Chapter 3: Cell Structure, Function, and Energy
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Cell
The smallest unit of life that can function independently.
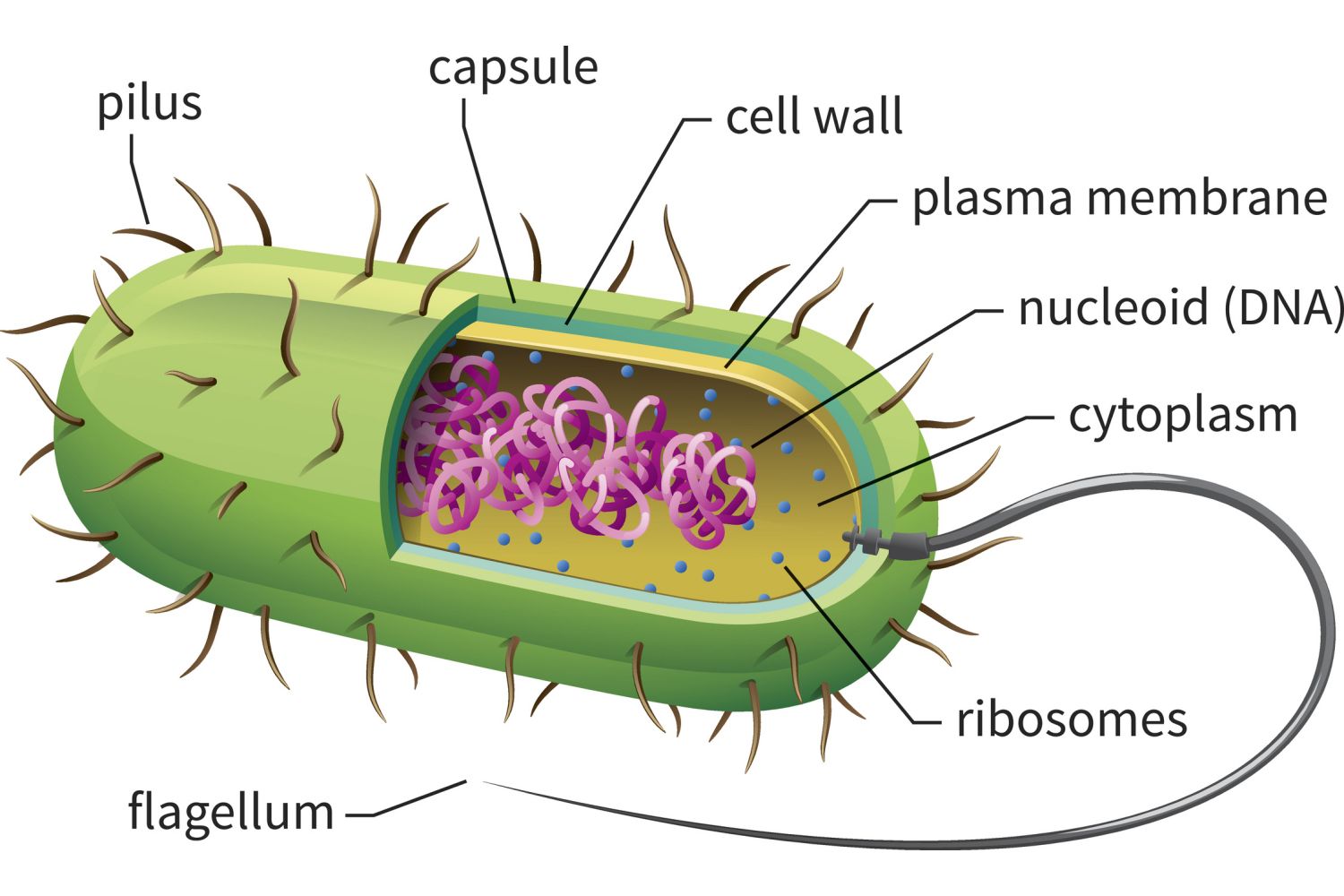
Prokaryotic Cells
Unicellular organisms that lack a nucleus and many organelles, containing a circular ring of DNA.
Example: Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryotic Cells
More complex cells that can be unicellular or multicellular, containing a nucleus, and membranous organelles.
DNA is located in their nucleus, bounded by a nuclear envelope.
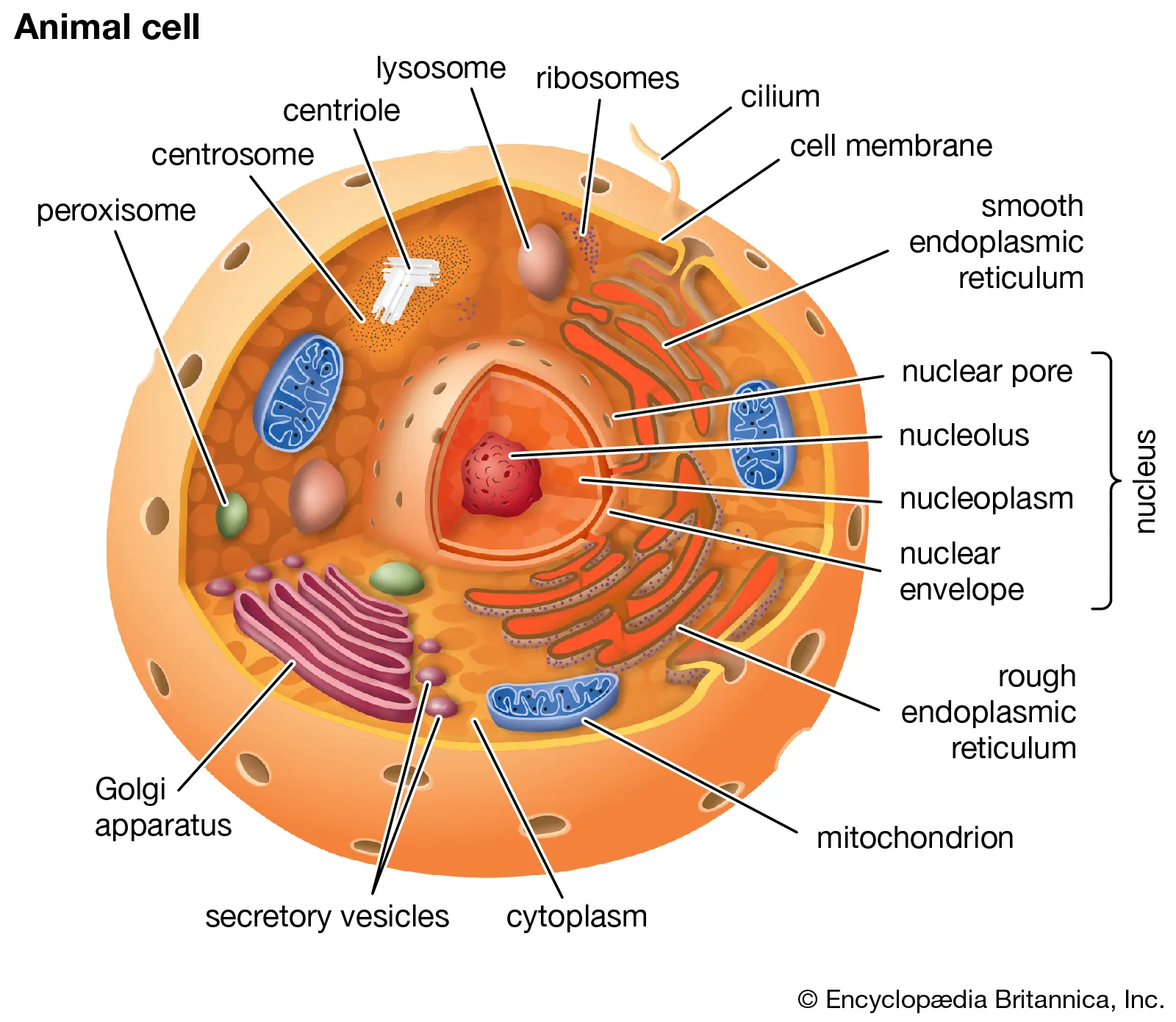
Compartmentalization
The presence of membrane-bound organelles in eukaryotic cells, each with specific functions.
