Combined Network+
1/498
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
499 Terms
Protocol Analyzer/Packet Capture
Software that captures data packets traveling over a network. Allows for detailed analysis of network traffic to identify issues, monitor performance, and ensure secure network transfer
ping
Sends ICMP data packets to test connectivity between two devices
tracert/traceroute (linux)
Traces the path packets take from the source to the destination, showing each hop along the route
In linux, it uses UDP by default. Can be configured to use ICMP echo request probes instead of UDP by using traceroute -I. traceroute -6 or traceroute6 for IPv6
windows:
tracert -d = switch to suppress name resolution
tracert -h = specify max number of hops
tracert -w = specify a timeout in ms. If, after increasing its value, if the destinations are then reachable, you probably have a bandwidth issue.
tracert -6 = ipv6
nslookup
Windows utility that queries DNS servers to find the IP address. Helps identifies DNS issues
dig
Querying DNS servers on linux, to help diagnose DNS issues. Can retrieve detailed info such as A, AAAA, CNAME, MX, and NS records
tcpdump
Linux command, captures and filters TCP/IP packets that are received or transmitted over a network. Can be automated (things like Wireshark and other GUI tools aren’t good at doing that)
tcpdump -i eth0
-r/-w switches write ouitput to a file and read the contents of the file
-e shows the ethernet header
netstat
Windows command showing incoming and outgoing connections, routing tables, and other network interface statistics
ipconfig/ifconfig/ip
Displays or configures the network configuration on the device
ipconfig=windows
ifconfig=older linux/mac
ip=modern linux systems
arp
Address Resolution Protocol command, displays or modifies the IP-to-MAC address translation tables used by ARP
nmap
A network scanning tool that discovers devices and services on a network and tells you if the host is working, and if/what ports are working. Done by sending packets and analyzing the responses
Different types of scans:
TCP SYN (-sS): A fast technique (aka half-open scanning), as the scanning host requests a connection without acknowledging it. The targets response identifies the port state
TCP connect (-sT): A half open scan requires nmap to have privileged access to the network driver so that it can craft packets
UDP scans (-sU): Scans UDP ports. As they don’t use ACKs, Nmap needs to wait for a response or timeout to determine the port state, so it can take a long time
Port range (-p): Dy default, scans 1000 commonly used ports, but can define a port range.
After services are discoverd, you can use Nmap with the -sV or -A switch to probe a host more intensively to discover the software/software version operating each port. This is known as fingerprinting
LLDP/CDP
Link Layer Discovery Protocol/Cisco Discovery Protocol. Network discovery protocols used to exchange information about devices on the same network.
LLDP: Vendor neutral protocol used to discover and share information between network devices, such as identity, capabilities, and neighbors.
Usage: Helps in identifying network topology, troubleshooting connectivity issues, and ensuring proper network config
CDP: A Cisco proprietary protocol similar to LLDP, specifically for Cisco networks to share info about connected Cisco devices
Usage: Facilitates network management and troubleshooting by providing detailed information about neighboring Cisco devices
Toner
Tool (tone generator and probe) for tracing/identifying individual wires or cables within a bundle.
Cable Tester
Verifies integrity and performance of network cables. Tests for continuity, signal strength, and wiring faults such as shorts, opens, and cross connections. Essential for validating new cable installations and diagnosing existing cable issues
Tap
A network tap is a hardware device that provides a way to access data flowing across a network cable. Creates a copy of data packets for monitoring and analysis WITHOUT interrupting the network flow. Used for network monitoring and security applications to analyze traffic for troubleshooting, performance, monitoring, and intrusion detection
Visual Fault Locator
Tool used to identify faults in fiber optic cables. Emits a visible red laser light that travels through the fiber, revealing breaks, bends, and faulty connectors
Command displaying the MAC address table of a switch. Used to help identify which MAC addresses are associated with which ports, helps for troubleshooting connectivity issues and ensuring proper network segmentation
show mac-address-table
Command displaying the routing table of a router/Layer 3 switch.
