Refraction and refractive index (L6)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is refraction?
The change in direction of a wave, because of a change in the wave's speed.
(Bending of light)
Why does refraction happen?
Because the wave is moving across a boundary between two mediums with different refractive indices.
- Different materials refract light differently
What happens when waves travel through matter?
When the waves have to travel through matter, they are slowed by the electronic charges in atoms.
How does light waves travel through different materials?
METALS
- They are full of free electrons, so they STOP the wave completely.
- The light energy is therefore REFLECTED making metals appear shiny.
OTHER MATERIALS
- ABSORB some or all of the light, so they look coloured or black (not shiny)
TRANSPARENT MATERIALS
- The waves are not stopped or absorbed
- They are SLOWED down and bend and change direction (refract)
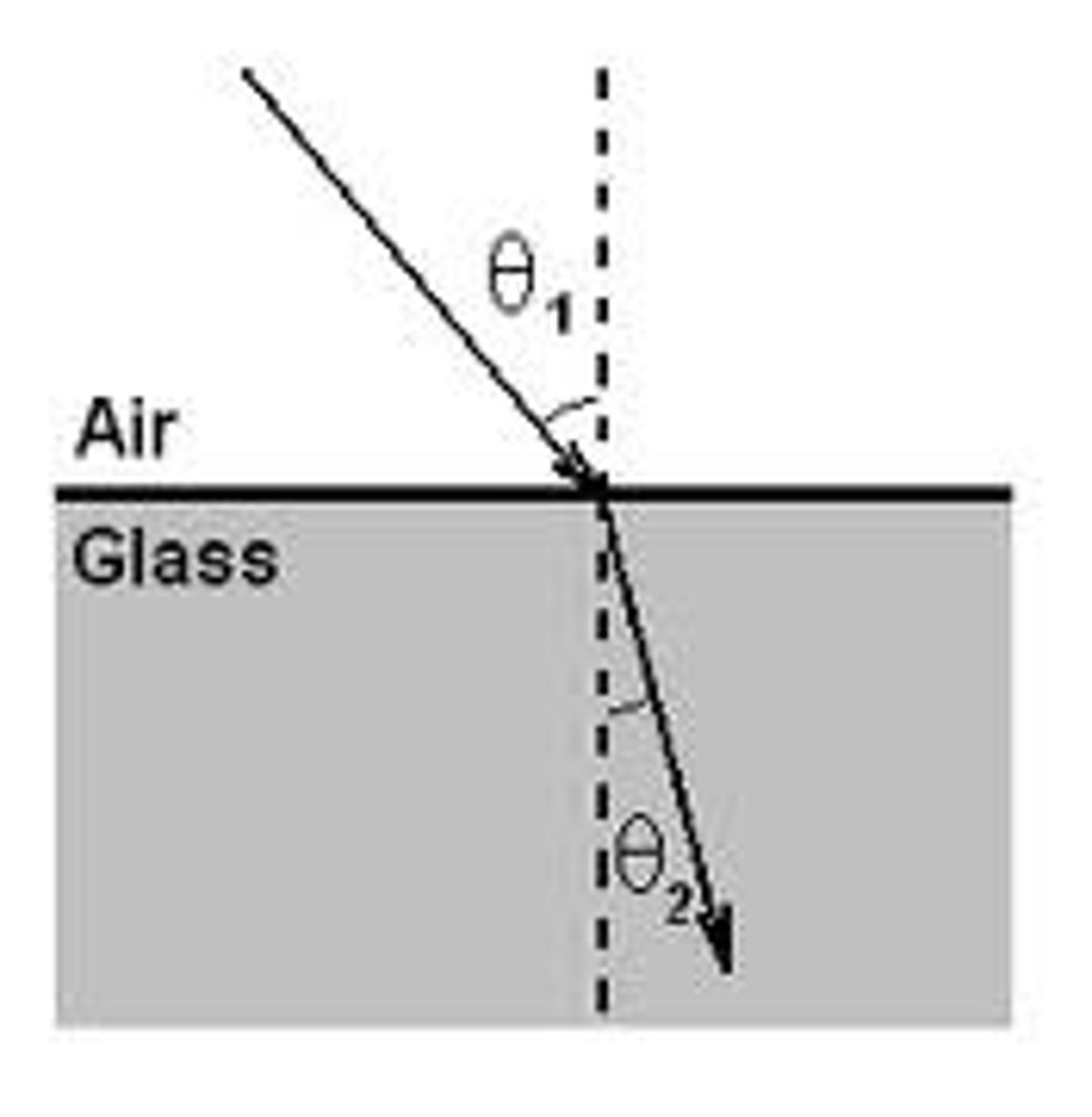
What happens when light travels from air to denser material?