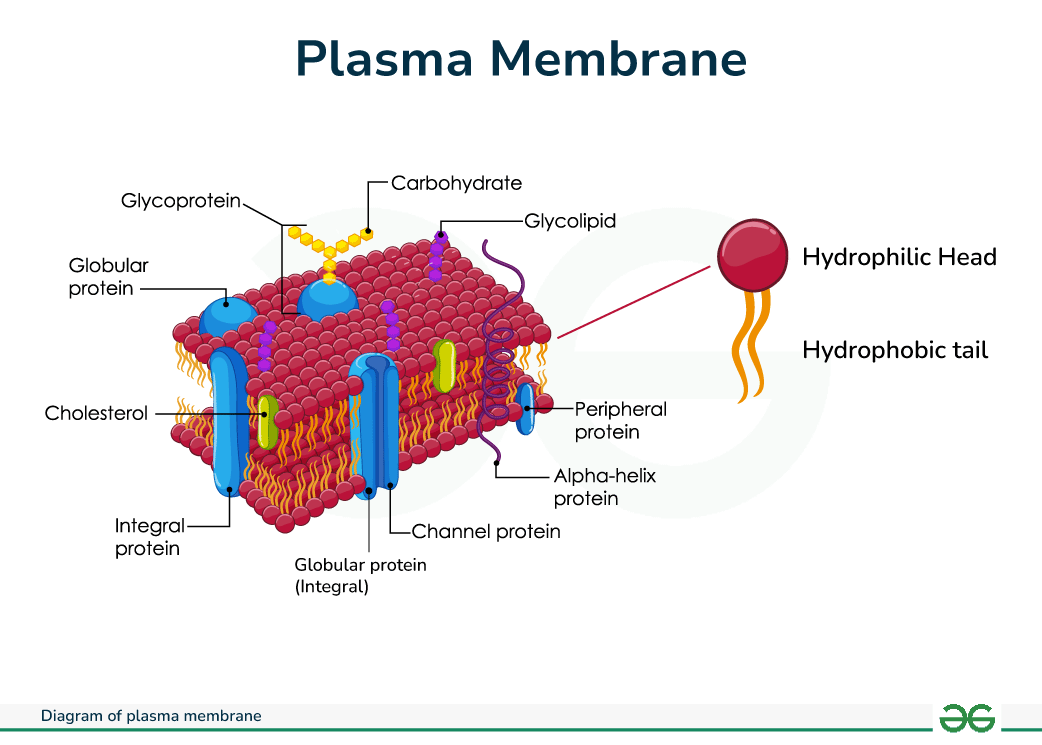
Plasma Membrane
Separates the cell from the external environment and controls the passage of substances into and out of the cell, such as organic molecules and wastes.
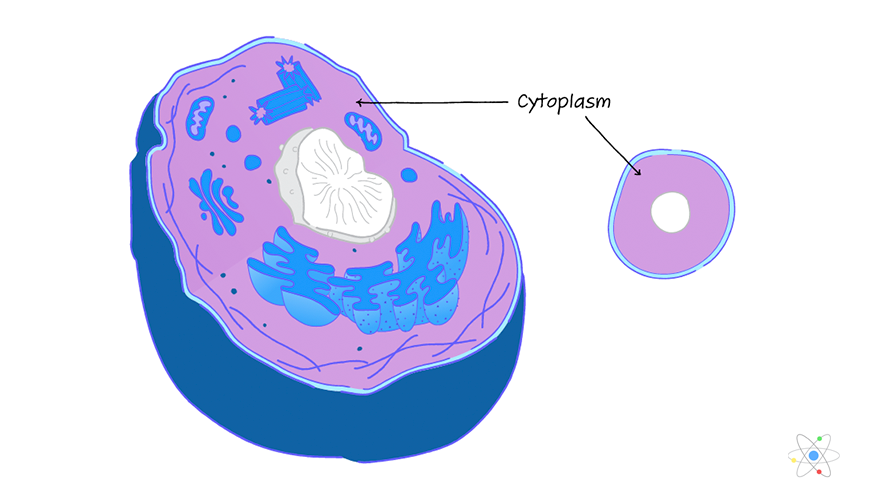
Cytoplasm
Provides structure to the cell and is the site of many metabolic reactions.
Organelles are found here
Nucleoid
Location of DNA in prokaryotes
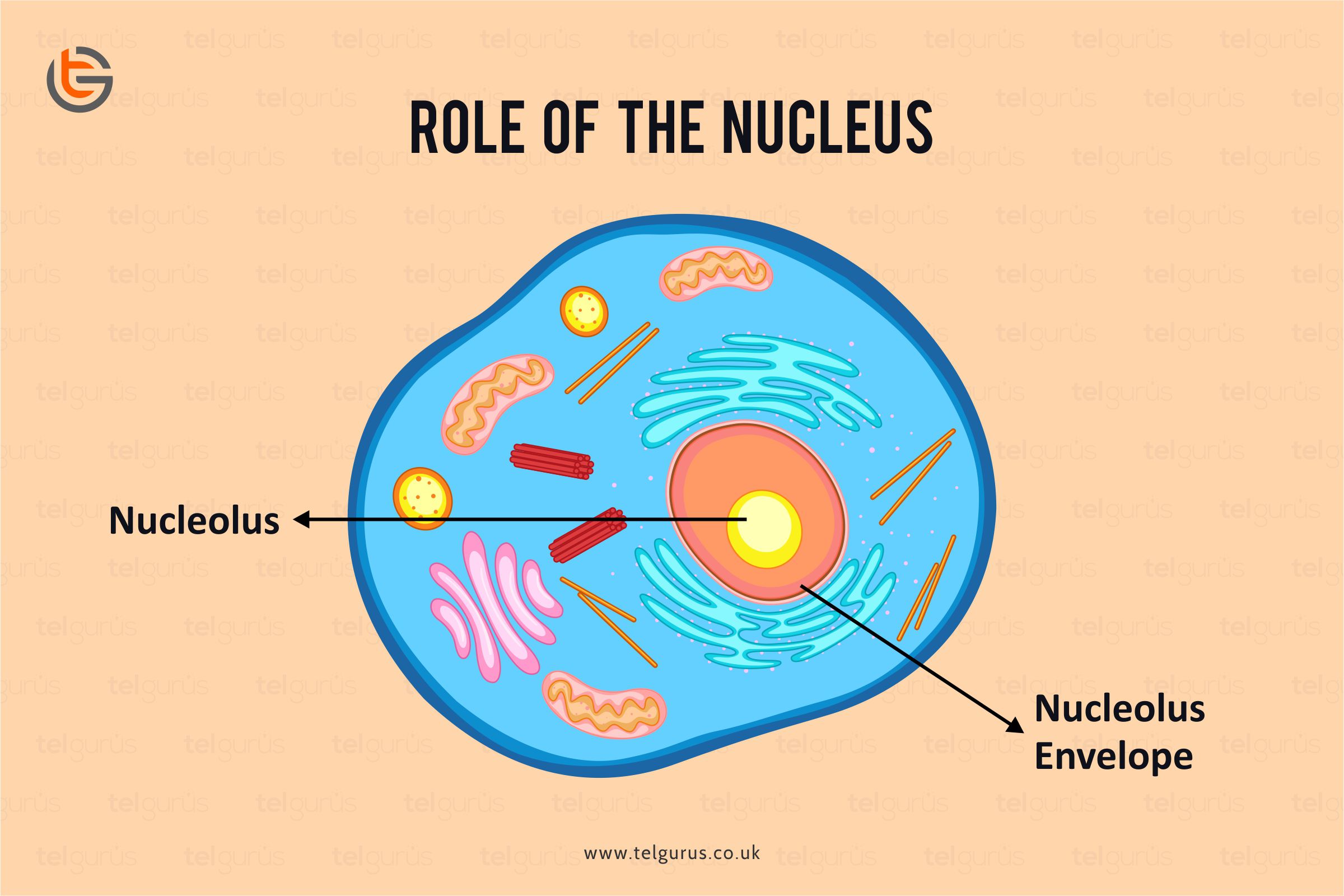
Nucleus
Organelle that houses DNA and directs the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins.
