1145 Final Exam, Hair, Skin, & Nails
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What are the three layers of the skin?
1. Epidermis
2. Dermis
3. Subcutaneous layer
What are the two layers of the epidermis?
-Stratum corneum (horny cell layer)
-Stratum germinativum (Basal cell layer)
What does the dermis contain?
-Connective tissue/collagen
-Elastic tissue
What are some epidermal appendages of the skin?
-Hair
-Sebaceous glands
-Sweat glands
-Nails
What are the two types of sweat glands?
-Eccrine glands
-Apocrine glands
Where is Vitamin D primarily produced within the skin?
Two innermost strata
-Stratum basal
-Stratum spinosum
Note: uv-B waves are required for adequate vitamin D*
What are the primary functions of the skin?
-Protection
-Prevents penetration
-Perception
-Temperature regulation
-Identification
-Communication
-Wound repair
-Absorption/excretion
-Production of vitamin D
What infection is associated with low Vitamin D over the age of 30?
Covid-19
What are some health history questions that can be asked about the hair, skin, and nails?
-Previous history of skin disease
-Allergies, hives, psoriasis, or eczema
-Change in pigmentation (size or color)
-Excessive dryness or moisture
-Pruritus
-Excessive bruising
-Rashes or lesions
-Medications
-Hair loss
-Change in nails
-Environmental or occupation hazards
-Self-care behaviors
What is pruritus?
Severe itching
What are some examples of environmental/occupation hazards?
-Outdoor sports enthusiasts (sun exposed)
-Coal workers
-Working with chemicals
Etc...
In what race is the incidence of melanoma noted to be 20 times higher?
White race is 20 times higher than African Americans, and 4 times higher than Hispanics
List variables that influence skin color?
-Emotional status
-Temperature
-Cigarette smoking
-Prolonged elevation of extremities
-Prolonged dependent position of extremities
-Prolonged inactivity
What equipment is needed to preform a skin exam?
-Strong direct lighting
-Small centimeter ruler
-Penlight
-Gloves
What is cyanosis of the skin?
Blue tint of the skin
-Can be central (Lips, tip of nose, face)
-Can be peripheral (Fingers, toes)
African American skin:
-Easier to see on feet, fingers, lips, and tongue
-Blue/Greyish coloration
Causes:
-Acute hypoxia
What is jaundice of the skin?
Yellow tint of the skin and eyes
-Commonly in sclera, palms of hands, soles of feet
Note: Babies with jaundice need immediate attention, can cause Brain damage if not treated (phototherapy)
What is erythema of the skin?
Redness of the skin surface
-Most common in primary skin lesions
Causes:
-Dilating of dermal blood vessels
-Edema
Example:
-Petechiae
What are some normal examples of color variations of the skin?
-Intentional tattoos, coining, or cupping
-Moles
-Freckles
-Patches (birthmarks)
-Striae (stretch marks)
What is coining (cao gio) of the skin?
-Alternative form of medicine
-Practiced in Southeast Asia
-Rubbing heated oil on the skin (chest, back, or shoulders)
-Vigorously rubbing of a coin in a linear fashion until red mark is seen
-Believed to allow "bad wind" to be released from body
-Used to treat fever, chills, headaches, colds, and cough
What is Hypothermia?
Cold skin
Generalized:
-Outside in a cold environment
Localized:
-Peripheral arterial disease
What is Hyperthermia?
Warm skin
Generalized:
-Fever
-Exercise
-Hyperthyroidism
Localized:
-Sun burn
-Venous disease
What is diaphoresis?
Excessive sweating
Causes:
-Hyperthyroidism (speed up of metabolism causes sweating)
What are normal findings of inspecting/palpating the skin?
Texture: smooth, soft, intact, even surfaces
Temperature/moisture: warm/dry
Mobility/turgor: skin is moved easily when lifted, and immediate returns after being released
Thickness: palms and soles of feet
Thinness: eyelids
How are calluses formed?
Friction or pressure of the skin
What is skin turgor?
Elasticity of the skin, how fast it returns to normal position
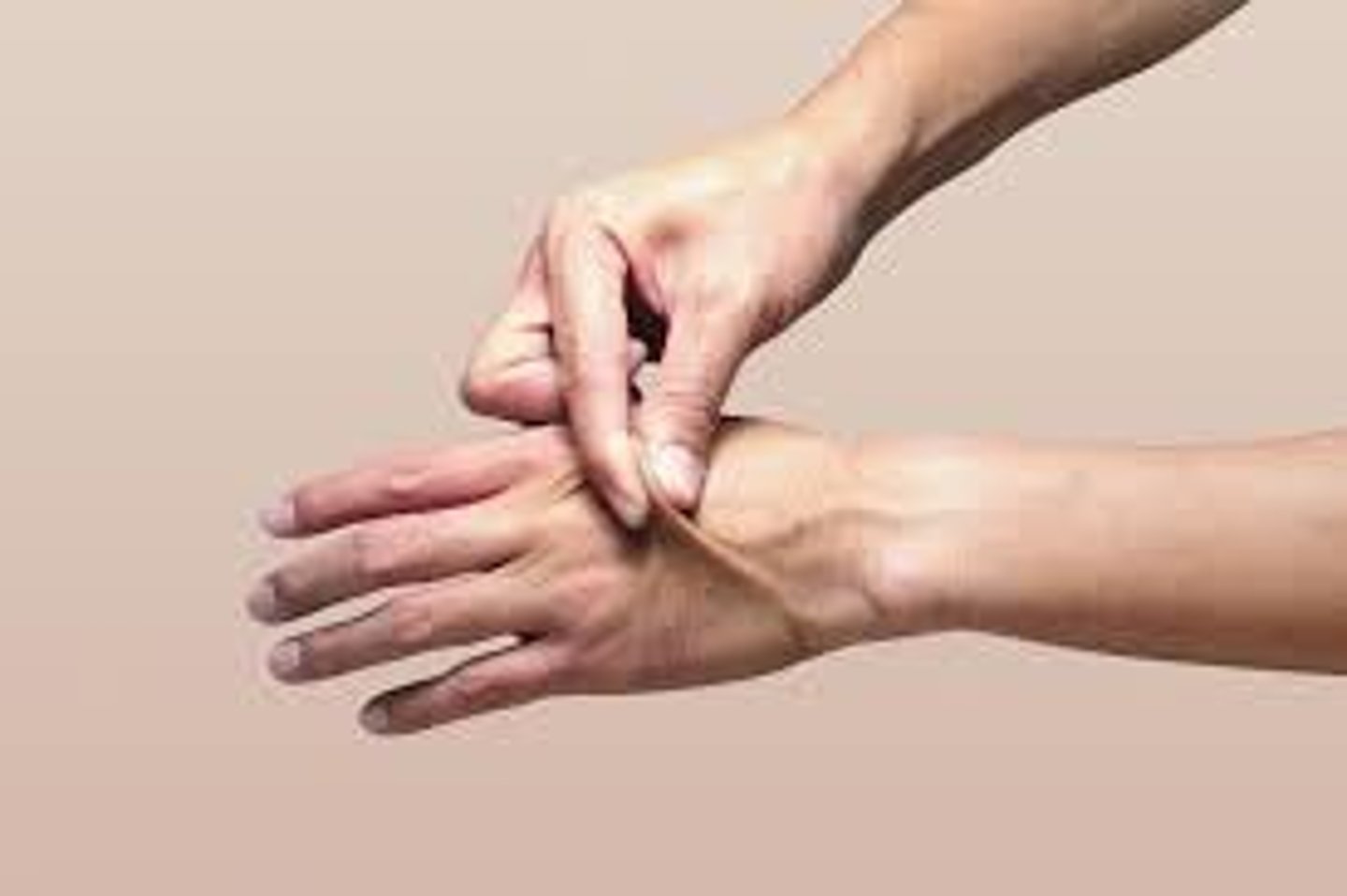

When can a decrease in skin turgor become a concern?
When it is seen in young individuals, this could mean they are dehydrated
When can a decrease in skin turgor be considered normal?
Within elderly patients, loss of elastin causes the elderly to have poor skin turgor
Note: skin turgor is not accurate in detection of dehydration within the elderly community
What is eccymosis?
-Bruising or discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes
-This is when blood seeps into tissues
Causes:
-Trauma
-Abuse
-Herpin injections (especially umbilicus area)
What is edema?
-Swelling because of excess fluid in interstitial places
-Usually it takes 5 kg before pitting is noticed
-1 kilo = 1 liter of water
What is the pitting edema scale?
1+ - 2mm pit
2+ - 4mm pit
3+ - 6mm pit
4+ - 8mm pit
Brawny edema: Fluid can no longer be displaced, tissues are firm and hard, skin is soft, moist, and warm
What are 3 things we should be doing when inspecting skin lesions?
-Observing for a change in structure
-Observing lesion characteristics
-Documenting the location, distribution, color, pattern, edges (flat or raised), and size of lesion
Name three different types of lesions?
-Primary lesions
-Secondary lesions
-Vascular lesions
What do we use to describe lesions?
-Color
-Elevation
-Pattern/shape
-Size
-Location/distribution
-Exudate (what color)
What does the American Dermatologic Association promote for health and self-care in terms of skin lesions?
ABCDEF rule:
A- Asymmetry
B- Border
C- Color
D- Diameter
E- Elevation/enlargement
F- Feeling
Note: Look for ugly ducklings
What are some abnormal nail findings?
-Clubbing
-Thinning/brittleness
-Inflammation
-Pitting
-Beau's lines
-Splinter hemorrhages
What are some normal findings of the nails?
-Shape is smooth/rounded with a 160 degree nail base
-Contour is flat and slightly rounded
-Nails are consistent
-Color is pink, or blanched
-The thickness is smooth and uniformed
-Nails are clean
-Nails should adhere to the nail bed
Note: it is normal to find slightly yellow, and possible black bands within African Americans nails
What is clubbing?
-Nail bed is greater than 160 degree angle
Cause:
-Chronic hypoxia (COPD)
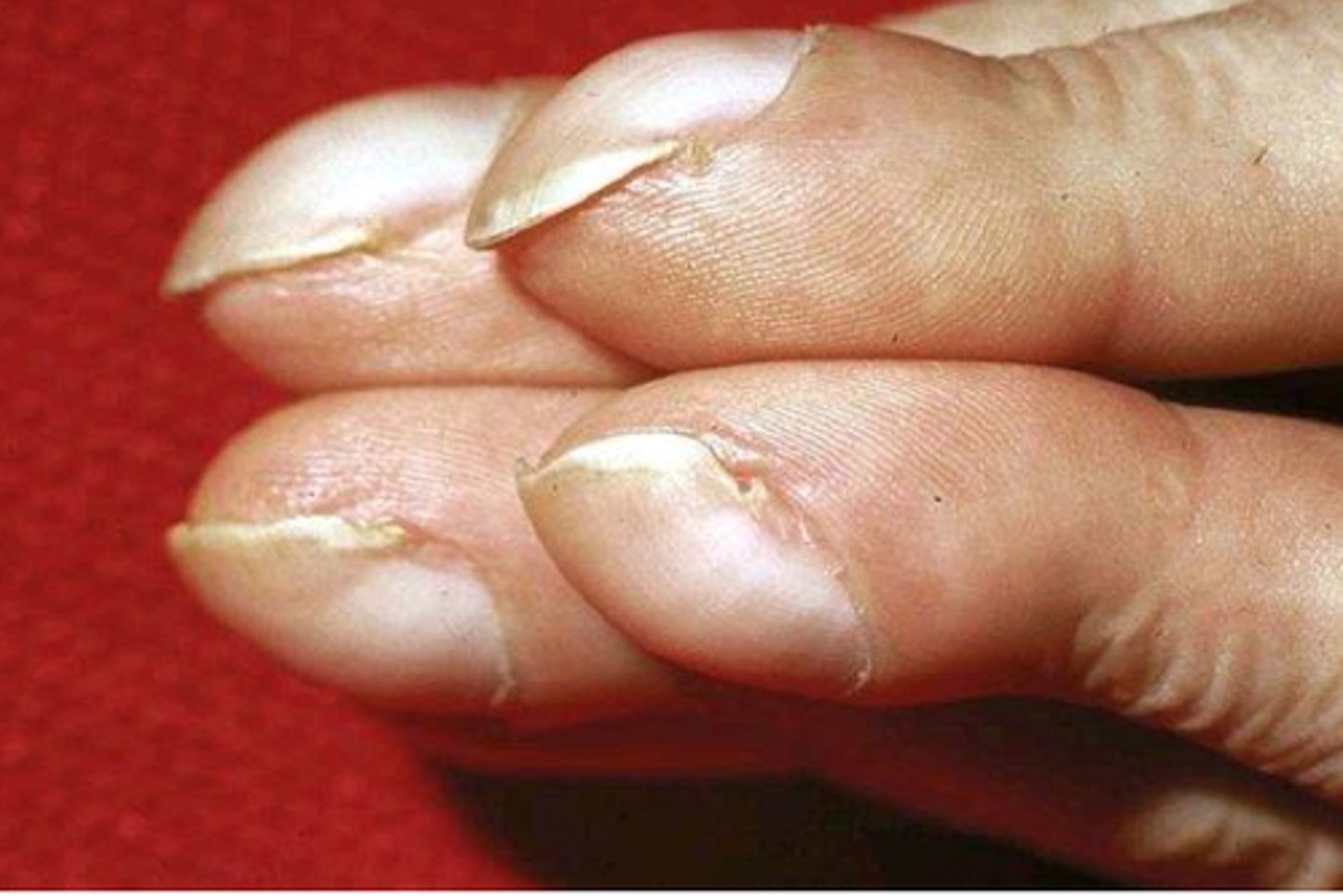
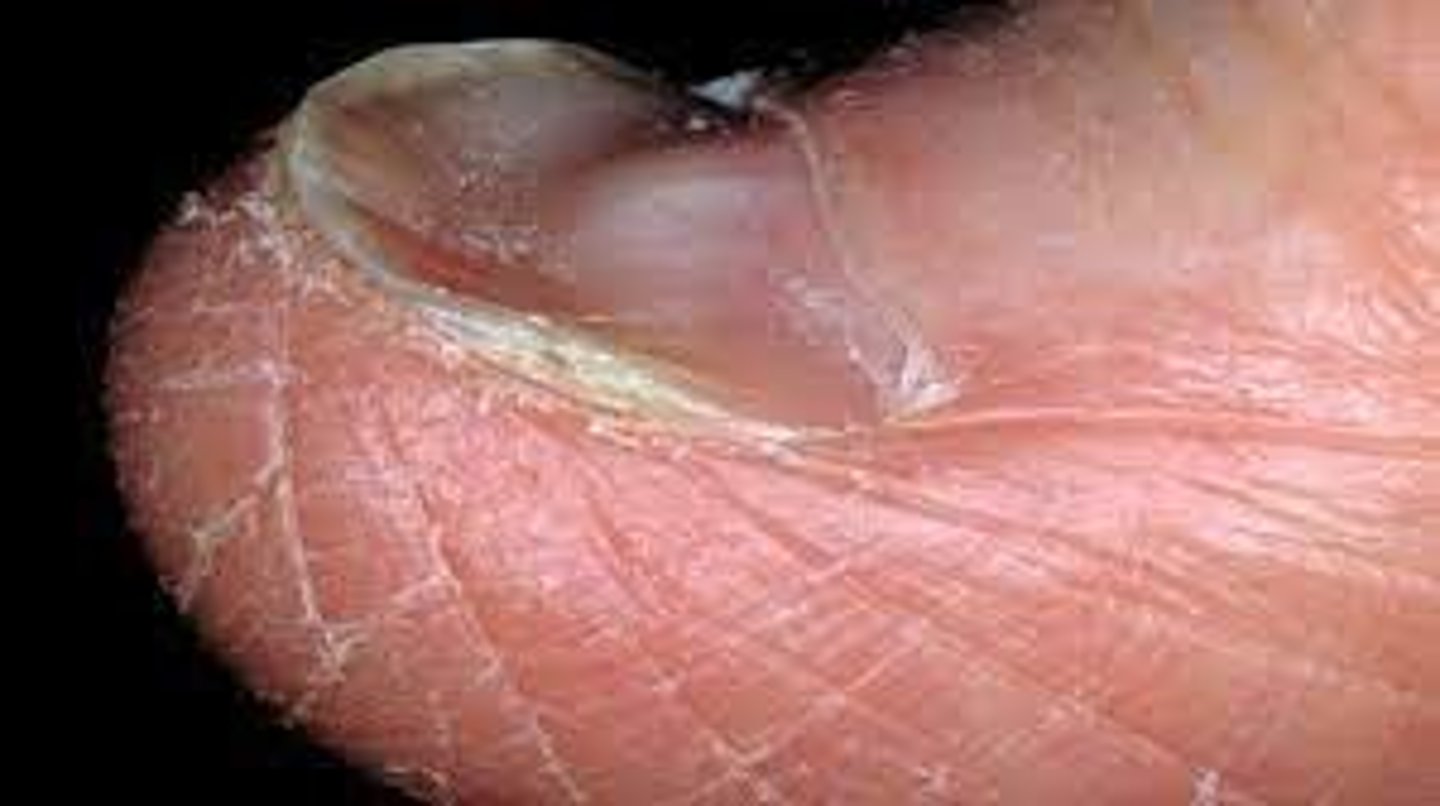
What is Onycholysis?
Separation of the nail plate from the nail bed, the nail will eventually fall off
Causes:
-Hyperthyroidism
-Warts
-Psoriasis
-Onychomycosis (fungal infection)
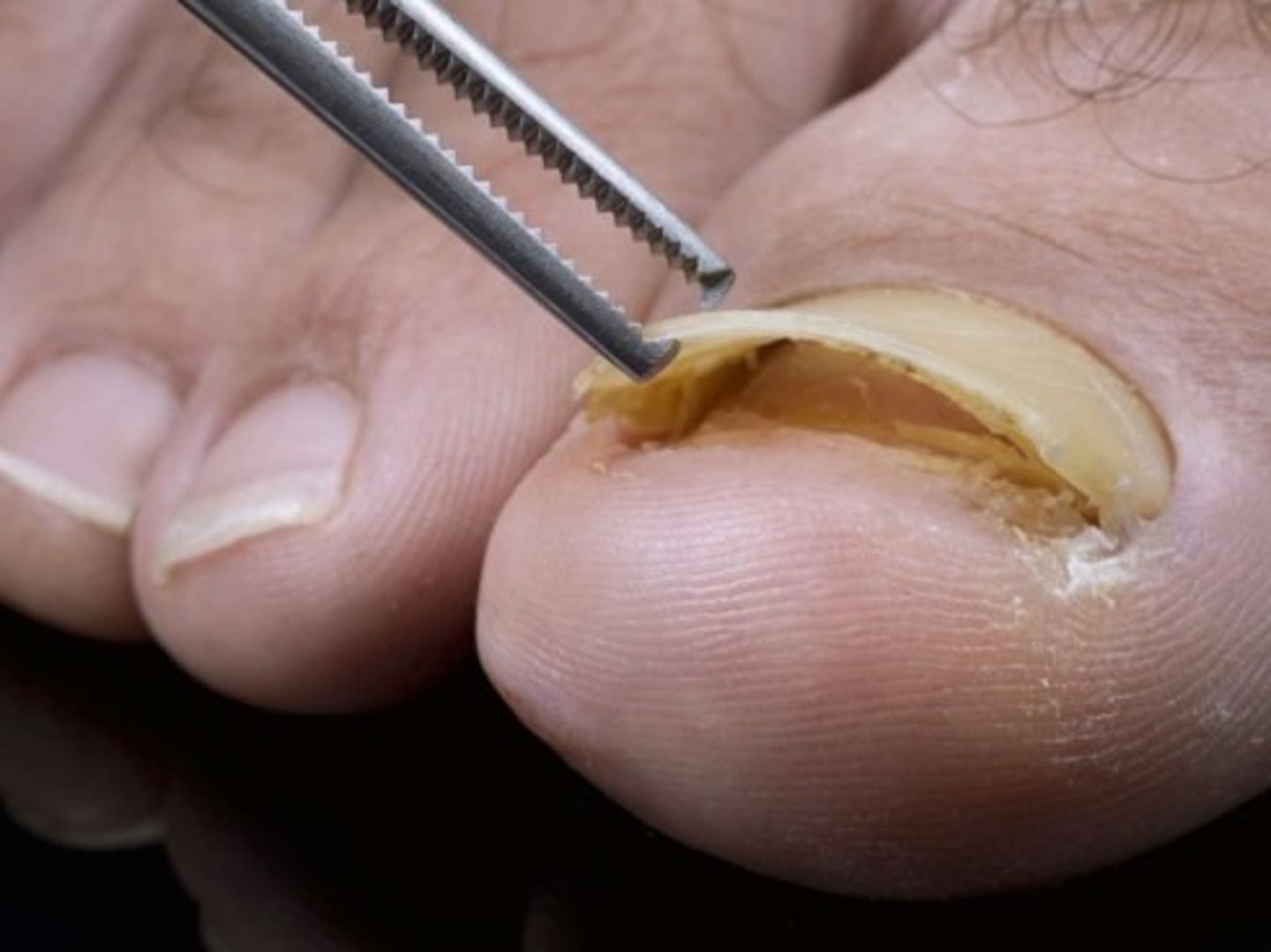
What is a Splinter Hemorrhage or Janeway's lesions?
