Muscle contractions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Tropism
Movement of organisms towards eexternal stimulus
Sacromeres
Composed of strands of actin & myosin protein. Responsible for muscle contractions.
Myofibrils
Contractile units, composed of repeating sacromeres
What stimulates the release of Ca2+
An action potential arriving at muscle fibres stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release.
What does Ca2+ bind to and why?
Ca2+ binds to tropomyosin
Move & expose myosin binding sites on actin filament.
Where does ATP attach to
Myosin head
What happens after ATP hydrolysis
Myosin head cocks towards Z line
What is powerstroke
Shortening of sacromeres by sliding actin and myosin more compactly
Z line
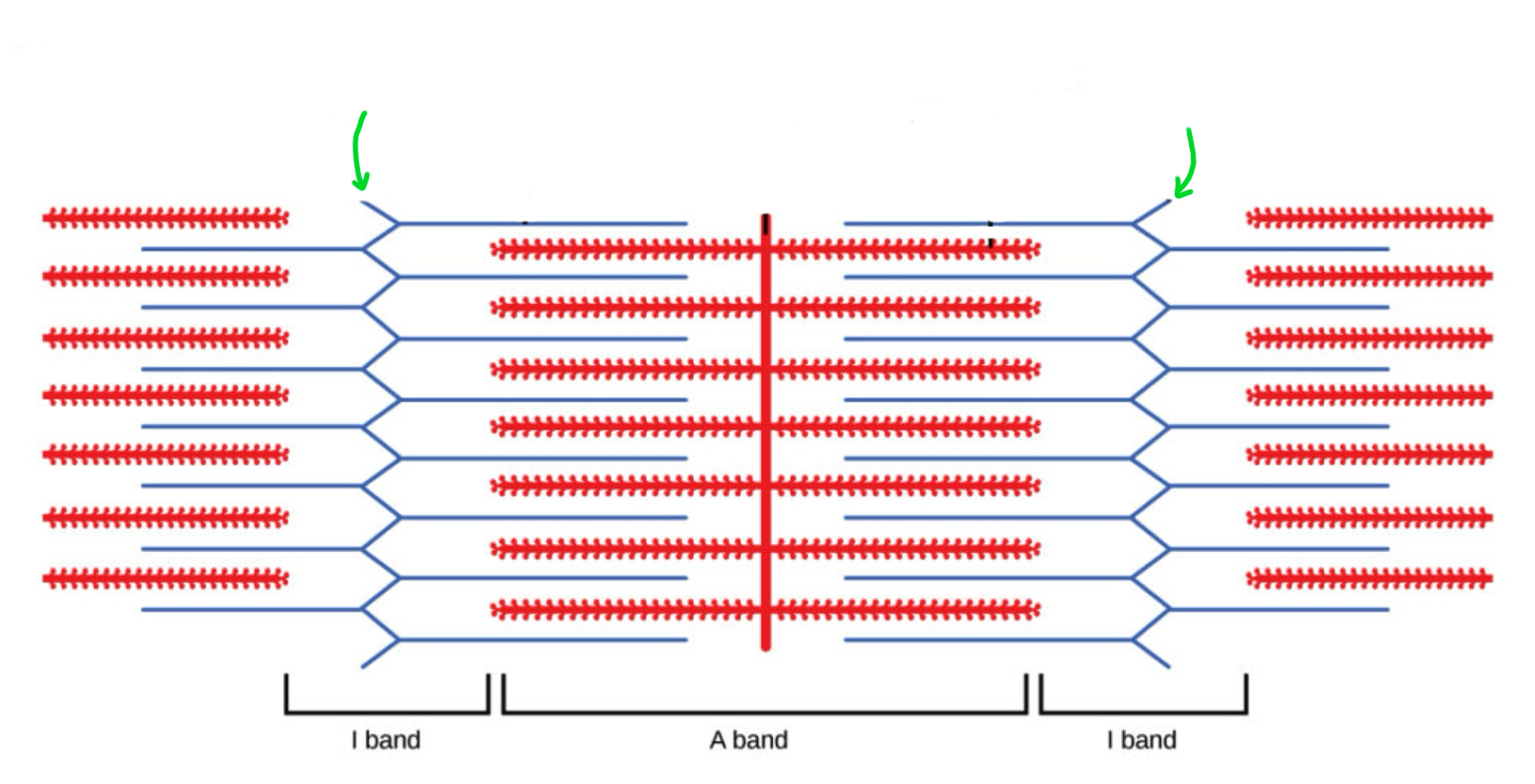
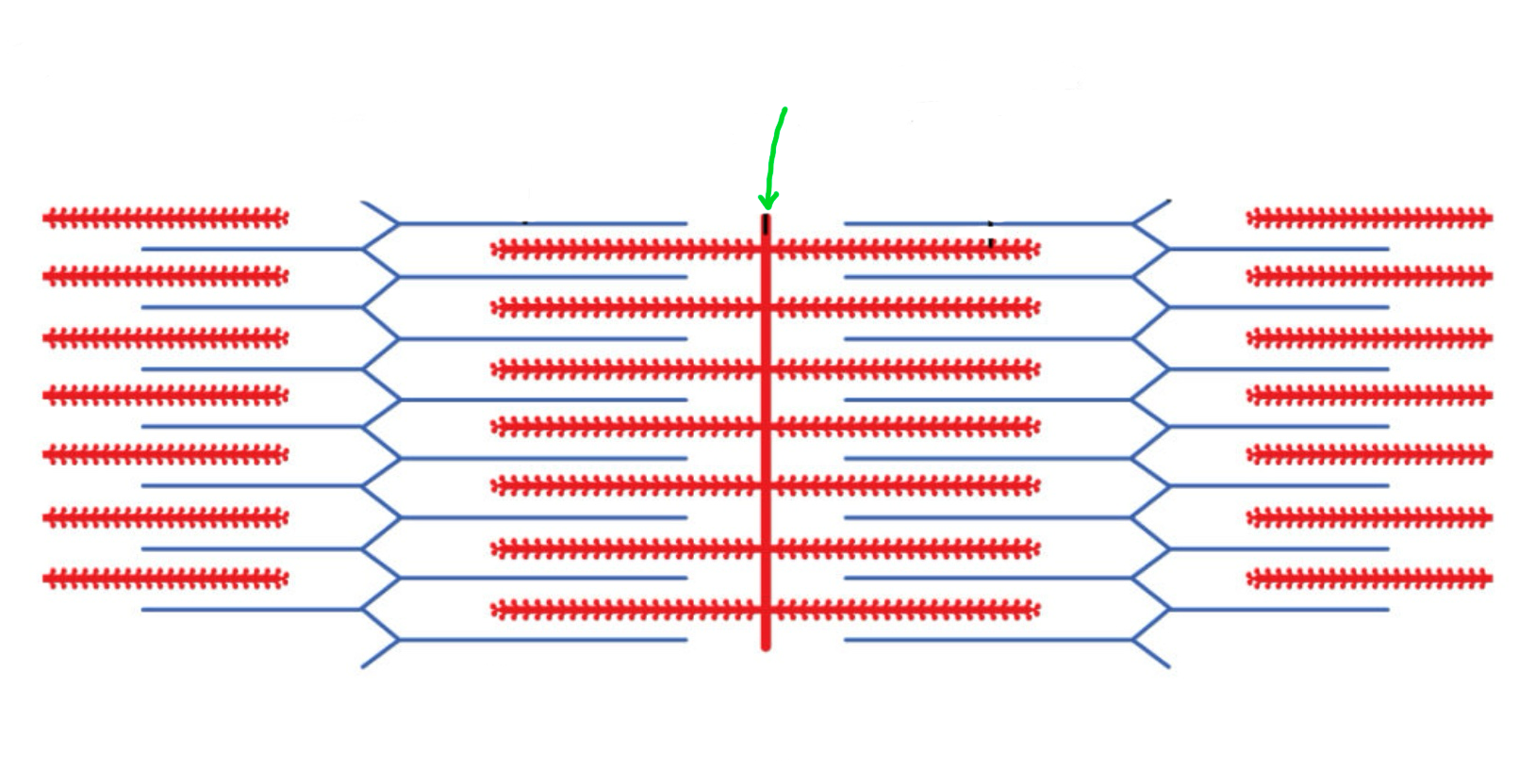
M line
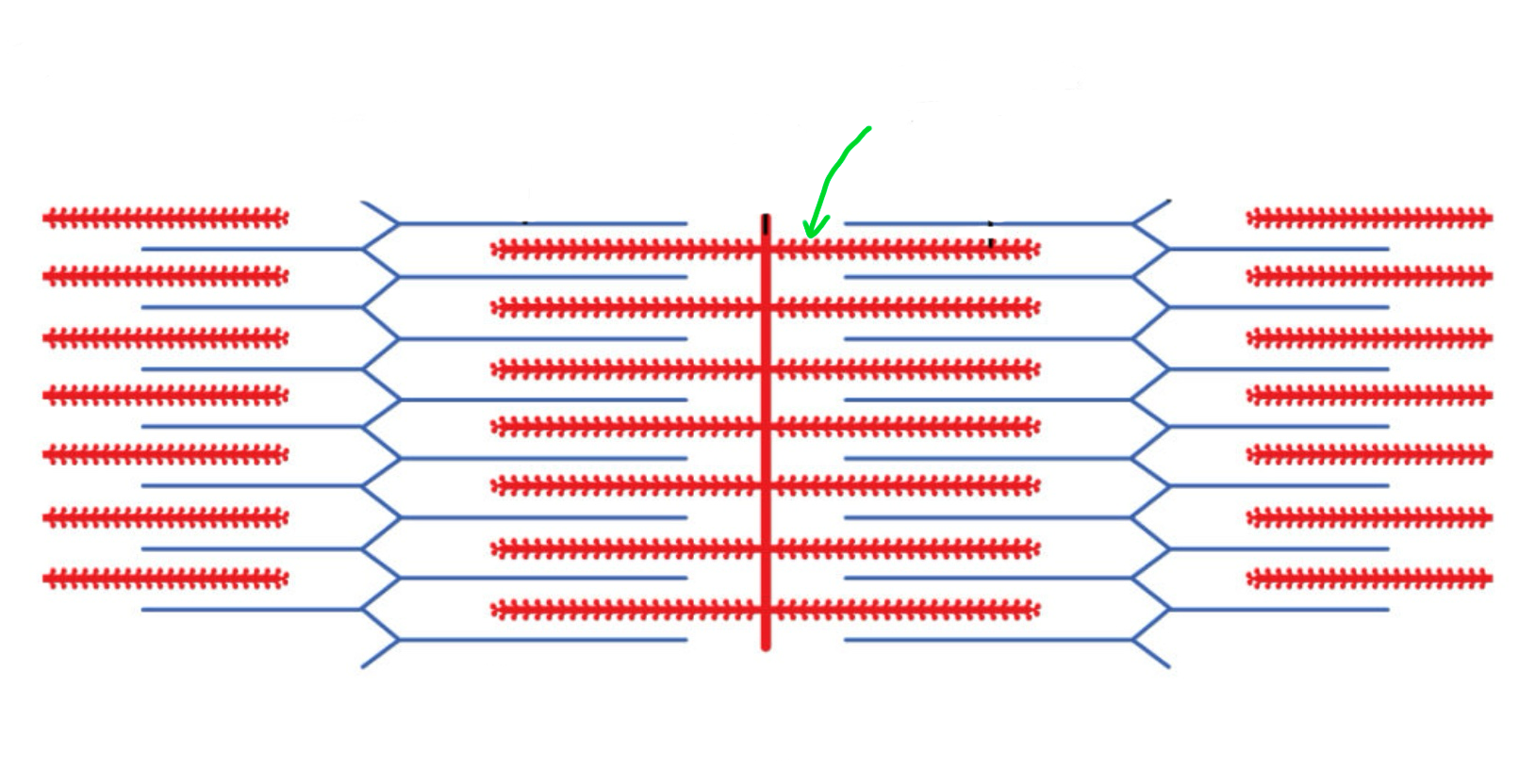