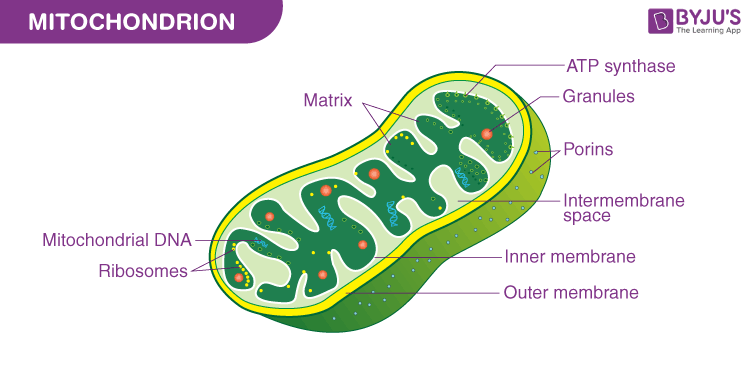
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell responsible for ATP production and cellular respiration.
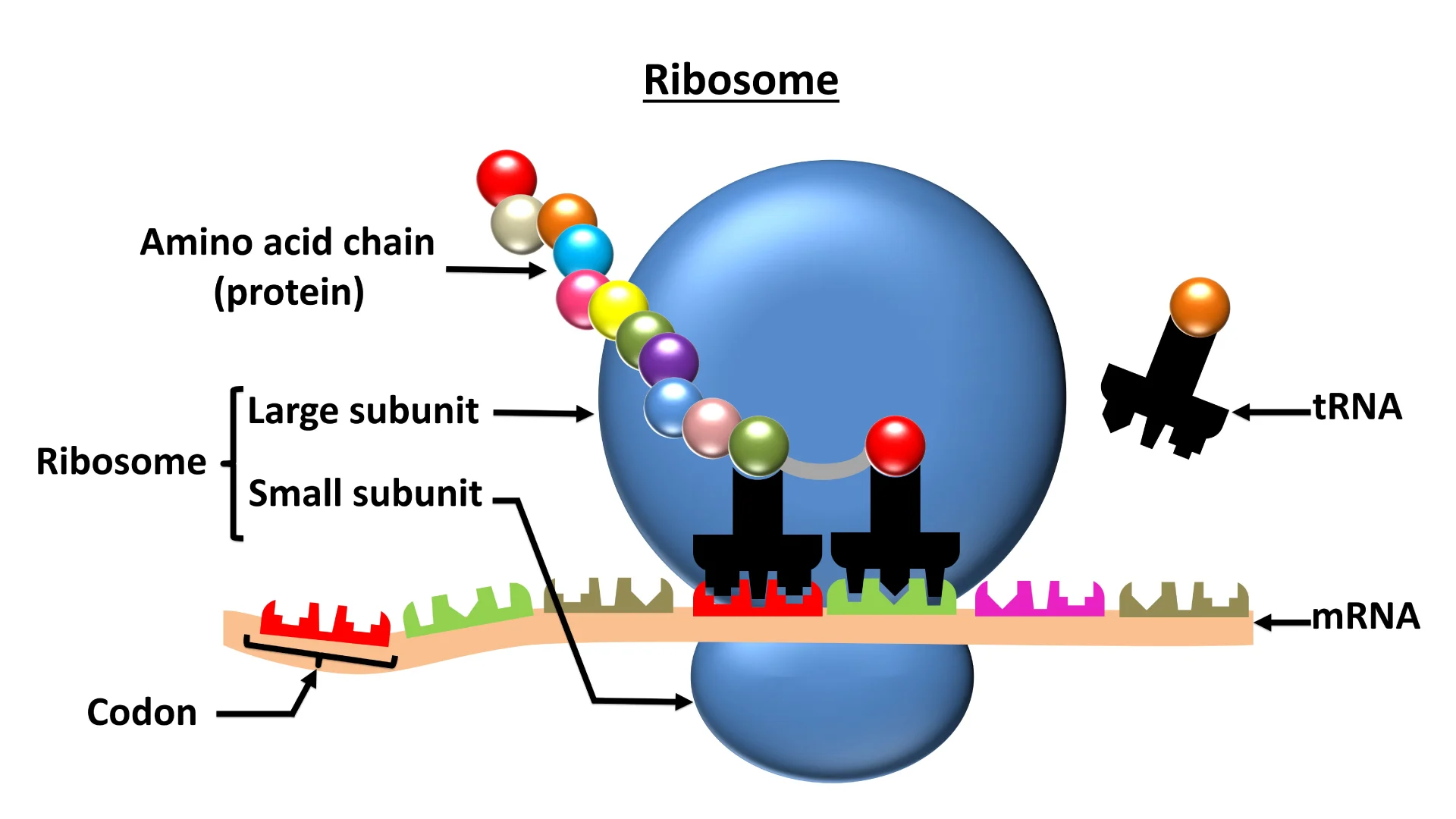
Ribosomes
Organelles responsible for protein synthesis.
Peroxisomes
Responsible for oxidizing and breaking down fatty acids/amino acids, and detoxifies poisons
Vesicles and Vacuoles
Organelles that store and transport substances
Acts as digestive function in plant cells.
