Structure of the atom & Electron Configuration
1/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the charges of proton, neutrons, and electrons?
P=+, N=0, E=-
What are the locations of the proton, neutron, electron?
P=nucleus, N= nucleus, E=outside of nucleus
What is the relative atomic mass for proton neutron and electron?
P= 1amu, N= 1amu, E=0amu
What do protons do?
Identify the element
What do electrons do?
Can be lost or gained, which changes the charge, does NOT affect the mass
What does neutrons do?
Elements can have varying numbers of neutrons, which changes the mass NOT the charge
How do you calculate the neutrons of an atom?
Mass #- atomic #(P+)= neutrons
What are the other names for mass number?
Relative atomic mass and nucleon number
If an atom is neutral, what would be the proton and electrons?
The protons and electrons would be equal
What is an isotope?
Atoms of an element with a different number of neutrons therefore they have a different mass number but number of protons remains the same so it is still the same element
What is hyphen notation?
Element name or symbol, hyphen, mass #— Cr-50
What is isotope notation?
Using the chemical symbol, the atomic number and the mass on the left-hand side on the top and bottom of the chemical symbol
What is a radioisotope?
And isotope of an element that has an unstable nucleus (used to kill cancer)
What is radioactive decay?
The process by which unstable nucleus rearranges itself (ex Radiotherapy to kill cancer or medical tracer)
How do you calculate relative atomic mass (Ar)?
Mass # x %
Mass # x %
Mass # x %
/100
=amu
How do you check that you have calculated the correct amu?
Check the PT(Within 0.2)
Should be closest to the mass # of the isotope with the greatest percent abundance
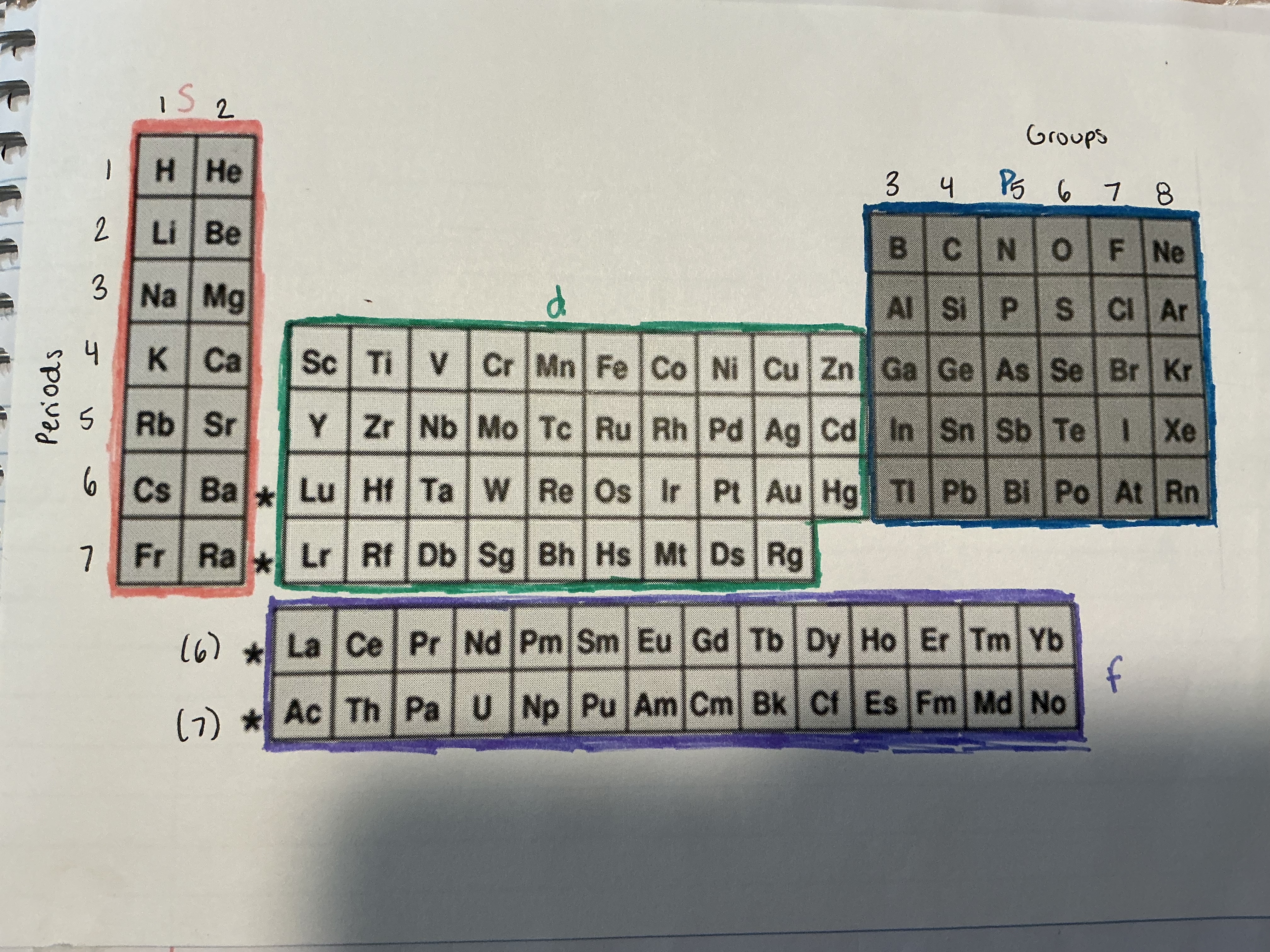
What are the periods and groups of the periodic table?
