of the liposome
Can carry drugs with intermediate logP partition between lipid and aqueous phases
Can carry water soluble and lipid soluble drugs
Examples of liposomal agents
Phosphatidylcholine
Phosphatidylethanolamine
Examples of liposome uses
Sterols, glycolipids, organic acids and bases, hydrophilic polymers, antibodies
Antimicrobial agents, chelating agents, peptides, proteins
What is the effect of alkyl chain lengths and unsaturation
Longer unsaturated hydrocarbon chains produce rigid bilayers with low permeability at room temperature
What is the effect of cholesterol
Makes the bilayer rigid
Makes the system more stable to retain the entrapped drug
Stable vs fluid bilayer systems
Stable systems can retain entrapped drugs for longer periods
Fluid bilayer systems are better for rapid release
What other factors can contribute to liposome stability
Lipid composition
Storage condition
Light
Oxygen
Temperature
Cholesterol
Inert atmosphere
At what point do liposomes swell
Spontaneously swell in water above Tm
What are the advantages of liposomes
Biocompatible/ biodegradable
Composed of natural phospholipids: Biologically inert, weakly immunogenic, low intrinsic toxicity
Good biodistribution around the body
Good at targeting specific receptors
How can liposomes improve the circulation of drugs
Altered toxicity profile of amphotericin B and Doxorubicin to make them less toxic to human cholesterol cells
Longer circulation in the body which increases tumour deposition of liposomes associated agents
What are the 4 types of liposomes
Conventional: neutral/negative charge used for passive targeting to cells
Sterically stabilised: hydrophilic coating used for prolonged circulation times
Immunoliposomes: targets antibodies and delivery of anticancer drugs
Cationic liposomes: positively charged used for delivery of genetic material (DNA is negative)
What are the advantages of conventional liposomes
Protect encapsulated molecules from degradation
Can passively target tissues e.g. spleen, liver
Rapidly taken up by mononuclear phagocyte systems
Can be used for antigen delivery e.g. HEP A vaccine
How are MPS targeted by liposomes
Deliver antiparasitic and antimicrobial drugs
Encapsulates immunomodulators in activated macrophages in cancers
What are long circulating liposomes (LIPOSOME + PEG = steric hindrance = longer half life)
Liposomes covalently attached to hydrophilic polymer/ polyethylene glycol
Highly hydrated PEG group creates a steric barrier
Prevents interactions with molecular and cellular components in biological component (aka stops the body from attacking/metabolize the drug too quickly)
Increasing the half-life and serum concentration of the drug
What is the structure of immunoliposomes
Specific antibodies or antibody fragments on the surface to enhance target site binding
Where can PEG components couple to
to the surface
to the terminal ends
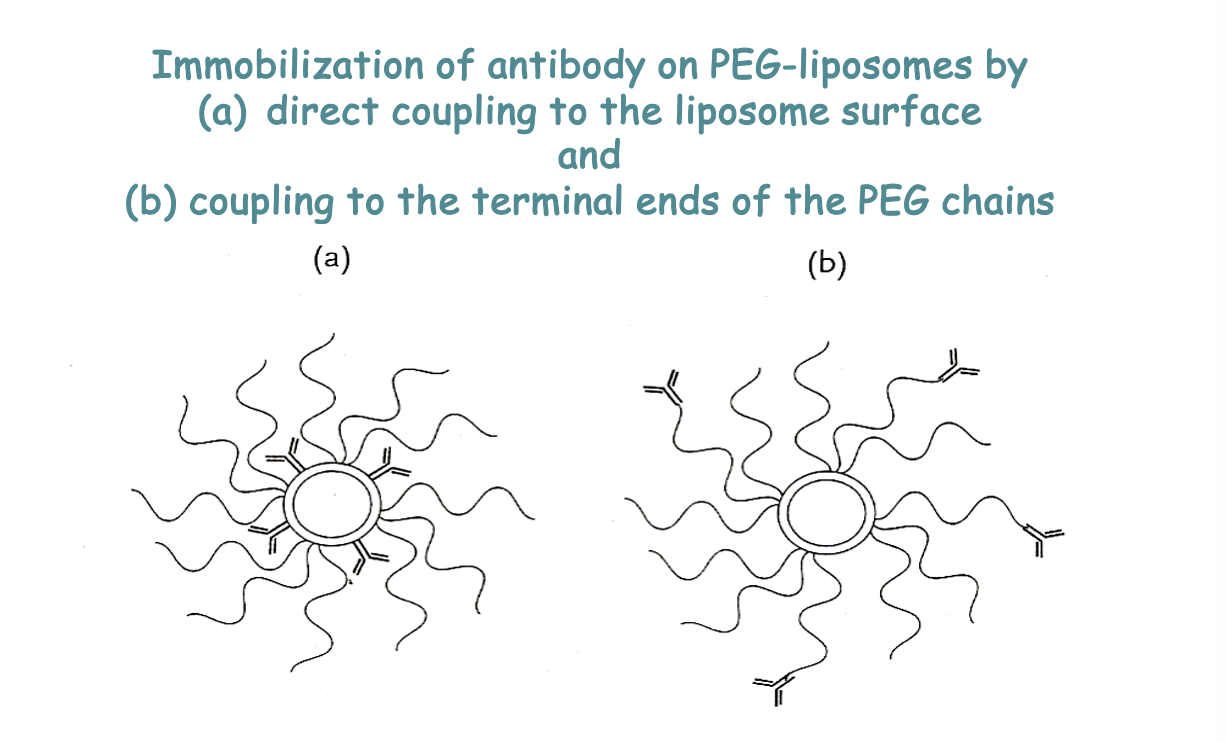
How does cationic liposomes deliver genetic material
Positive lipid component neutralizes negatively charged DNA
Causes DNA to condense into a compact structure
Can form an aggregate or DNA surrounded by lipid bilayer
Describe which liposomes can induce toxicity/reaction
Cationic: activates complements inducing ADR
PEGylated liposomes: activates transient reaction