Chapter 7 - Biol 233
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Condyle
rounded articular projection
Facet
smooth, nearly flat articular surface
Head
bony expansion carried on a narrow neck
Crest
Narrow ridge of bone; usually prominent
Epicondyle
projection above a condyle
Line
Narrow ridge of bone; less prominent than a crest
Process
any bony prominence
Protuberance
a bony outgrowth or protruding part
Spine
sharp, slender, or narrow process
Trochanter
Two massive processes unique to the femur
Tubercle
Small rounded projection or process
Tuberosity
Rough elevated surface
Alveolus
A pit or socket (tooth socket)
Fossa
a shallow, broad, or elongated basin
Fovea
small pit
Sulcus
a groove for a tendon, nerve, or blood vessel
Canal
a tubular passage or tunnel in a bone
Fissure
a slit through a bone
Foramen
a hole through a bone, usually round
Meatus
A canal
Sinus
air-filled space in bone
Axial Skeleton
Skull and associated bones, thoracic cage, and vertebral column
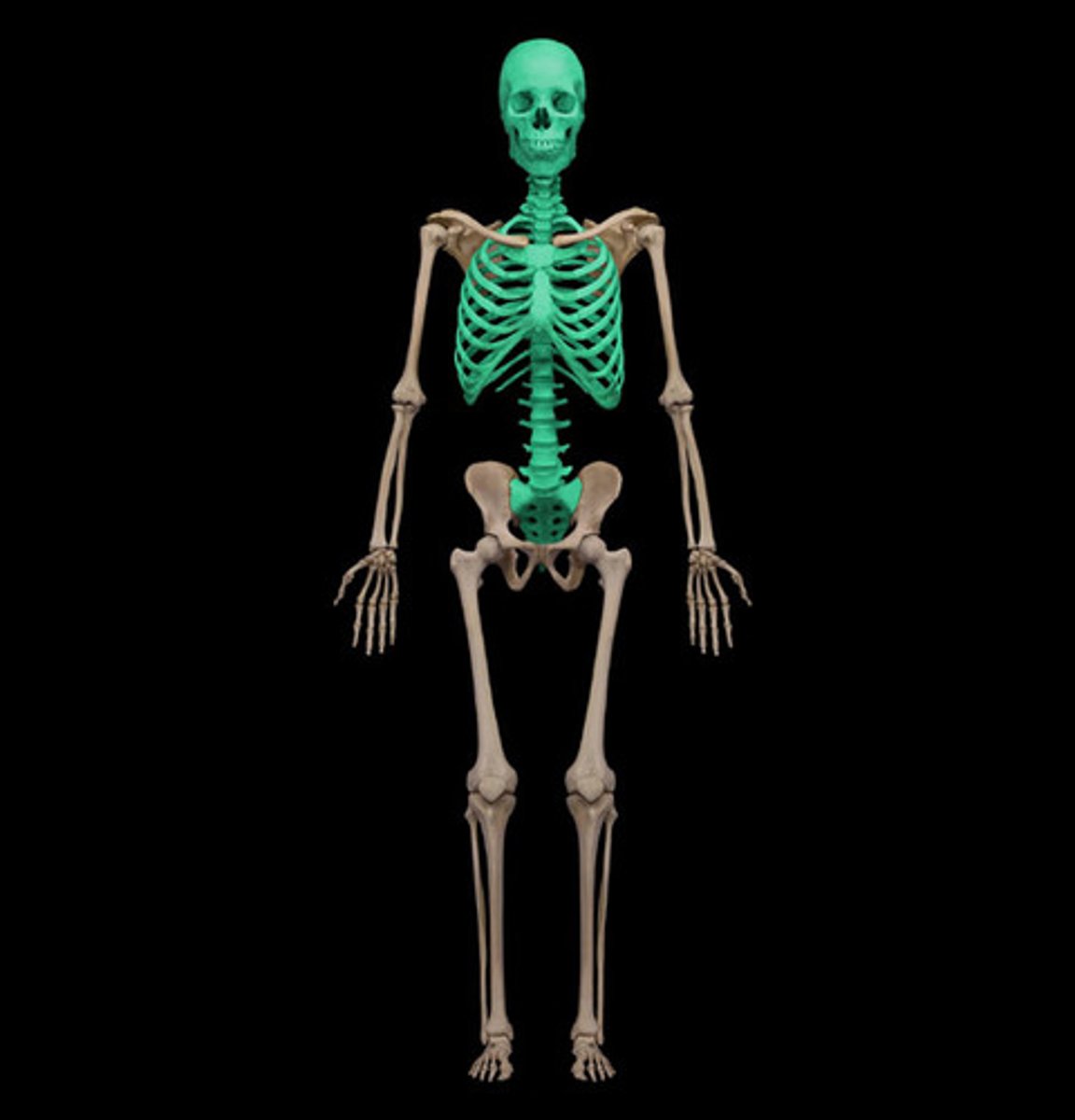
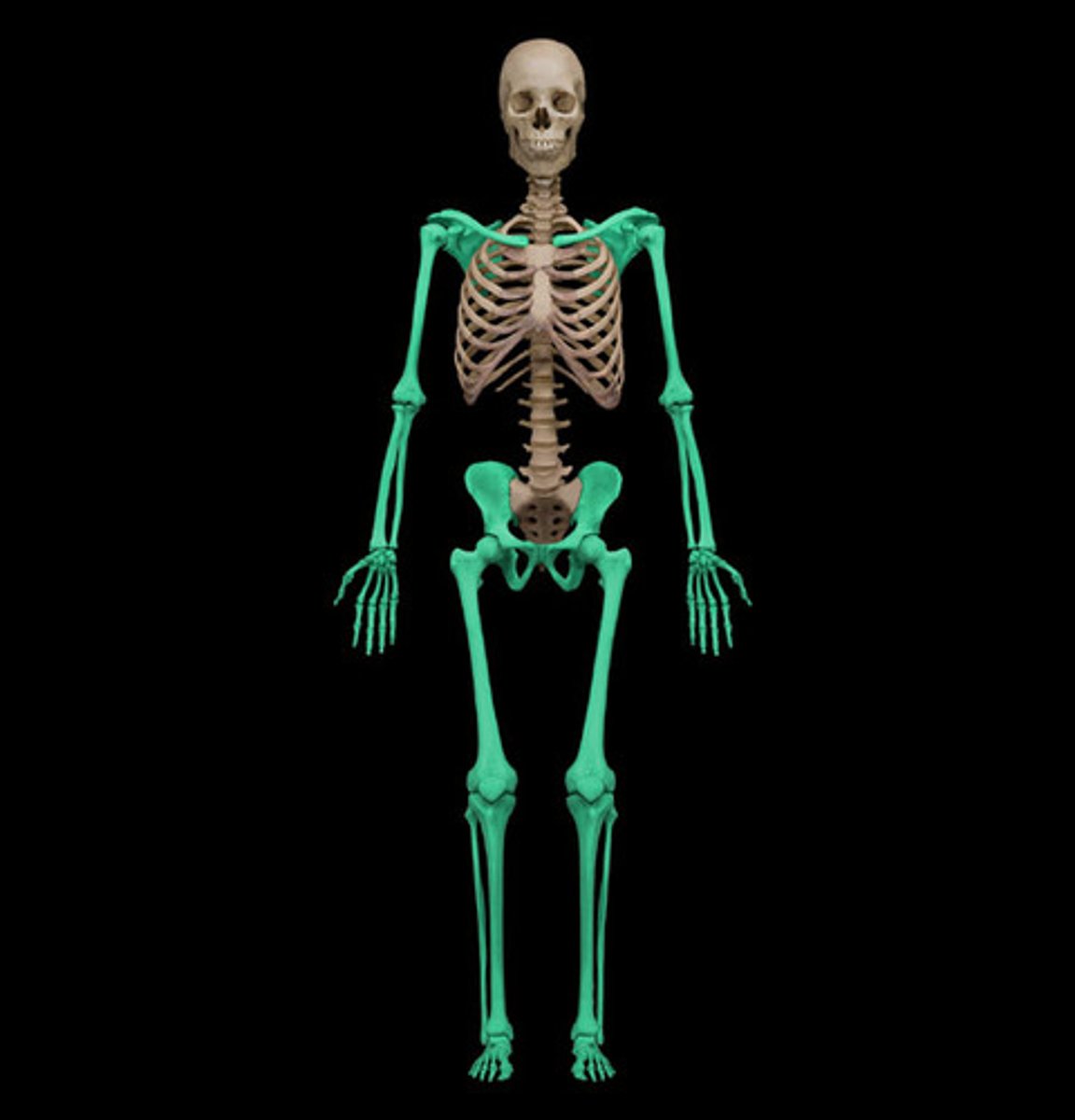
Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral girdle, upper limbs, pelvic girdle, and lower limbs
Functions of the Axial Skeleton
1. Provides a framework; support and protects
2. provides extensive surface are for the attachment of muscles of head, neck. and trunk
3. Stabilizes or positions part of the appendicular skeleton
4. Performs respiratory movements
Functions of the Appendicular Skeleton
Allows for movement and manipulations of objects (moving objects around)
Thoracic Cage Bones
Thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12), Ribs, and Sternum