Shows active routes, route sources, and next-hop addresses
Essential for verifying correct routing and diagnosing routing issues
Helps ensure data packets are taking the optimal path through the network (doesn’t work for Cisco - show ip route instead)
show ip route
show interface
Command providing detailed info about the status and configuration of network interfaces.
Displays interface status, traffic statistics, and error counts
Useful for diagnosing issues such as link failures, duplex mismatches, and interface errors
Helpful for physical layer issues (show interfaces on cisco)
show config
Displays the current configuration of the network device.
Shows all configured settings, including IP addresses, routing protocols, and security settings
Useful for verifying config consistency and identifying misconfigurations.
(show runnin-config on Cisco)
show arp
Shows ARP table
Maps IP addresses to MAC addresses
useful for troubleshooting IP-to-MAC resolution issues
Can help in identifying/resolving connectivity issues related to ARP, ensuring reliable IP communication
show vlan
Command displaying info about VLAN configs
Shows VLAN IDs, names, and associated ports
Useful for verifying VLAN setup and troubleshooting VLAN related issues
Ensures proper network segmentation and enhances security by managing VLAN configs effectively
show power
Command providing info about the power status and consumption of PoE devices
Displays power allocation, usage, and available power
Useful for managing PoE budgets and diagnosing power related issues
Switching Issues
Can disrupt network connectivity and performance. Common switching issues include problems with the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Proper implementation/management of STP is crucial for preventing network loops and mainlining efficient data flow. Addressing issues with root bridge selection, port roles, and port states ensures a stable/reliable network environment
Root Bridge Selection
In STP, the root bridge is the central reference point. Typically the most powerful device.
Determined by the lowest bridge ID, which consists of a priority value and the MAC address
Issues: Incorrect root bridge selection can lead to suboptimal network performance
Resolution: Adjust bridge priorities
STP Port Roles
STP assigns specific roles to switch ports.
Port roles:
Root port: Best path to the root bridge
Designated Port: Best path to a designated network segment
Blocked port: Prevents loops by not forwarding traffic
STP Port States
STP ports transition through several states to ensure network stability
States:
Blocking: Prevents traffic to avoid loops
Listening: Prepares to forward traffic without adding to the MAC table
Learning: adds MAC addresses to the table without forward
Forwarding: Actively forwards traffic
Issues: Incorrect port states can cause connectivity problems
Resolution: Verify/configure port states appropriately
Incorrect VLAN Assignment
Can cause network segmentation/communication/security issues
Verify and correct VLAN assignments, along with regular audits
ACLs
Used to control network traffic by specifying which users or systems can access network resources and under what conditions. Review and regularly audit ACLs
Route Selection Issues
Issues can cause suboptimal routing, increased latency, and network failures
Stale Routes
Routes that are no longer valid but remain in the routing table and can cause misrouting of packets
Resolution: Regularly update and clean routing tables to remove outdated routes
Misconfigured Static Routes
Incorrect static route entries can lead to packet loss and routing loops. Resolution: Verify static route configs
Dynamic Routing Protocol Conflicts
Inconsistent routing information due to misconfigured or conflicting routing protocols
Resolution: Ensure proper configuration and compatibility of dynamic routing protocols like OSPF, EIGRP, and BGP
Default Route Issues
Default routes act as a catch-all, forwarding packets to a specified gateway when no more specific route matches the destination. Default routes are essential for simplifying routing tables, especially in small or edge networks.