Thin reddish-brown lines of blood under the nails
Causes:
-Endocarditis (infection of the heart valve)
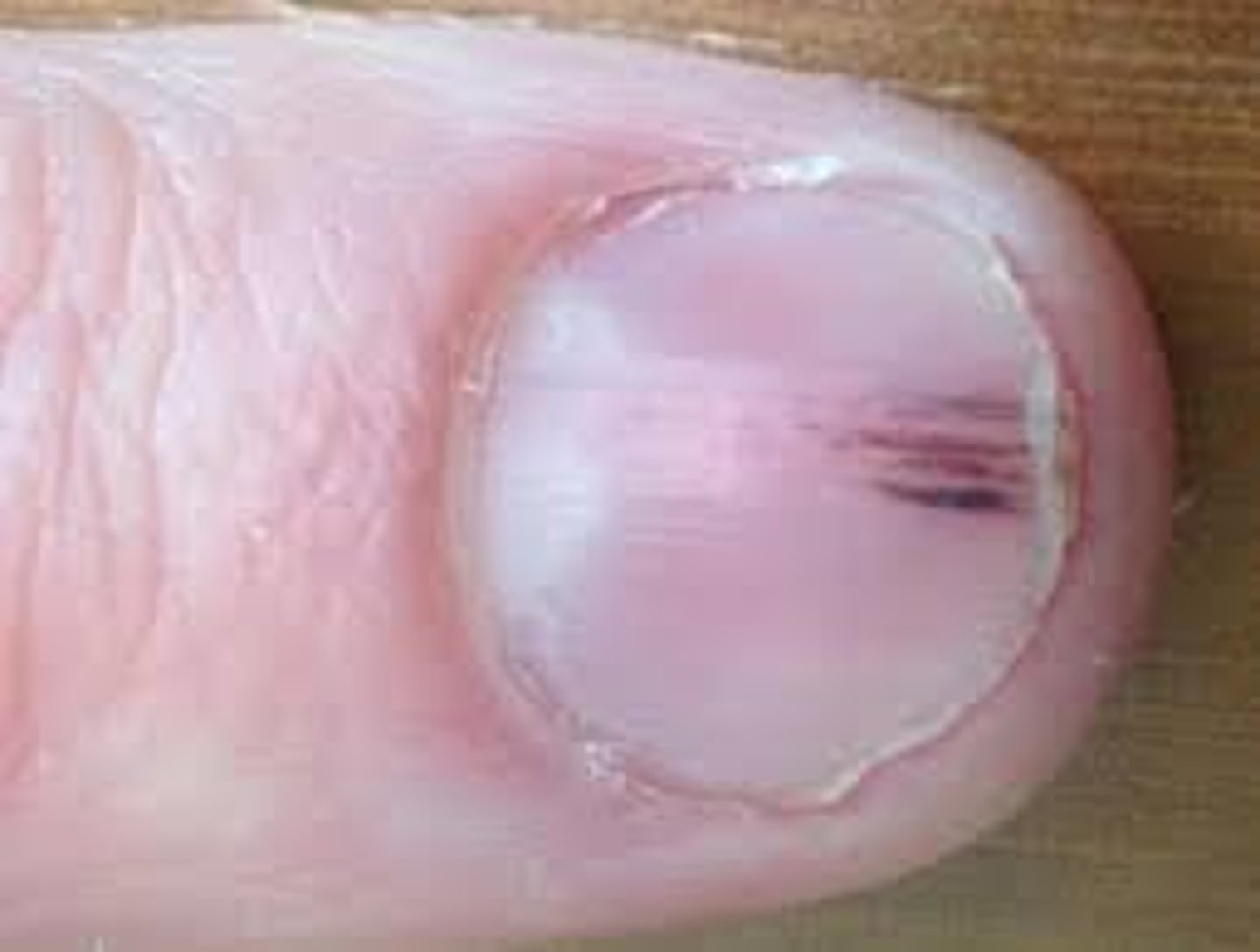
What are Beau's lines?
Transverse depressions in the nail
Causes:
-Trauma
-Exposure to cold
-Raynaud's disease
-Episodic disease serious enough to disrupt nail growth
Raynaud's disease:
-Areas of the body that feel numb or cool
-When arteries that supply the blood constrict
-Limits blood supply to extremities
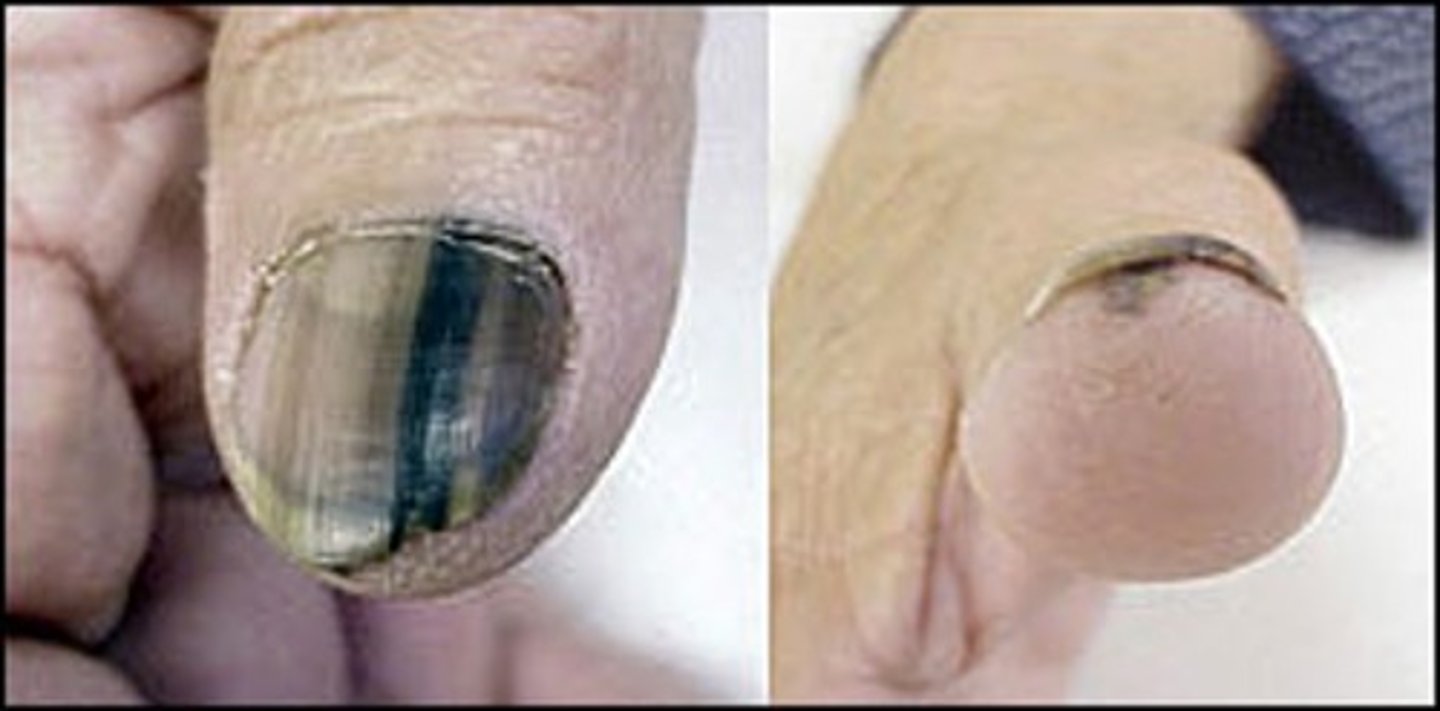
What are Melanotic Bands of the nail?
-Longitudinal black bands of nails caused by pigmentation under the nails
-Disrupts nail growth
-Biopsy is needed to rule out melanoma (cancer)
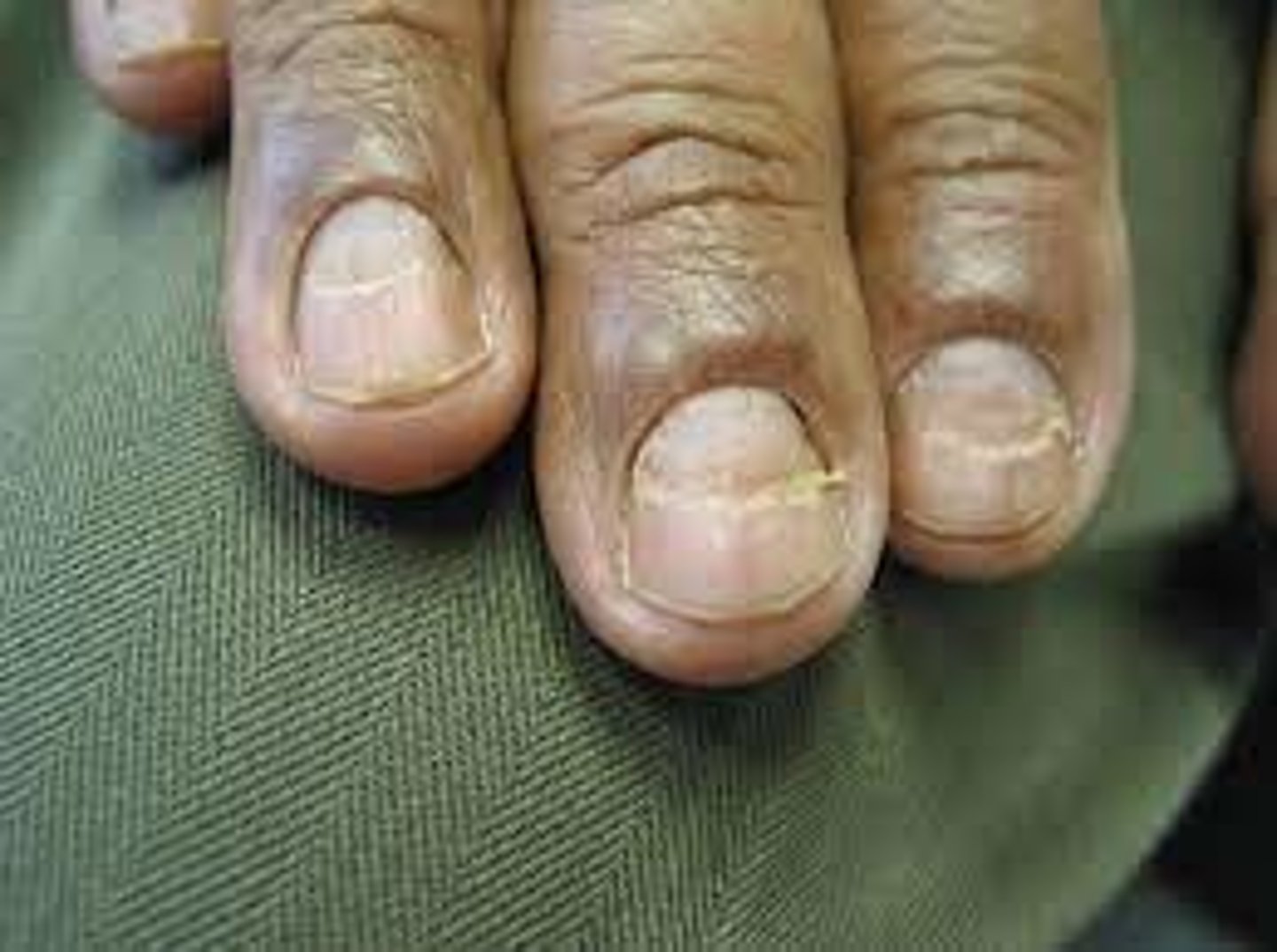
What is Nail Pitting?
Small depression on the nail surface
Causes:
-Exposure to chemicals
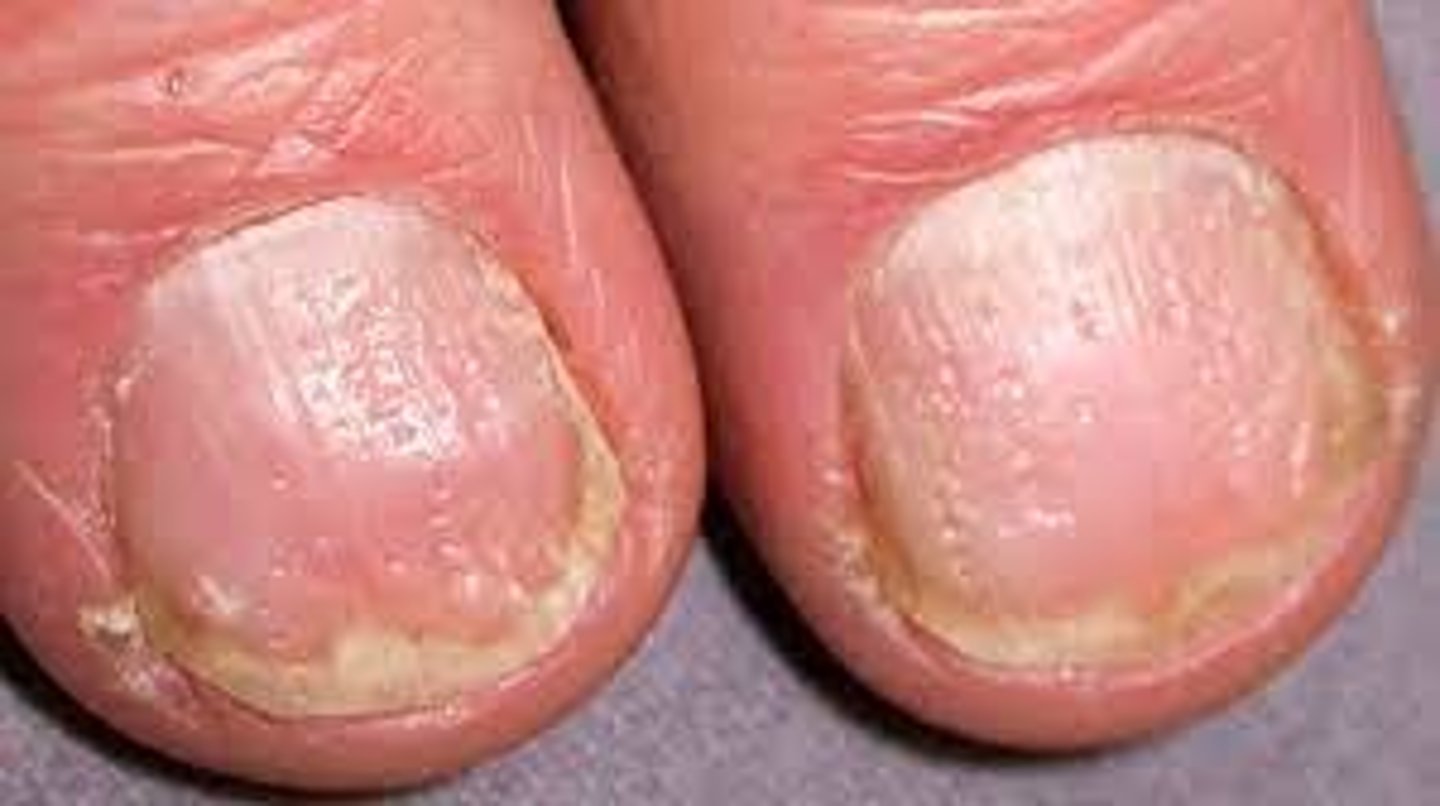
Leukonychia
White spots on the nail plate
Causes:
-Trauma (construction workers)
-Manipulation of the cuticle
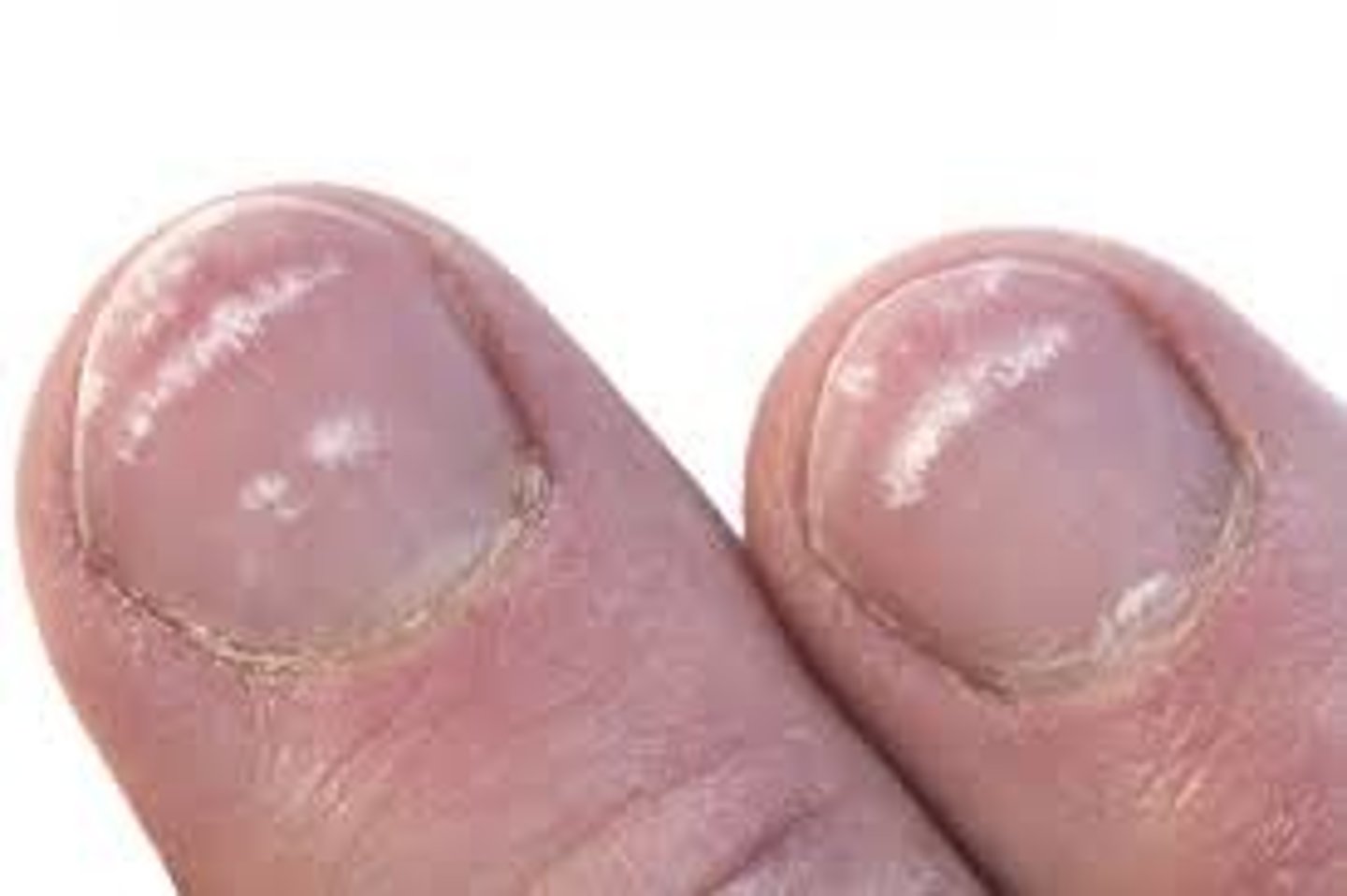
What is Koilonychia or Nail Spooning?