If light travels from AIR → DENSE MATERIAL
From Air to Glass or Water the waves refract (slows down and bends) towards the normal line
E.g.
Air → Glass/Water
- Refractions occurs as they are different materials w/ different refractive indices.
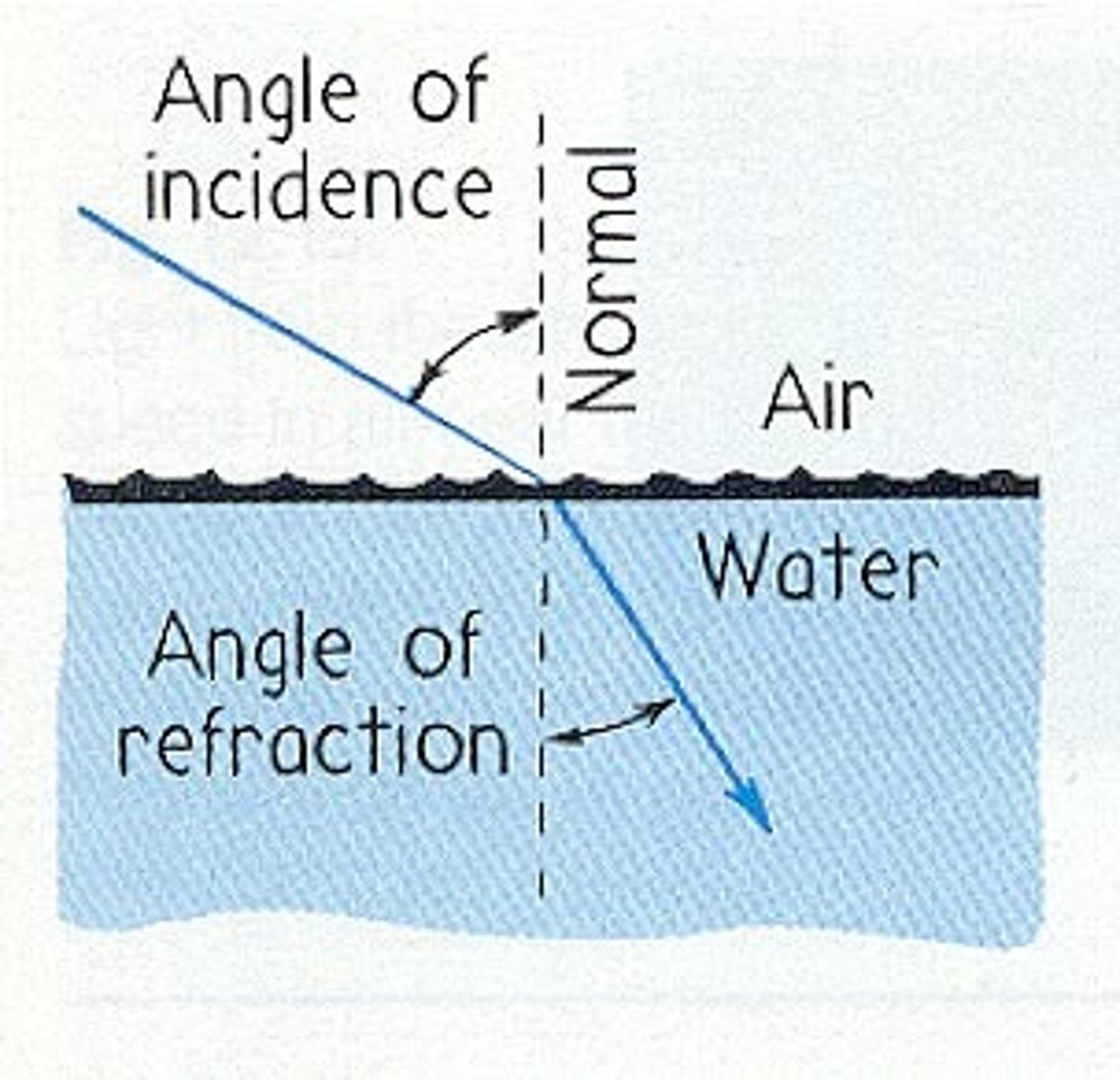
What happens when light travels from a dense material to air?
