Mechanisms of thyroid hormone action and impaired sensitivity to thyroid hormones
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Thyroid hormones T4/T3 are …. soluble?
Lipid soluble, but still requires a transporter
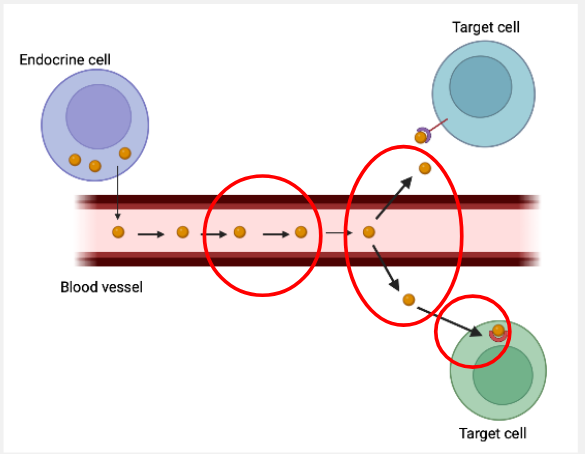
How do thyroid hormones exert their effects?
To reach target cells:→ travel in the blood stream bound to carrier proteins
To bind to thyroid hormone receptors:→ intracellular receptors
→ need to cross the plasma memebrane
What are the 2 thyroid hormone binding proteins?
Thyroid binding globulin (TBG)
transthyretin (TTR)
What is Fre hormone hypothesis?
Free hormone + binding protein ←→Hormone-protein complex
There is an equilibrium between the free and protein bound form of the hormone
Hormones bound to hormone binding proteins are inactive- only the free hormones can enter cells to exert biological effects
T3/T4 transport into cells is…? and what can inhibit it?
Saturable
Can be inhibited by amino acids
In some cells types it depends of Na+
Role of passive diffusion is limited
Thyroid hormones rquire trasnporter proteins
to facilitate their transport across cell membrane
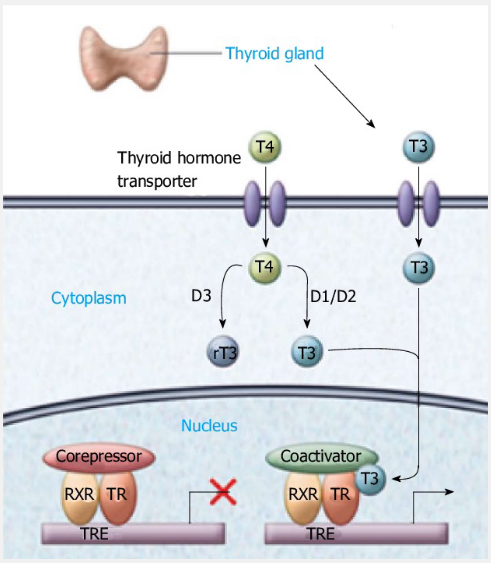
What do transporters vary in?
Substrate spectra
Tissue distribution
Affinity for THs
MCT8 is the most specific TH transporter identified to date
Whats is important about tissue distribution?
Thyroid hormone transporters are co-expressed in many tissues
Variable tisse distribution in huan adult tissues
Patterns of expression vary further with development, between different cell types within tissue between species
What happens in T3 uptake by MCT8?
T3 uptake though the process of facillitated diffusion.
Placental MCT8 knockout decreases the uptake of T3.
What mutation causes MCT8 deficiency?
SLC16A2
Causes a change in serum thyroid hormone levels
Sever psychomotor retardation
What are the different types of SLC16A2 mutations and what are their effects of MCT8 localisation and function?

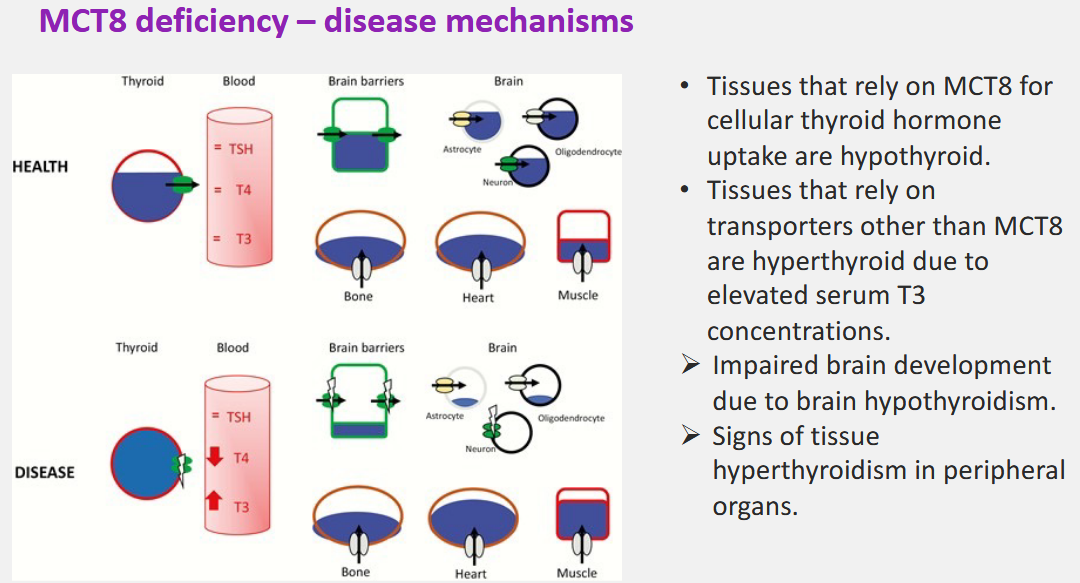
What are the clinical characteristics of MCT8 deficiency?