-Nails that have lost their convexity, becoming flat or concave in shape
-Opposite of nail clubbing
Causes:
-Iron deficiency anemia
-Polycythemia
-Coronary disease
-Syphilis
-Strong alkalis (soaps)
-Petroleum products
-Plummer Vinson's Syndrome
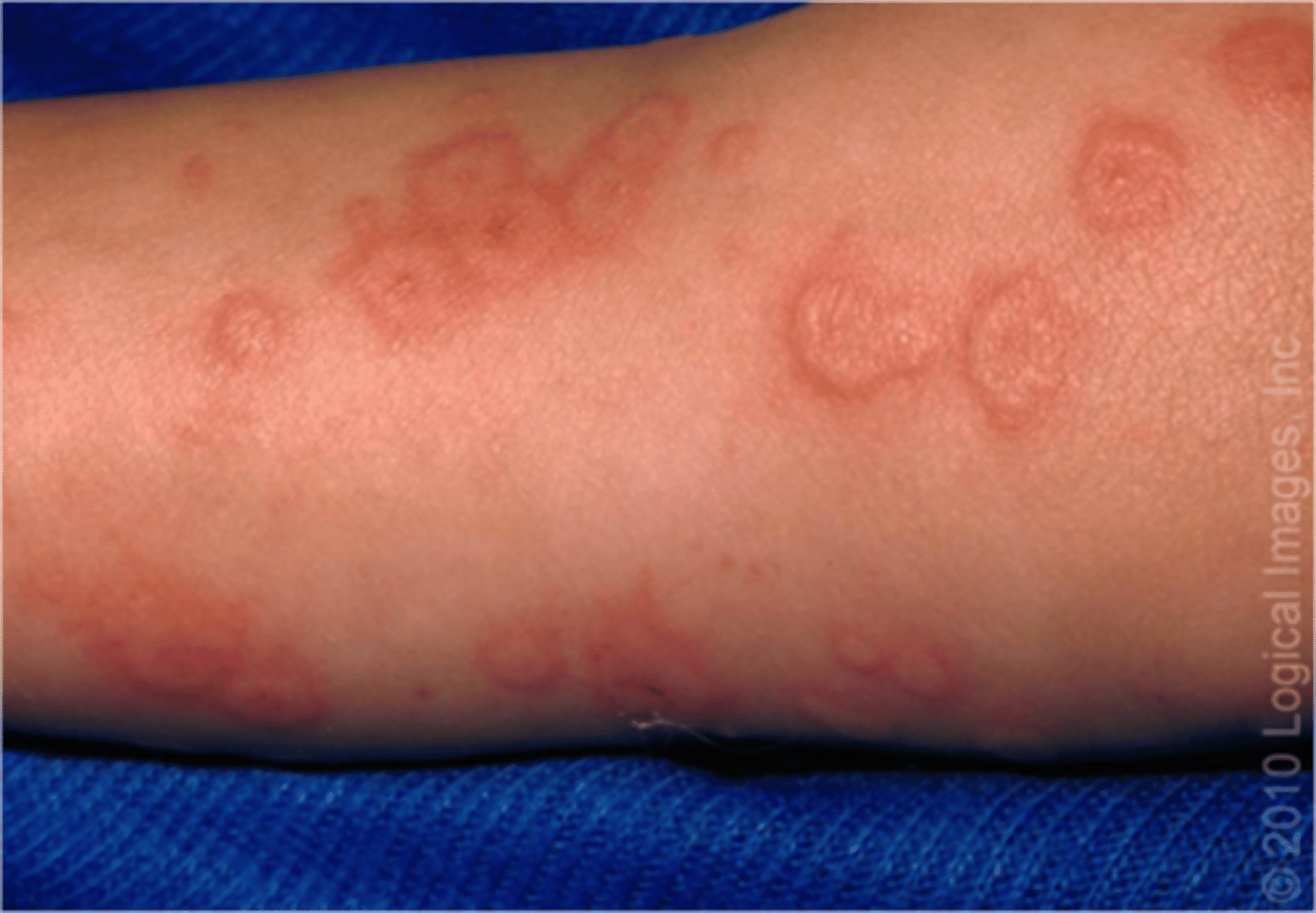
Erythema Multiforme
-Skin immune reaction that is triggered by infection or medication
-Main symptoms is a rash on the body that resembles a bullseyes
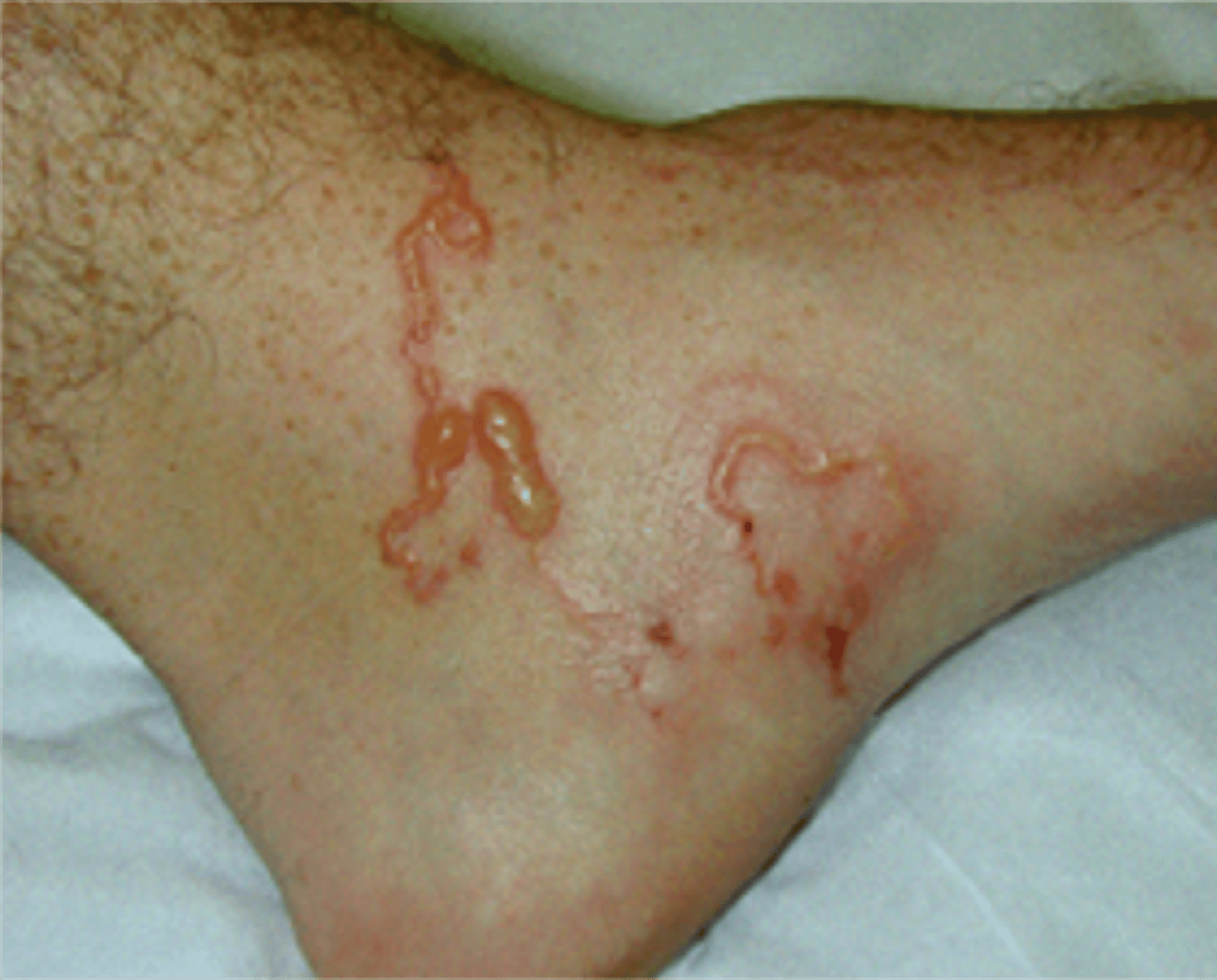
Cutaneous Larva Migrans
-Parasitic skin infection caused by hookworm larvae
-Infects cats, dogs, and other animals
-Infects humans when walking on sandy beaches barefoot
-Coming in contact with moist soft soil that has been contaminated with animal feces
What are examples of primary lesions?
-Macule
-Papule
-Patch (birth mark)
-Plaque
-Nodule
-Wheal
-Tumor
-Urticaria (hives)
-Vesicle
-Bulla
-Cyst
-Pustule
What is a primary lesion?
A lesion that occurs normally or develops as a direct result of a condition
What is a secondary lesion?
Lesions that evolve from primary lesions or due to another condition
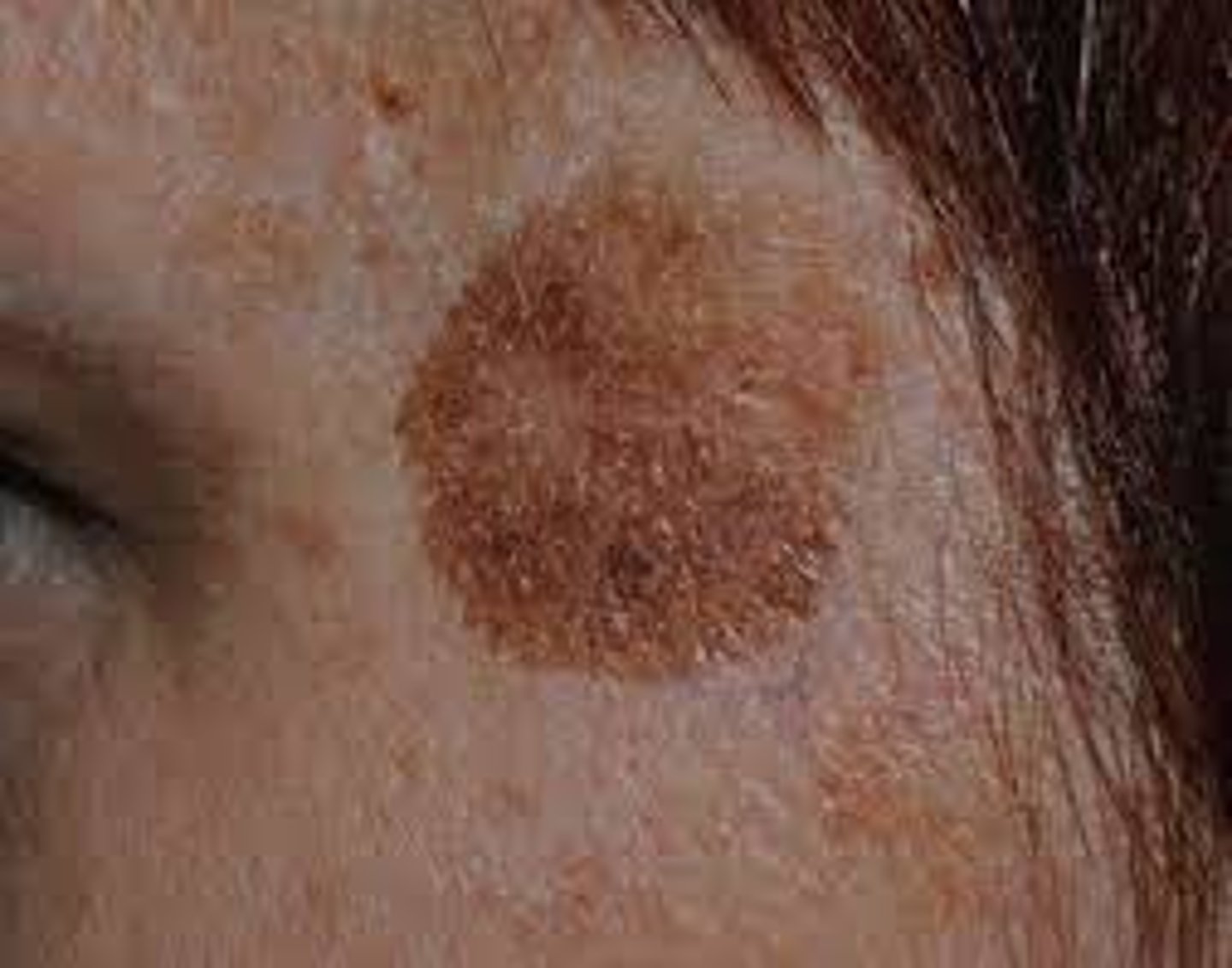
Macule (Primary)
-Flat, circumscribed area that is a change in color of the skin
-Less than 1 cm
Examples:
-Moles (nevi)
-Freckles
-Scarlet's fever (erythematous macules)
-Mesales
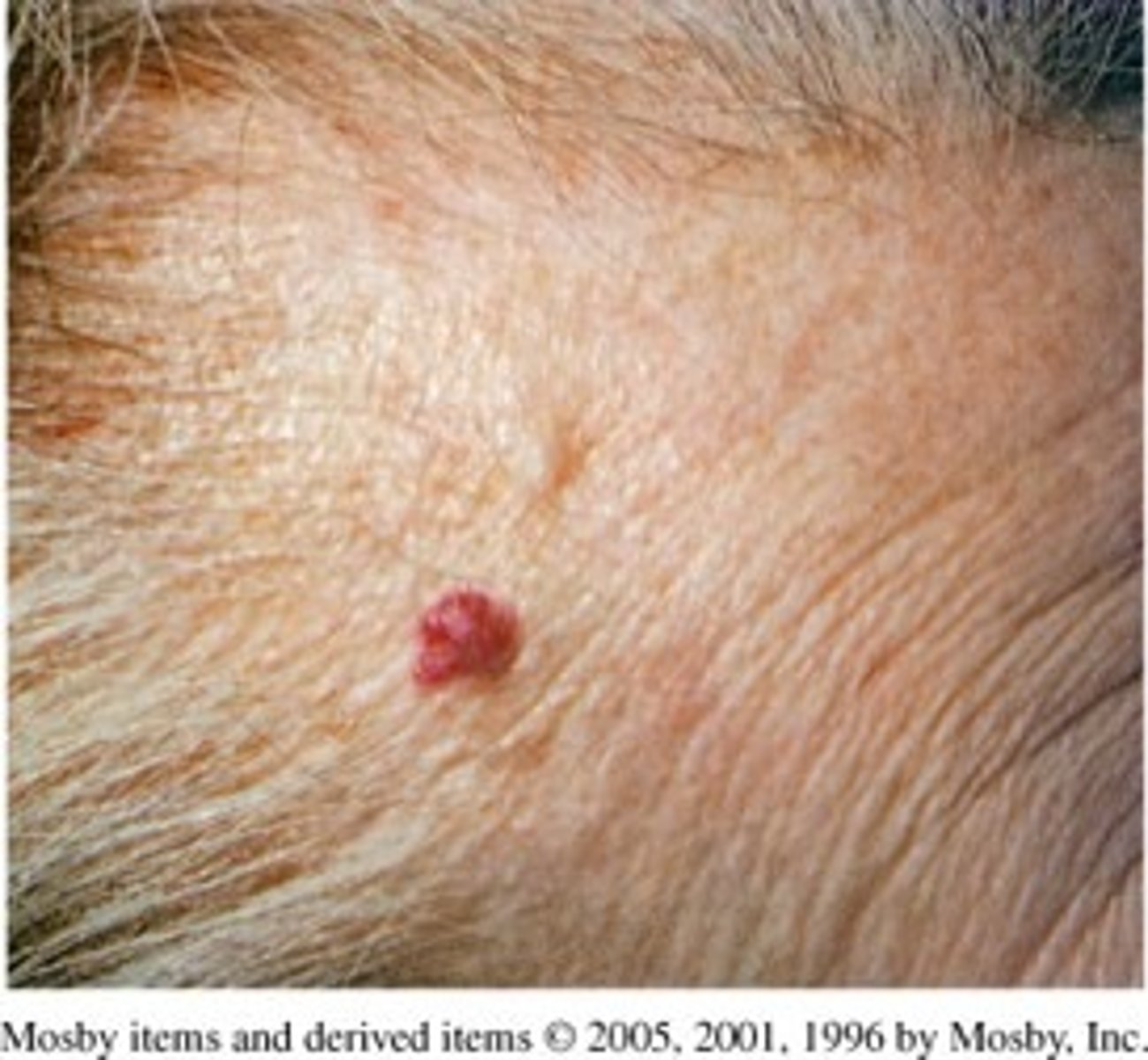
Papule (Primary)