Missing Default Route: Absence of a default route can cause packets destined for unknown networks to be dropped
Incorrect Default Route: Misconfigured default routes can direct traffic to the wrong gateway, causing connectivity issues
Address Pool Exhaustion
Occurs when the available IP addresses in a networks DHCP scope are depleted
Common issues:
Over-subscription: Too many devices for a limited pool
Improper scope config: DHCP scopes are not configured to meet network demands, leading to insufficient IP allocation
Leased IPs Not Released: Devices not releasing IP addresses properly/quickly enough
Resolutions:
Expand the DHCP scope or subnet to include more IP addresses
Implement IP address management (IPAM) to monitor and optimize IP address allocation
Ensure proper lease times/release mechanisms are configured
Incorrect Default Gateway
Common issues:
Misconfigured Gateway Address
gateway outside subnet
multiple gateways
resolutions:
Verify/correct default gateway IP address on affected devices
Address subnet issues
Incorrect IP Addresses
Manual config errors, or static vs DHCP conflicts. Double check IP config, and/or use DHCP reservations
Duplicate IP Address: Can occur with overlapping DHCP scopes, DHCP leasing an IP address that’s already in use. Can use IPAM tools to detect/resolve IP conflicts as well as ensure scopes don’t overlap
Congestion/Contention
Occurs when network demand exceeds capacity, leading to slowdowns and delays.
Causes: Excessive data transfers, or malware
Bottlenecking
Common causes:
Insufficient bandwidth on a network link
Overloaded network devices
Resolutions:
Identify/upgrade the problem device
Implement better load balancing
Bandwidth
Maximum data transfer rate of a network connection. Exceeding it causes slow network performance
Resolutions:
Monitor bandwidth usage and optimize allocation
Implement traffic shaping and prioritization policies
Throughput Capacity
The actual rate at which data is successfully transmitted through the network
Issues:
Network inefficiencies and congestion can reduce throughput
Discrepancies between theoretical bandwidth and actual throughput
Resolutions:
Optimize network configurations and reduce interference
Ensure hardware and software are capable of supporting desired throughput levels
Latency
Delays in transmission and congestion.
Use high speed connections and optimize routing paths.
Packet loss
Packets failing to reach their destination, leading to incomplete transmission
Issues:
Causes include network congestion, faulty hardware, and interference
Leads to retransmissions, reduced throughput, and degraded application performance
Resolutions:
Improve network infrastructure and hardware reliability
Use error detection
Common causes:
Server, router, or switch is overloaded
Power outage
Firewall is blocking packets
Malicious actors
Faulty firemware
Jitter
Variability in packet arrival times, leading to choppy audio/video. Implement QoS and use jitter buffers
Overlapping channels
Results in increased interference and reduced throughput. Symptoms include degraded signal quality and slower network speeds
Resolutions:
Configure access points to use non-overlapping channels (such as 1, 6, 11 on 2.4ghz)
Implement automatic channel selection
Signal degradation
Leads to weaker signal strength and high error rates. Symptoms include intermittent connectivity, slower data transfer rates, and higher packet loss. Optimize access point placement and use signal boosters/repeaters to extend coverage
Insufficient wireless coverage
Can result in dead zones, conduct a wireless site survey/heat map to ensure proper coverage
Client Disassociation Issues
Frequent disassociation causes unstable connections and constant reconnecting. Symptoms include interrupted network access and inconsistent performance
Ensure strong and stable signal strength to fix
Roaming Misconfiguration
Poorly configured roaming can lead to slow handoffs between access points, causing temporary disconnections
Symptoms include lag during movement within the network and dropped connections
Resolutions: Optimize roaming settings on access points for smoother transmissions
STP vs UTP
Using UTP in environments with high electromagnetic interference instead of STP can result in signal degradation and data corruption (microwaves, fluorescent lights, etc)
Signal Degradation
Occurs when the quality of the signal diminishes over distance or due to interference, leading to poor network performance. Common causes include incorrect cable types, physical damage, EMI/RFI
Crosstalk
When one cable/channel interferes with a signal on another cable/channel. Two types:
Near-End Cross Talk (NEXT): Interference measured at the transmitting end
Far-End Cross talk (FEXT): Interference measured at the received end
Using incorrect or low quality cable can increase risk. Effects include corrupted data, reduced transmission speeds, and decreased network reliability/performance
Attenuation
Gradual loss of signal strength as it travels through a cable or medium. Increases with distance. Can affect the quality of the communication, need to use repeaters or amplifiers to maintain signal integrity
Improper Termination
Issues:
Signal loss and reflection, leading to data transmission errors and reduced network performance
Increased electromagnetic interference, causing further degradation of signal quality
Transmitter (TX)/Receiver (RX) Transposed
Happens when the transmitter and receiving wires are incorrectly connected, leading to communication failures.
