Economics 2, chapter 4 - the labour market
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is meant by a country’s working age population?
The number of individuals within a country’s total population who are of working age
What three statuses can an individual who is working age have?
Employed
Unemployed
Not in the labour force
What is labour force?
Number of individuals who, in the working age populations, are working or actively looking for a job (ALSO UNEMPLOYED PEOPLE)
What is labour force participation rate, or activity rate?
Ratio between a country’s labor force and its total working age population
What is employment rate?
The portion of the country’s working age population that is employed
What is unemployment rate?
Ratio between the number of unemployed individuals and the total labour force
What are the three things that the international labour organisation (ILO) considered when seeing if a working age person is unemployed?
Without work during the reference period
Currently available for work
Seeking work
In Belgium what two things might the unemployed individuals who are registered at the office national de lemploi (ONEm) be?
A) beneficiaries of unemployment benefits
B) registered but non-beneficiaries of unemployment benefits
What is frictional unemployment?
Frictional unemployment refers to the short-term unemployment that occurs when people are between jobs or entering the workforce.
What is meant by matching process?
Assigning the right employee to the right employer
What is natural unemployment?
Unemployment level in “neutral” economic conditions (i.e. GDP equals potential GDP), and which depends on the structural characteristics of an economy
What are meant by cyclical variations in unemployment?
Can be positive or negative depending on the business cycle
What three things does the duration of unemployment affect costliness wise?
A) the size of the income loss
B) the size of qualification depriciation (scarring effect of unemployment when you stay out of work long you lose your skill)
C) the speed at which unemployment rate will drop after emerging from a crisis (hysteresis)
What is hysteresis?
) the speed at which unemployment rate will drop after emerging from a crisis
What is scarring effect of unemployment?
The long-term impact on an individual's skills and employability as a result of extended periods of unemployment, often leading to decreased income and job prospects.
What is Okun's law?
A hypothesis that relates unemployment to economic growth, suggesting that for every 1% increase in the unemployment rate, a country's GDP will be an additional roughly 2% lower than its potential GDP.
What is the WS-PS model? And what are the two components?
The WS-PS model (Wage-Setting and Price-Setting model) describes the interaction between wages and prices in the labor market, illustrating how wages are set by the labor market conditions and how that affects the overall economic activity.
The wage setting (WS) curve : wages are negotiated
The price setting (PS) curve : firms set prices
What three ways ways can wages be negotiated?
By intersectoral, sectoral or company collective bargaining (employer - unions)
By individual negotiation (employer - employee)
Set by employer
What is reservation wage?
The minimum wage level at which a worker is willing to accept a particular job, reflecting the lowest compensation acceptable for their efforts.
Look at these and memorize one of each
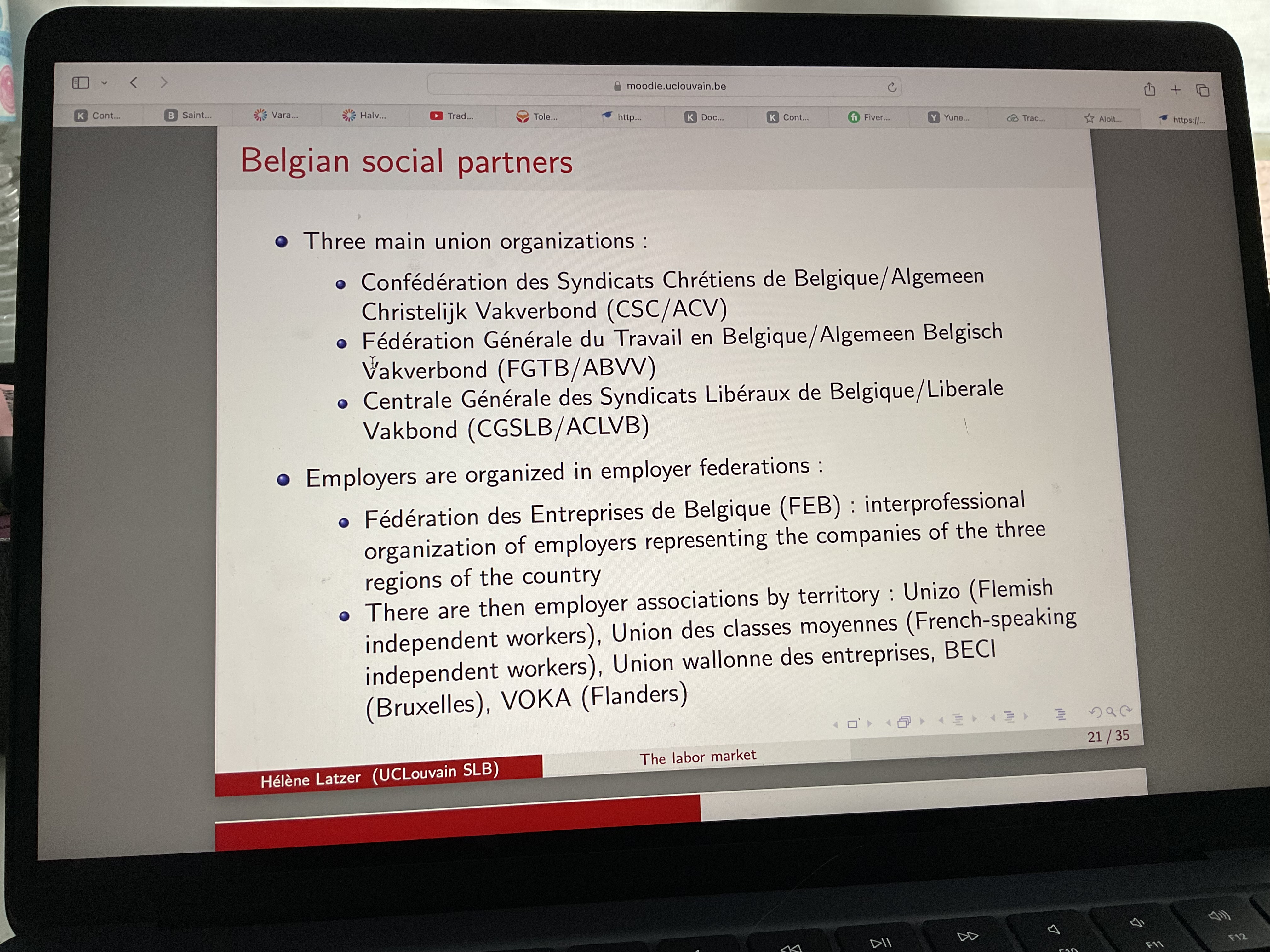
What are collective labor agreements (CLA)?
Agreement concluded between one or more trade union organisations and one or more employer organisation or one or more employers
They fix minimum level of wages, and have a legal status in their own right
Explain institutional framework for setting wages through CLAs

What is potential GDP?
Potential GDP refers to the maximum output an economy can produce without generating inflation, representing the ideal level of production when all resources are fully employed.