Myosin
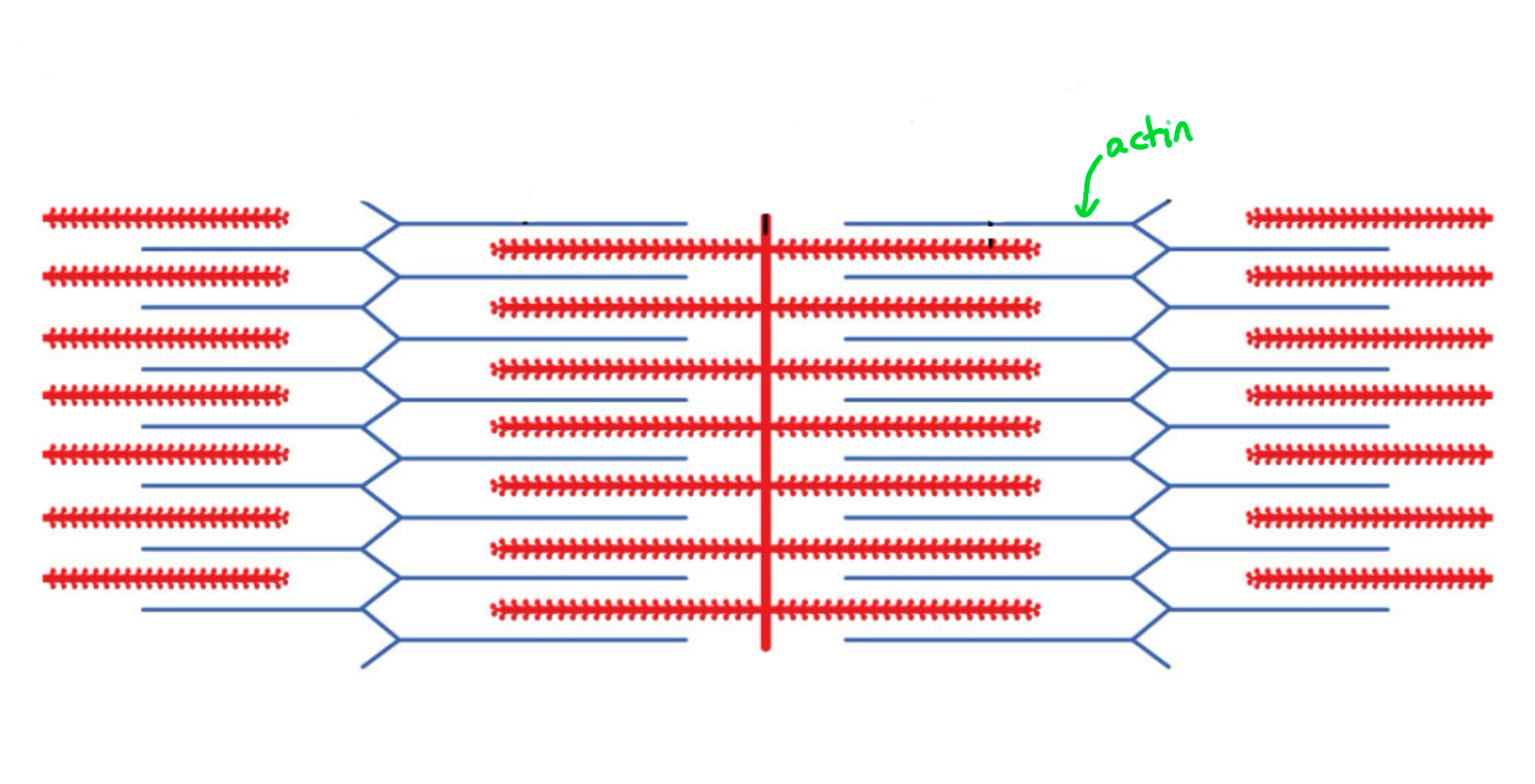
Actin
Light band
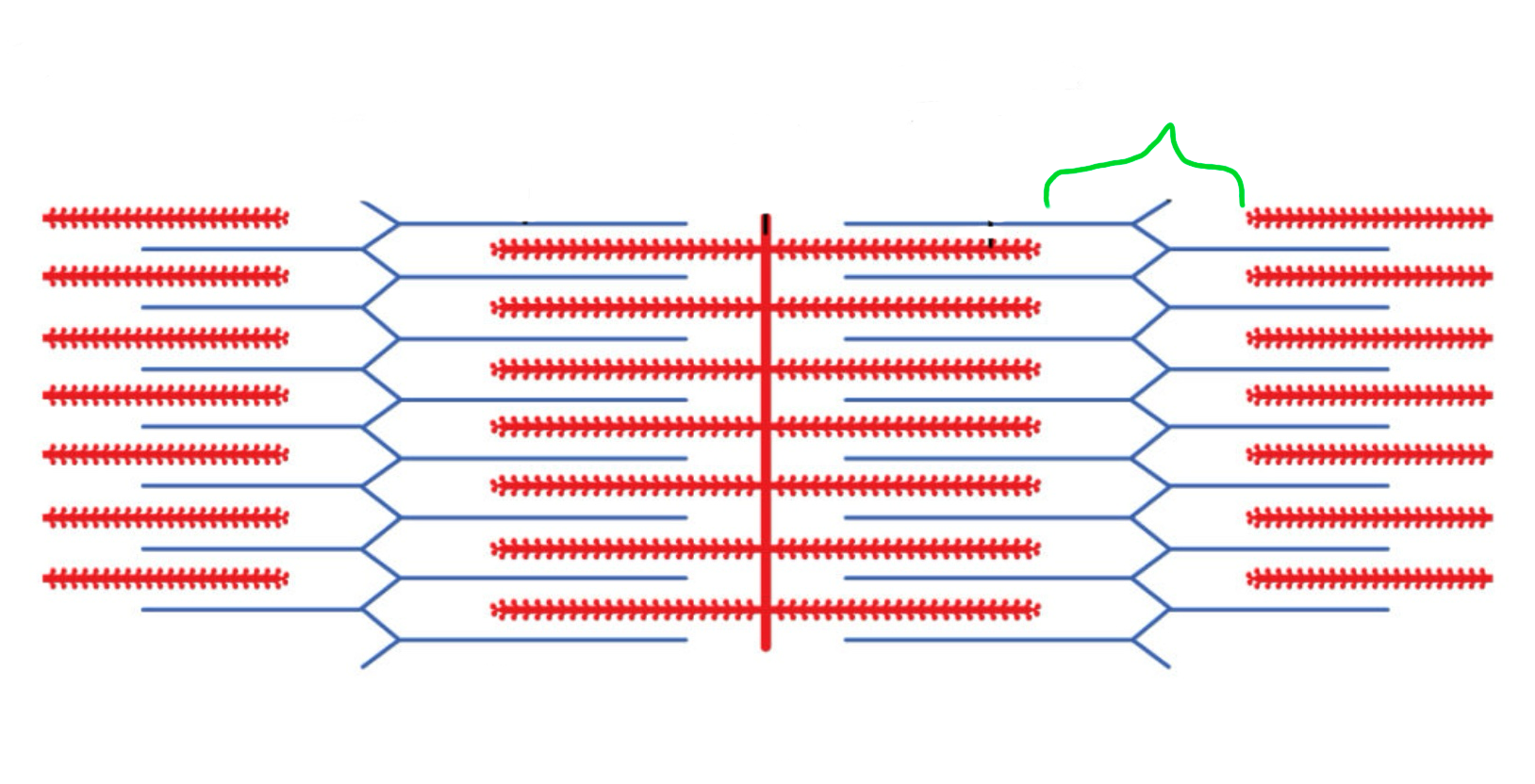
Dark band
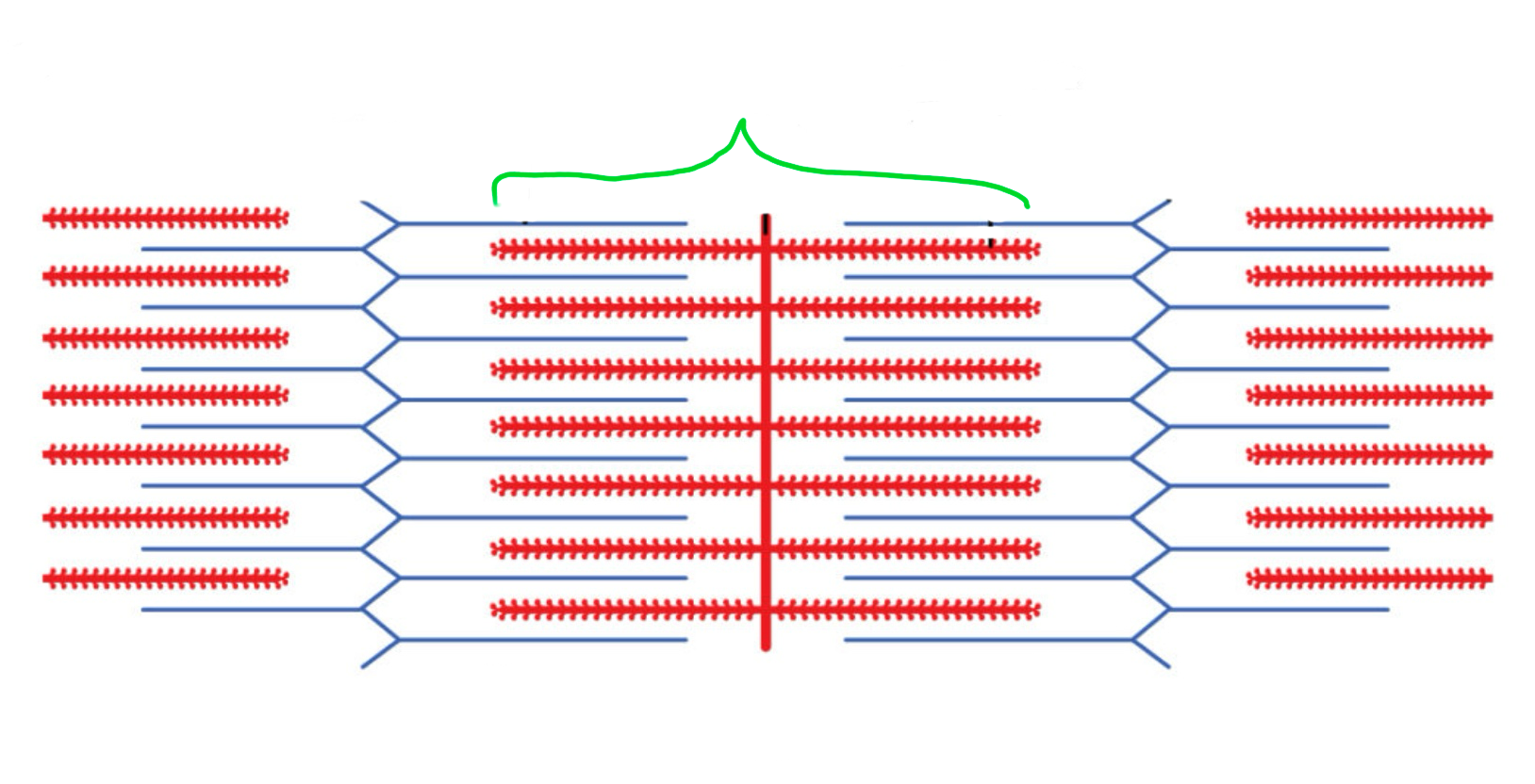
What is Titin
Long fibrous elastic protein that stretches from Z line to M line. Acts as molecular spring.
Purpose of Titin
Helps sacromeres to recoil after stretching to prevent over extension of muscle
Intercostal muscles
Muscles involved in ventilation
Internal intercostal muscle location
Deeper within muscles
External intercostal muscle location
Surface of muscle
Orientation of Internal intercostal muscle
diagonally along direction of ribs
Orientation of External intercostal muscles
Parallel to direction of ribs
What is titin and what is its purpose?
It is a very long protein (longest in human body)
Connects z-line and m-line, acts as spring to keep actin and myosin in place.