Periods are the horizontal rows and groups are the vertical columns
What does the S orbital look like?

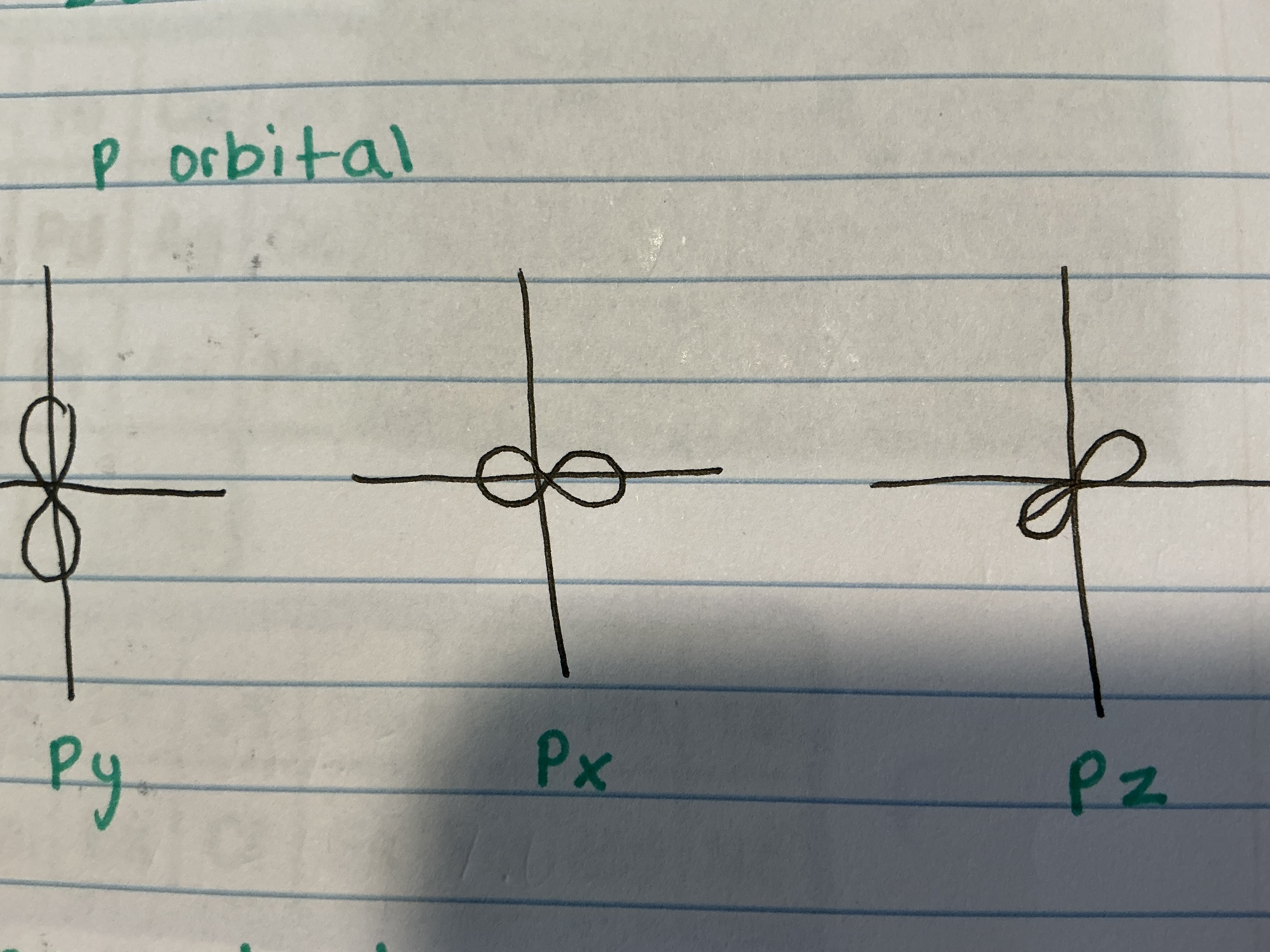
What do the P orbitals look like and what are the different types?
Py, Px, Pz
What are the maximum # of E- per principle quantum #?
2e-
8e-
18e-
32e-
List the atomic orbitals, and how many e- are present?
1s(1)2s(1)2p(3)3s(1)3p(3)4s(1)3d(5)4p(3)5s(1)4d(5)5p(3)6s(1)4f(7)
How many electrons are in each box or orbital?
Two per box (ex 2p(3) holds 6 electrons)
For S and P block elements, how can you identify the group, block, and period based on the electron configuration?
The large coefficient= Highest level-period
The letter next to coefficient= block
Exponent= valence e- group
If there is an SNP orbital, how do you determine the group of the element from the electron configuration?
Add the exponent on the S orbital with the exponent on the P orbital= Group
Which blocks are the periodic table divided into?