Issues:
Devices cannot establish a proper link, leading to a complete loss of communication between networked devices
troubleshooting becomes more complex, as the issue is often not immediately obvious
Interface issues
Can significantly impact network performance, leading to reduced efficiency and more troubleshooting needs.
Monitoring interface counters helps identify problems
Increasing Interface counters
Interface counters track various metrics related to network traffic and errors. Increasing errors can indicate potential issues
CRC Errors
Cycle Redundancy Errors. Occurs when there is a mismatch in the data checksum, indicating data corruption during transmission. Causes:
Faulty cable
EMI
Hardware Failures
Results in data retransmission, increased latency, and reduced throughput
Runts, Giants, Drops
Runts: Packets smaller than the minimum allowed size (usually less than 64 bytes)
Giants: Packets that exceed the maximum allowed size (usually greater than 1518 bytes for ethernet frames)
Drops: Occur when packets are discarded due to congestion, buffer overflow, or configuration issues
Port status issues
Can affect network connectivity/performance. Make sure to understand port statuses
Error Disabled
A port in error disable status has been automatically shut down by the network device due to a detected issue
Cause:
Security violations, such as port security breaches
network problems, such as excessive errors or link flaps
Administratively Down
A port that has been manually disabled by an Admin
Suspended
Refers to a port that has been temporarily disabled, usually due to network policies or dynamic configurations
Causes: Policy enforcement, such as violation of network access controls or dynamic adjustments by protocols like LACP
Power Budget Exceeded
When the Total Power consumption of connected PoE devices exceeds the available power budget of the switch, some devices wont receive proper power
Incorrect Standard
Need to ensure each device/switch has the same PoE standard
Transceiver Issues
Transceivers are modules used to connect network devices via fiber optic or copper cables, and issues with them can affect transmission. Mismatched transceivers and signal strength problems are common issues
Mismatched transceivers: Incompatible transceivers can cause connectivity/performance issues.
Symptoms:
No link light
Data errors
Intermittent connections
Resolution: Ensure they’re from the same manufacturer/standard
Poor signal strength
Can result in data transmission errors and reduced network performance
Symptoms:
High error rates
dropped packets
no connectivity
Resolution: Check/clean fiber optic connectors, ensure proper cable length and quality, and verify transceiver specifications to maintain adequate signal strength
Step 1: Identify the problem
Gather information, look at system logs, talk to the user, ask questions. ie "“Could you access the file server yesterday? What can’t you access on it? Did you have a map drive for it?:
Step 2: Identify a Theory of Probable Cause
Step 3: Test the theory to determine the cause
Step 4: Establish a plan of action to resolve the problem and identify potential side effects
Ste
Step 5: Implement the solution or escalate as necessary
Step 6: Verify full system functionality and implement preventative measures if applicable
Step 7: Document findings, actions, outcomes, and lessons throughout the process
Top-to-bottom/bottom-to-top OSI model
Either start troubleshooting from either the top (application layer) down, or the bottom (physical layer) up, depending on the symptoms