Thoracic Cage Functions
1. Protects the organs of the thoracic cavity
2. Muscle attachment points for muscles involved in respiration
3. Maintenance of the position of the vertebral column
4. Movements of the pectoral girdle and upper limbs
True Ribs (1-7)
Attach directly to the sternum
False Ribs (8-12)
ribs that do not have a direct attachment to the sternum
Ribs 8-10
vertebrochondral ribs
Ribs 11 and 12
floating ribs
Cervical Region
Cervical vertebrae (C1-C7)
Thoracic Region
Thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12)
Lumbar Region
Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L5)
Sacral Region
Sacrum (fused sacral vertebrae) S1-S5
Coccygeal Region
Coccyx (fused coccygeal vertebrae) C01 to C03-05
Spinal curvatures
cervical curvature, thoracic curvature, lumbar curvature, sacral curvature
Cervical curvature
Secondary curve, develops as an infant leans to balance weight of the head on vertebrae of the neck
Thoracic Curvature
Primary curve, accommodates the Thoracic organs
Lumbar curvature
Secondary curve, balances weight of trunk over the lower limbs; develops with ability to stand
Sacral/Pelvic curvature
Primary curve, accommodates the abdominopelvic organs
Kyphosis
Humpback, bent or slouching posture. The thoracic curvature is exaggerated
Kyphosis causes
Osteoporosis with compression fractures, intervertebral disc degeneration between thoracic vertebrae, abnormal vertebral growth
Lordosis
Lumbar curvature is exaggerated
Lordosis causes
Pregnancy, obesity, and weakness of the muscles of the abdominal wall.
Scoliosis
Lateral crookedness
Scoliosis causes