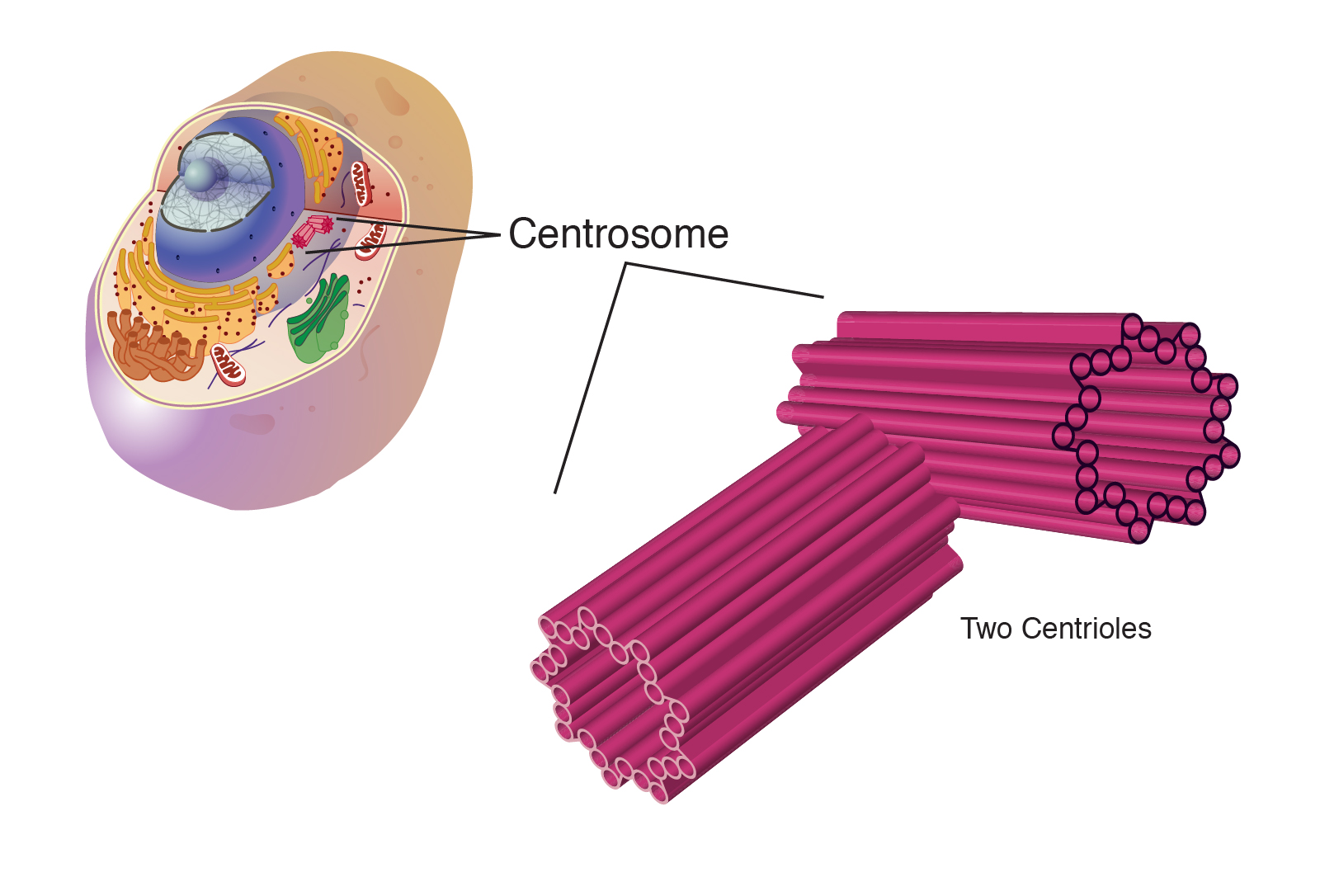
Centrosome
Plays a role in cell division of animal cells
Organizing center of microtubules in animal cells.
Lysosome
Organelle that digests macromolecules and recycles worn-out organelles
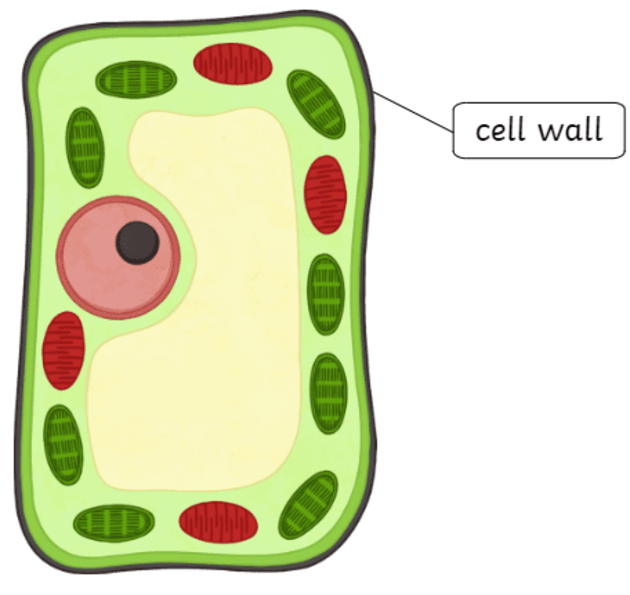
Cell Wall
Acts as protection and support for a cell’s shape
Found in bacteria and some plants
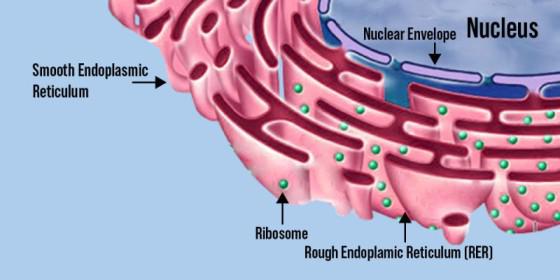
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Modifies, sorts, tags, packages, and distributes lipids (smooth ER) and proteins (rough ER)
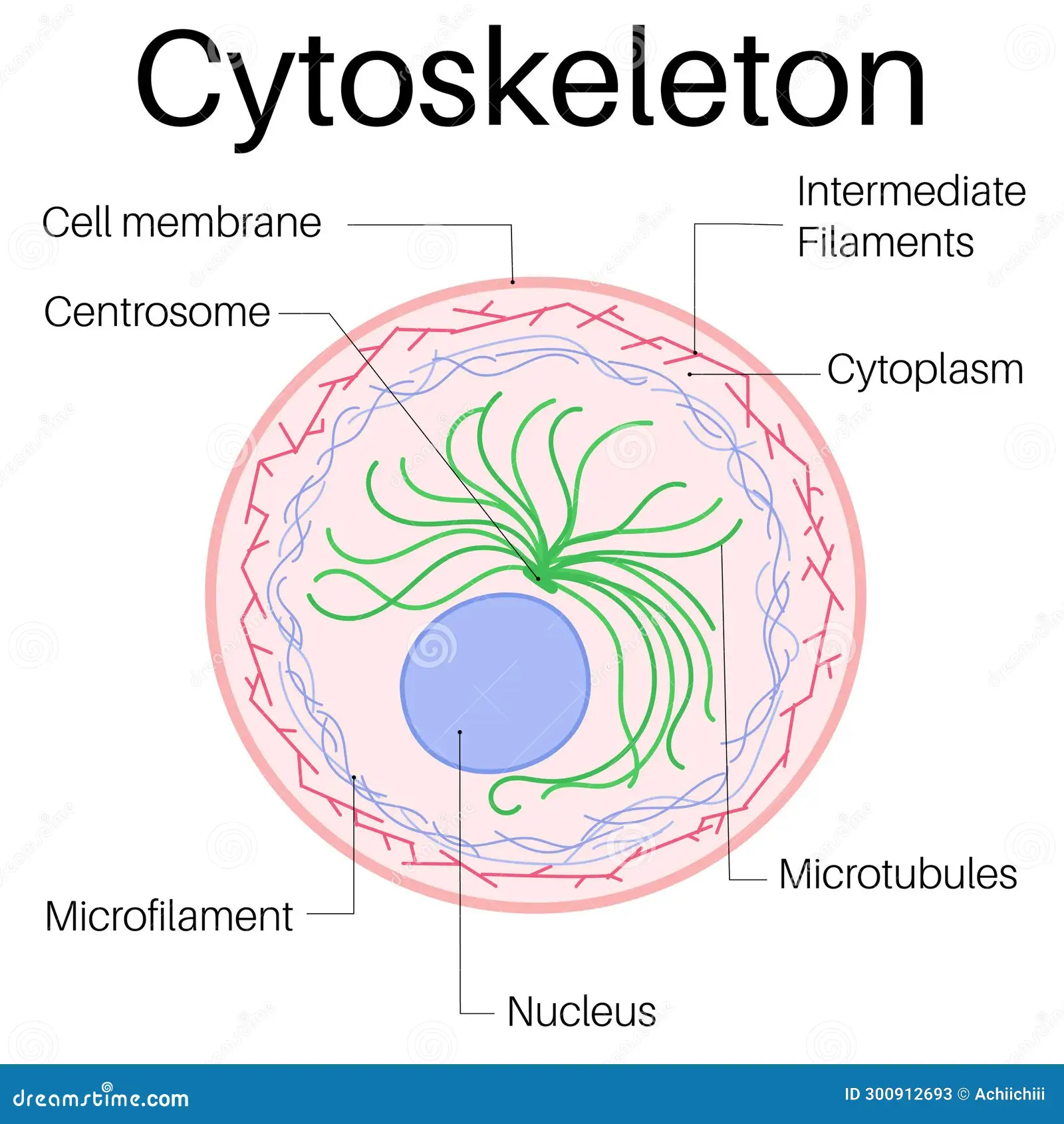
Cytoskeleton
Maintains a cell’s shape by securing organelles, allowing cytoplasm and vesicles to move within the cell, and enables unicellular organisms to move independently.