CIA Triad
Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability
Confidentiality
Access Controls: Mechanisms such as passwords, biometric verification, or access cards that limit resource access to authorized personnel
Encryption
Secure Communication: Using secure protocols like SSl/TLS for transmitting data to prevent interception by unauthorized entities
Integrity
Protecting data from unauthorized changes to ensure that it is reliable and correct. Key aspects:
Data accuracy
Data consistency
Data trustworthiness
Various methods are used, such as Cryptographic hash functions and digital signatures, Access controls as well
Availability
Ensuring data, systems, and services are accessible to authorized users when needed. Ways to do so:
Fault tolerance
Backup Systems
Risk
Asset: Anything within an environment that should be protected
Asset Valuation: A dollar value assigned to an asset based on actual cost and non-monetary expenses
Threats: Any potential occurrence that may harm the asset
Threat Agent/Actors: People, programs, hardware, or systems that used threats to cause harm
Threat events
Threat Vectors: A threat/attack vector is the path or means by which an attack/attacker can gain access to a target in order to cause harm
Vulnerabilities: Weakness in an asset or the absence or the weakness of a safeguard or countermeasure that could be exploited
Exposure: Actual or anticipated damage from a threat
Safeguards: Anything that removes/reduces risk
Attack: The threat exploiting the vulnerability, (the attempt to attack/exploit it)
Breach: The occurrence of a security mechanism being bypassed or thwarted by a threat agent (a successful attack)
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
A framework of business processes, policies, and technologies that facilitates the management of electronic or digital identities. Ensures the right people can access the right resources at the right times for the right reasons. Crucial for security and regulatory compliance
MAC (Mandatory Access Controls)
A security model in which access rights are regulated by a central authority based on different levels of security clearance. Use case: Common in government and military systems where classified info is involved.
Key aspect: Users cannot change access permissions… they are set and enforced by a system admin
DAC (Discretionary Access Control)
Security model where the resource owner decides on access levels. Most flexible access model. Used in environments where users need control over the resources they own, like file permissions etc.
Key aspect: Risk of users granting excessive access potentially leading to security breaches
RBAC (Role Based Access Control)
Assigns permissions based on a user’s role in an organization. Common in corporate environments. Streamlines access management
Rule Based Access Control
Access decisions are based on a set of rules defined by a system admin. Useful in environments requiring stringent access control, like securing network resources.
Key aspect: Rules can be based on various criteria, such as source/destination IP in firewalls
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
Uses policies that evaluate attributes of users, the environment, and resources. Effective in complex environments with diverse and dynamic user attributes.
Key aspect: Provides fine-grained control, allowing for more nuanced access decisions based on multiple factors (like access based on location, time, browser you use, etc)