Altered cirulating levels of thyroid hormones (low T4, elevated T3, normal or borderline high TSH)
(assocaited with hypothyroidism) Neurological phnotype: severe interllectual disability, failure to achieve motor milestones, absence of speech dev, feeding problems
Peripheral phenotype (associated with hyperthyroidism): loss of weight, muscle wasting, tachycardia, increased perspiration
HOWEVER NORMAL PRENATAL GROWTH AND NO EVIDENCE FOR INCREASED PRENATAL OR NEONATAL MORTALITY
What is the disease mechanism of MCT8 deficiency?
T3 levels are elevated but it is not well know what causes this?!
What are the different theraputic approches for MTC8 deficiency?
Use of T3-analogues that bypass MTC8 for their cellular entry, but once inside the cell bind to the TH-R
Gene Therapy: supply MCT8-deficient cells with wildtype MCT8 protein, so it produces MCT8 transporters.
Treatement with chaperones to enhance surface translocation of mutant MCT8 that retain transport activity (Type 2 mutations)

What is the function of Deiodinase enzymes?
Activationa dnd deactivation of thyroid hormones
→which either activates the prohormone thyroxine (T4cap T sub 4 𝑇4 ) into the bioactive hormone tri-iodothyronine or inactivates T4 and T3 into inactive forms
What is the function of Dio1 and Dio2?
Convert T4 to T3, the active hormone
Dio1 more important in rodents
Dio2 more important in humans
What is the function of Dio3?
Dio3 deactivates T4 to rT3 (inactive metabolite)
T2 inactive metabolite is generated by T3 or rT3
in mice double Dio1 and Dio 2 knockout does not affect peripheral T3 levels
in humans some polymorphisms in Dio genes affect plasma levels of thyroid hormones
essential for normal mouse myogenesis and muscle regeneration
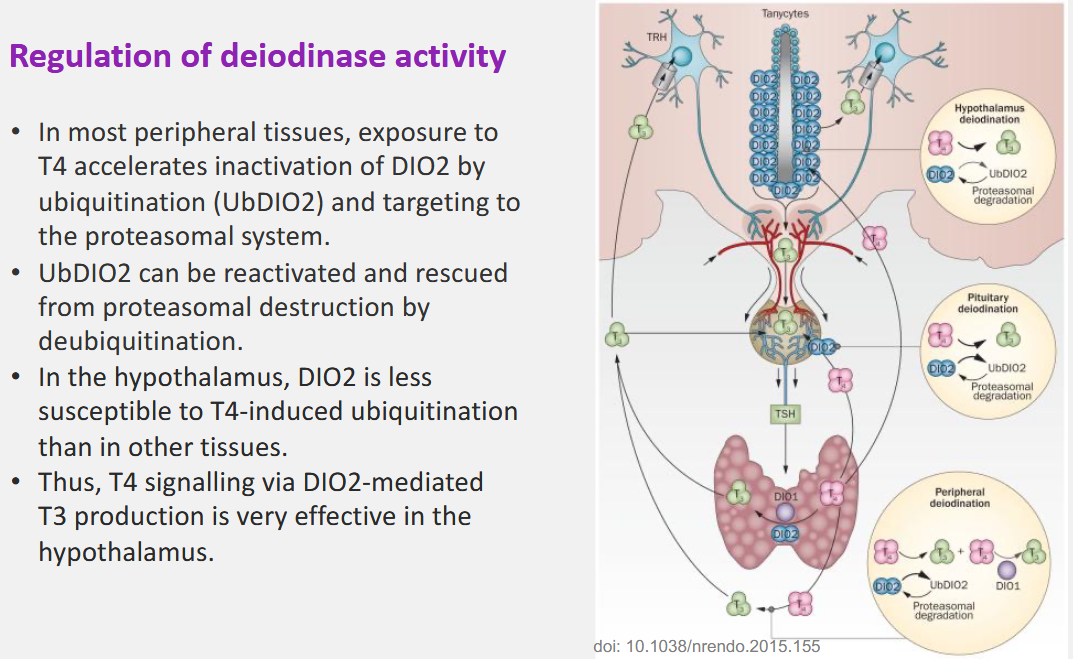
How is Deiodinase activity regulated?
TR: Finish the last slides about genomics and t receptors?