-Solid (firm), elevated lesion with no visible fluid
-1/2 to 1 cm
Examples:
-Elevated mole
-Skin tag
-Warts
-Cherry angioma
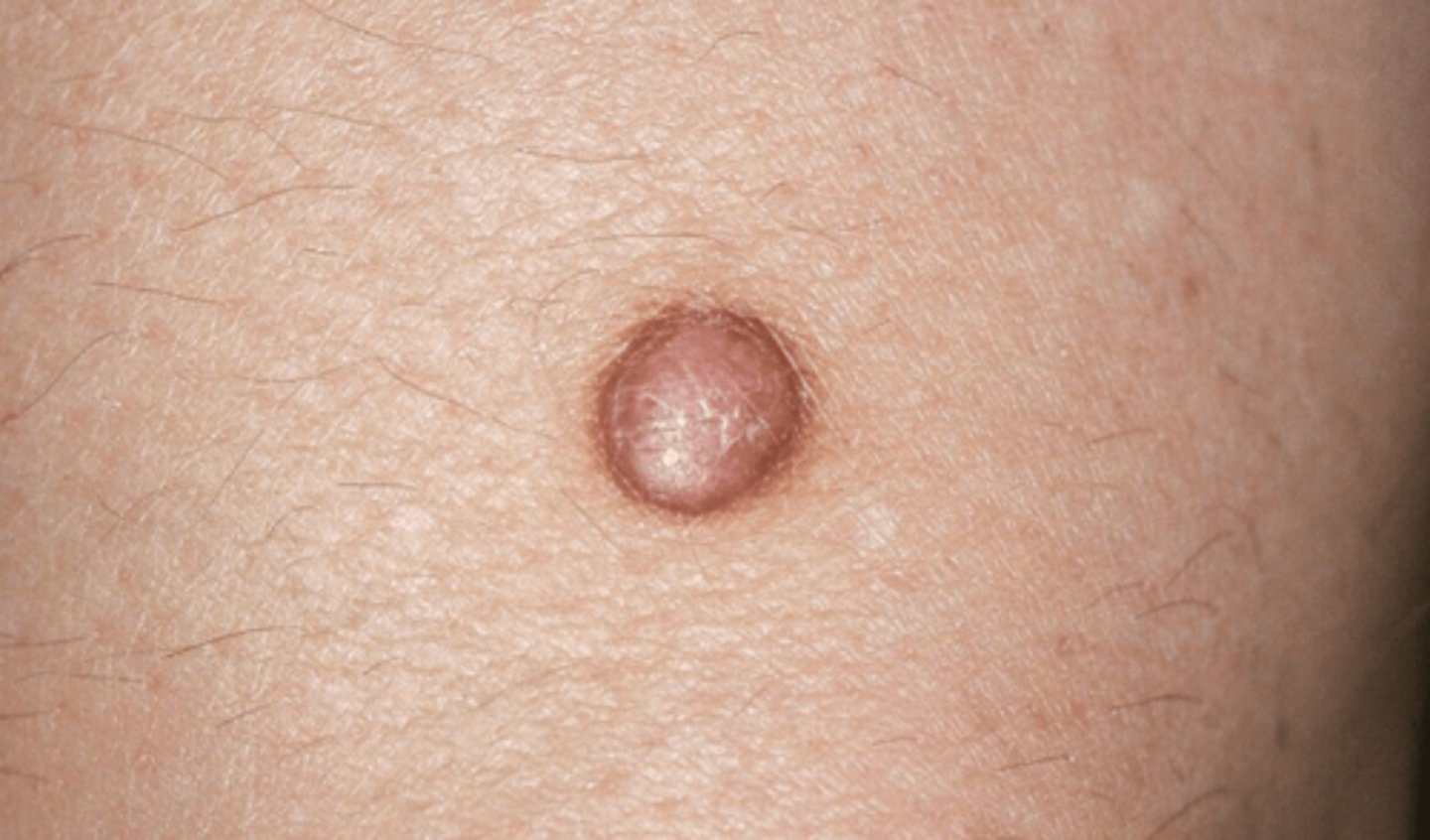
Nodule (Primary)
-Elevated, firm, circumscribed lesion, larger/deeper than papule
-Located in dermis, subcutaneous tissue, or epidermis
-1/2 cm or more
Example:
-Dermatofibroma
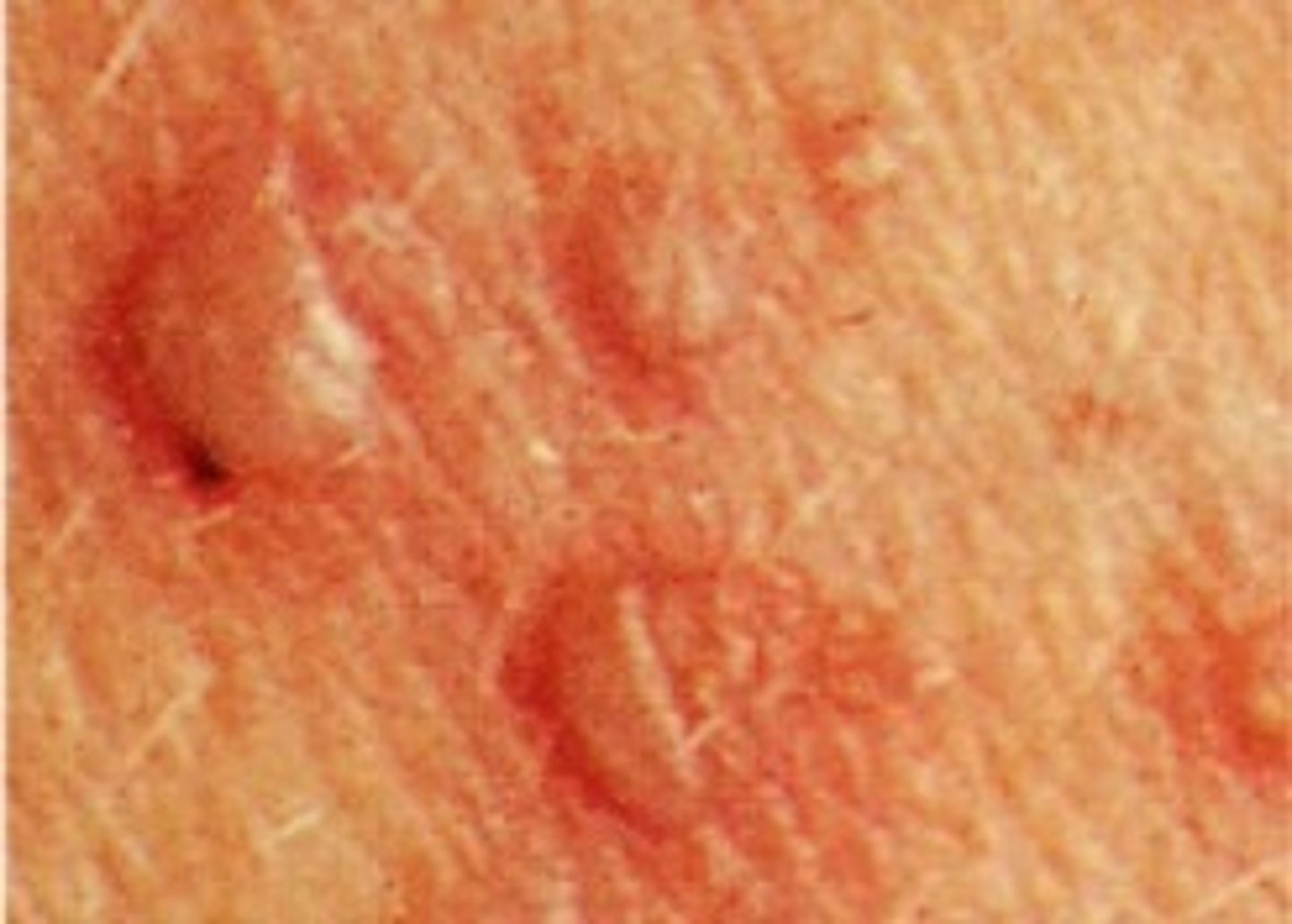
Wheal (Primary)
-Elevated, irregular, or round, flat-topped area
-Fluid with edematous (fluid-filled) and erythematous (red)
Causes:
-Insect bites
-Allergic reactions
-Hives
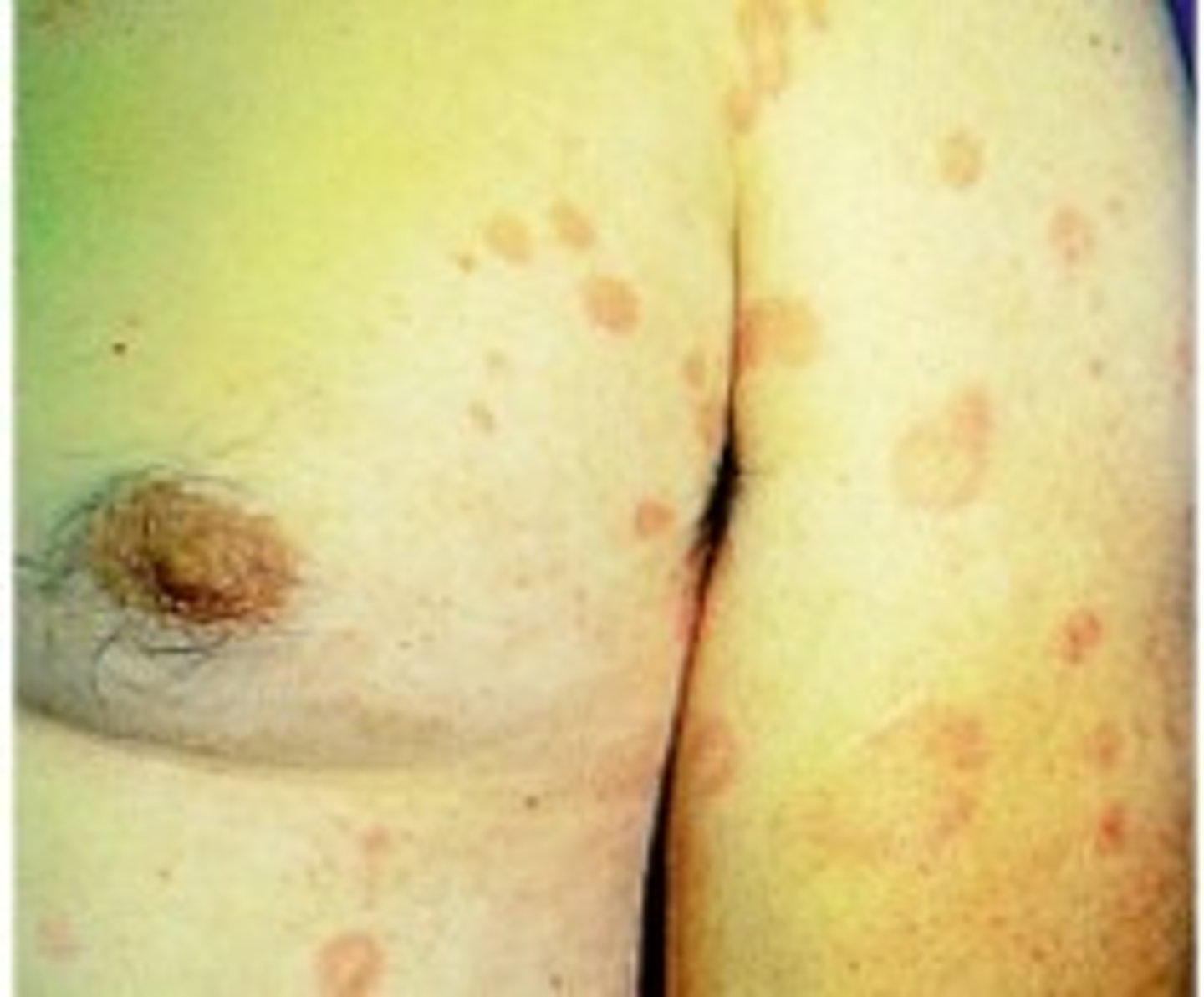
Vesicle & Bullae (Primary)
-Epidermal elevation in skin
-Contains clear fluid (serous)
-Less than 1/2 cm
-If bigger than 1/2 cm considered a Bullae
Examples:
-Chicken pox
-Blisters
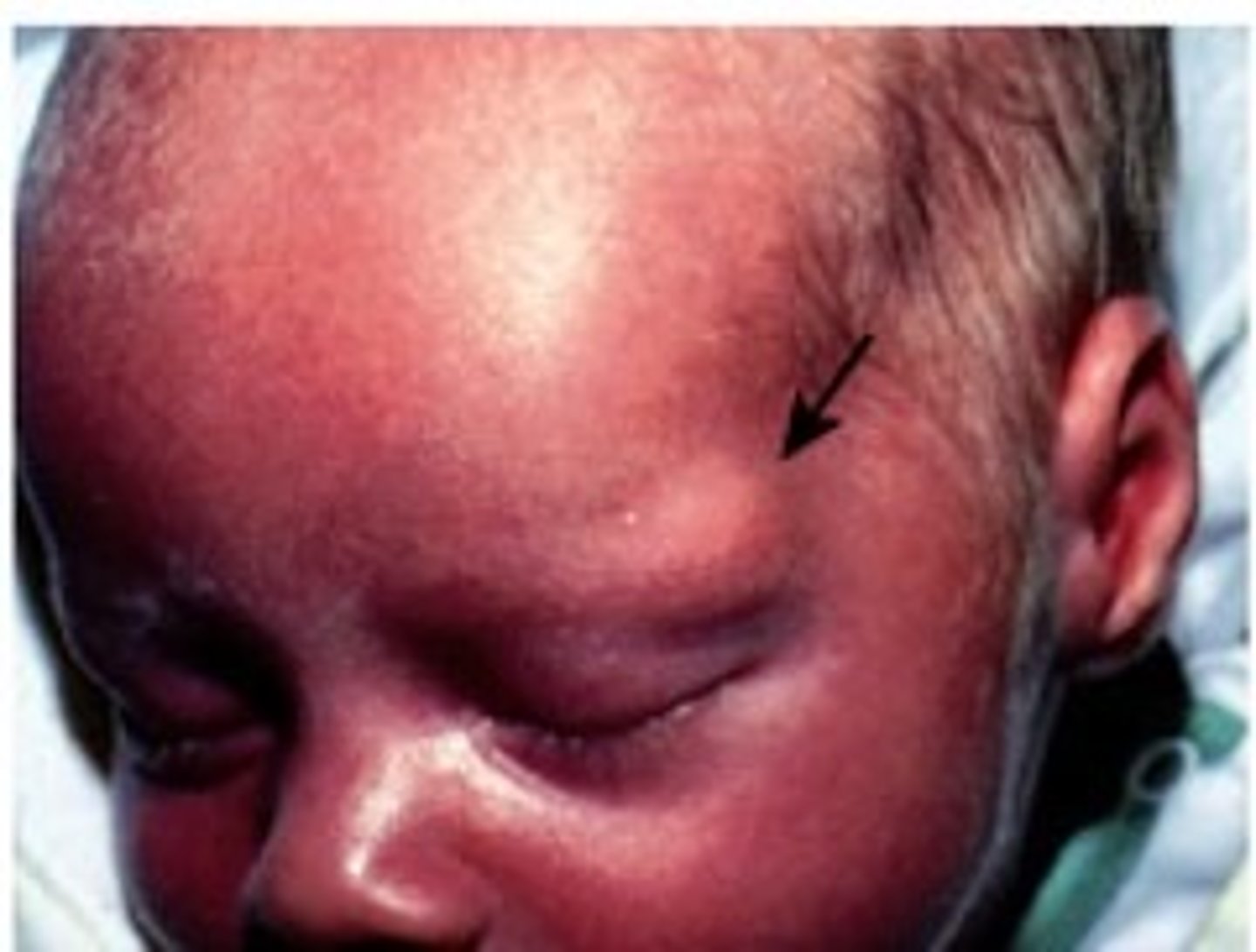
Cyst (Primary)
-Closed sac that contains liquid or semisolid material
Causes:
-Cystic acne
-Sebaceous cyst
Note: can get infected (antibiotics)
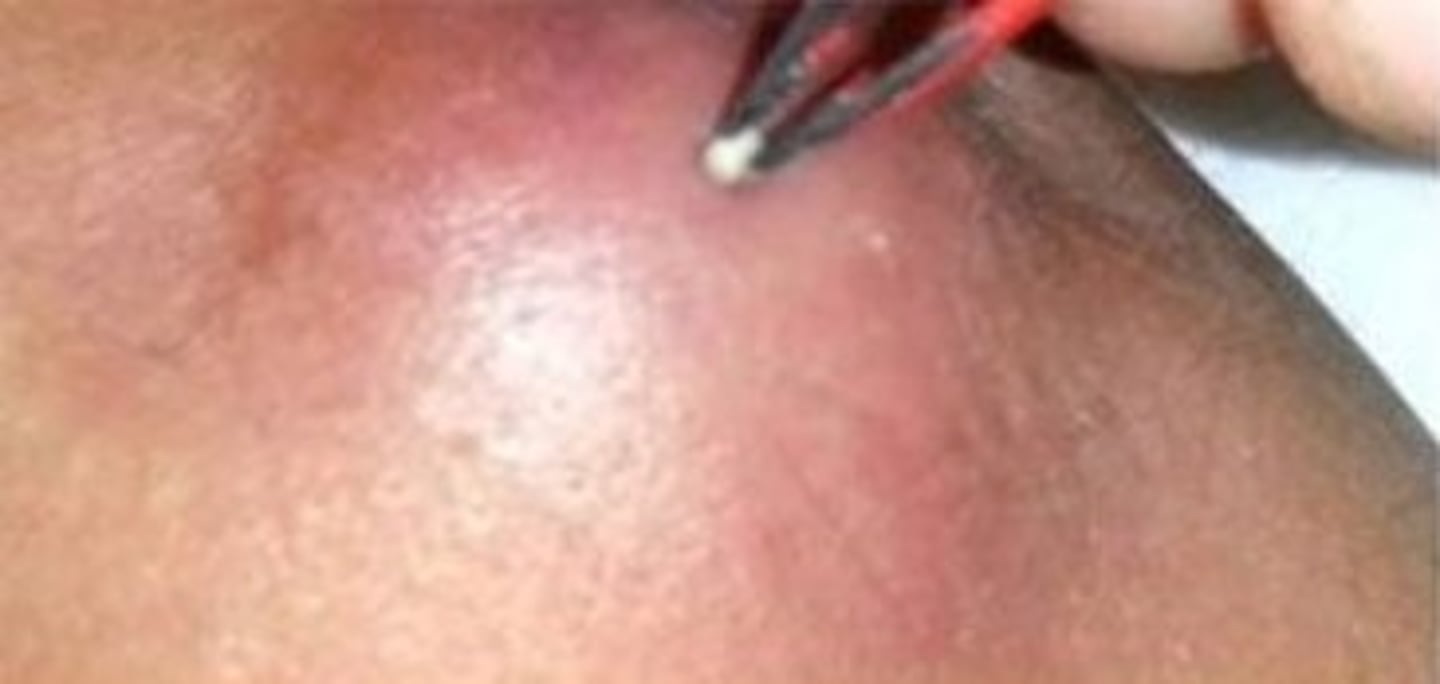
Sebaceous cyst (Primary)
-Sac under the skin filled with sebum or oil from a sebaceous gland
-This can grow to a large size and may need to be excised
Pustule (Primary)
-Circumscribed elevation of the skin
-Contains purulent exudate (white, yellow, greenish-yellow)
Examples:
-Acne
-Herpes simplex
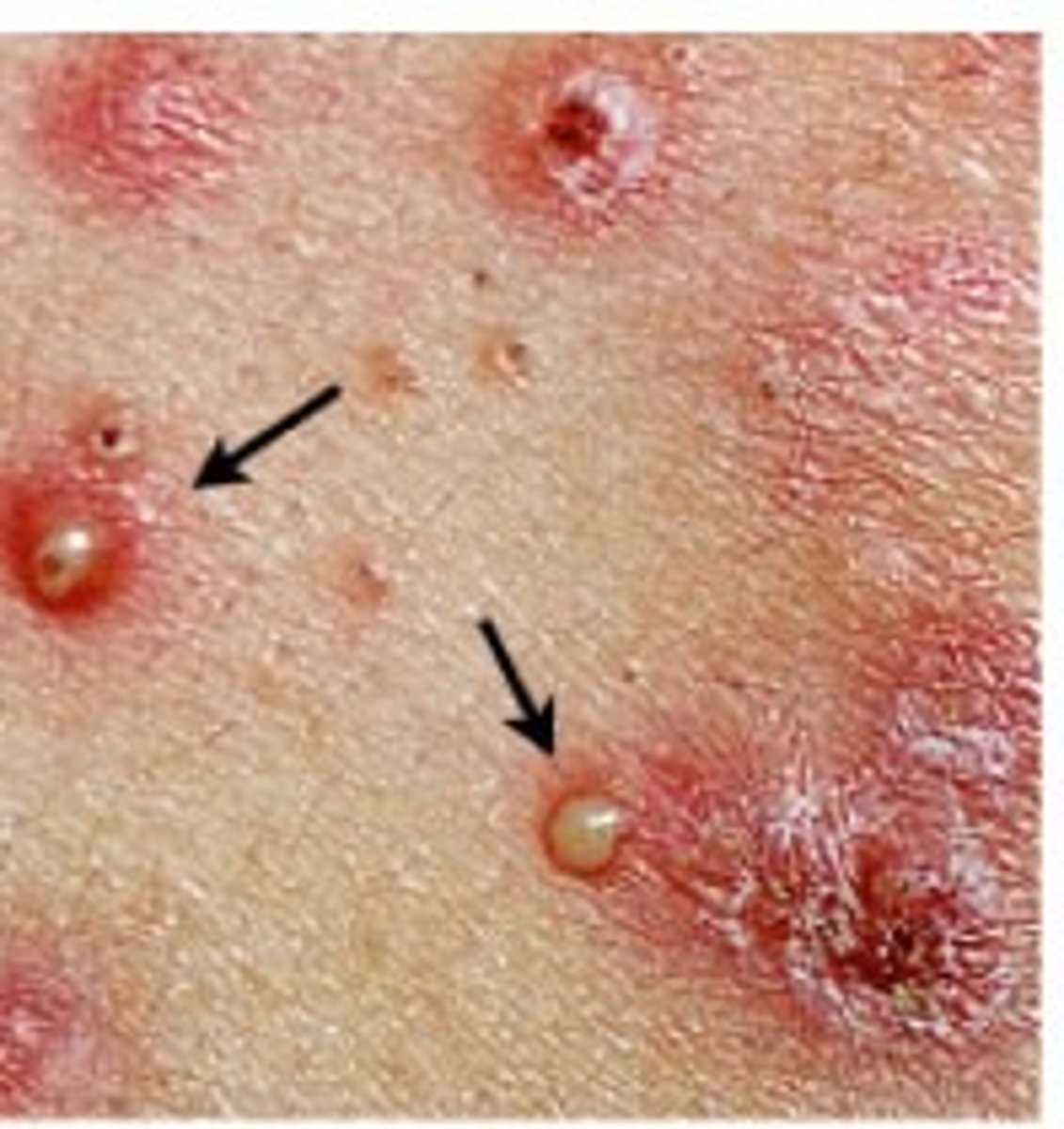
What are examples of secondary lesions?