SSO Importance
Reduced password fatigue
Centralized Authentication Control (Easier to enforce security policies)
Reduced IT workload (Simplified management of user accounts)
LDAP
Protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services, like user and group details, over a IP network
Federation
The process of linking and managing identities/credentials across different systems and organizational boundaries (SSO for multiple sites/apps/websites)
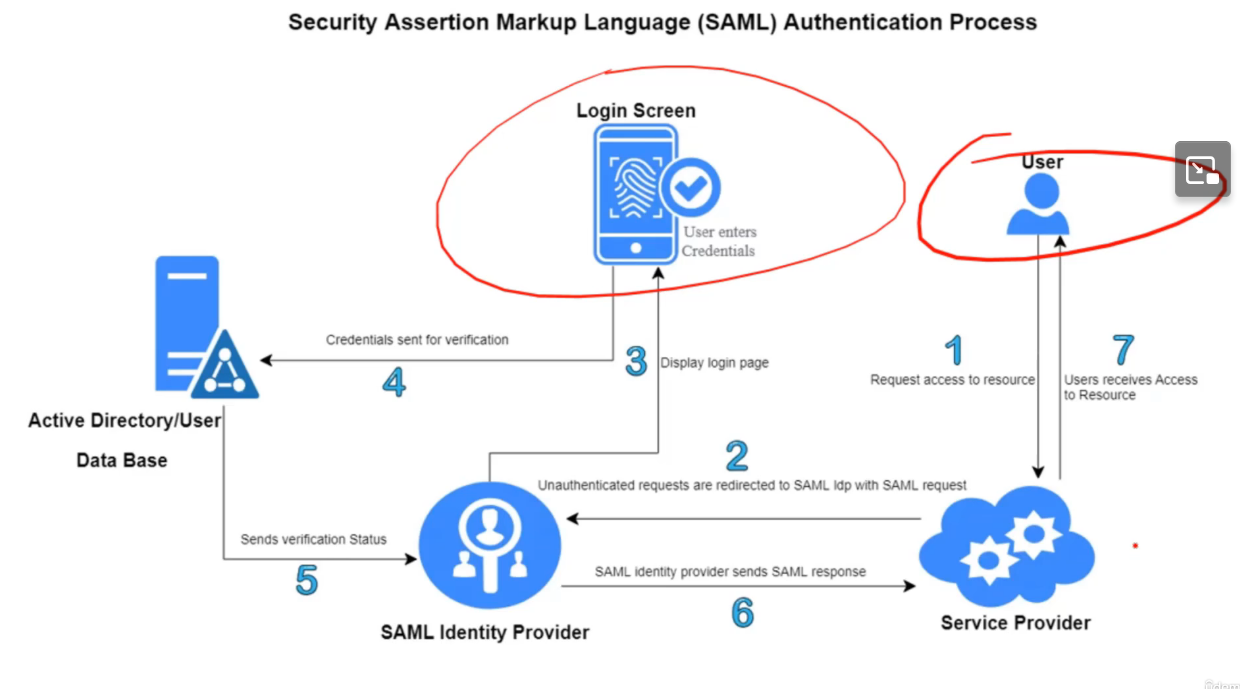
SAML
Security Assertion Markup Language, an open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, specifically between an identity provider and a service provider. Very popular for federation
Usage: Widely used for SSO to allow users to log in to multiple applications with one set of credentials
Uses XML for data exchange. Particularly useful in enterprise-level SSO
Key Components:
Identity Providers (IdPs): Services that authenticate users and provide identity information to service providers. Examples: Okta, Microsoft Azure AD, and Google Identity. Attestation (formal verification that something is true) is done with the IdPs.
Service Providers: The applications or services that rely on information from the IdP to provide access to the user (like Best Buy, Facebook, New sites, etc)
OAuth
Open standard for access delegation. Used to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords. Commonly used for authorizing third-party applications to access a user’s data without exposing their credentials.
Is about authorization not authentication, and is used to grant limited access on behalf of the user
OpenID Conect
An identity layer on top of OAuth 2.0. Allows clients to verify the identity of the end-user based on authentication performed by an authorization server. Primarily used for authentication in modern web applications and mobile applications
Geofencing
Limiting access to resources (using GPS, RFID, WiFi, or cellular data) based on location, using either a mobile device or RFID tag for instance.
Deception and Disruption Technology
Refers to a set of cybersecurity strategies/tools designed to mislead, confuse, or disrupt the actions of malicious actors. used to create traps or illusions that protect real network assets by diverting attackers to decoy systems/files
Honeypot
A security mechanism setup to detect, deflect, or study hacking attempts. Acts as a decoy, imitating a real computer system, network, or information system, but is isolated and monitored. Provides valuable info about their techniques/intentions without endangering the actual network
Honeynet
A network of honeypots. Simulates a network environment to attract attackers. More complex, but can provide deeper insights
Honeyfiles
Decoy files placed with an network’s file systems. Appears legitimate and contains attractive data, but are monitored for access. Unauthorized access can alert security personnel
Honeytoken
Any decoy data or token inserted into a system. Could be a fake user account, database record, or any other type of digital bait that when interacted with indicates a compromise or unauthorized access
Data locality
Refers to the geographical location where data is stored, processed, and managed. Compliance with data locality regulations ensures that data handling practices meet regional legal requirements
PCI DSS
Payment Card Industry and Data Security Standards. Involves implementing encryption, access control, and regular monitoring to protect cardholder data from breaches and fraud