[CYTOGENETICS] FLUORESCENCE IN-SITU HYBRIDIZATION (FISH)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
FLUORESCENCE IN-SITU HYBRIDIZATION
(FISH)
Same as karyotyping (purpose)
Specializes in specificity
FLUORESCENCE IN-SITU HYBRIDIZATION
(FISH)
Can be used to detect what specific parts are deleted or duplicated
Study certain sequences
True
T/F:
In karyotyping, we cannot locate sequences (lacks specificity)
Hybridization
In FISH, we first denature the DNA molecule before we can study the interest
We are to facilitate the formation of new bonds
FLUORESCENCE IN-SITU HYBRIDIZATION
(FISH)
a cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind specifically to a part of chromosomes complementary to their sequence
Useful in detecting and mapping the presence or absence of particular DNA sequences within chromosomes
FLUORESCENCE IN-SITU HYBRIDIZATION
(FISH)
applied to provide the specific localization of genes on chromosomes
Rapid diagnosis of trisomies and microdeletions is acquired using specific probes
FLUORESCENCE IN-SITU HYBRIDIZATION
(FISH)
Enable us to detect trisomies and microdeletions
True
T/F;
in FISH, We are studying the chromosome (intact)
Interphase and Metaphase
Two phases of cell division where we can do FISH
Know the location of the DNA you are specifically interested in
First step of FISH
NCBI
lists all the locations of the DNA
100-1,000 nucleotides
number of fluorescent labeled probes to develop
The longer the probe, the greater the specificity; Better visualization
Heat the cells at 90-95 degree Celsius (to destroy Hydrogen Bonds)
How do we denature and separate the DNA strands and allow probe access to the target DNA
Probes can bind to them when denatured
Unique from the karyotype
Cool down to 65-70 degree celsius the probe
How do we hybridize or facilitate new bonds
Purpose: make new bonds
But the DNA can also renature on itself (possible)
Lower or cooler temp
Longer probes to hybridize require what temperature
Fluorescent microscope
Microscope used in FISH
1) Locate the DNA
2) Generate complementary sequence
3) Denature the DNA
4) Hybridization
5) Analyze
Summary of steps of FISH
UV light
The fluorescent tag needs to be stimulated by _____ light because it is not visible to the naked eye (for fluorescent)
Somatic cells
Cells used in FISH (Somatic or Sex)
Metaphase Cells
Gold standard and routinely done
Done on cultured cells
Allows direct visualization of chromosomes and exact position of signals
> Can detect translocations
Metaphase Cells
Useful in the detection of structural changes in the genome
> Arranged from biggest to smallest
Amniocytes
Chorionic villous cells
Lymphocytes
Cells from bone marrow aspirates or solid tumors
Fibroblasts
Samples of metaphase cells
Interphase Cells
May also be done on uncultured specimens
Advantageous in the rapid screening of many nuclei for prenatal diagnosis and newborn studies (fast TAT)
> We do not have to culture the cells anymore
> Mas madali by 48-72hours
48-72hours