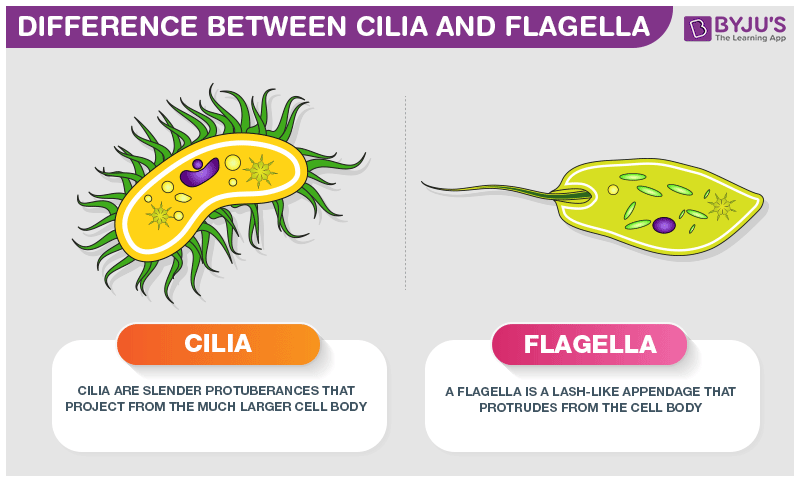
Flagella and Cilia
Responsible for cellular locomotion
Solute
A substance dissolved in a liquid
Example: Sugar
Solvent
The liquid portion of a solution (usually water)
Concentration
The measure of how much solute is present per volume of solvent.
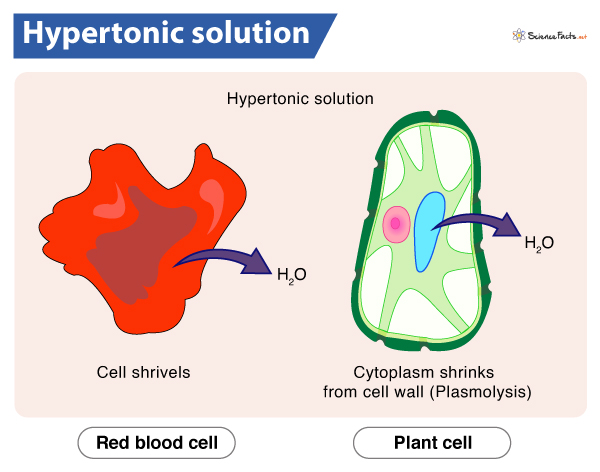
Hypertonic
When a solution has a higher concentration of solute compared to solvent.
Example: More sugar than water.
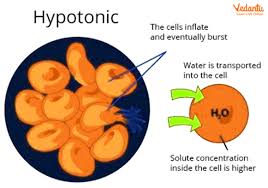
Hypotonic
When a solution has a higher concentration of solvent compared to solute.
Example: More water than sugar.
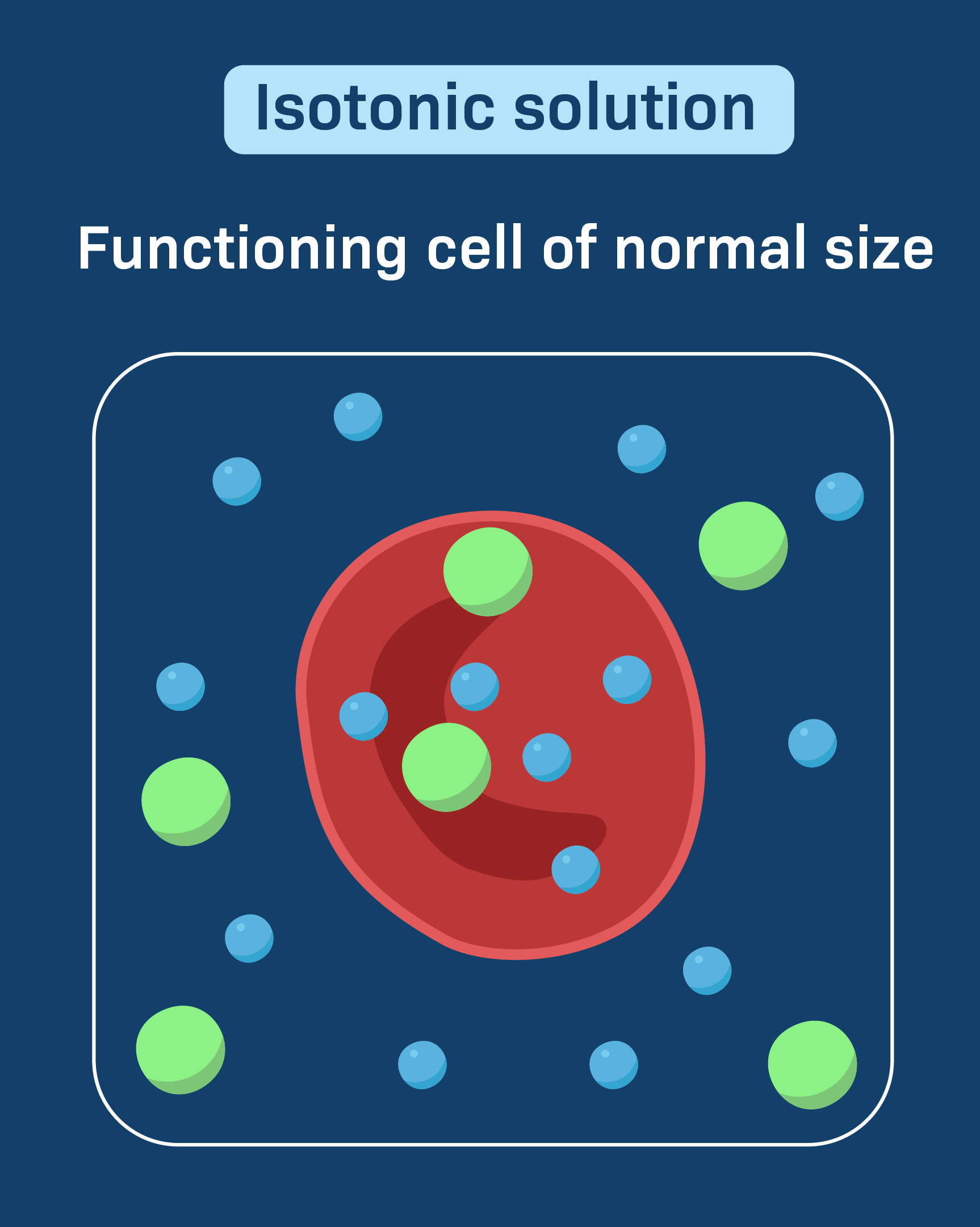
Isotonic
When a solution has an equal concentration of solute and solvent.
