bio Nutrients and transport in Flowering plants (photosynthesis) (chapter 12)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
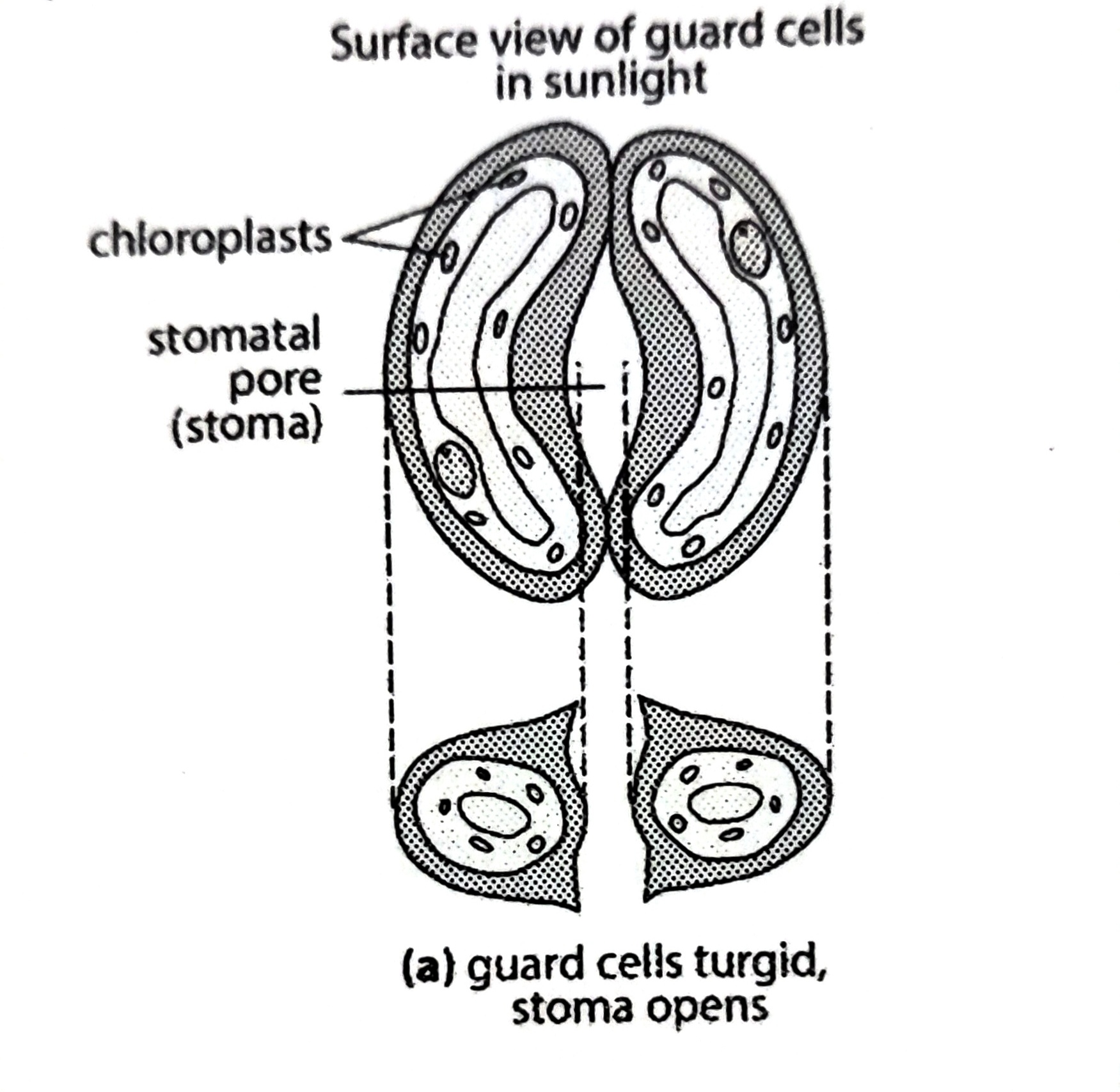
how does a guard cell become turgid? (stomata open)
1. guards cells have chloroplast and manufacture glucose photosynthesis
2. glucose concentration increases, water potential decreases in cell sap
3. water enters the guard cells by osmosis
4. becomes turgid and more curved
5. thin outer wall expands more than the thick inner wall
6. stomata opens
how does the guard cell become flaccid? (close)
1. excess sunlight causes excess evaporation of water
2. guard cell becomes flaccid
3. stomata closes
-prevents excessive loss of water

photosyntheis def
light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and converted to chemical energy. Chemical energy is used to synthesise glucose from water and carbon dioxide. oxygen is released in the process
what are the factors affecting the rates of photosynthesis?
1. Light intensity
2. carbon dioxide concentration
3. temperature
4. water supply
5. light wavelength
6. chlorophyll concentration
7. pollution
rate of photosynthesis def
rate of oxygen production per unit mass of green plant tissue
how does the light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis?
1. the rates of photosynthesis would go up ⬆️ as light intensity is increased ⬆️
how does the carbon dioxide concentration affect the rate of photosynthesis?
⭐ carbon dioxide is absorbed by the leaf for photosynthesis
1. ⬆️ carbon dioxide concentration ⬆️ rate of photosynthesis
rate of photosynthesis will plateau, carbon dioxide is no longer the limiting factor
how does the temperature affect the rate of photosynthesis?
⭐ photosynthesis is dependent on temperature as it is a reaction catalyzed by enzymes
1. temperature ⬆️ KE ⬆️ frequency of effective collisions between enzyme and substrate ⬆️ rate of photosynthesis ⬆️
2. optimum temperature of enzyme = max photosynthesis
3. high temperatures cause enzymes to be denatured
why are most lifeforms complete
1. converts energy from the sun into chemical energy, which is required by other organisms
2. removes CO2 from the atmosphere
3. produces O2 for other organisms to respite
4. energy in fossil fuels
limiting factor
a limiting factor is a factor that affects the rate of a reaction. the rate of reaction cannot increase unless the value of the limiting factor is increased