-Crust
-Scale
-Fissure
-Erosion
-Ulcer
-Excoriation
-Scar
-Atrophic scar
-Licenification
-Keloid
Crust (Secondary)
-Dried drainage or blood, slightly elevated
-Varies in size and color (red, black, tan, mixed)
Example:
-Sab on abrasion
-Eczema
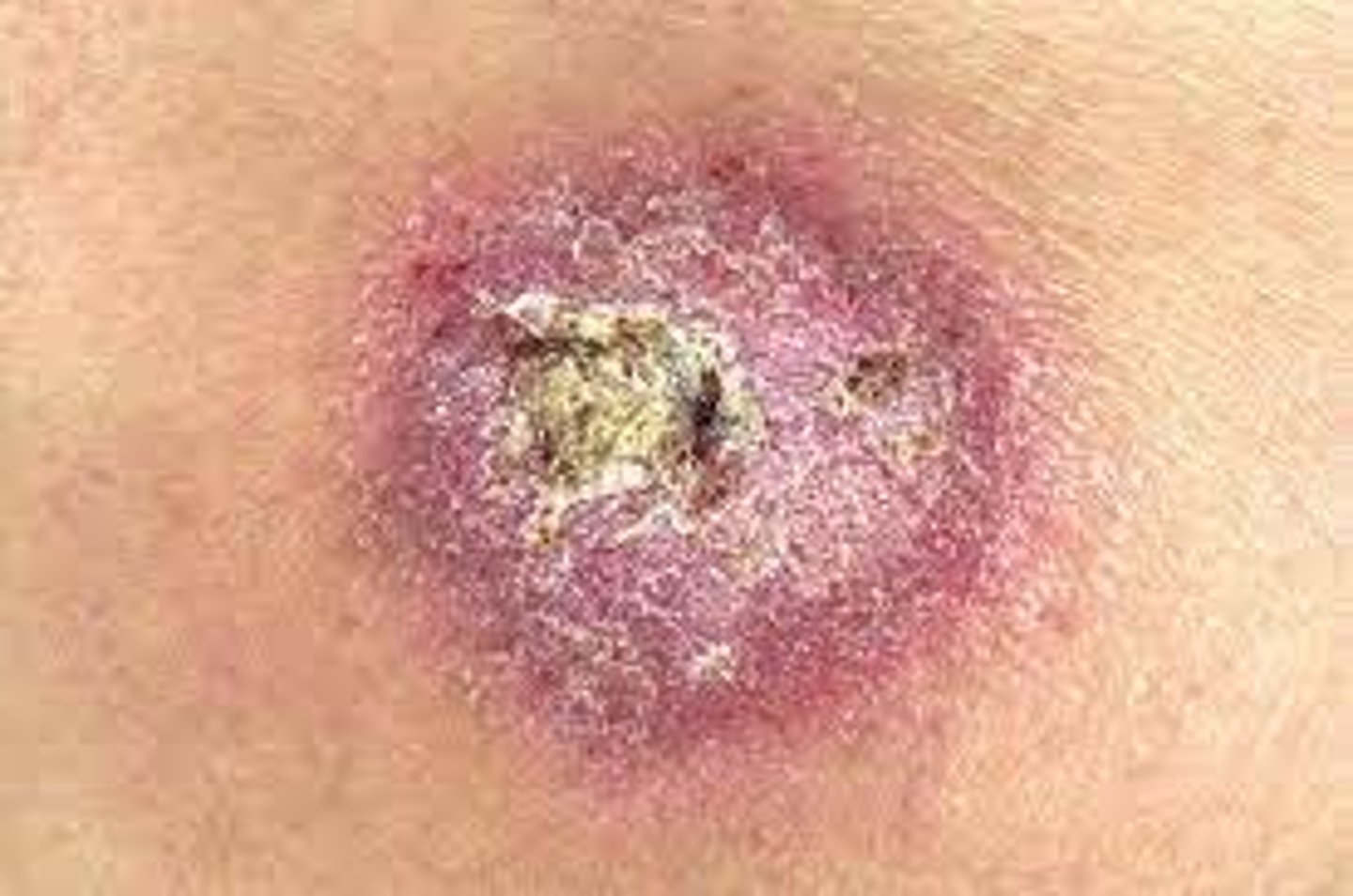
Scale (Secondary)
Dry, flaky, dead skin
Cause:
-Venous stasis
-Edema
Note: lotion (it might snow)
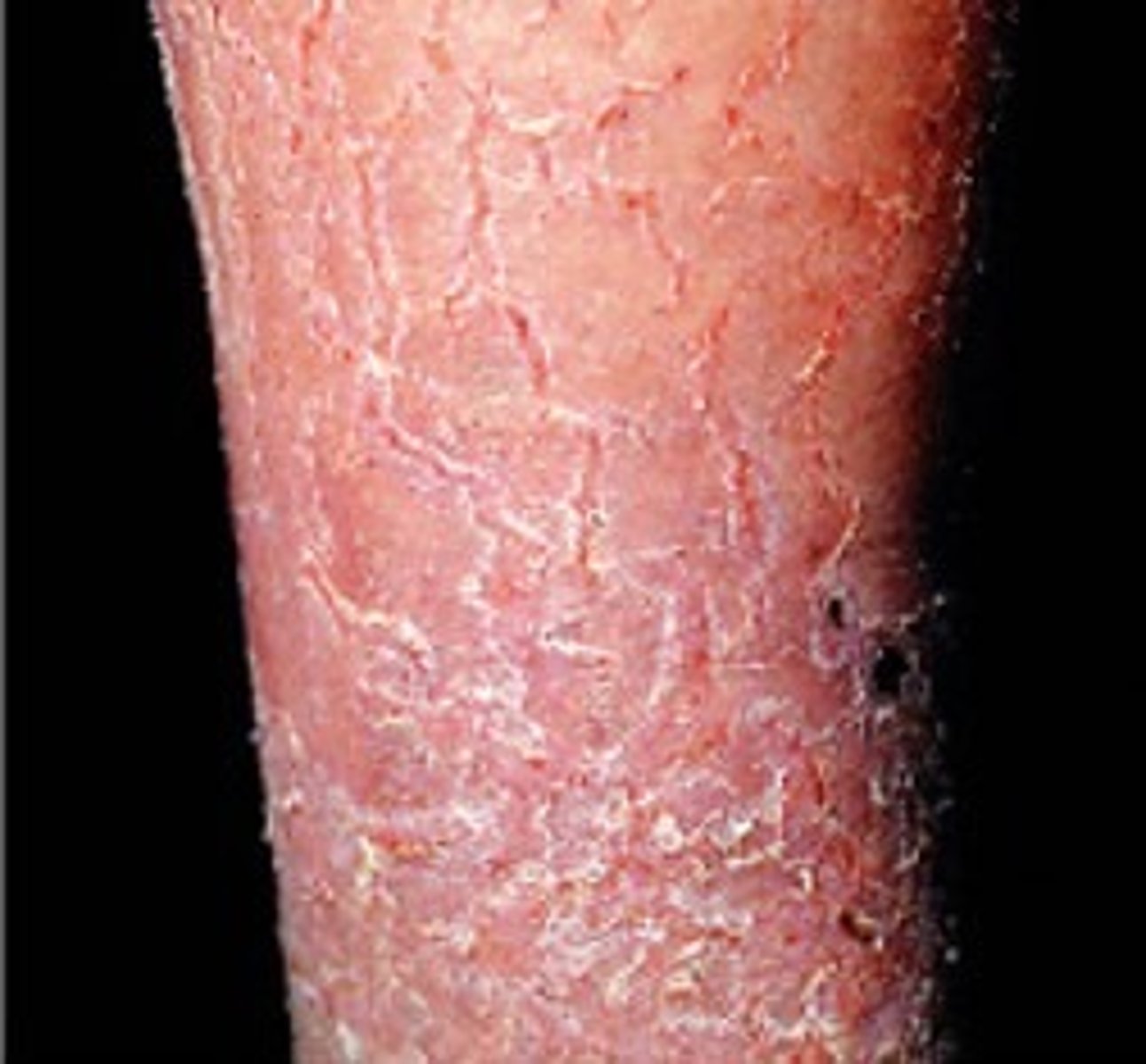
Fissure (Secondary)
Laceration in the skin
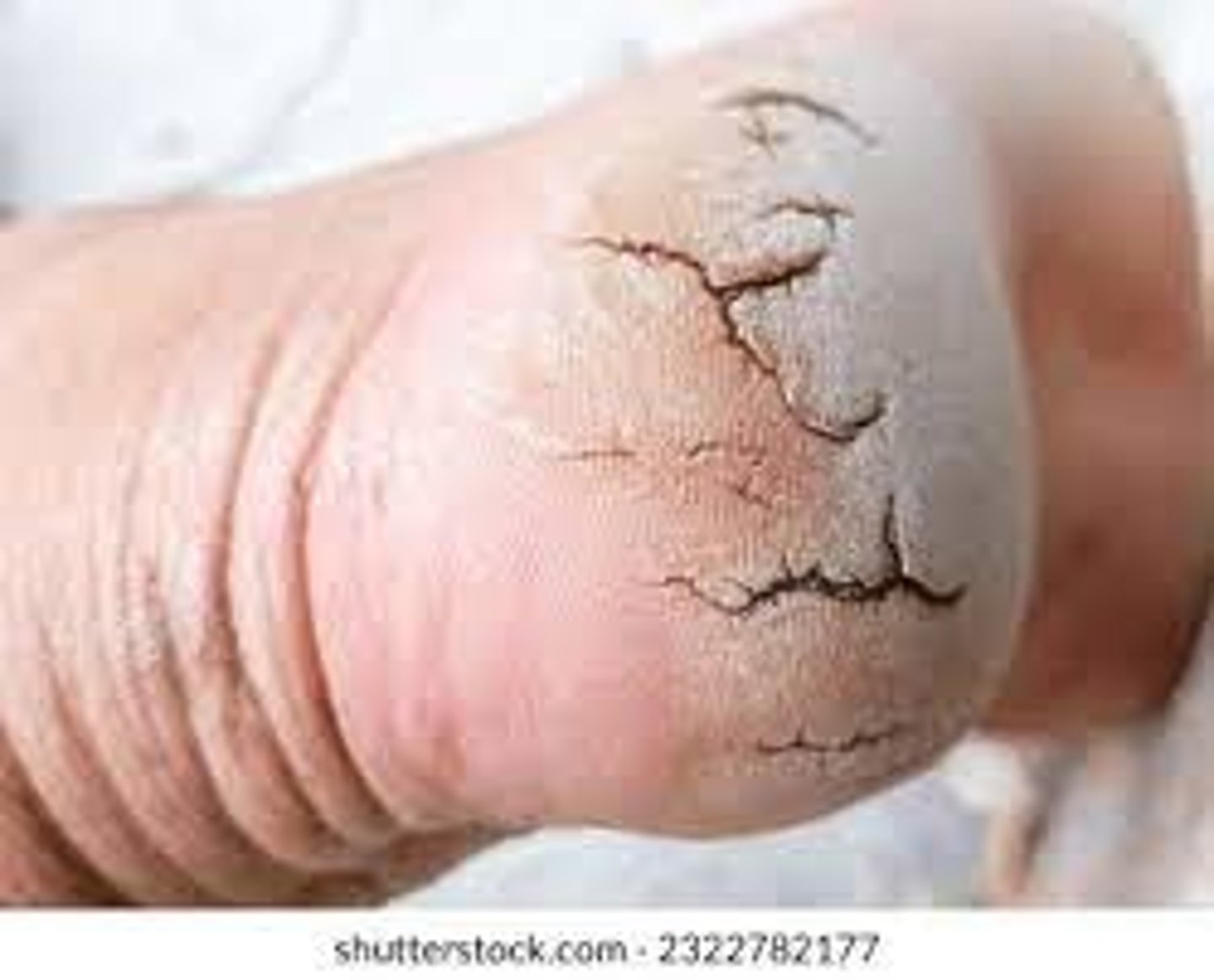
Erosion (Secondary)
-Loss of a part of the epidermis, depression
-Moist and glistening
Examples:
-Cavity in the skin due to acne
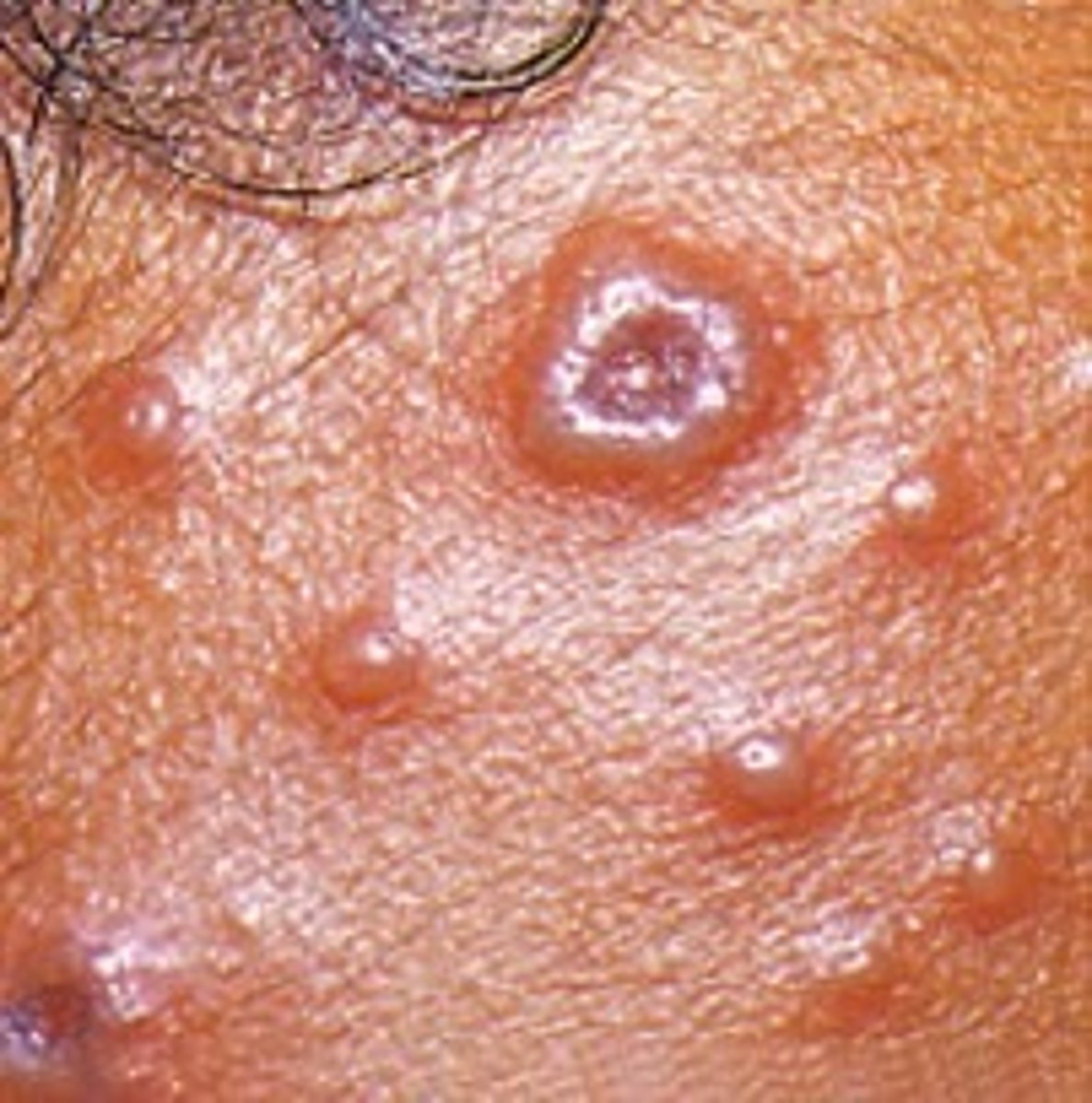
Ulcer (Secondary)
-Loss of epidermis and the dermis
-Concave (varies in size)
-Caused by pressure or friction
Note: has to heal by secondary intention, these can happen over night
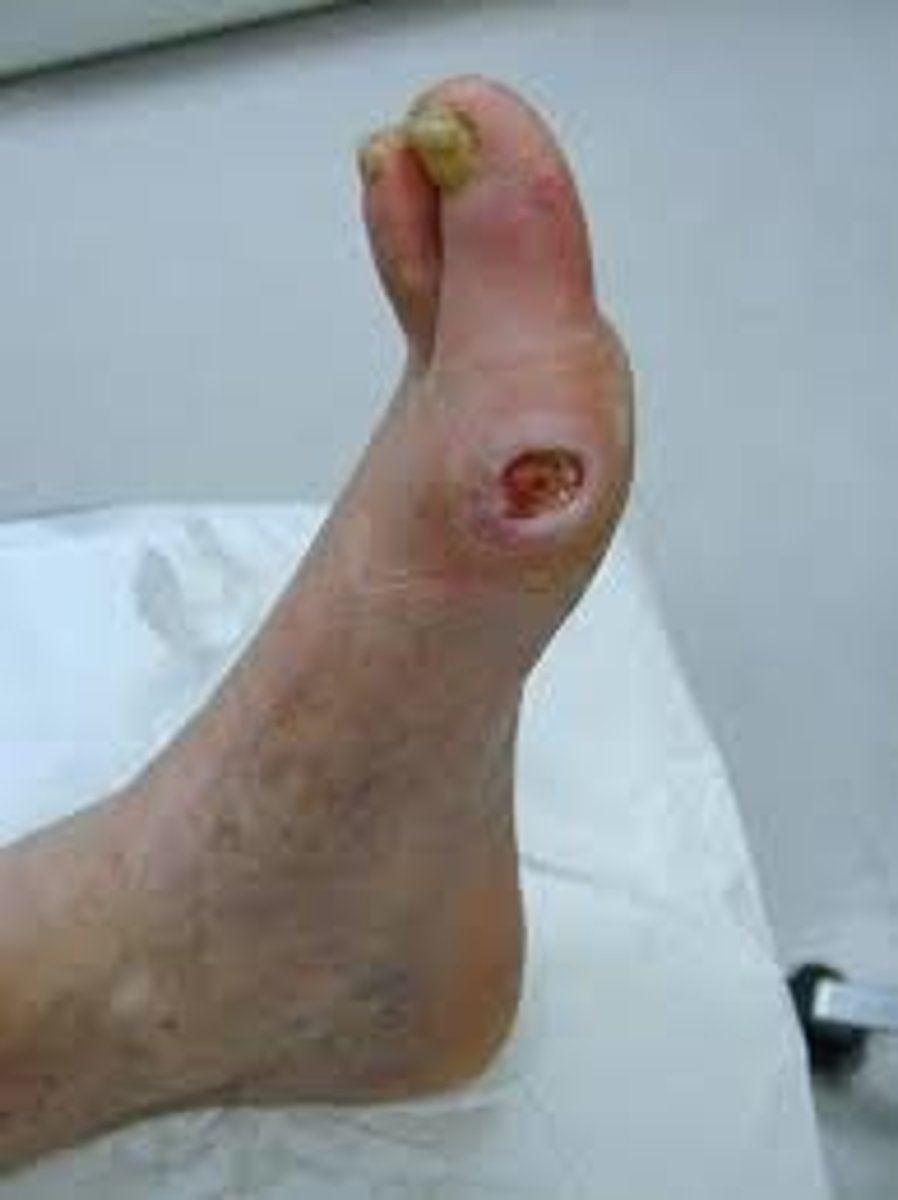
Excoriation (Secondary)
Loss of epidermis caused by urine or stool on the skin (diaper rash)
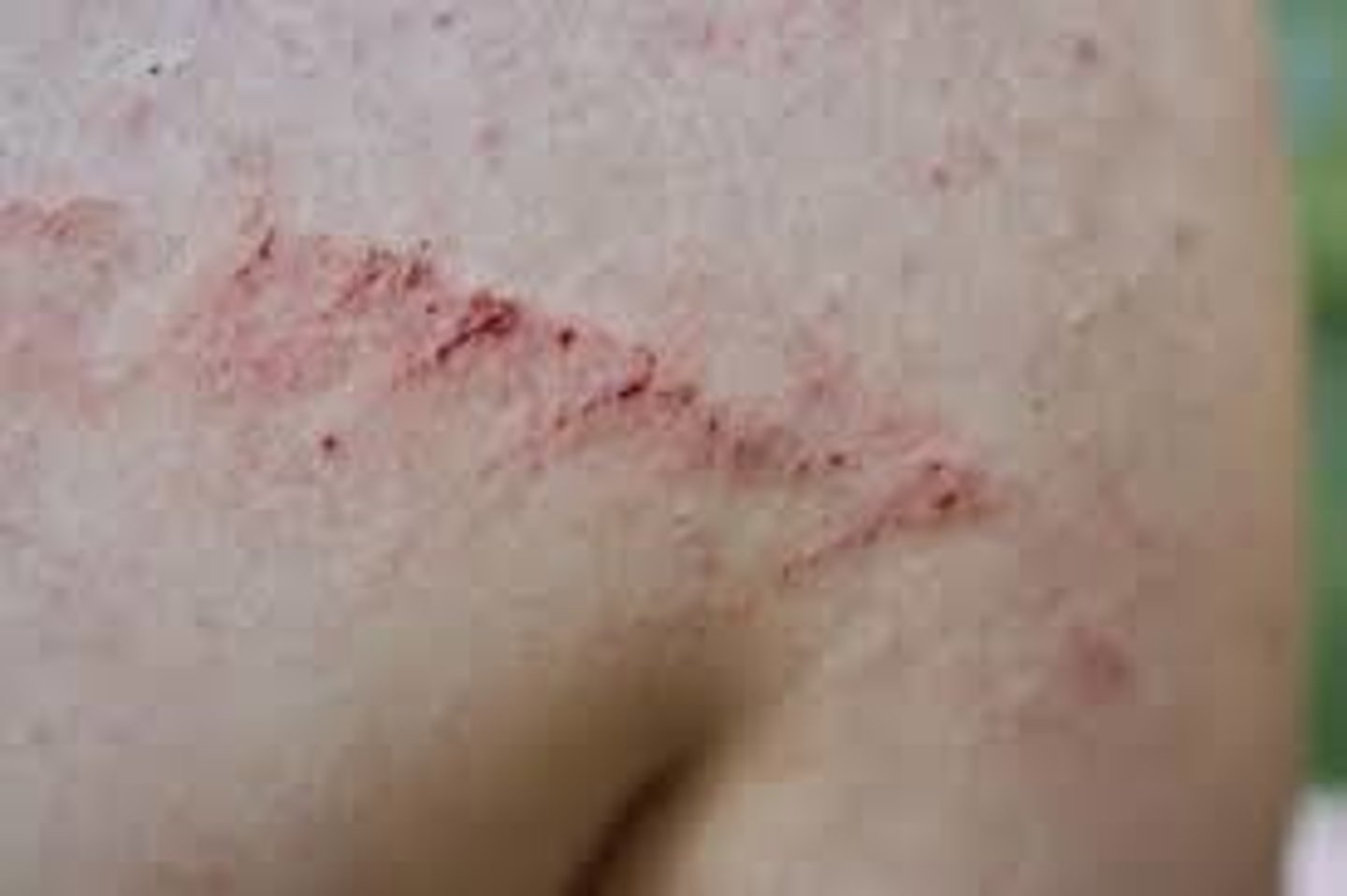
Scar (Secondary)
Thin to thick fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin following an injury or laceration of the dermis
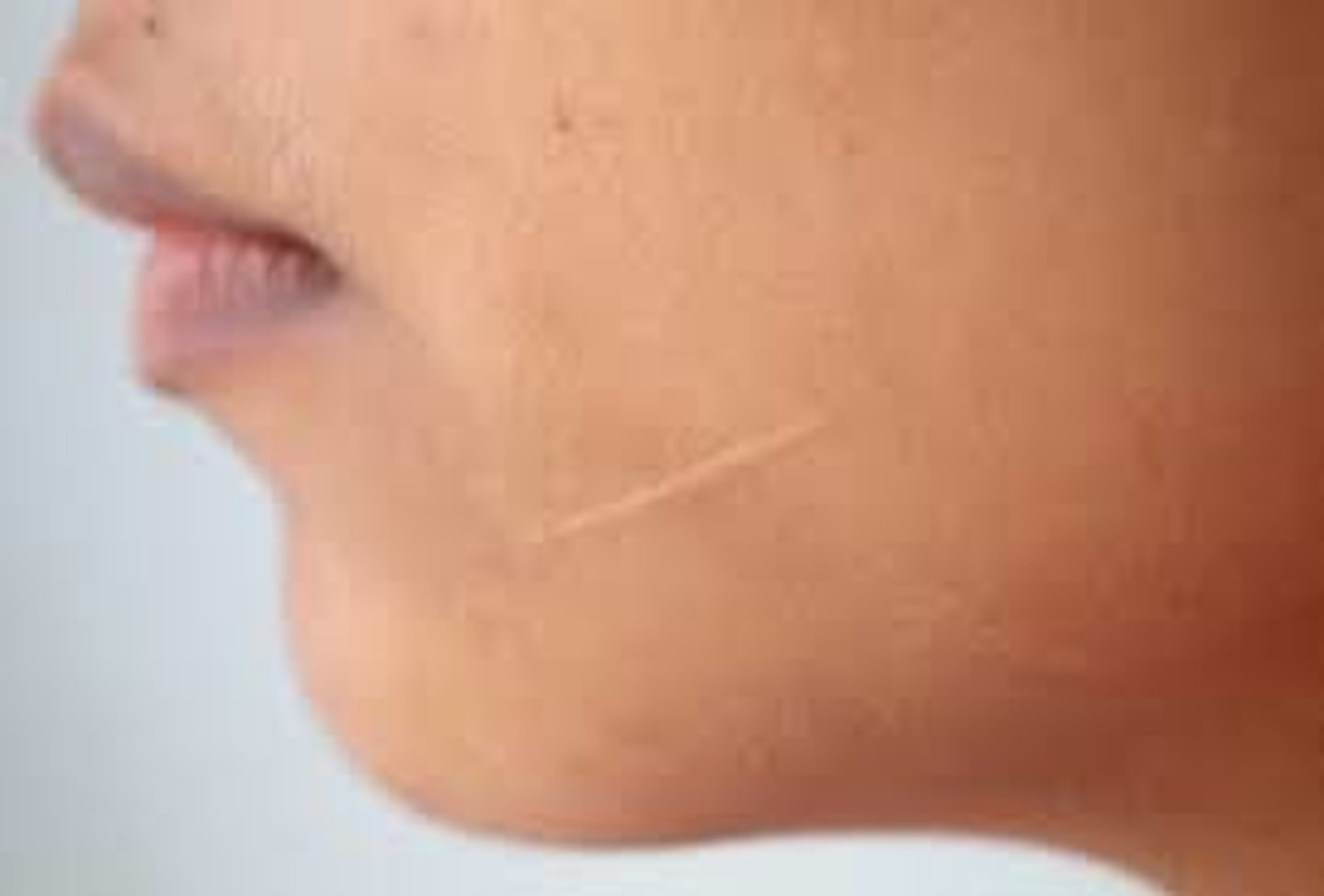
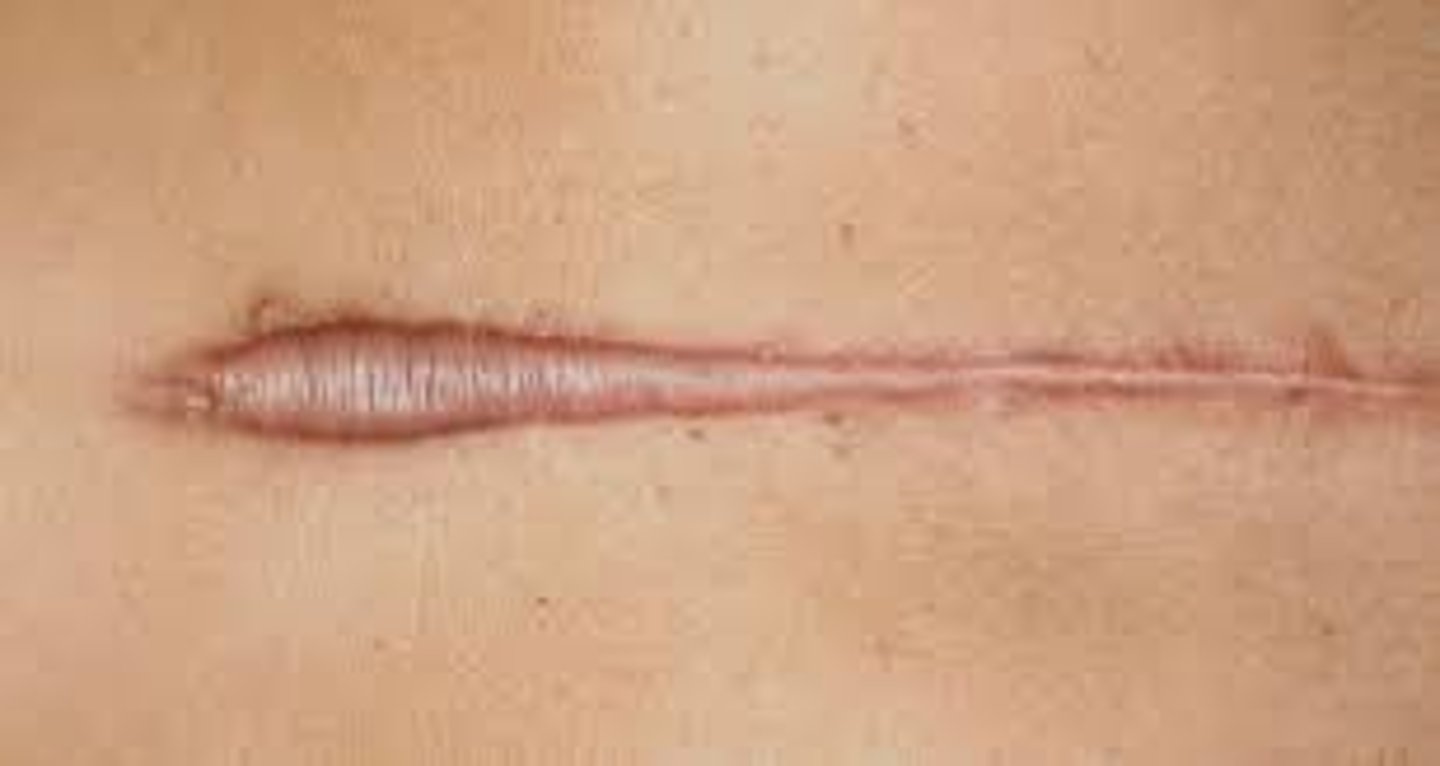
Atrophic scar (Secondary)