Example: Same amount of water and sugar
Passive Transport
No energy required
Movement is due to a gradient (differences in concentration, pressure, or change)
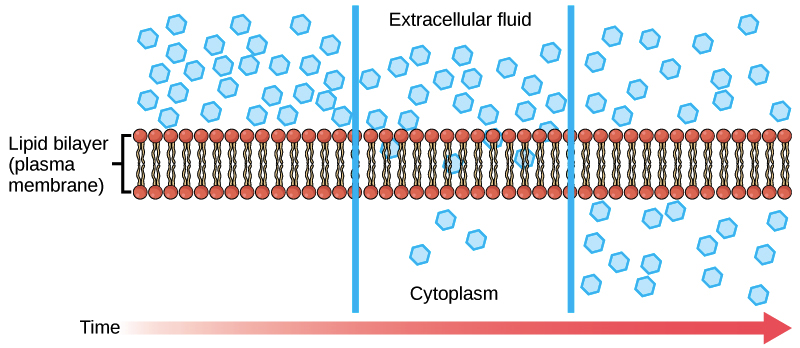
Diffusion
Movement of solute from higher concentration to lower concentration
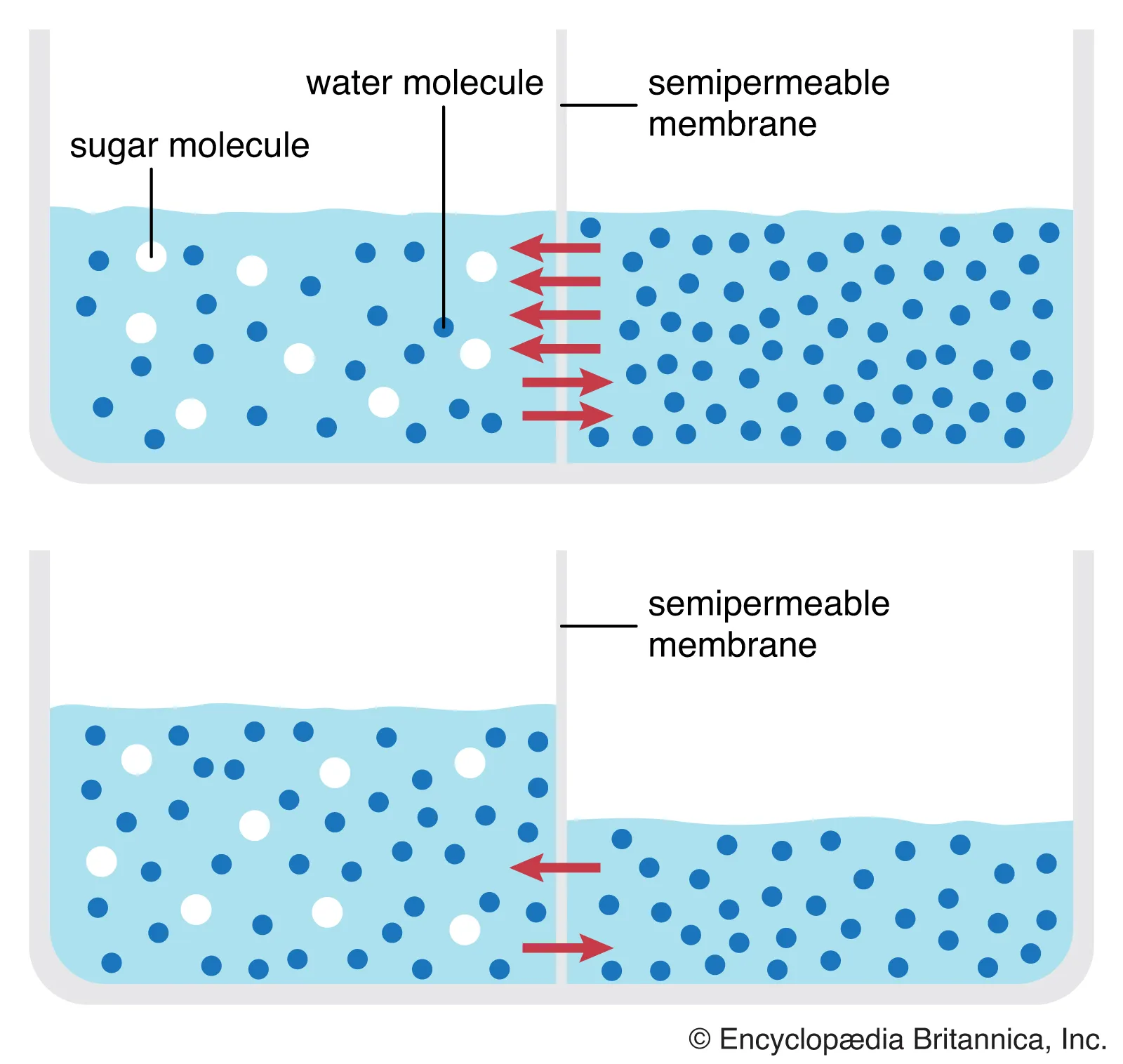
Osmosis
Movement of water (solvent) across a semipermeable membrane
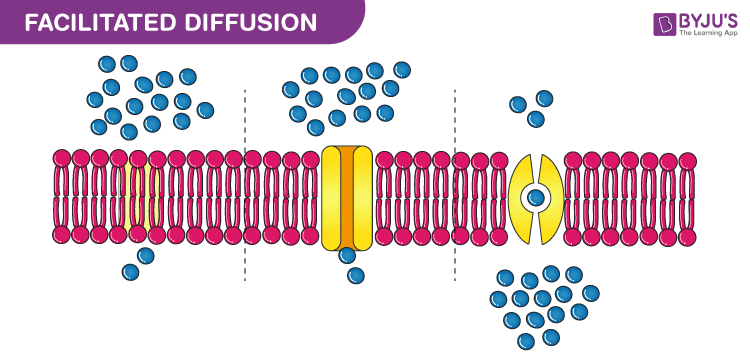
Facilitated Diffusion
Solute particles are moved across a membrane with the help of transport proteins.
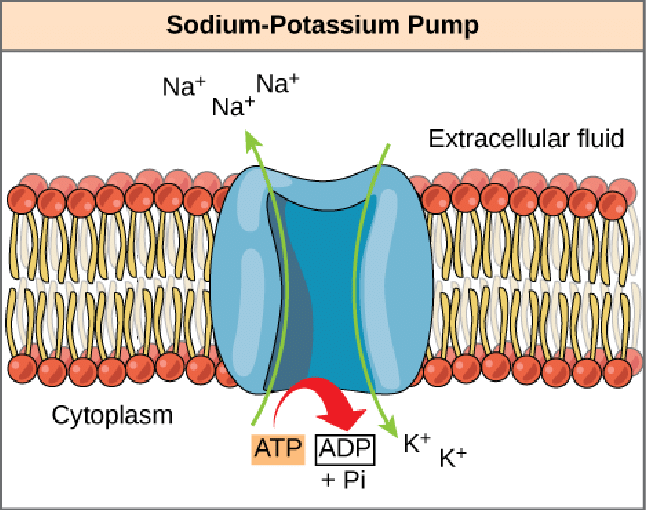
Active Transport
Energy in the form of ATP is required for this kind of transport.
Movement is against the concentration gradient (low to high).
Example: Sodium potassium pumps in our body are a way of active transport.
Endocytosis
The process of moving substances into a cell.