Hours we can save if we use interphase cells in FISH
Interphase Cells
Also beneficial in the study of samples with a low mitotic index, such as most solid tumors
Interphase Cells
Major disadvantage is the inability to detect unknown structural chromosomal changes
You can never find out translocation
Amniocytes
for ploidy analysis during prenatal studies
Peripheral blood smears
for ploidy analysis in newborns
Bone marrow aspirate smear or direct harvest
translocation, or copy number analysis in cancer studies
Duplication
We we see 2 nuclei in the interphase, we can deduce a _______ type of aberration
Deletion
What can be the interpretation if we cannot see any nucleus in the interphase cells of FISH
Urinary and Respiratory tract
Amniocytes can be harvested from the epithelial cells of what tract or tissues of fetus
Cells from bone marrow aspirates or solid tumors
Rare if we are dealing for some types of lukemia
We see more immature cells rather than the peripheral blood (matured cells)
FISH probes
Complementary sequences of target nucleic acids (DNA, RNA, or nucleic acid analogs) tagged or labeled with fluorophores
Size ranges from 20 to 1000 base pairs (20-25 starting will be OK for PCR)
Direct Labeling
fluorophores are directly attached to the probe
less sensitive but easier to perform
Ex. FITC, rhodamine, and cyanines
Indirect Labelling
chemical conjugation of the nucleic acid with a nonfluorescent molecule that can bind fluorescent material after hybridization
They are like molecular bridges
Needs a binding molecule in a form of biotin
Ex. Biotin and Digoxigenin
5' end of the DNA
What end of the DNA ang nilalagyan ng probes
True
T/F:
Not every nucleotide is fluorescent; Just enough to produce visible light
90-95 degree celsius
How hot is the temp for denaturing DNA
Locus Specific Fish Probes
Used if we want to know deletions and translocations
Metaphase probe
Binds to a particular region of a chromosome
Used when only a small portion of a gene is isolated and wants to determine on which chromosome the gene is located, or how many copies of a gene exist within a particular genome
Single color FISH probe
Designed to cover a gene of interest
Dual color FISH probe
Designed to cover any 2 genes for the detection of any aberrations.
Allows simultaneous detection of numerical abnormalities of two to three regions in one FISH assay
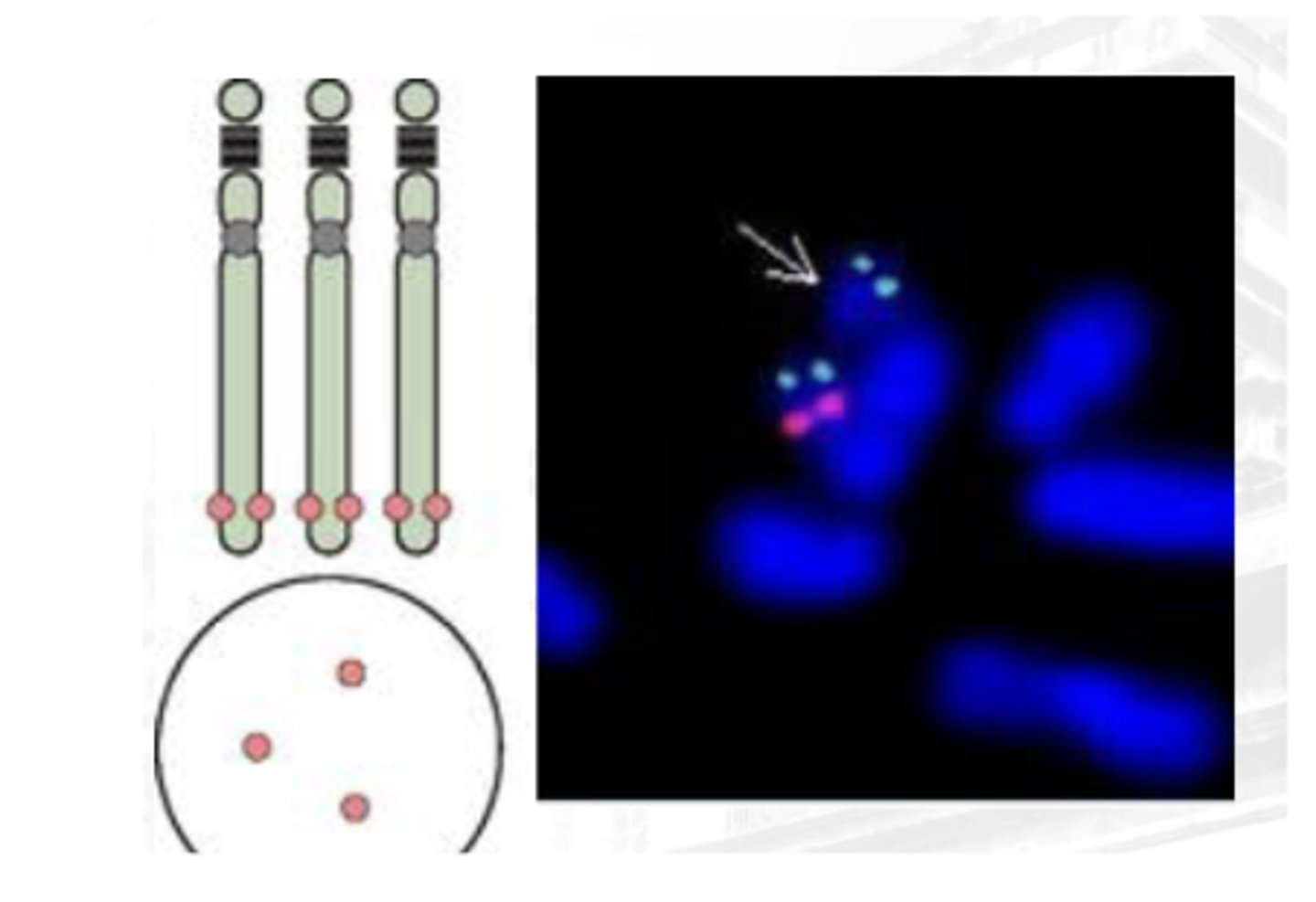
APHLOID OR CENTROMERIC REPEAT
For deletion
Parang C-banding
Generated from repetitive sequences found in the middle of each chromosome
Used to determine whether an individual has the correct number of chromosomes or if there is aneuploidy in the patient’s genome
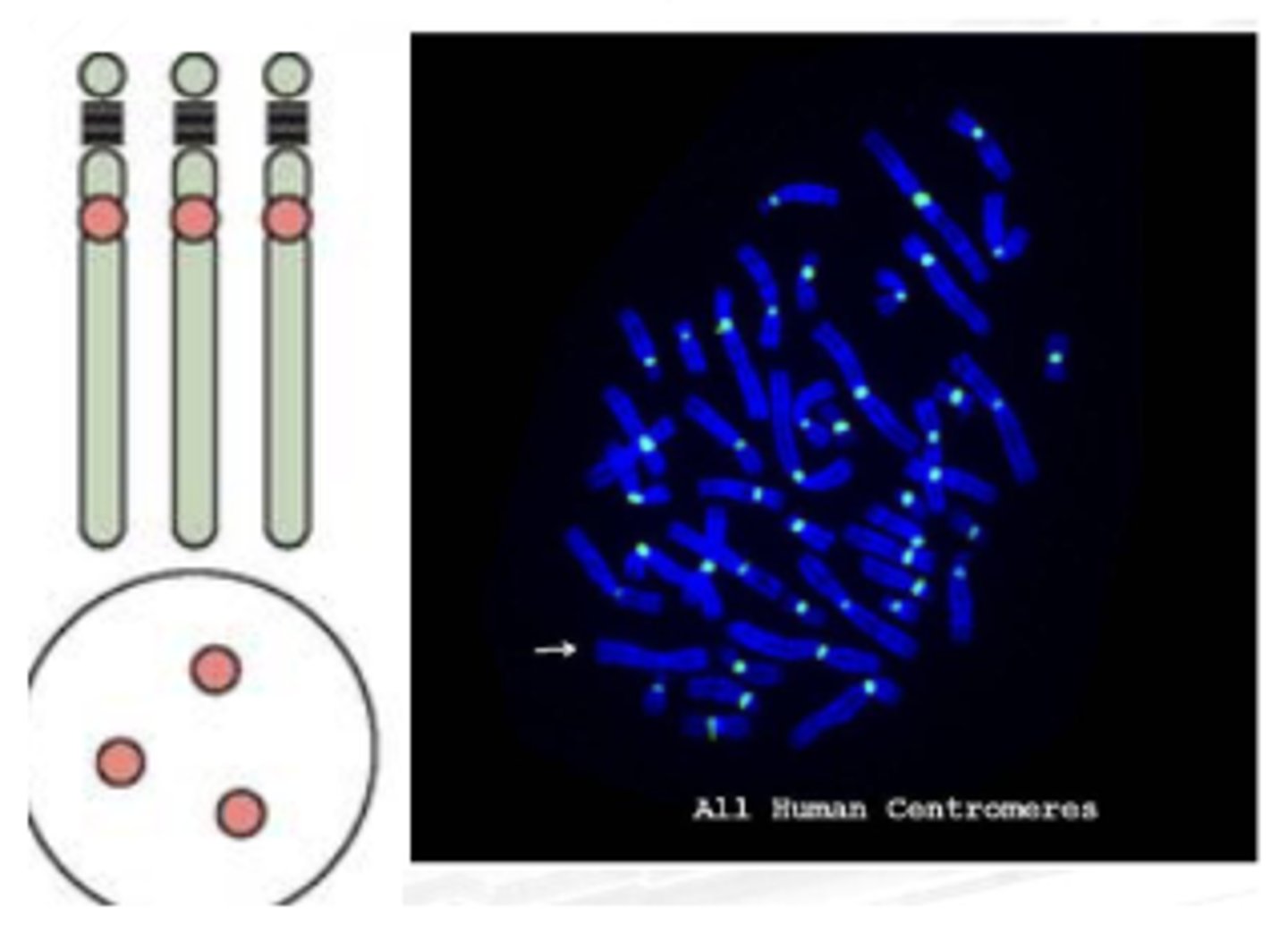
APHLOID OR CENTROMERIC REPEAT
Example application:
Magagamit to check for abnormality by counting the centromere.. For example, ang human ay may 23 pairs, so dapat may 46 centromeres lang ang makikita mo. Pag 48 nakita mo then may idea ka na either may aneuploidies or dicentric chromosome.