Scar resulting in a skin depression because of lost tissue
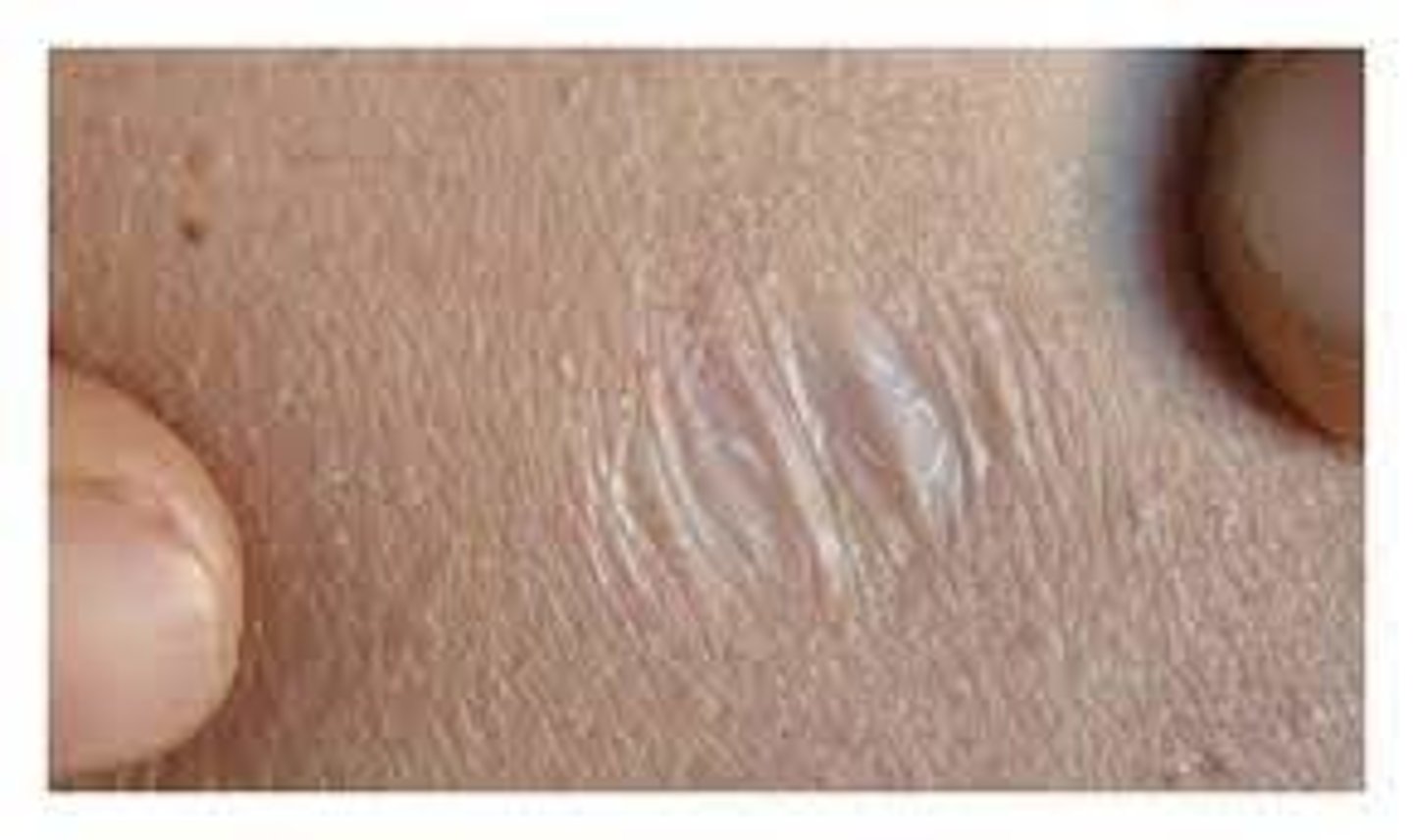
Keloid (Secondary)
-Overgrowth of tissue on a wound
-Progressively enlarging scar
-Laser can remove this, but it often returns
Examples:
-Earrings (piercing)
-Lacerations
Note: common in African Americans
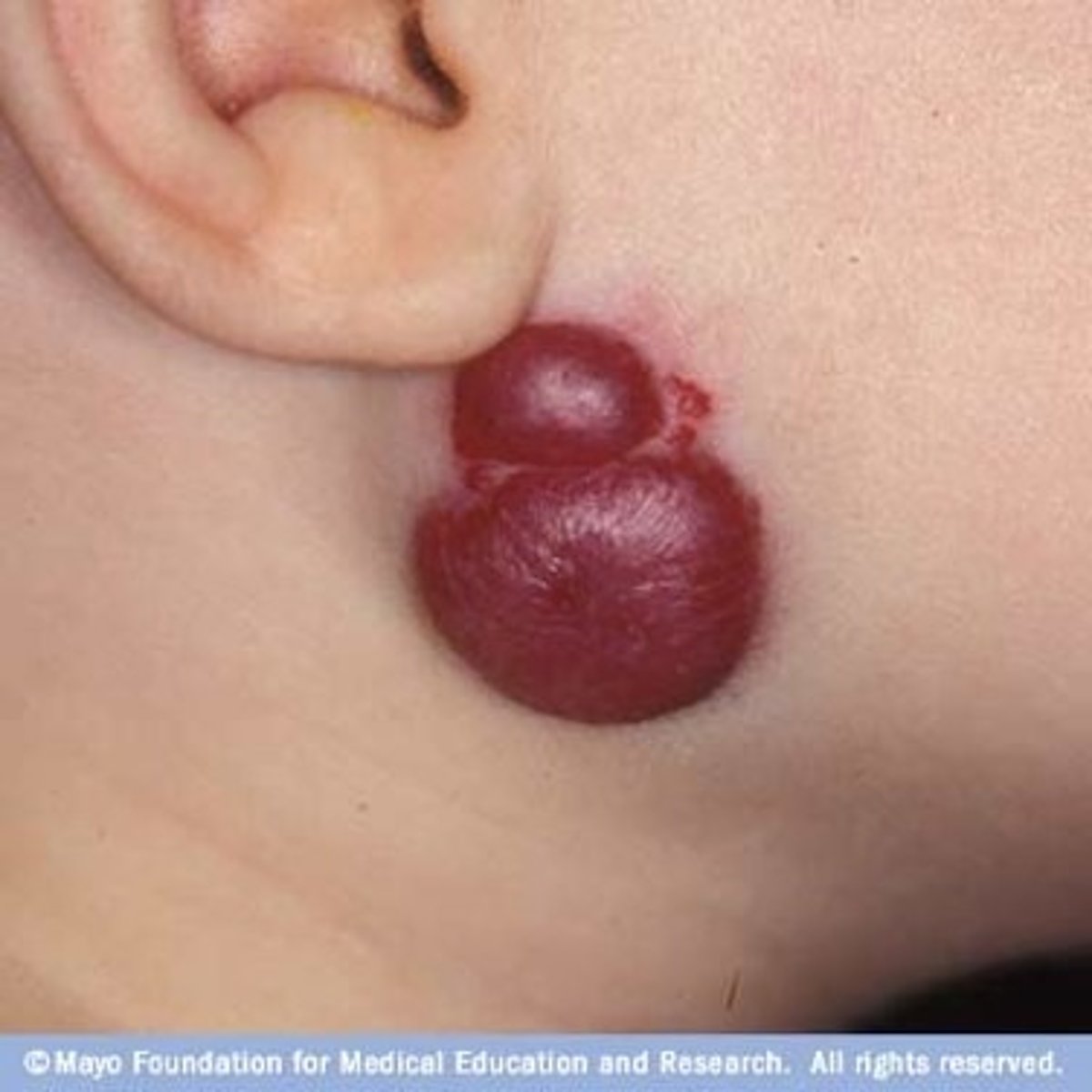
Hemangioma/strawberry hemangioma (Primary)
-Form of a birthmark
-Bright red patch or nodule of extra blood vessels in the skin
-Grows during first year of life (recedes over time)
-Benign, not associated with other medical conditions
Examples of Common Abnormal Skin Lesions:
-Primary contact dermatitis
-Labial herpes simplex (cold sore)
-Allergic drug reaction
-Tinea corporis (ringworm)
-Herpes zoster (shingles)
-Psoriasis
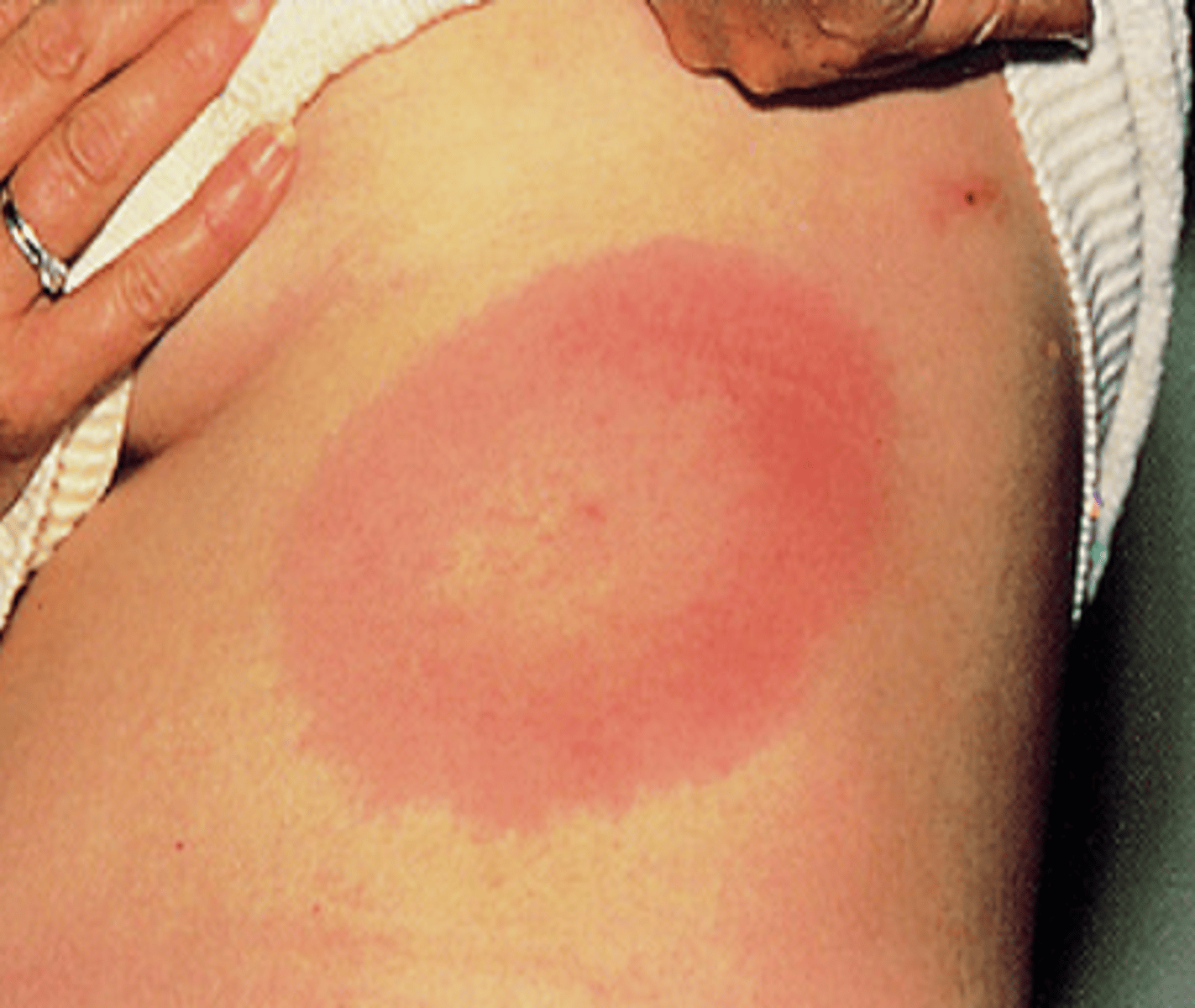
-Lyme Disease (Erythema migrans)
-Basal cell carcinoma
-Squamous cell carcinoma
-Malignant melanoma
-Chicken pox
-Steven johnson
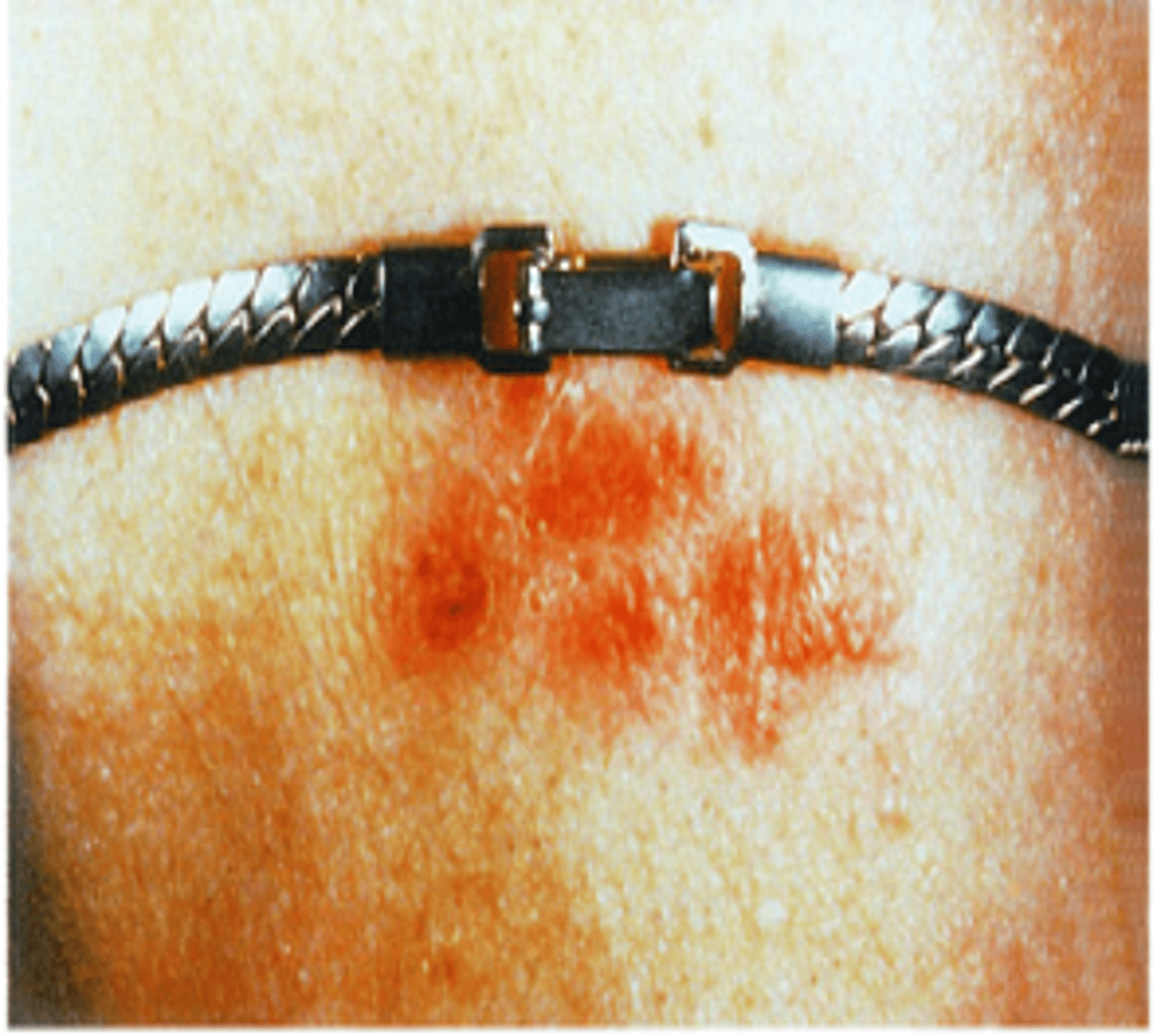
Contact dermatitis (Primary)
Inflammatory reaction of the skin in response to irritant or allergen such as metals, plants, chemicals, and detergents
Common causes:
-Jewelry (NICKEL in metal)
-Belts
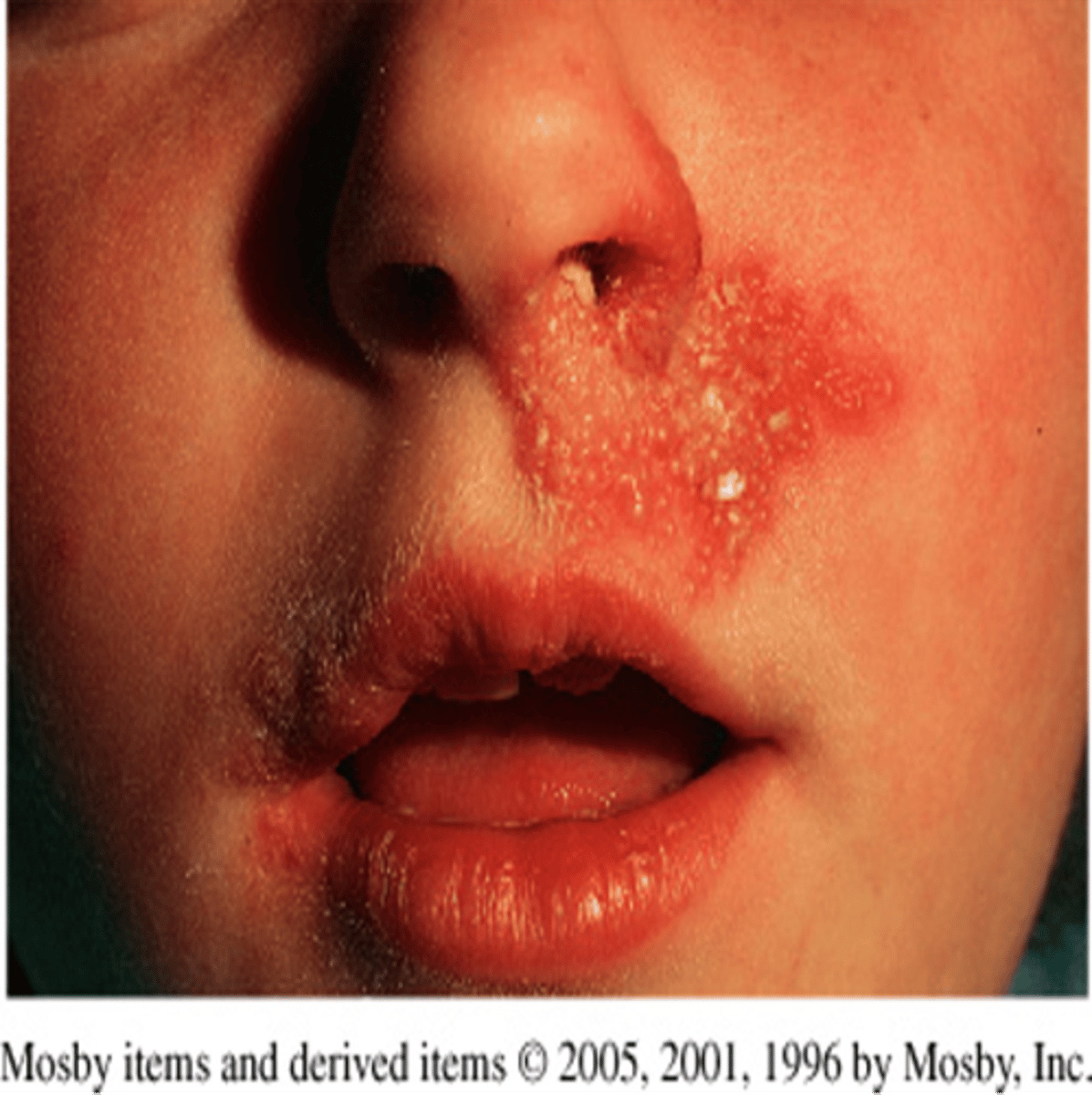
Herpes simplex (Secondary)
-Chronic non-curable condition transmitted by contact