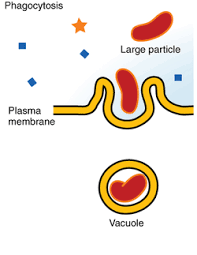
Phagocytosis
Cell eating
When cells engulf particles
The cell membrane surrounds the particle and pinches off to form an intracellular vacuole
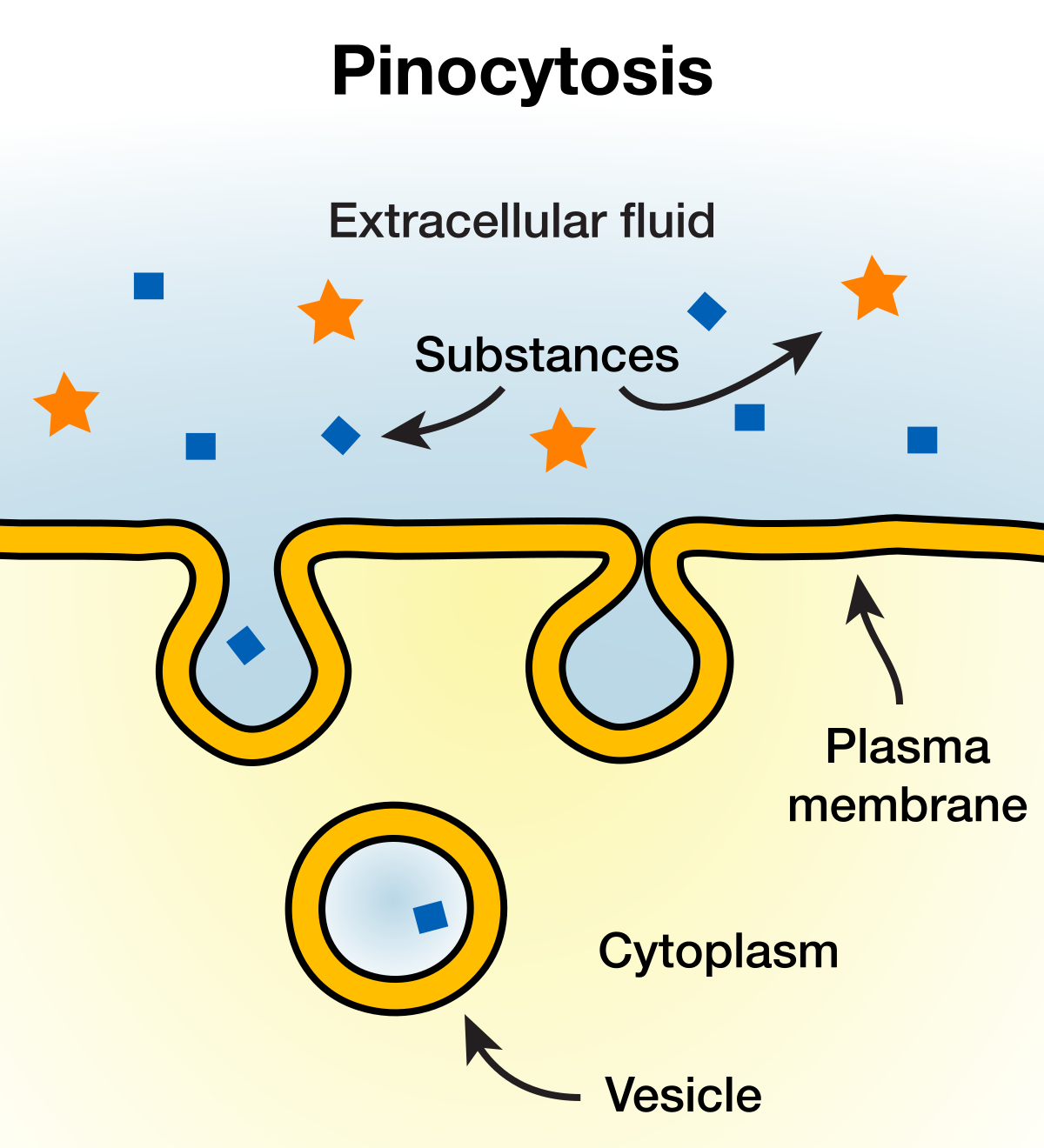
Pinocytosis
Cell drinking
Movement of liquids into a cell
The cell membrane surrounds a small volume of fluid and pinches off, forming a vesicle
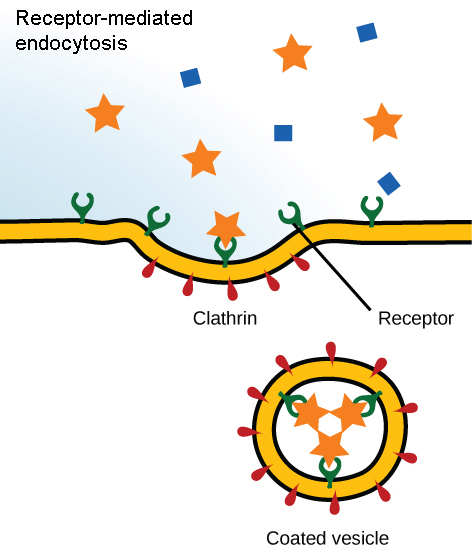
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Uptake of substances by the cell is targeted to a single type of substance that binds at the receptor on the external cell membrane
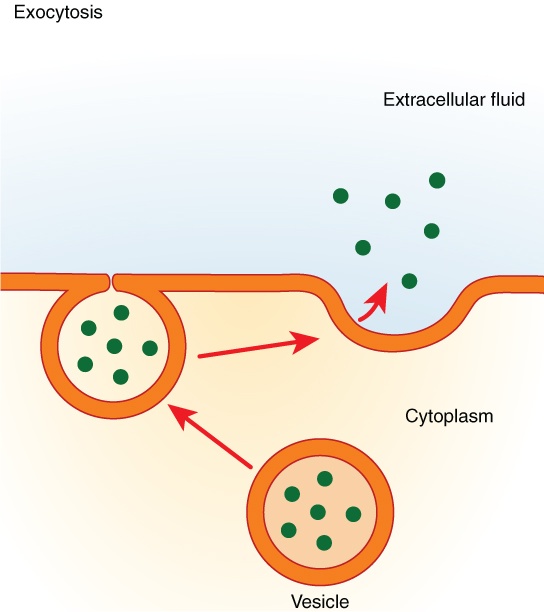
Exocytosis
The process of moving substances out of a cell.
A vesicle transports a substance and fuses with the cell wall, releasing the substance into the extracellular fluid.
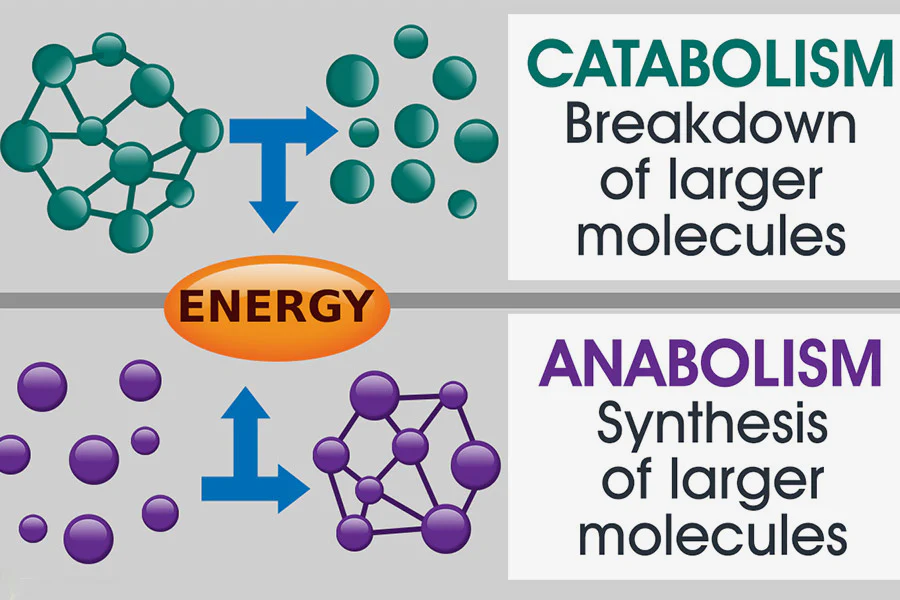
Metabolism
All biochemical reactions taking place in an organism, including anabolic and catabolic pathways.