SUBTELOMERIC PROBE
Locate the subtelomere
Specific to the subtelomere region of chromosome
Useful in the detection of subtelomere deletions and rearrangements
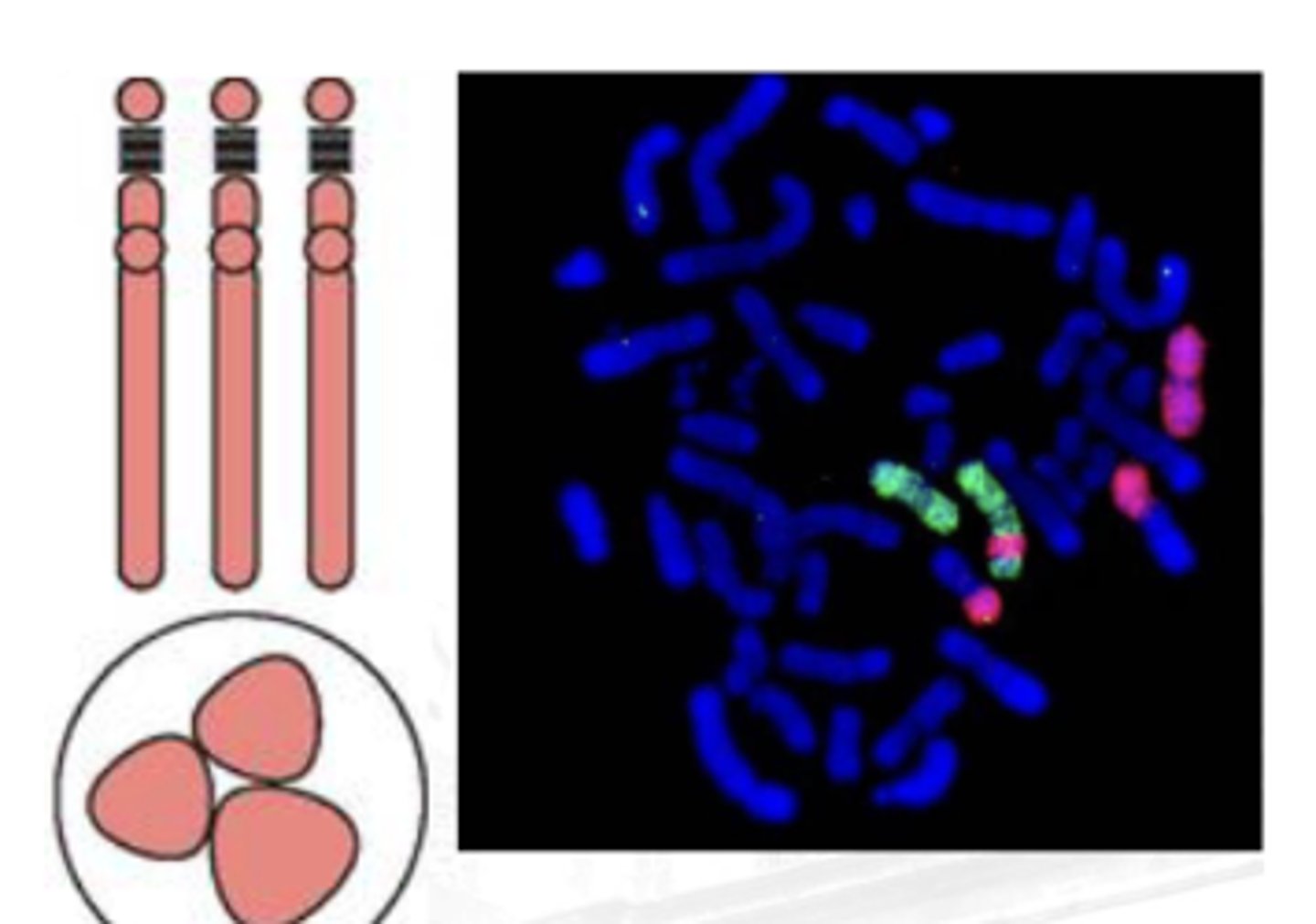
Whole Chromosome Probe
A collection of smaller probes that bind to the whole length of the chromosome
Useful in the examination of chromosomal aberrations
(Sir clive thinks that this is used if the DNA is in between the p-arm and the q-arm and he does not see the purpose of using whole chrome probes)
PRE-NATAL FISH PROBES
Stargets chromosome 13,18,21 X, and Y
Because this is prone to trisomies of duplication and any aberrations
formamide/ salt solution
FIRST STEP
Probe and target DNAs are denatured using high-temperature incubation in a ________
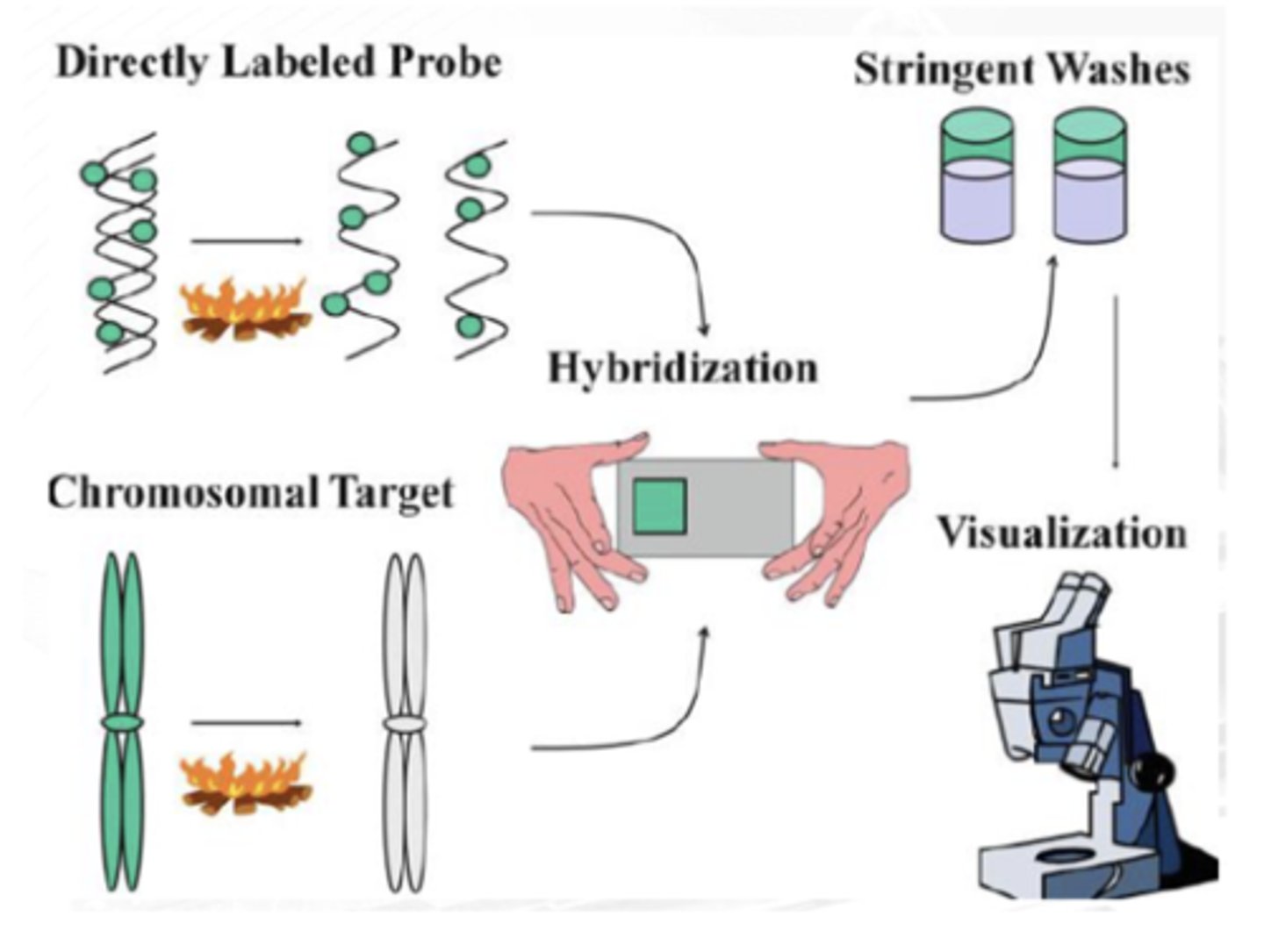
stringent washing
SECOND STEP
Probe sequences hybridize to the complementary target sequences, and nonspecific binding is eliminated via ____________
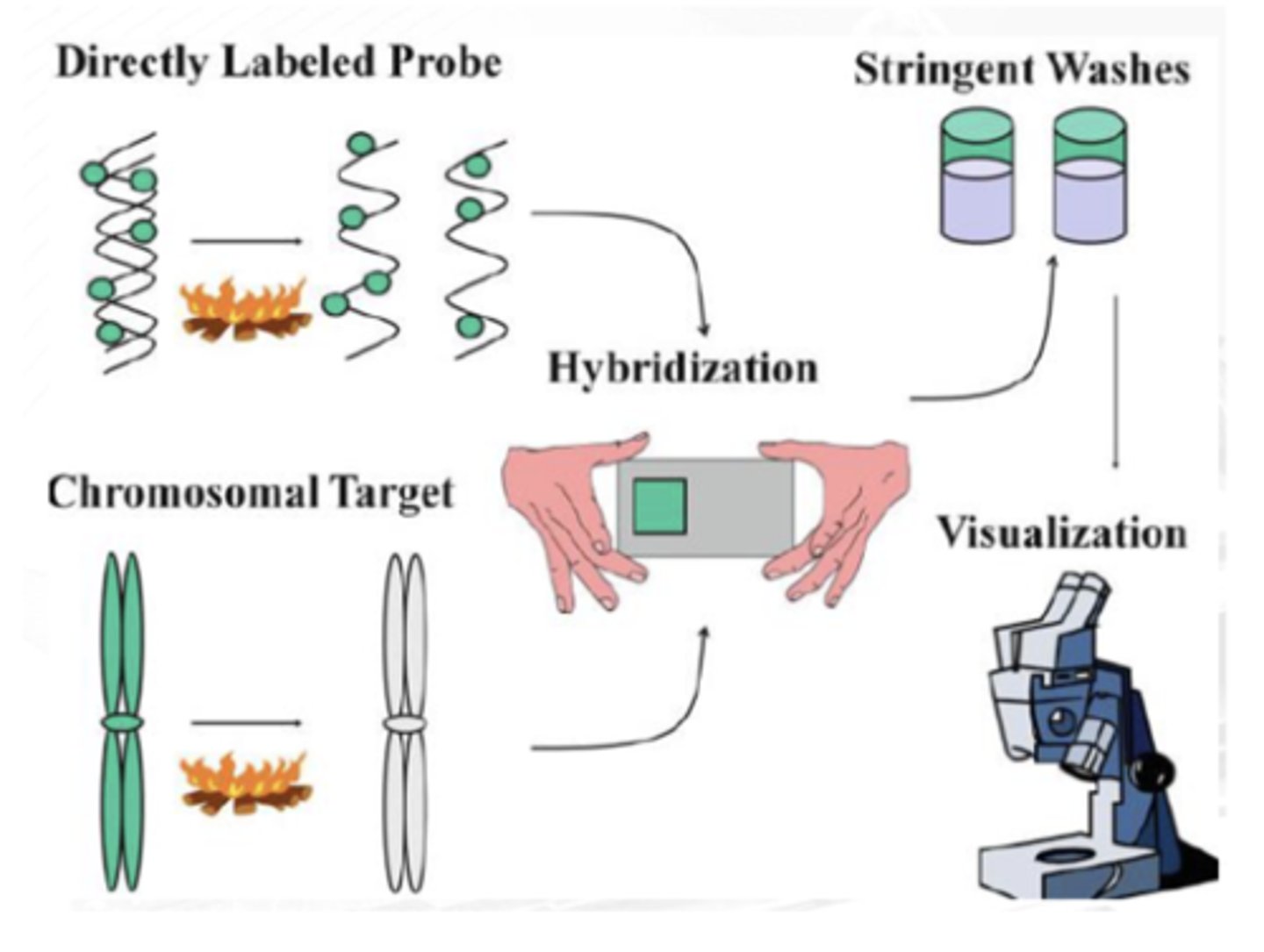
fluorescence microscopy
THIRD STEP
The probe hybridization is detected with ______________ microscopy