Development problems (damage to vertebral bodies), muscular paralysis affecting one side of the body, and it is idiopathic in girls during adolescence
Female pelvis characteristics
Smoother, lighter and wider than a male pelvis. Less prominent muscle and ligament attachments. Pelvis modifications for childbearing
Female Sacrum
Broader with the inferior part directed more posteriorly
Male Sacrum
Sacral promontory does not project as far anteriorly in females
Female Pelvic inlet
Oval shaped
Male Pelvic inlet
Heart-shaped
Female Subpubic angle
90 degrees or more in females
Male Subpubic angle
Less than 90 degrees in males
Female ilium
More shallow and flared laterally in females
Female ischial spines
Farther apart
Female Ischial tuberosities
turned laterally
Male Ischial tuberositites
Turned medially
True Pelvis (Lesser Pelvis)
Encloses the pelvic cavity. Includes the Pelvic brim and Pelvic outlet
Pelvic Brim
Upper edge of true pelvis. Encloses pelvic inlet
Pelvic outlet
Inferior outlet of true pelvis
False pelvis (Greater Pelvis)
Encloses the inferior portion of the abdominal cavity
Longitudinal arches of feet
Medial longitudinal arch, lateral longitudinal arch
Curvature between posterior and anterior parts of the foot
Transverse arch
Curvature between medial and lateral borders of foot
Spina Bifida
Open spine or split spine. Condition resulting from failure of the vertebral laminae uniting during development
Laminectomy
Surgery that creates space by removing bone spurs and tissues associated with arthritis of the spine
Herniated Disc
Fibrocartilaginous pad of intervertebral disc slips out of place or ruptures