-Outbreaks can be triggered by sun, stress, and fever
-Highly contagious lesions (direct contact)
-Cold sores
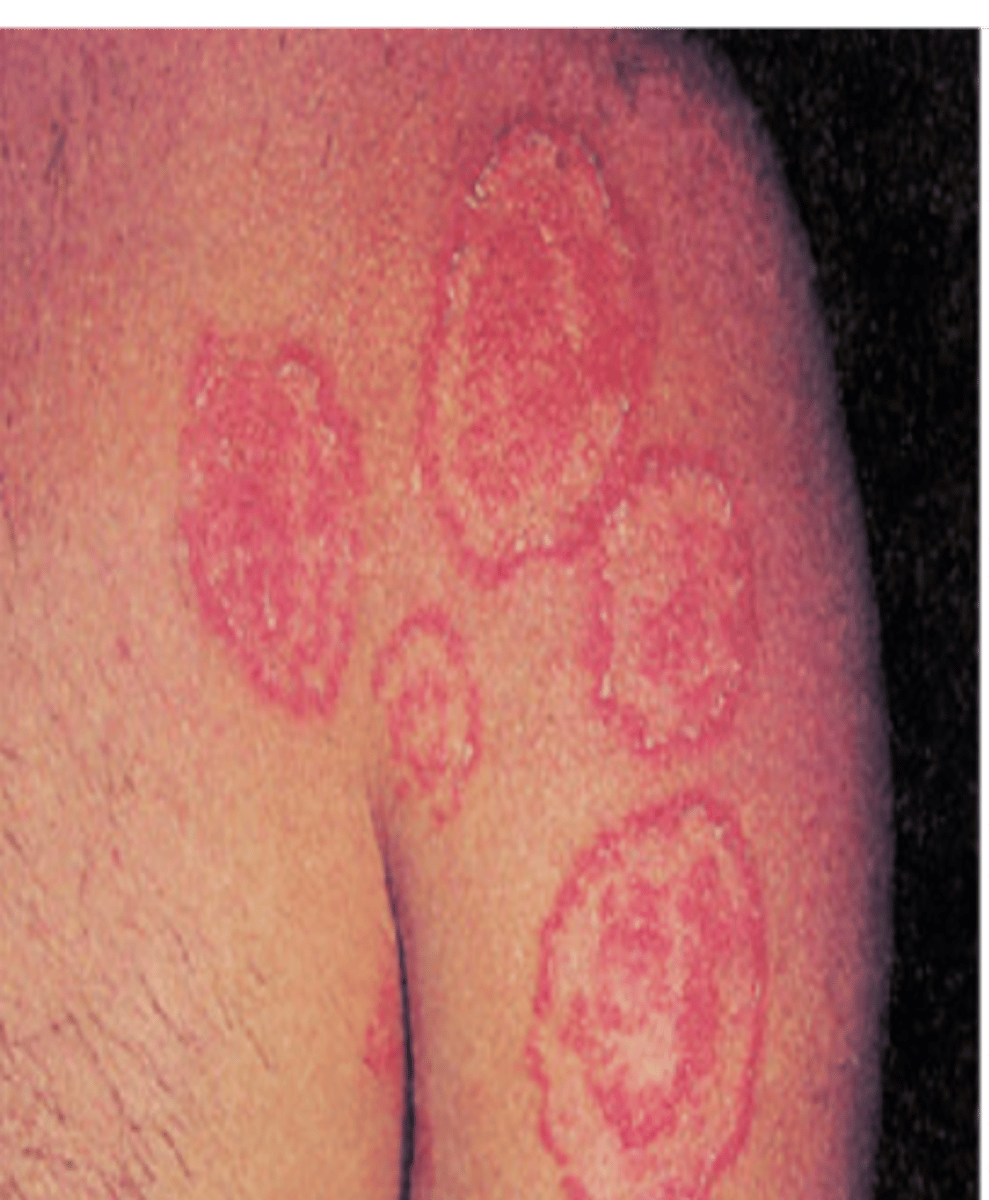
Tinea corporis (Secondary)
-Ringworm (fungal infection)
Treatment:
-Antifungal cream/powder
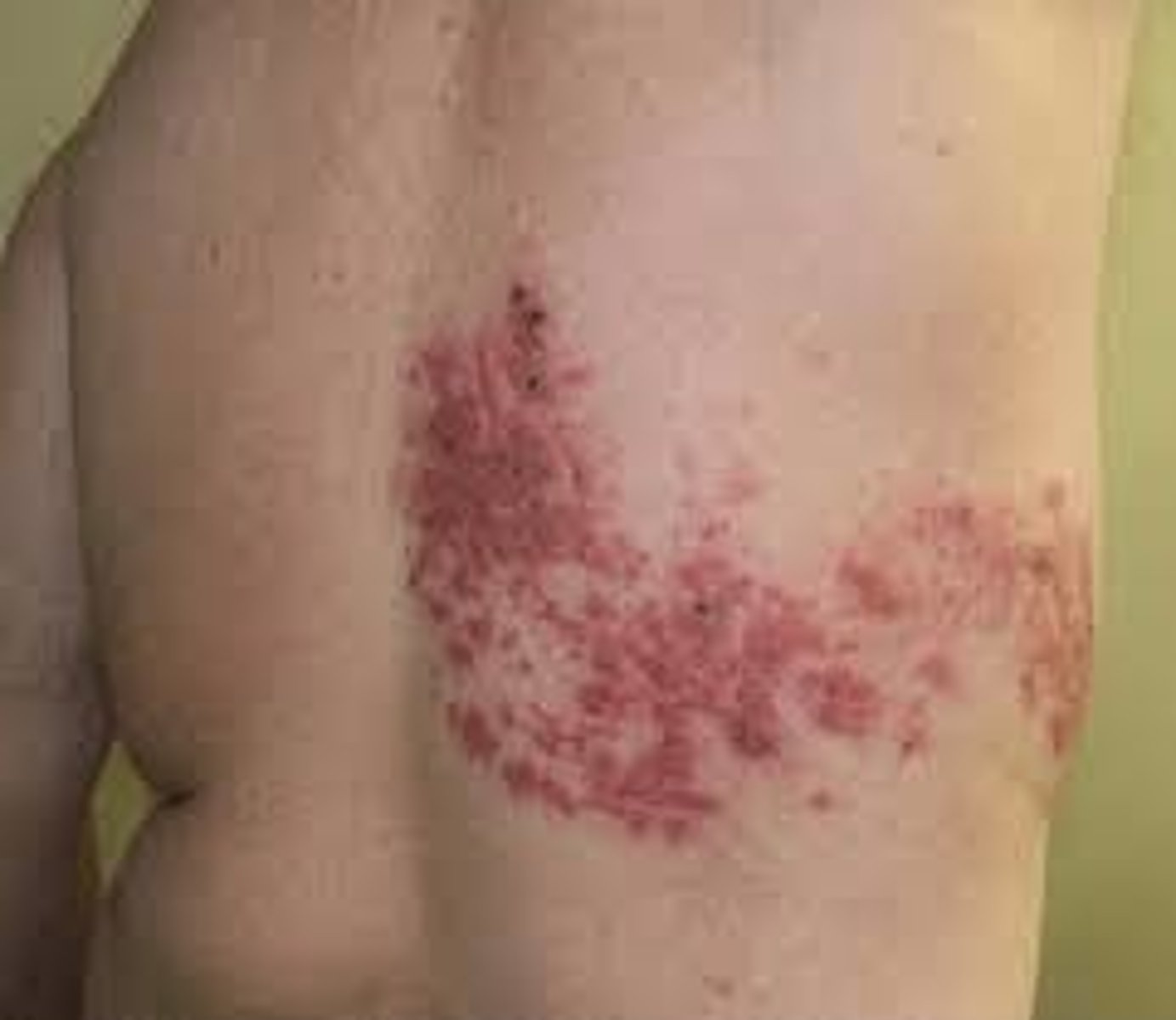
Herpes Zoster (Secondary)
-Shingles
-Usually along nerve track (unilateral)
-Contagious if draining pustules are present
-Vaccine are given for this for individuals 55 and up (2 part series, 6 months apart)
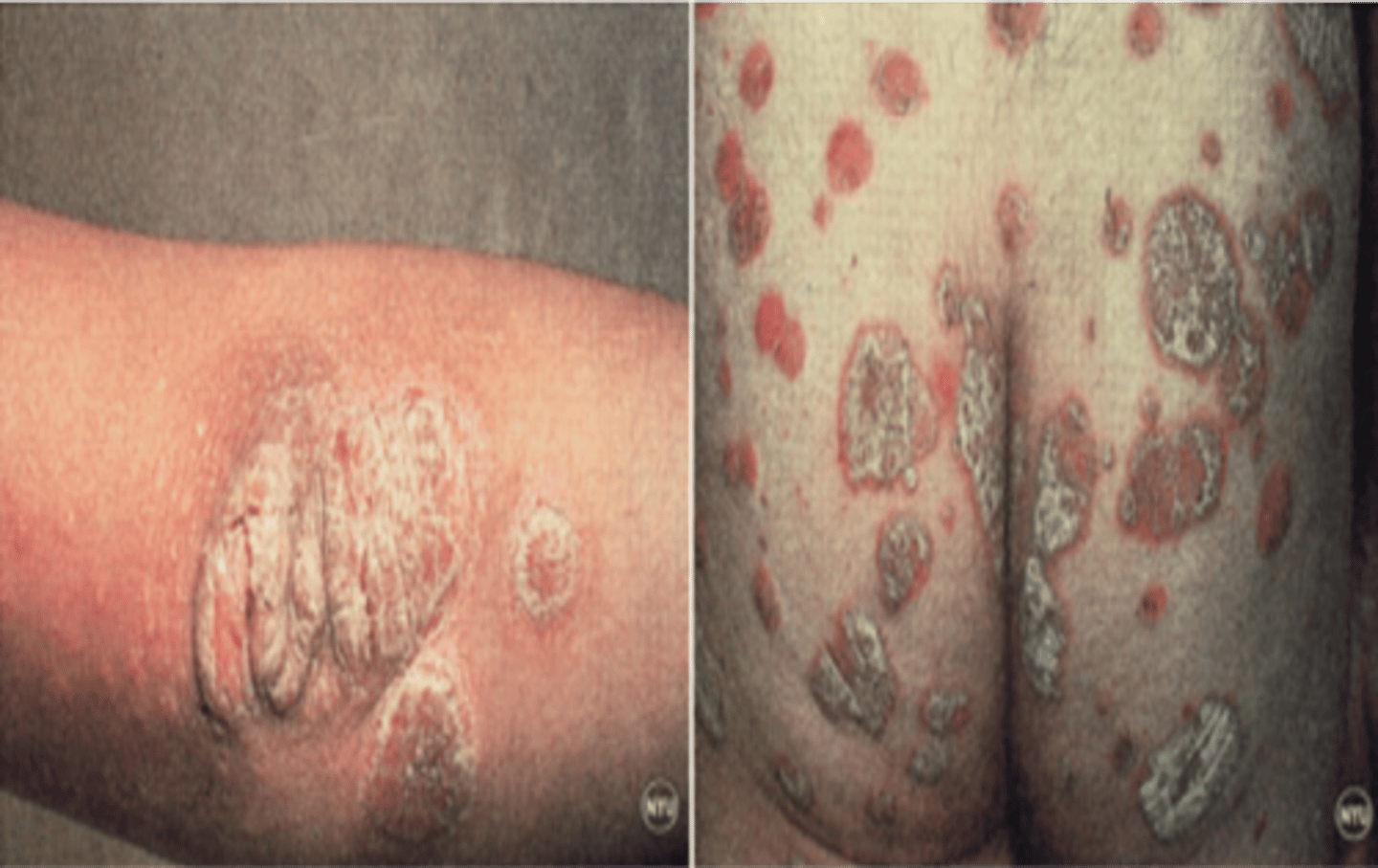
Psoriasis (Secondary)
-Chronic skin disorder that can occur at any age
-Develops by age 20
-Inflammation of cytokines from helper T-cells causes overacting immune system
Treatment:
-UV light
-Creams
Lyme disease (Secondary)
-Tick-borne disease
-Causes erythema migrans
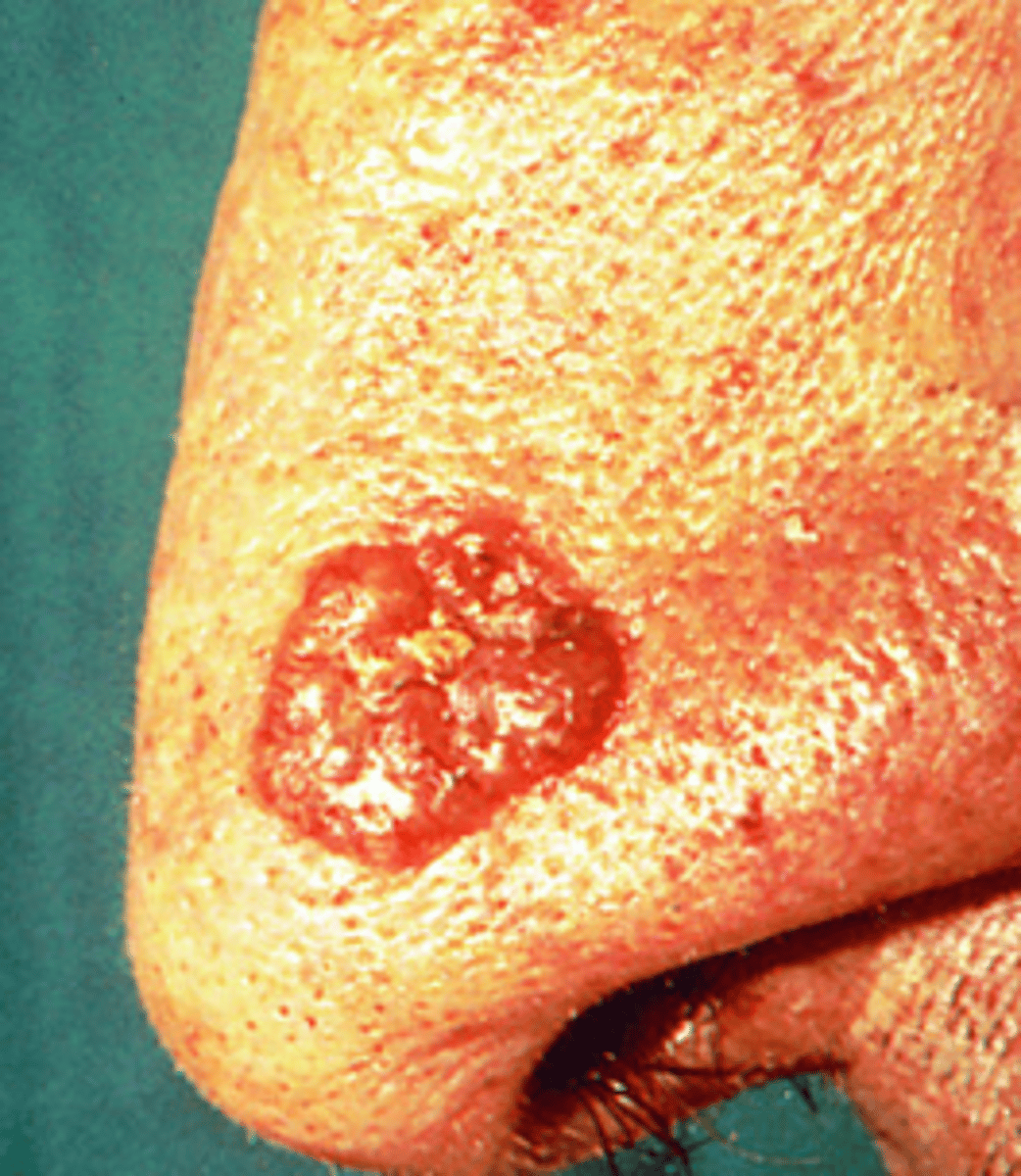
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
-Most common form of skin cancer
-Predominantly affects light skin individuals (40-80)
-Locally invasive (rarely metastasizes)
-More common in males
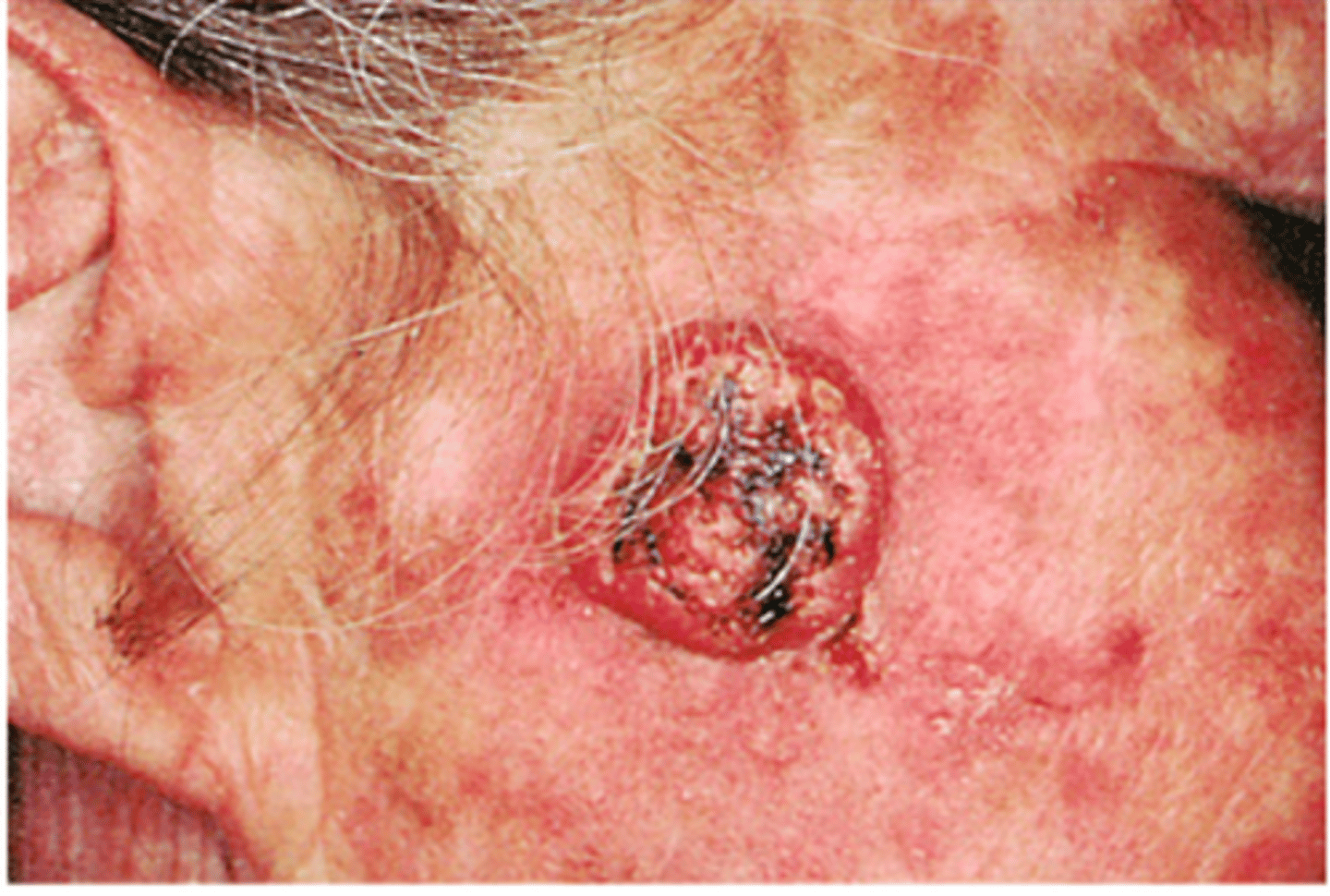
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-2nd most common form of skin cancer
-Head and neck (most common places)
-Result of excess sun/ultraviolet light exposure