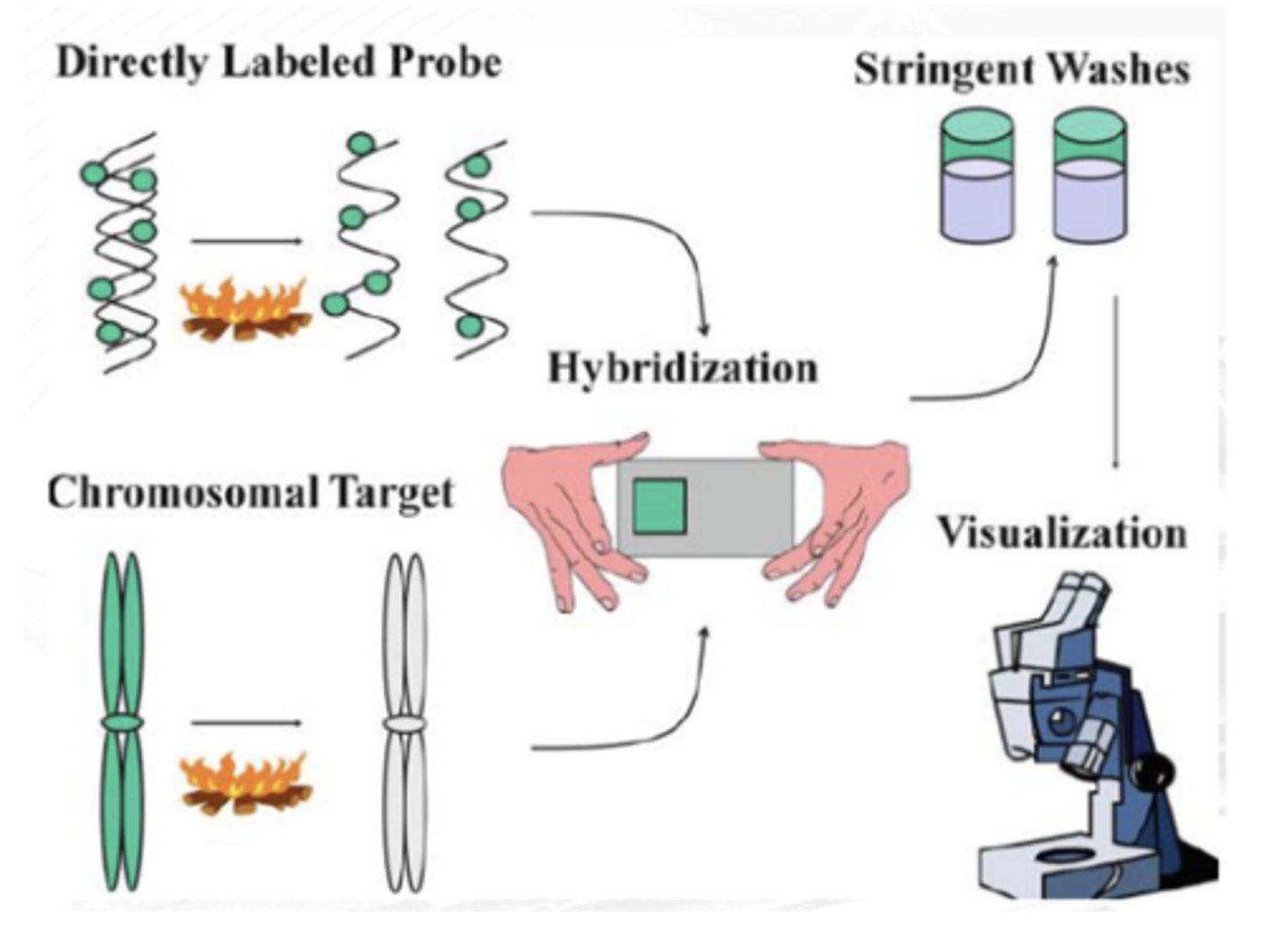
Not diluted properly with hypotonic saline solution
Reason why FISH specimen are overlapping
Duplication
In the event that only green is seen (color), it is interpreted as a ________ type of aberration.
Deletion
In the event that only red is seen (color), it means there is a ________.
Yellow Color
Color of normal FISH
3'-5'
Direction of STRAND OF DNA IN A MICRO-ARRAY
5-3
Direction of
GREEN: ORIGINAL STRAND
RED: COMPLIMENTARY STRAND
COMPARATIVE GENOMIC HYBRIDIZATION (CGH) on METAPHASE CELLS
We have to extract DNA
Good for deletions and duplication, only (gain or losses)
COMPARATIVE GENOMIC HYBRIDIZATION (CGH) on METAPHASE CELLS
a technique that uses DNA from the cells of interest, rather than using a standard karyotype, for chromosomal analysis.
This can be very useful, especially in some cancers when only DNA is available rather than any growing cells.
COMPARATIVE GENOMIC HYBRIDIZATION (CGH) on METAPHASE CELLS
This technology has been used successfully for clinical analysis, particularly with cases that have a low (or no) mitotic index.