If light travels from DENSE MATERIAL → AIR
- The waves speed up so bends away from the normal line
E.g.
Water/Glass → Air
- Refraction occurs as they are different materials w/ different refractive indices.
What is the refractive index?
It is the angle that the light bends depends on the speed.
- The light travels through the 2 materials.
- We can work out the angle if we know the speed of light through the material.
- If a material has the refractive index of 1 (n=1) then the speed of light travel is the same of speed of light in a vacuum (3x10⁸)
- So refractive index of air is 1
What is the Refractive Index Formula?
n = c/v n = sin I/ sin r
n = Refractive index (no units)
c = Speed of light in a vacuum (3.oo x 10⁸ ms⁻¹)
v = Speed of light through the material (ms⁻¹)
sin i = angle of incidence
sin r = angle of refraction
What is the normal line?
A line at right angles to the surface of a transparent medium, that passes through the point where a ray enters or exits.
What is the incidence angle?
The direction of the incoming ray
ON CALC
if angle of incidence is 55⁰
To get Sini press sin (55) = o.819
What is the critical angle?
It is the angle at which the angle of incidence causes an angle of bending to be to be at 90⁰.
- This angle is critical because changing the angle of incidence from this critical angle can either cause the light to be refracted or reflected.
- If we change the angle of incidence making it greater than the critical angle of light would be reflected (not refracted)
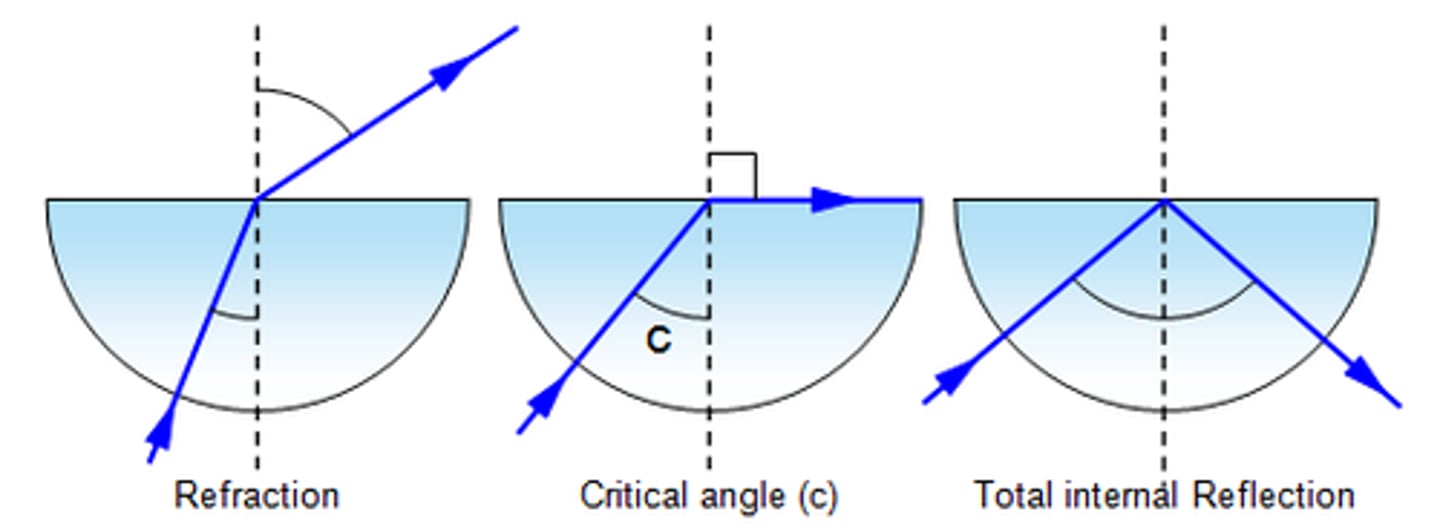
What is total internal reflection?
If the angle of incidence is longer than the critical angle, all the light would be reflected.
This is called total internal reflection.
- If the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle the light would reflect along the 90⁰ boundary.
Sin c (critical angle) = 1/n