-Predominantly common in whites
Treated:
-Chemically
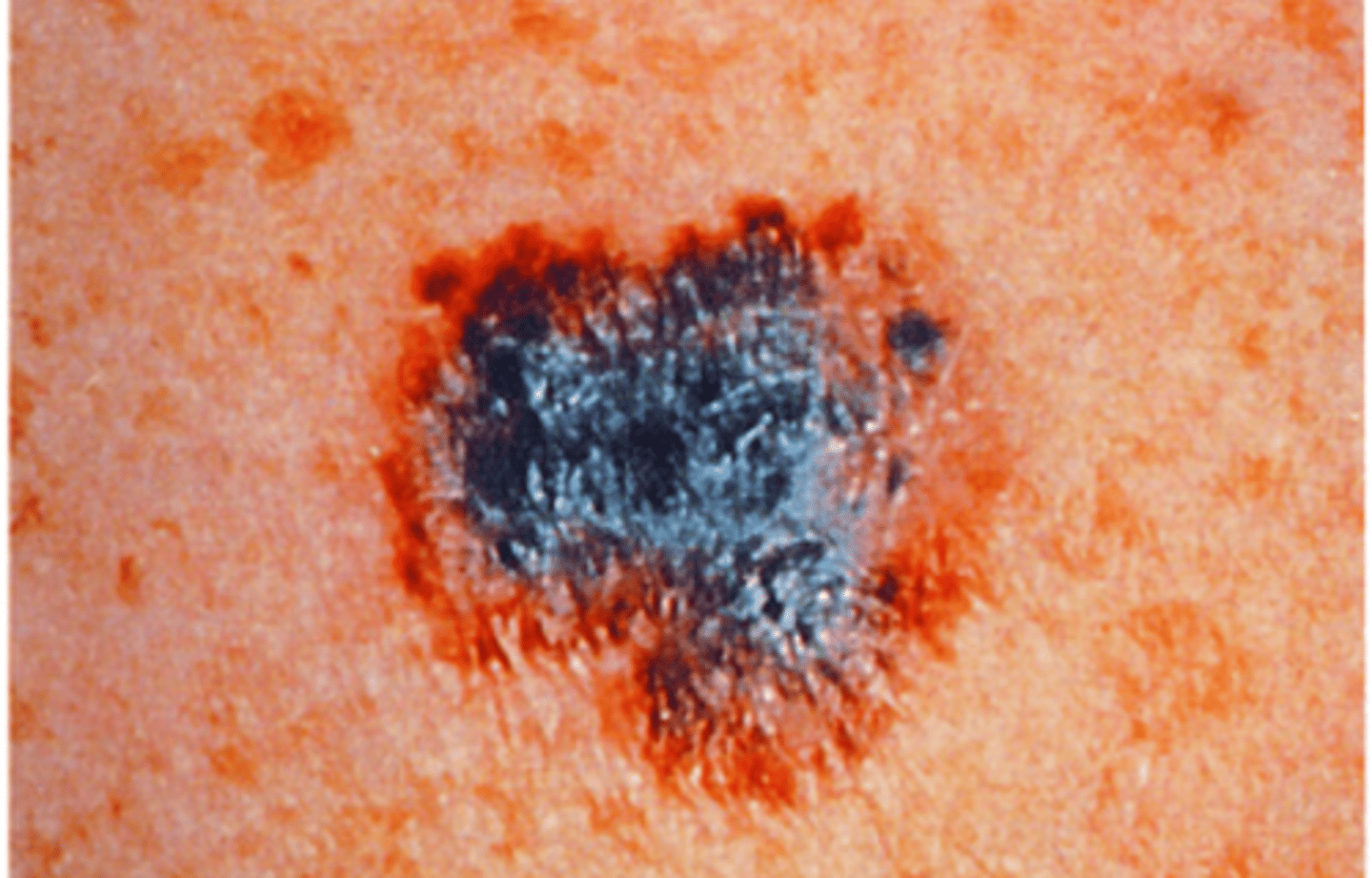
Malignant Melanoma
-Most serious form of skin cancer
-Use ABCDEF evaluation
-20x higher in Whites than African Americans, 4x higher in Hispanics
-More than 6mm
-More than two abnormal lesion characteristics
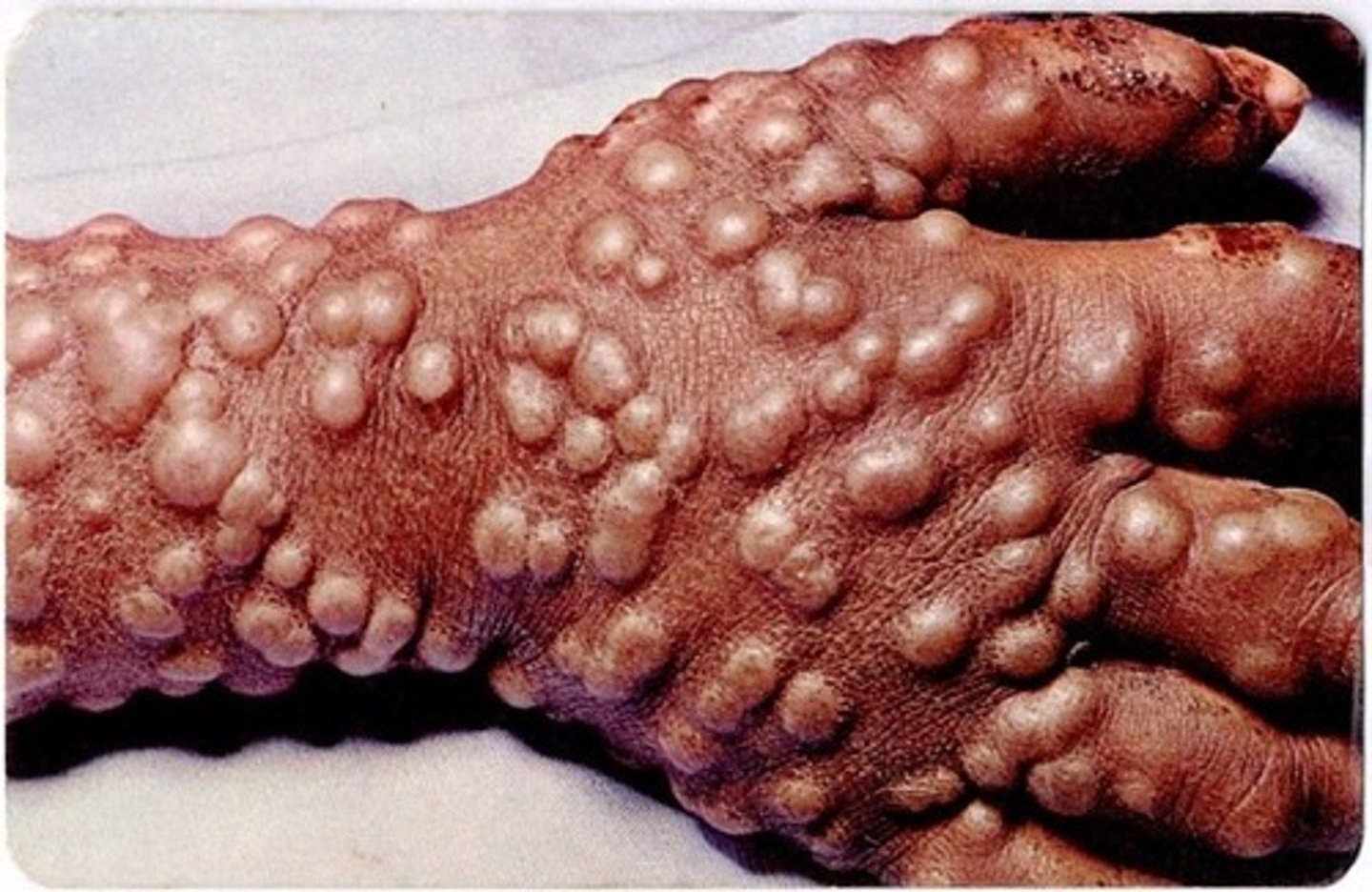
Smallpox (variola major)
-Biological weapon
-Infectious disease caused by variola virus
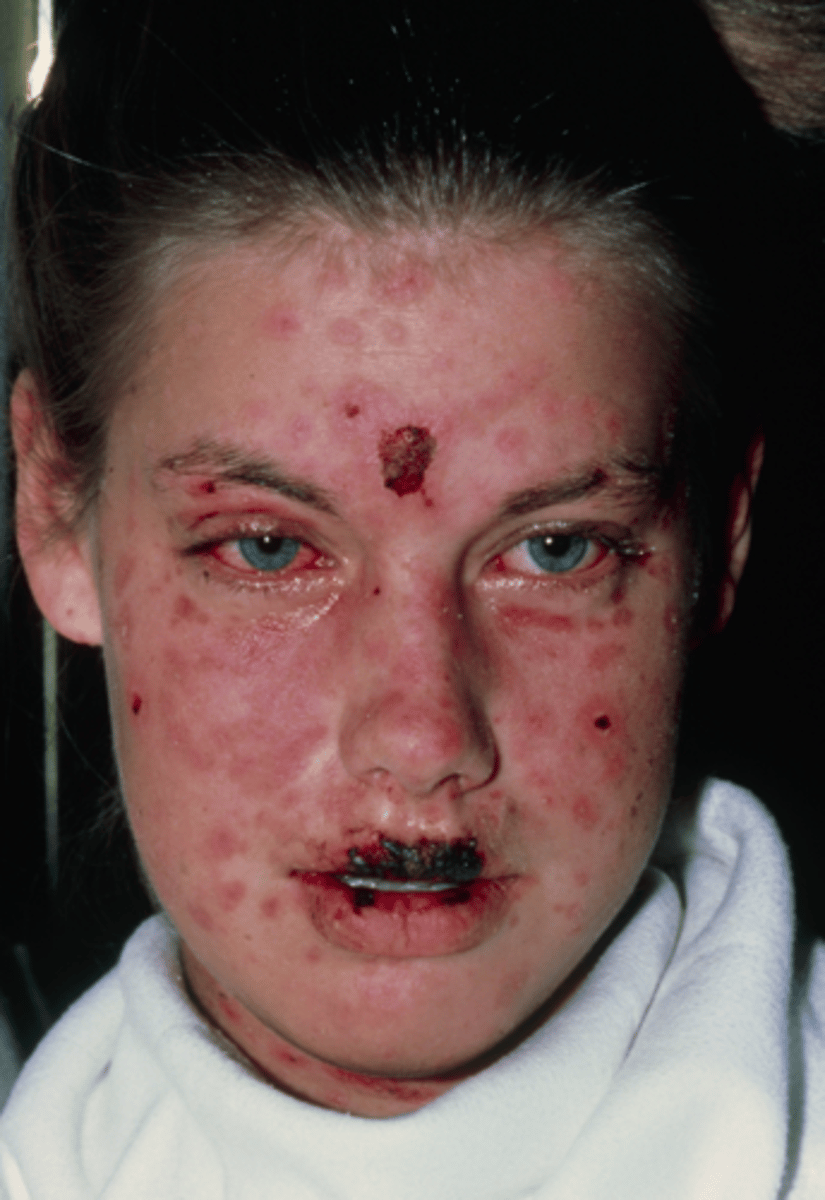
Steven Johnsons Syndrome (SJS)/Toxic epidermal necrolysis
-Severe cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions
-Causes: sulfa drugs, antiseizure drugs, antibiotics (most common)
-Macules and lesions rapidly spread
-Epidermal blistering, necrosis, sloughing
-Clinical syndrome
Treatment:
-TREAT AS A BURN
-Supportive care
-Cyclosporine
-Plasmapheresis
-IV immune globulin
-Corticosteroid therapy
-Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors
Mortality rate:
-7.5% in children
-20-25% in adults
-Lower with early treatment
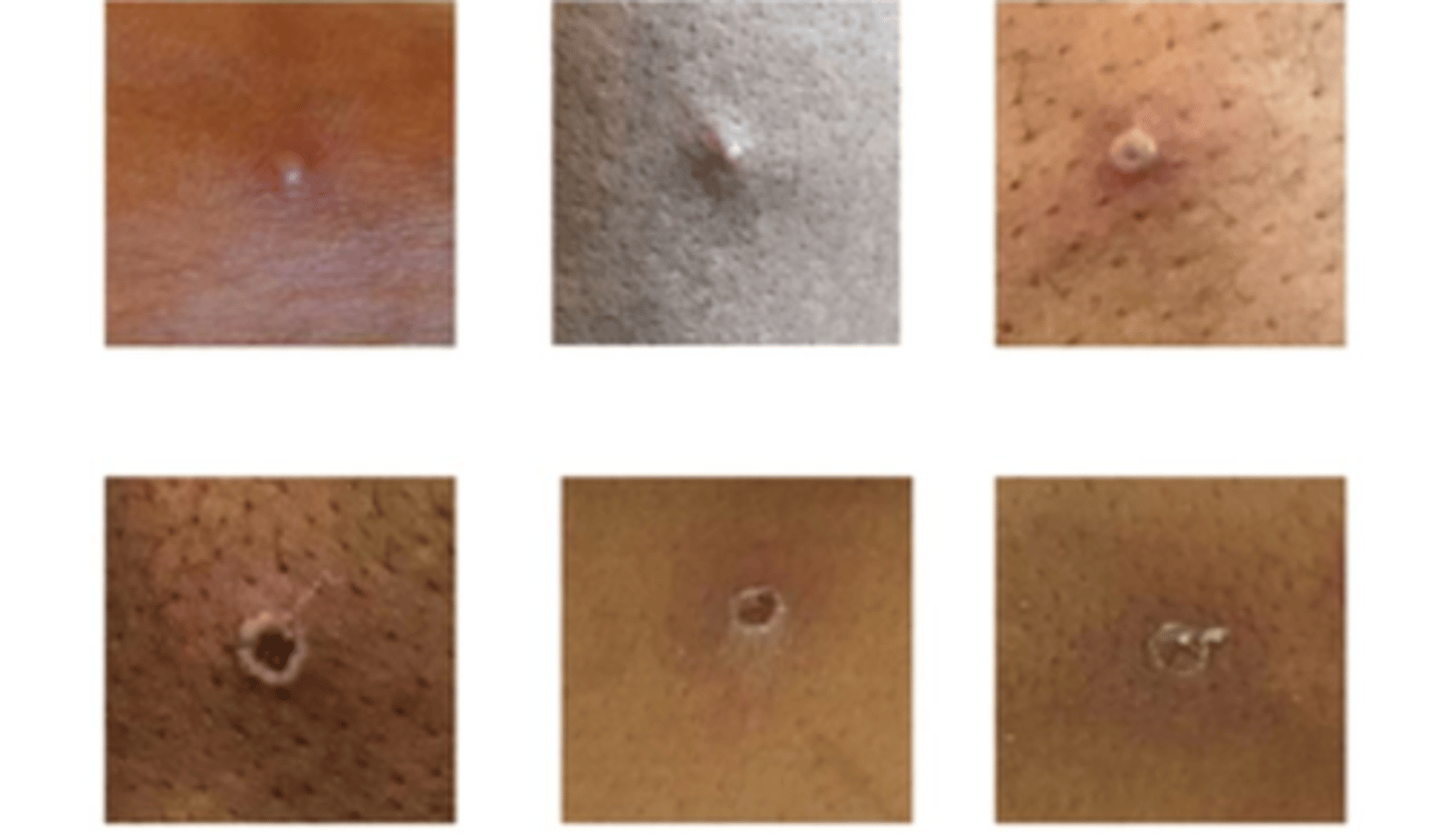
Anthrax
-Biological weapon
-Serious infectious disease caused by bacteria
Monkey pox
-Disease caused by infection with mpox virus
-Blister then scab
Candida of the oral mucosa
-Erythema or white spots
-Antifungal treatment