It is not useful for detecting balanced rearrangements
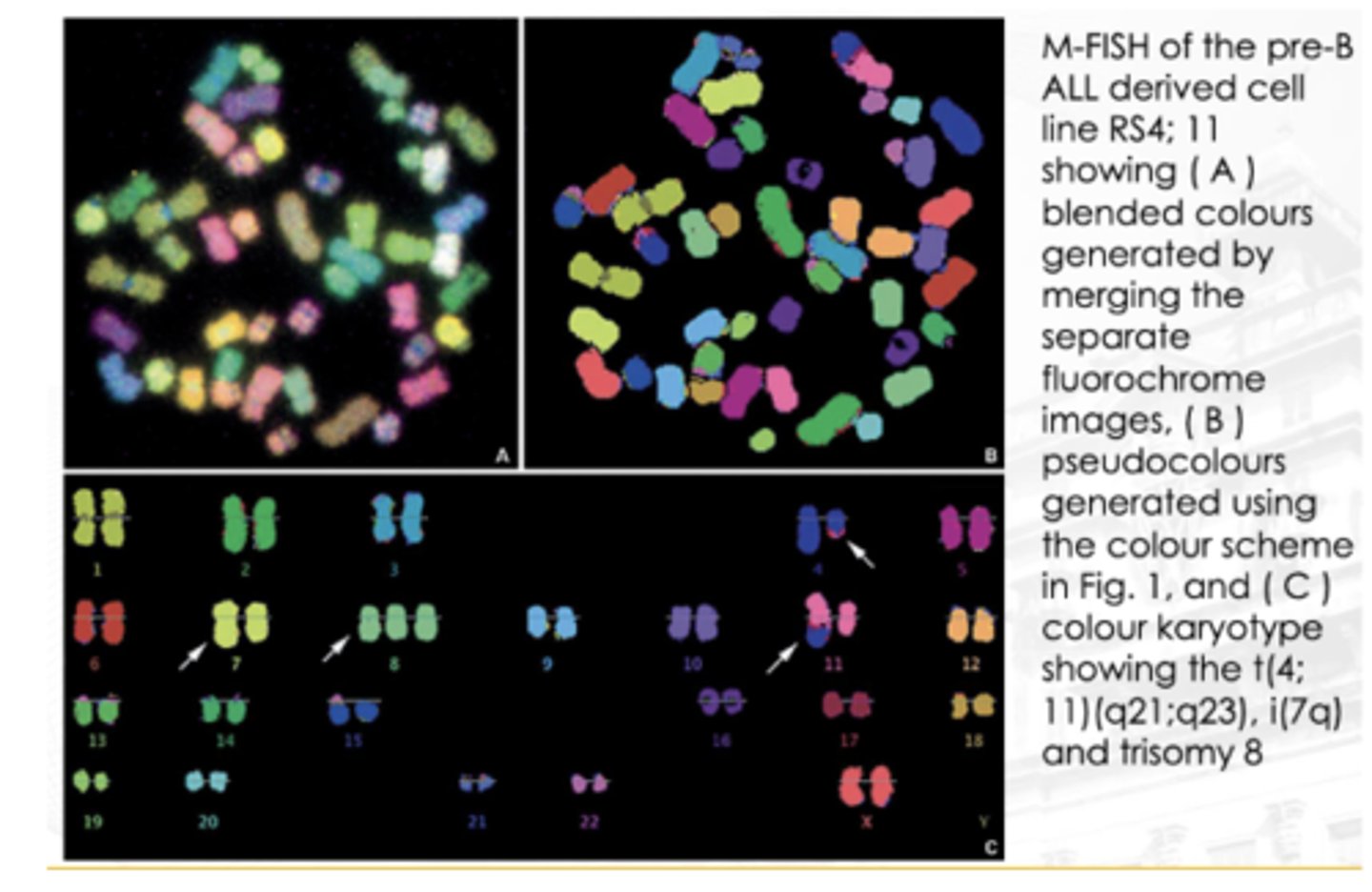
Multiplex FISH (M-FISH)
A technique that allows the investigator to view a karyotype so that each chromosome is “painted” with a different color
Ratio-labeled probes are used to create a distinct computer-generated false color for each chromosome
Useful for complex rearrangements, such as those seen in neoplastic disorders and solid tumors
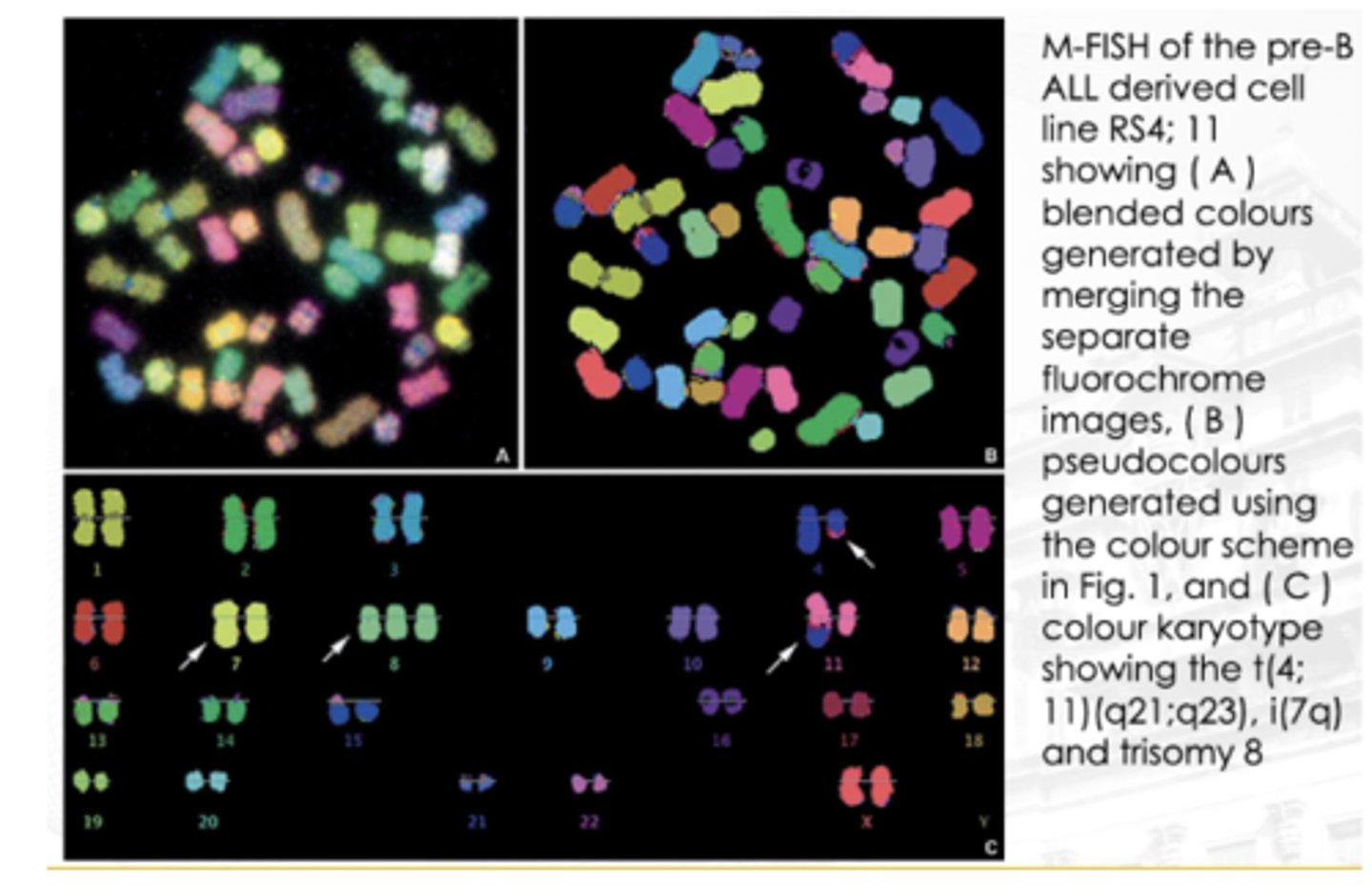
Multiplex FISH (M-FISH)
If you observe the image, particularly chromosome 4, makikita mong may translocation. Dun sa may bandang dulo nya, nag-iba ‘yung color. ‘Yung part na ‘yon (red) ay galing sa chromosome 11. Nagkaroon ng translocation ‘yung chromosome 11 papunta sa 4.
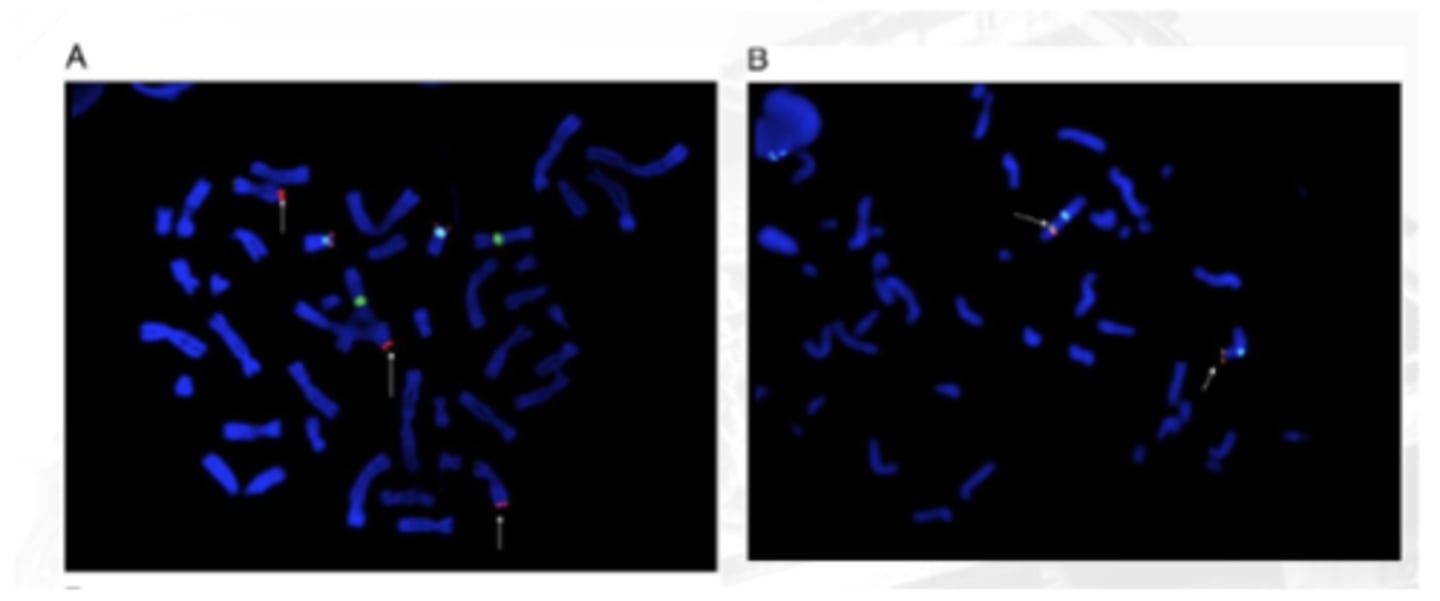
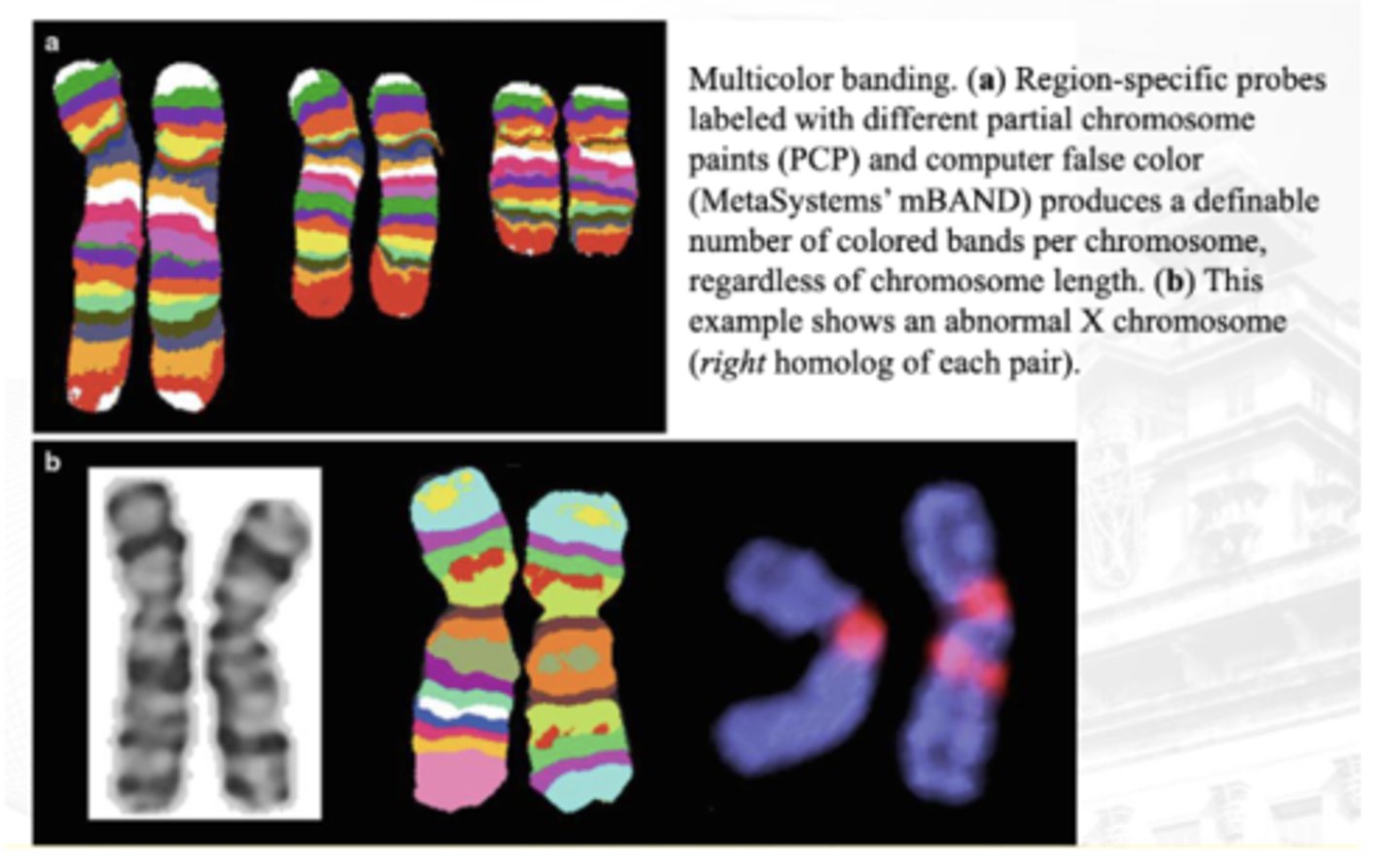
Multicolor Banding Analysis
Uses chromosome-specific mixtures of partial chromosome paints that are labeled with various fluorochromes
A computer program analyzes metaphase chromosome data and produces a pseudocolored, banded karyotype with an estimated resolution of 550 bands, regardless of chromosome length
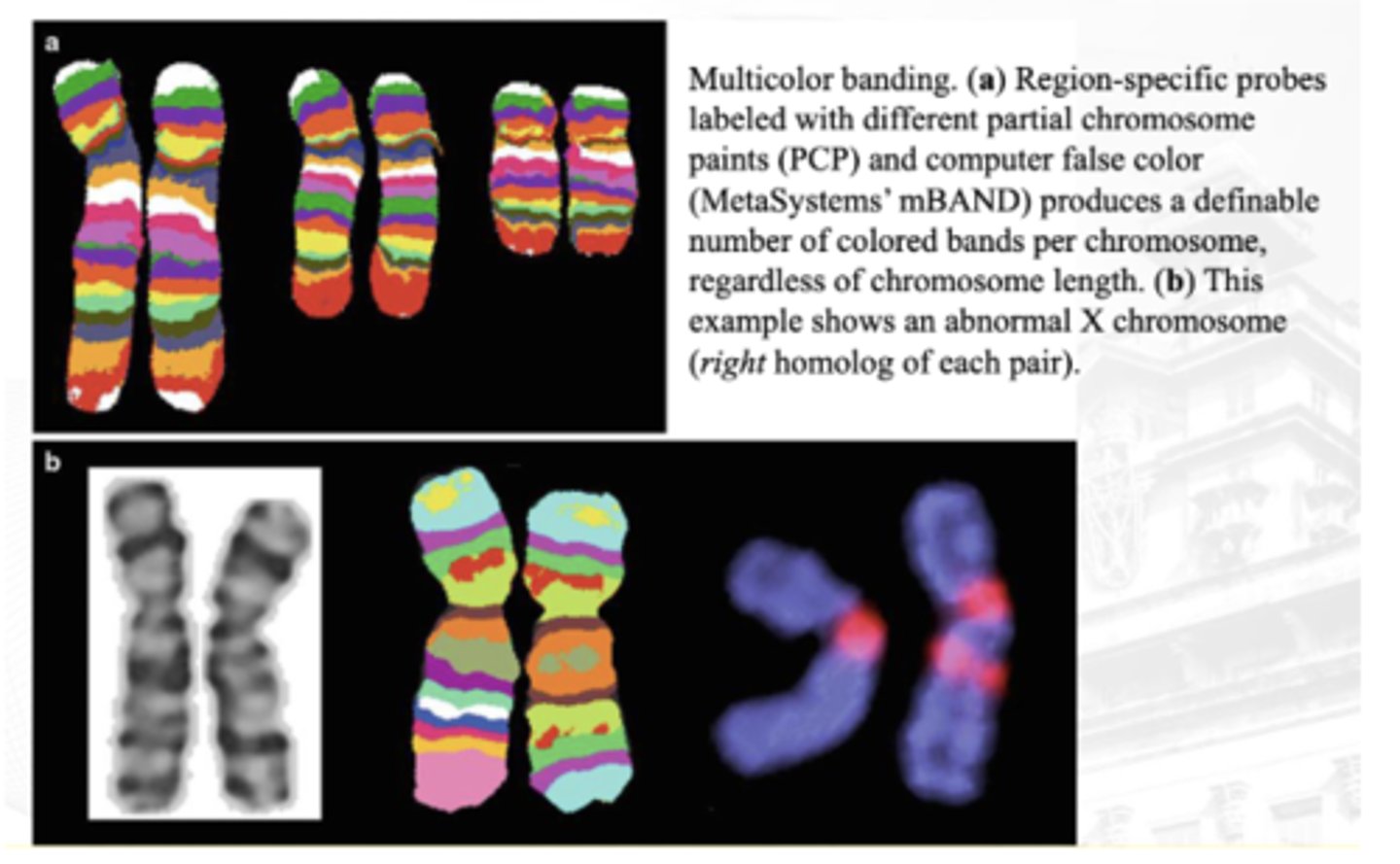
Multicolor Banding Analysis
Advantageous for the determination of breakpoints and the analysis of intrachromosomal rearrangements, and can be particularly useful in preparations with shorter chromosomes
image B (in the q arm - no corresponding colors)
between A and B which is abnormal as per multicolor banding analysis?
Fiber FISH
A technique that is almost entirely used for research
It allows the chromosomes to be stretched out and elongated
The probes are applied and can be physically ordered on the fibers
This provides a much higher spatial resolution and allows for correct orientation and placement of probes and for precise mapping of probes
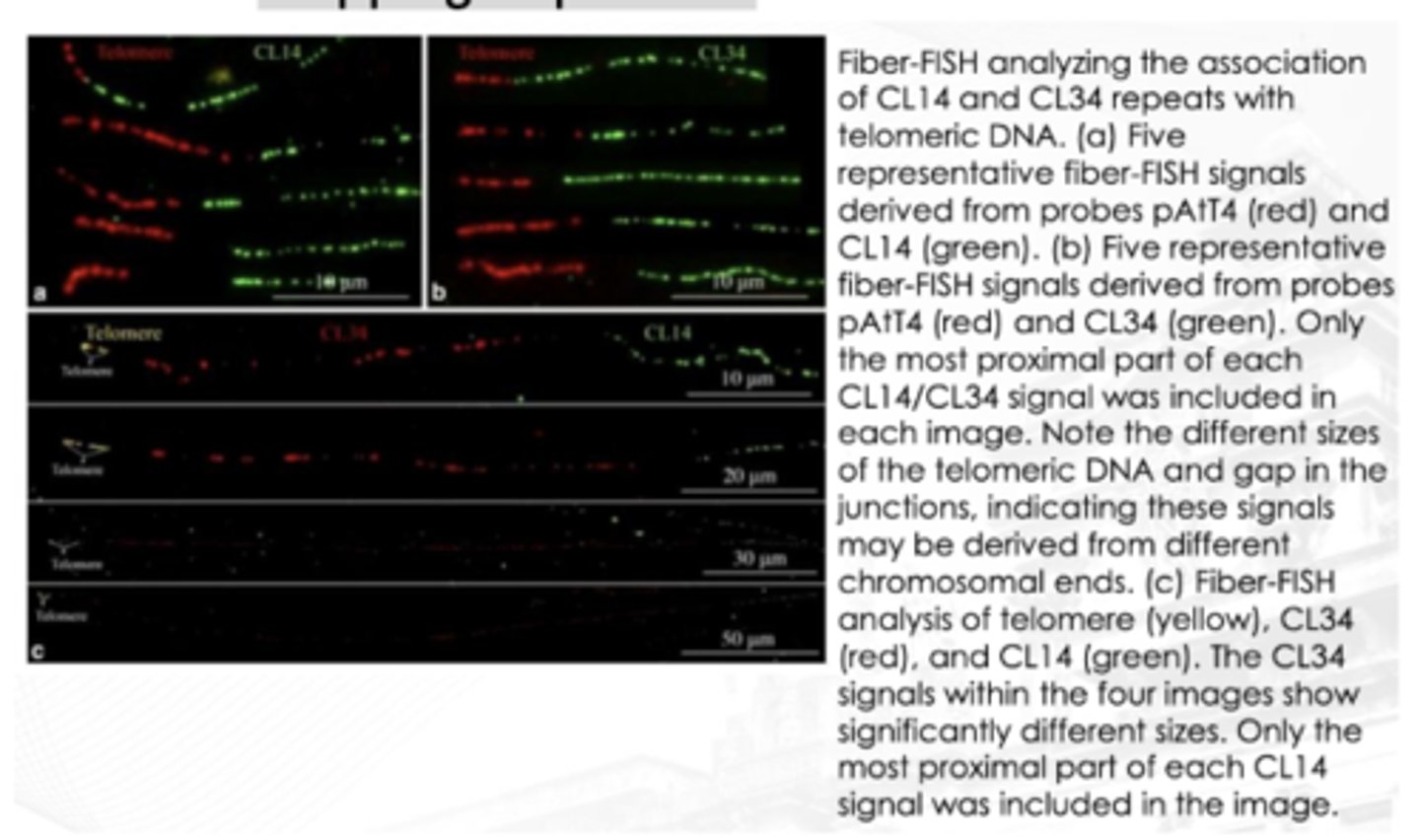
True
T/F:
for Fiber FISH analysis, the stretched out part or highlighted part is usually the telomere
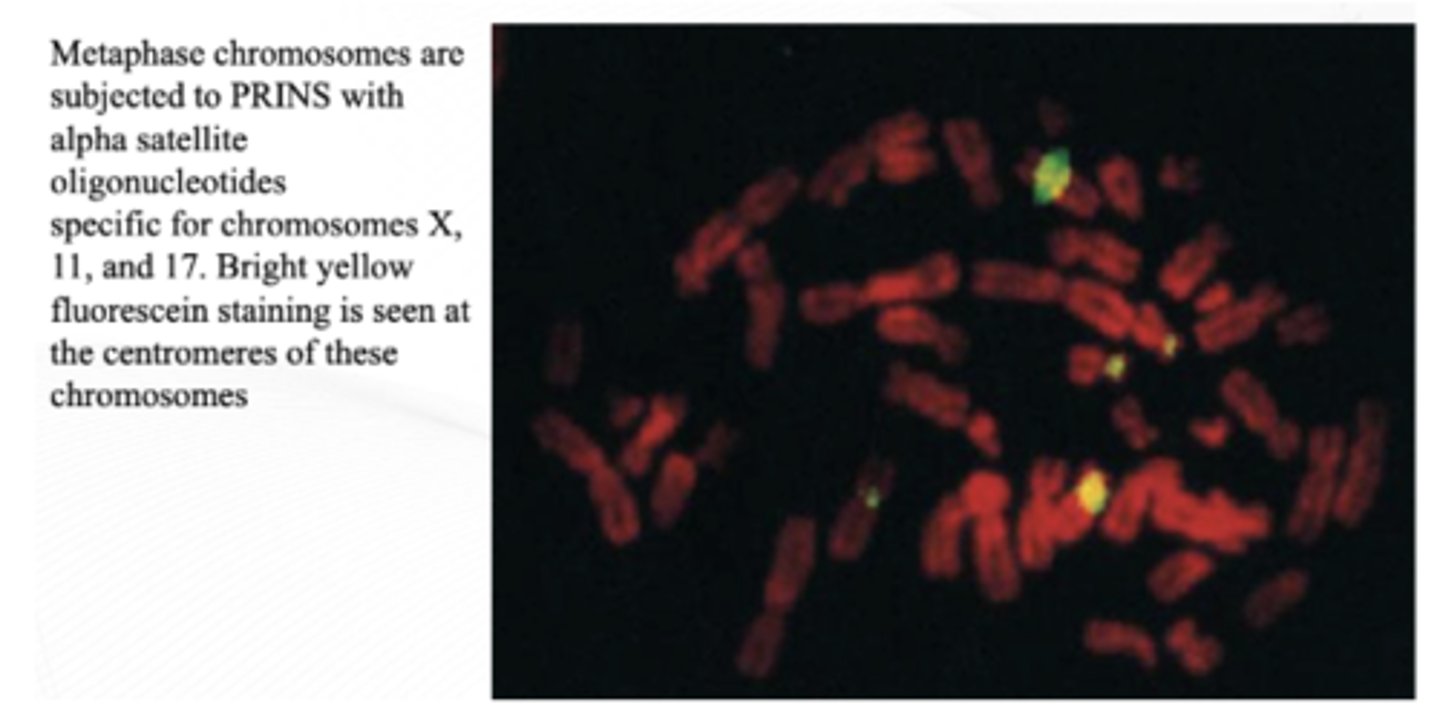
Primed In Situ Labeling (PRINS)
Essentially, PCR on a slide
Primers of interest are hybridized on a slide and then subjected to cycles of denaturation, reannealing, and elongation that are used to incorporate labeled nucleotides. The labels are then detected fluorescently, or labeled nucleotides are incorporated during the reaction
Can differentiate hybridization with the alpha satellite sequences for chromosomes 13 and 21, something that cannot be done with traditional FISH
Reverse FISH
Used to identify material of unknown origin
This unidentified material, such as a marker chromosome or duplication, is flow sorted or microdissected off a slide after G-banding. The DNA from this material is extracted, PCR-amplified, and labeled with a fluorochrome. This is then used as a probe and hybridized to normal or patient metaphase chromosomes to identify the origin of the unknown material
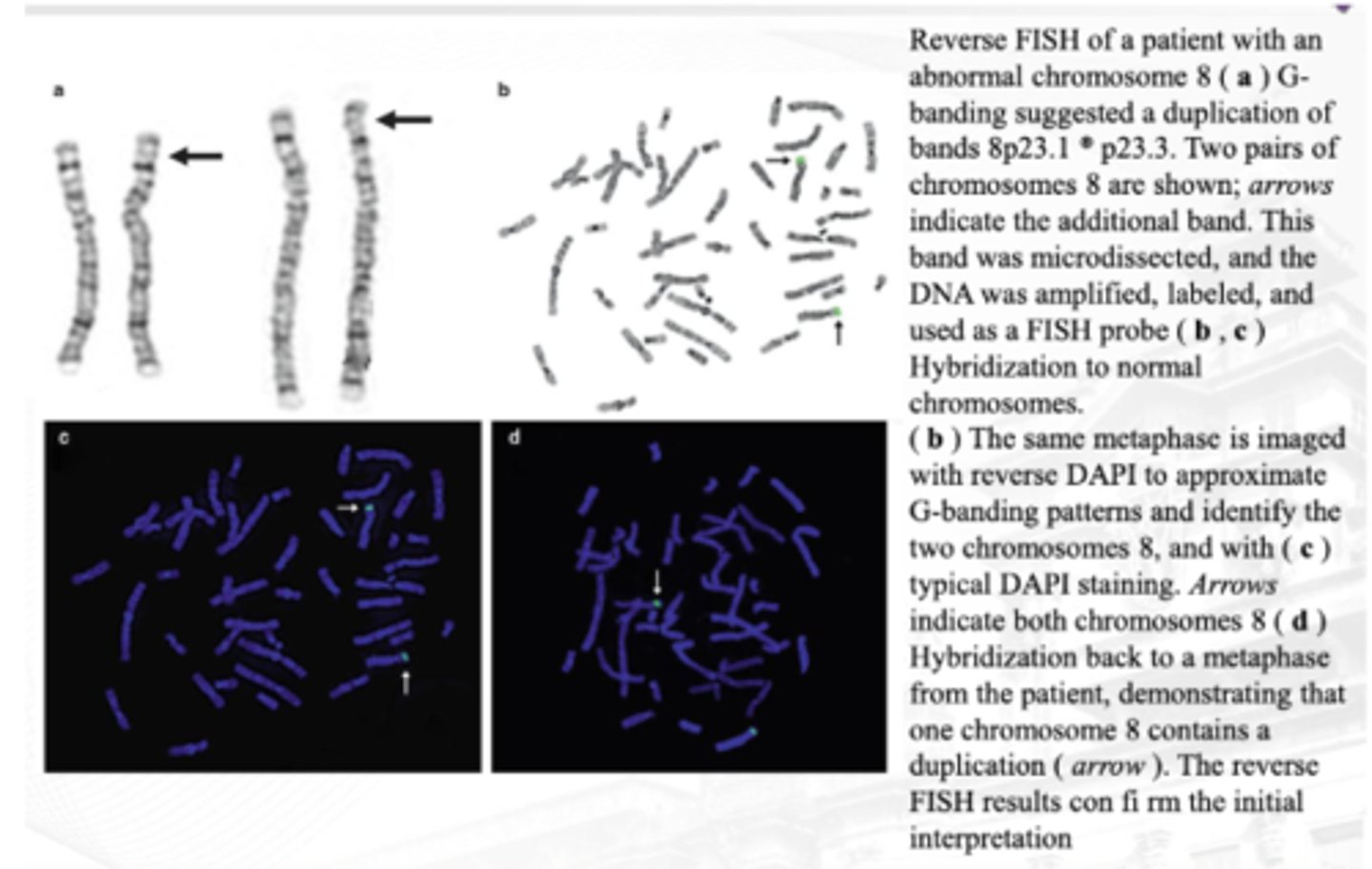
Reverse FISH
Patient with abnormal chromosome 8 is targeted.
Ginawa muna 'yung typical karyotyping.
● Additional bands are microdissected and amplify the particular part lang!
● Parang nag-reverse banding ka muna then nadetect mo sya by banding techniques, then 'yung additional band, you use that to prepare the probe for your FISH
● BANDING TECHNIQUE NG KARYOTYPE FOLLOWED BY FISH