Anabolic - small molecules are built into large ones, energy is required.
Catabolic - large molecules are broken down into small ones, energy is released.
Enzymes
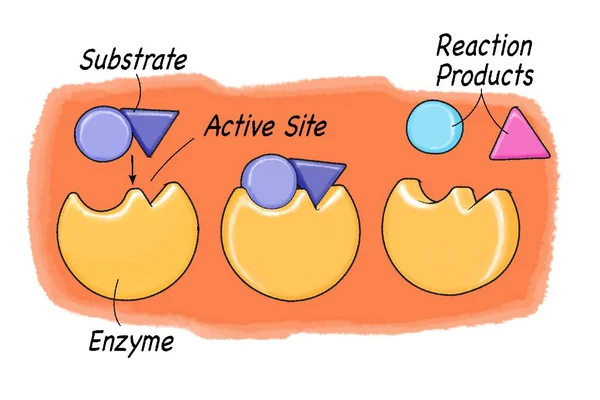
Biological catalysts that lower activation energy and facilitate chemical reactions.
Made of proteins, reusable, highly specific, have an active site, used in very small accounts.
Substrate Complex
The binding of an enzyme to its substrate, forming a complex that lowers activation energy.
Regulation of Enzyme Activity
Environmental factors like pH, temperature, salt concentration, and in some cases, cofactors or coenzymes affect enzymes.
Competitive inhibition - an inhibitor binds at an active site and competes with substrate.
Non-competitive inhibition - allosteric inhibition or allosteric activation
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
The process of breaking down carbohydrates to produce ATP in the presence of oxygen.
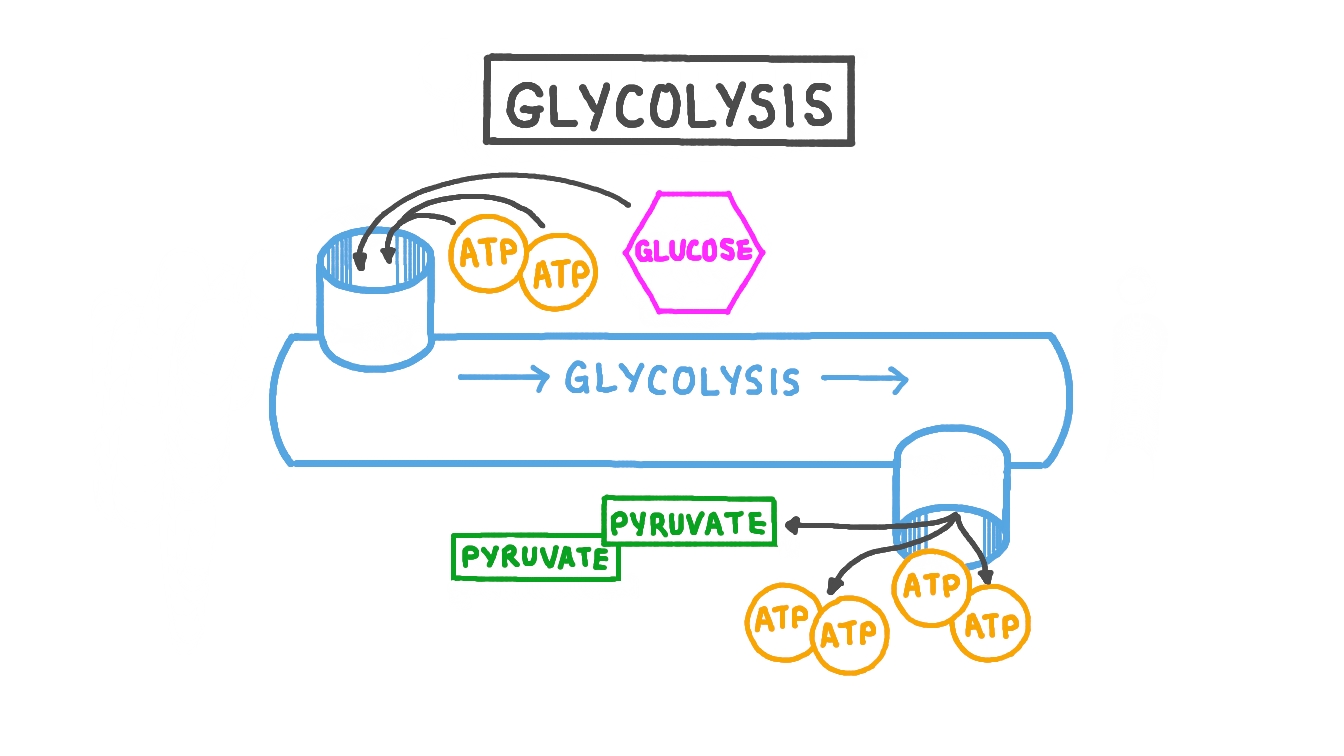
Glycolysis
The first step of cellular respiration where glucose (six-carbon sugar) is converted into two molecules of pyruvate (a three-carbon sugar.
Produces about 4 ATP but 2 are used in the process, which means there are 2 net ATP.
Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle
Acetyl CoA (two-carbon molecule) combines with a four-carbon molecule, ultimately regenerating the four-carbon starting molecule
Produces 2 ATP, NADH, and FADH2 while releasing carbon dioxide.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
The final stage of cellular respiration where most ATP (32) is produced via the electron transport chain.
NADH and FADH2 deposit their electrons into the electron transport chain, turning back into their “empty” forms (NAD+ and FAD)
Anaerobic Respiration
The process of producing ATP without oxygen, including fermentation pathways.
Alcoholic fermentation
Converts pyruvate to CO2 and ethanol
Lactic acid fermentation
Converts pyruvate to lactic acid
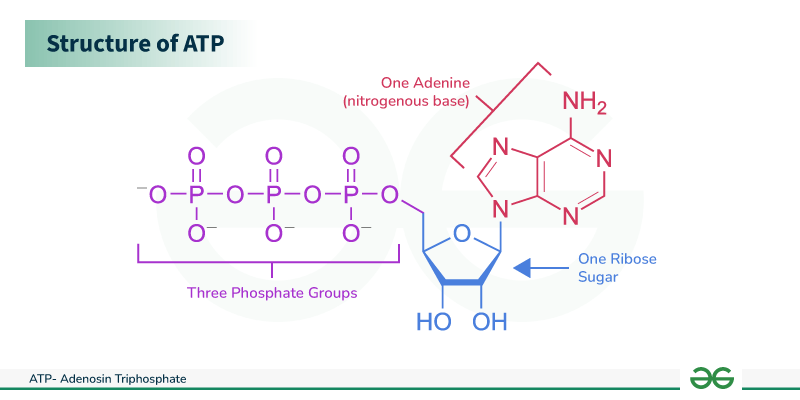
ATP
The energy carrier molecule used to power cellular activities, composed of three phosphate groups, adenine, and ribose.
Cleavage of each high energy phosphate releases energy when ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP.