APES - Unit 7 - Geology, Rocks, and Minerals
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
rocks
a combination of one or more minerals in earth's crust
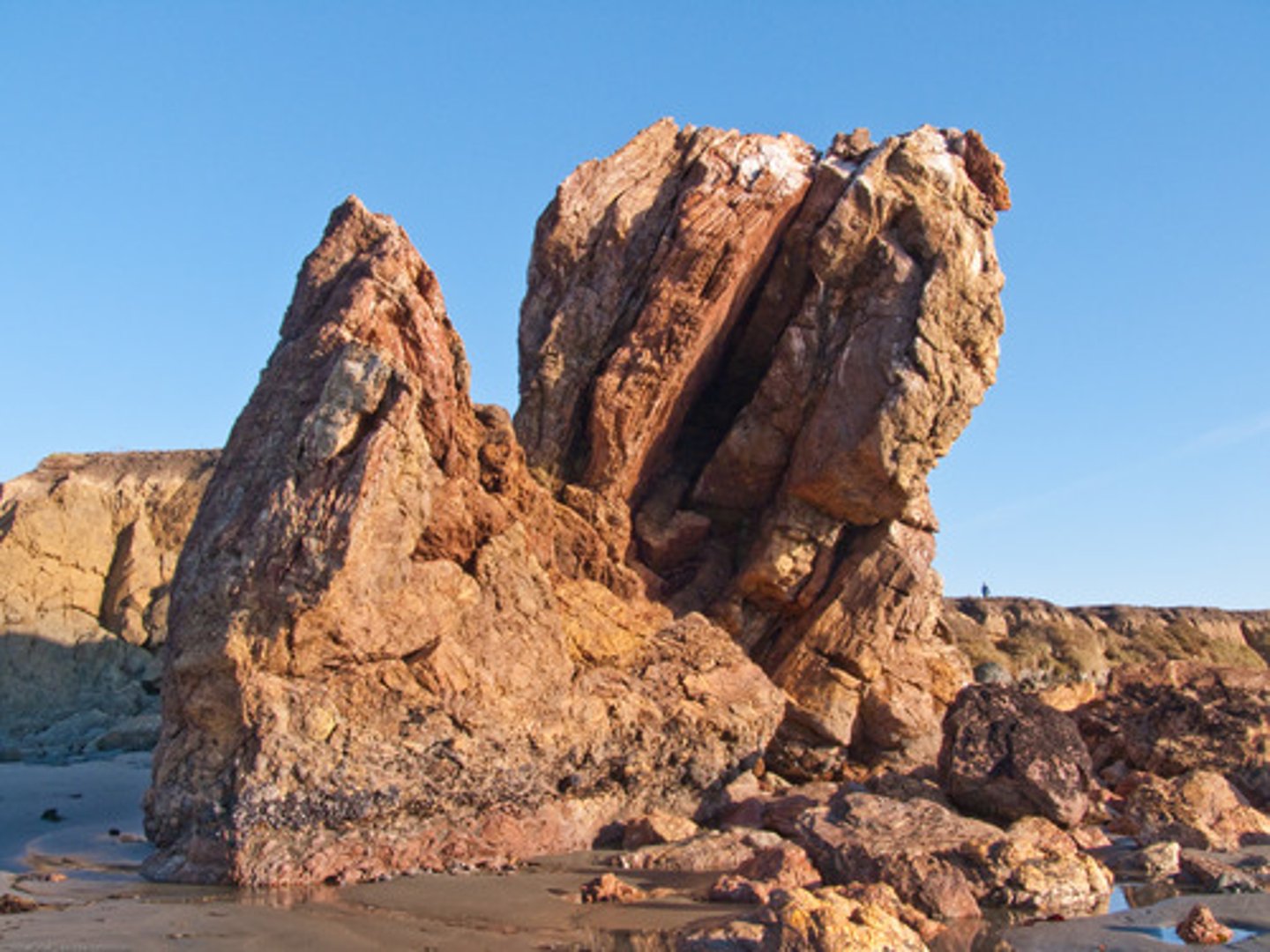

sedimentary rock
a type of rock; organic material cemented together

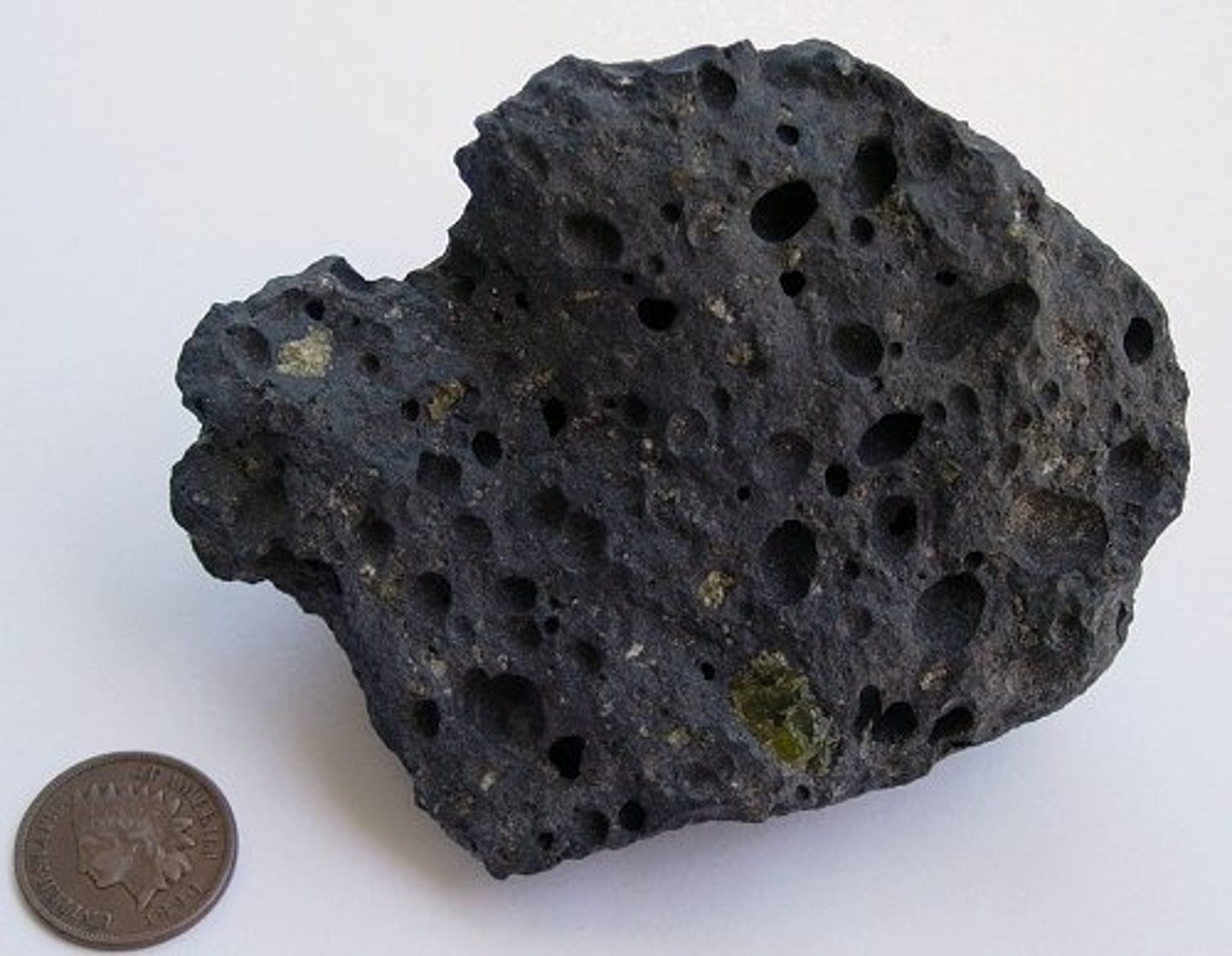
igneous rock
a type of rock that forms as a result of magma welling up and cooling; ex: granite

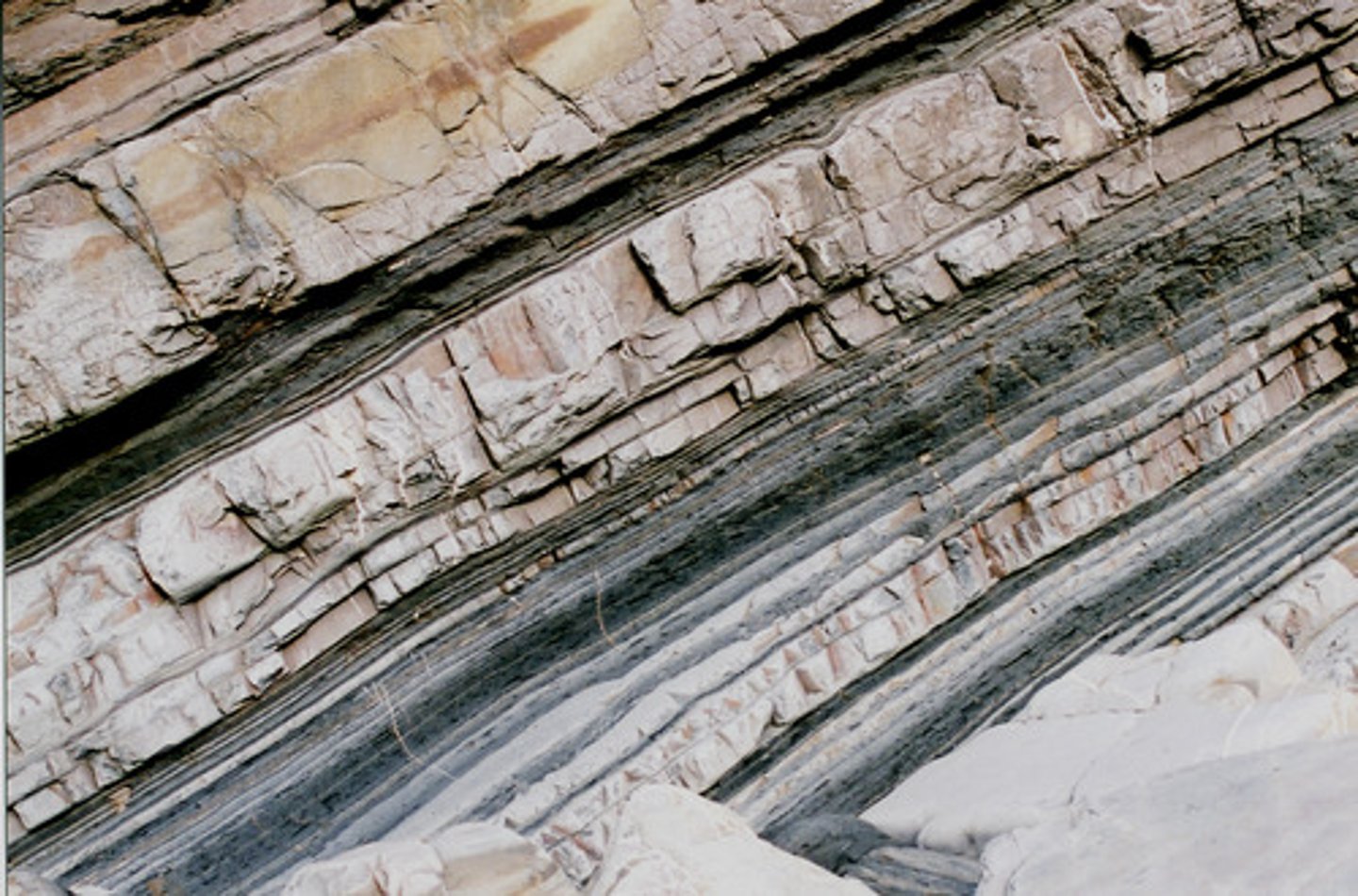
metamorphic rock
a type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemically reactive substances, or a combination of 2 or more of these; ex: marble
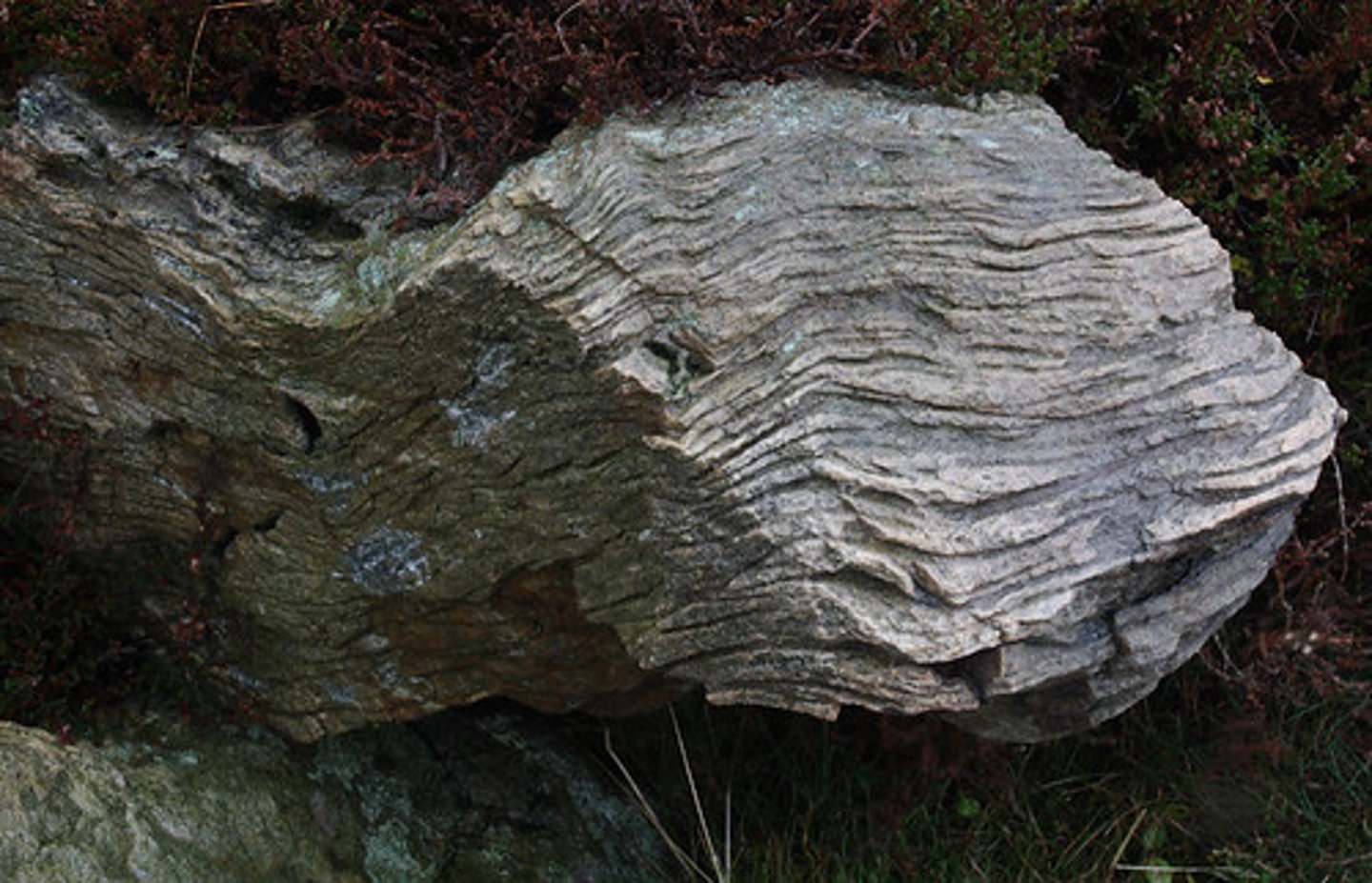

minerals
a naturally occurring or inorganic compound
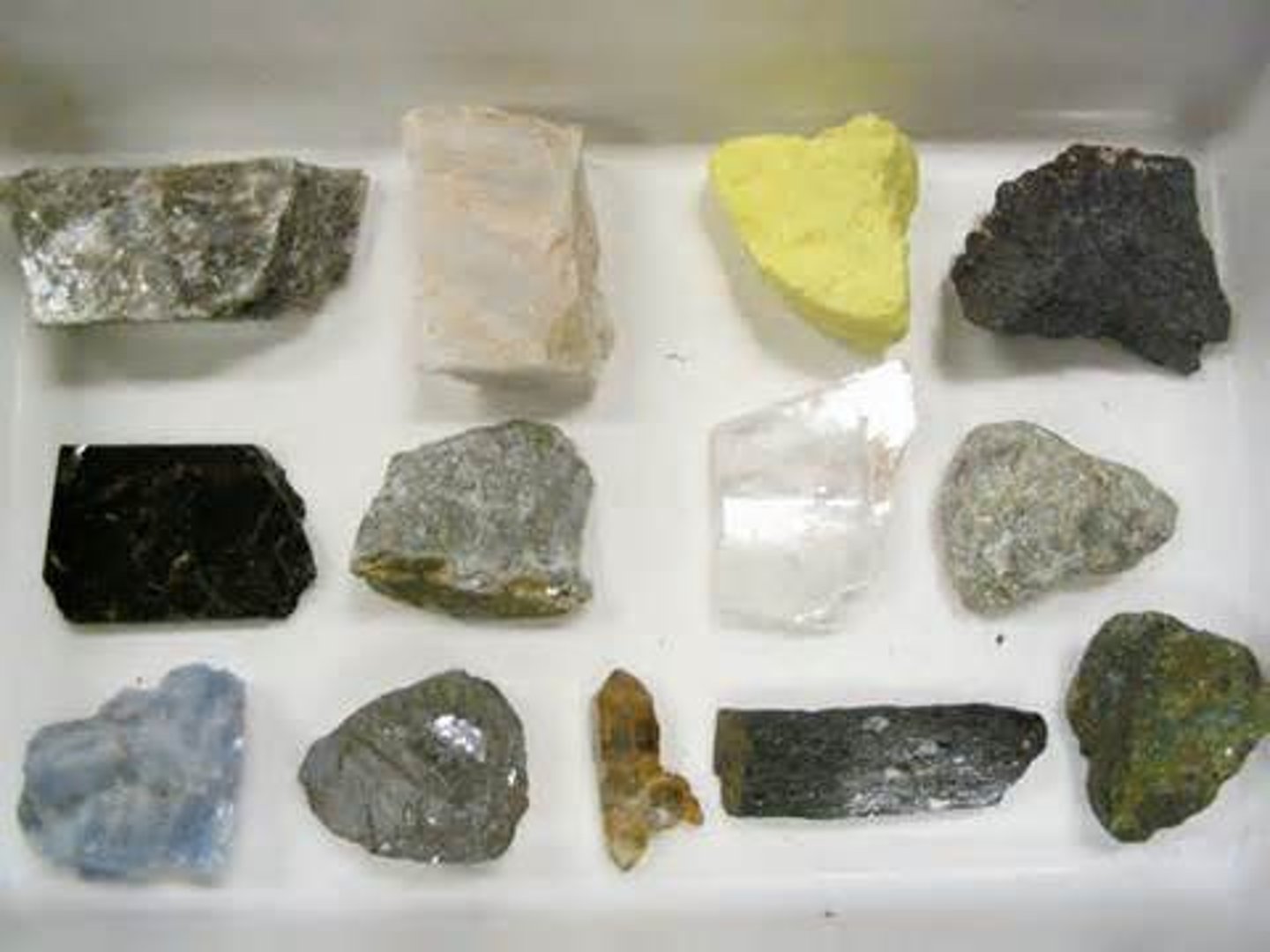

mineral resources
minerals that can be mined and processed at an affordable cost
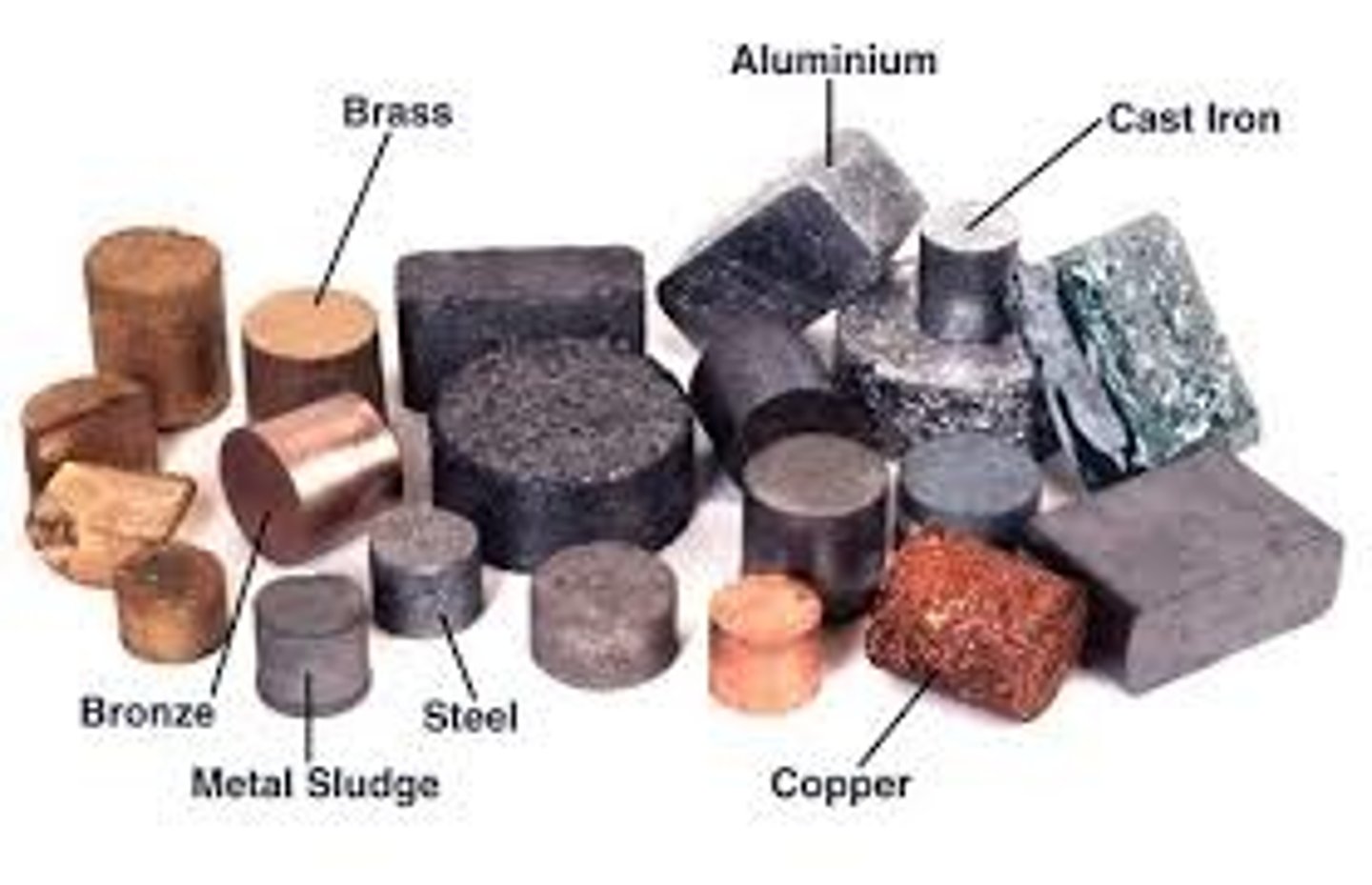

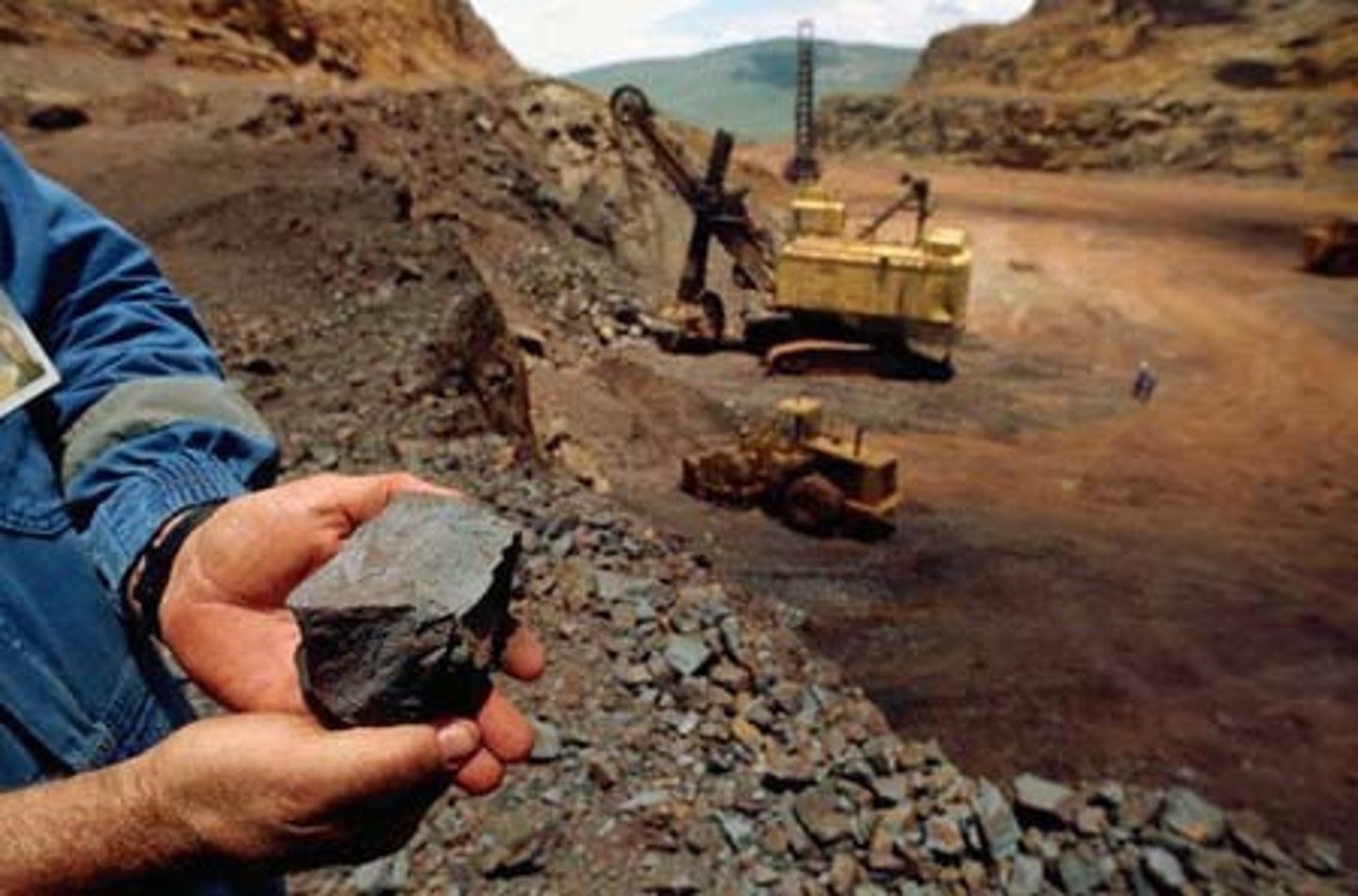
ore
a rock that contains a large enough concentration of a mineral making it profitable to mine; contains mineral resources

economic depletion
when the costs of finding, extracting and processing a resource exceed its economic value

tailings
rock waste in piles or ponds— contains toxic metals

smelting
the process of heating ore to remove the metal resource; produces liquid and solid hazardous waste

full-cost pricing
goods and services include internal costs and external costs (environmental/human harm); ex: car
sandy soils
a type of soil with a large particle size and thus large pores; water moves through rapidly-- not ideal

clay soils
a type of soil with a small particle size and thus small pores that tend to be compact; causes water to move slowly-- plants can become water-locked

loam
a type of soil with equal parts of sand, clay, silt, and humus; water moves slowly-- ideal

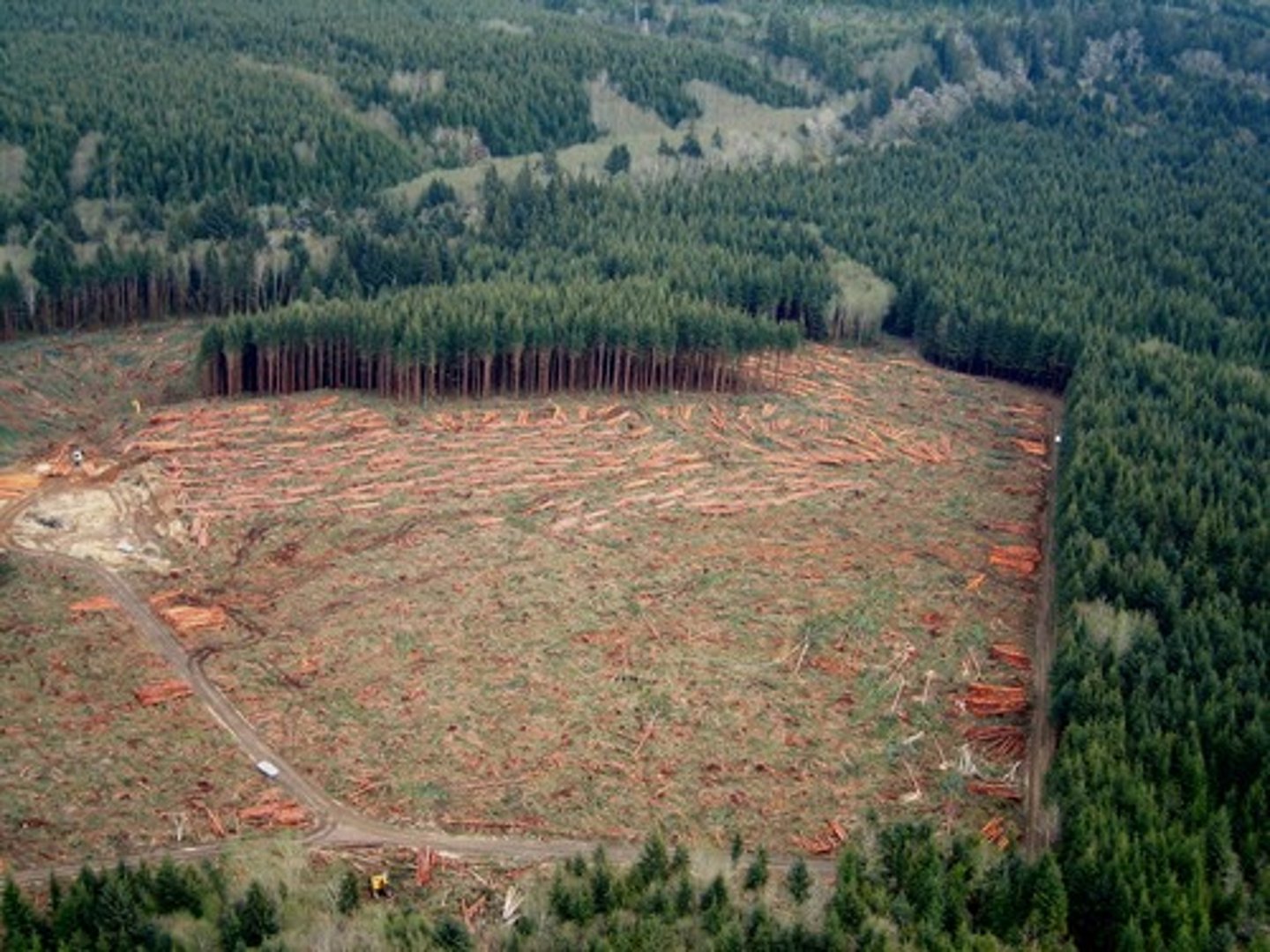
clearcutting
the process of cutting down all the trees in an area at once

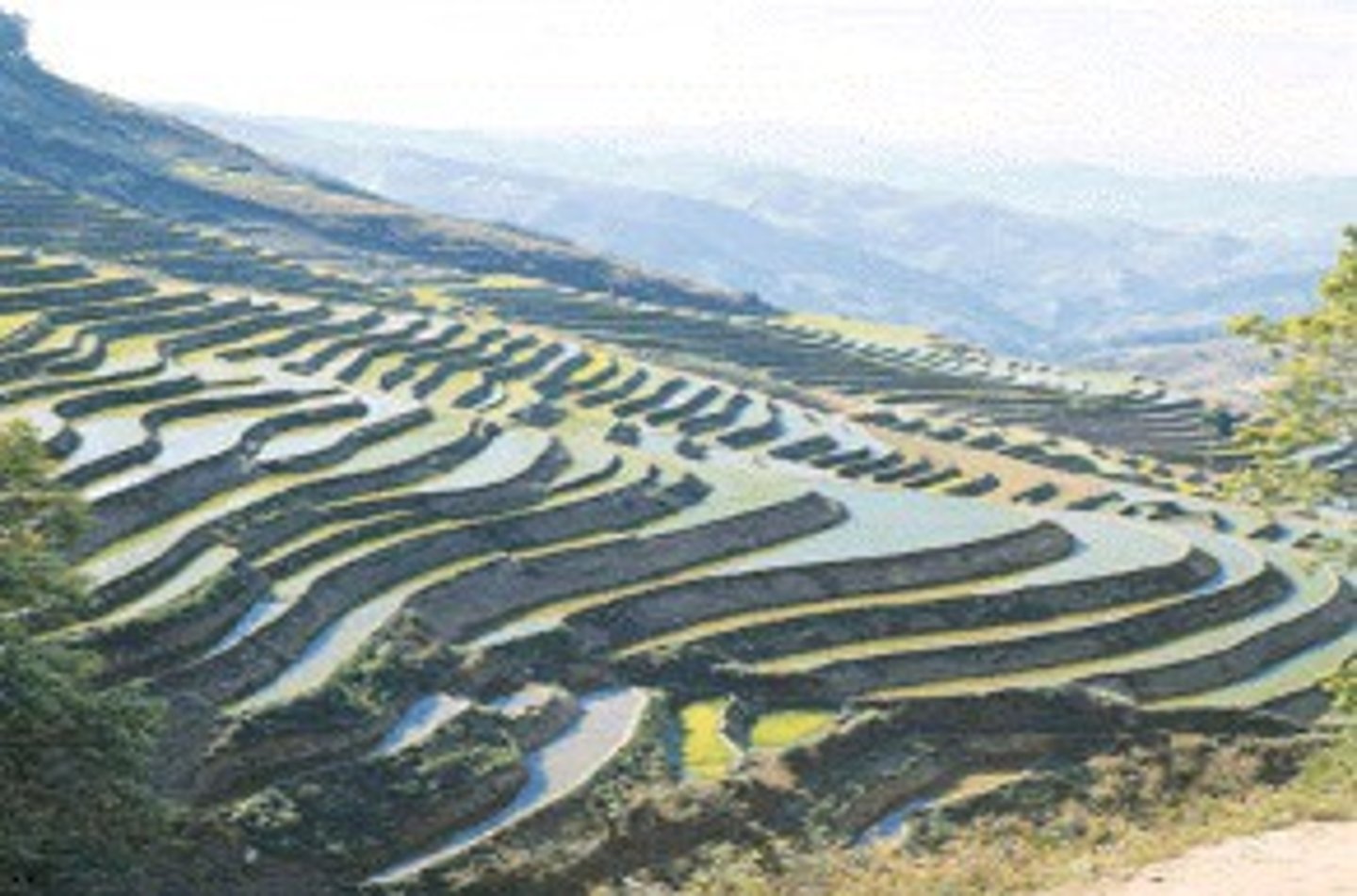
terracing
steep slopes that are converted to terraces

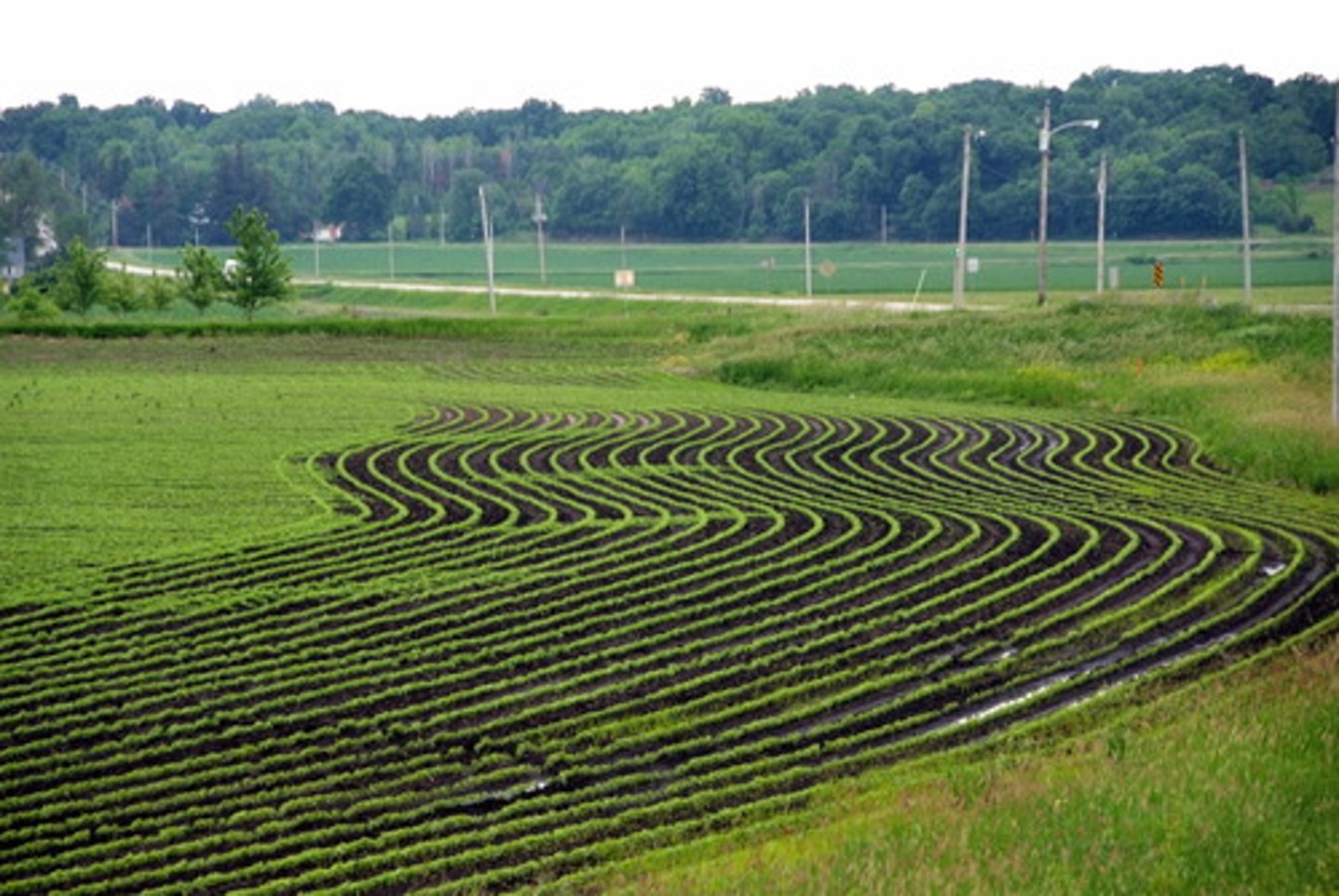
contour planting
plowing and planting crops in rows across the slope of the land, opposite to the direction of water flow, to reduce soil erosion and water runoff

stripcropping
alternating rows of crops
conservation tillage
planting new crops through crop residue
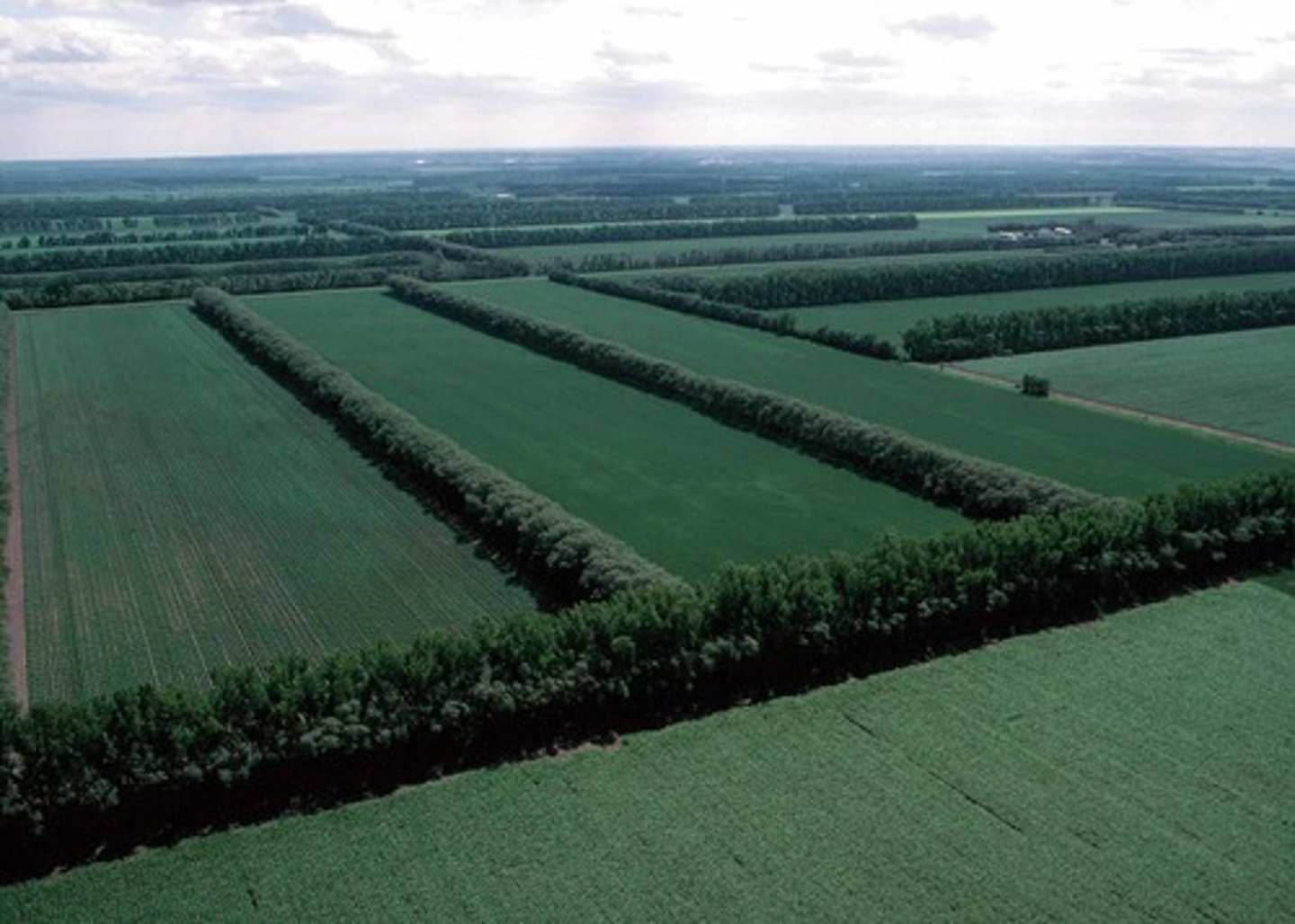
windbreaks
rows of trees or shrubs surrounding cropland

free-range grazing
animals are allowed to roam free and graze as needed on open land

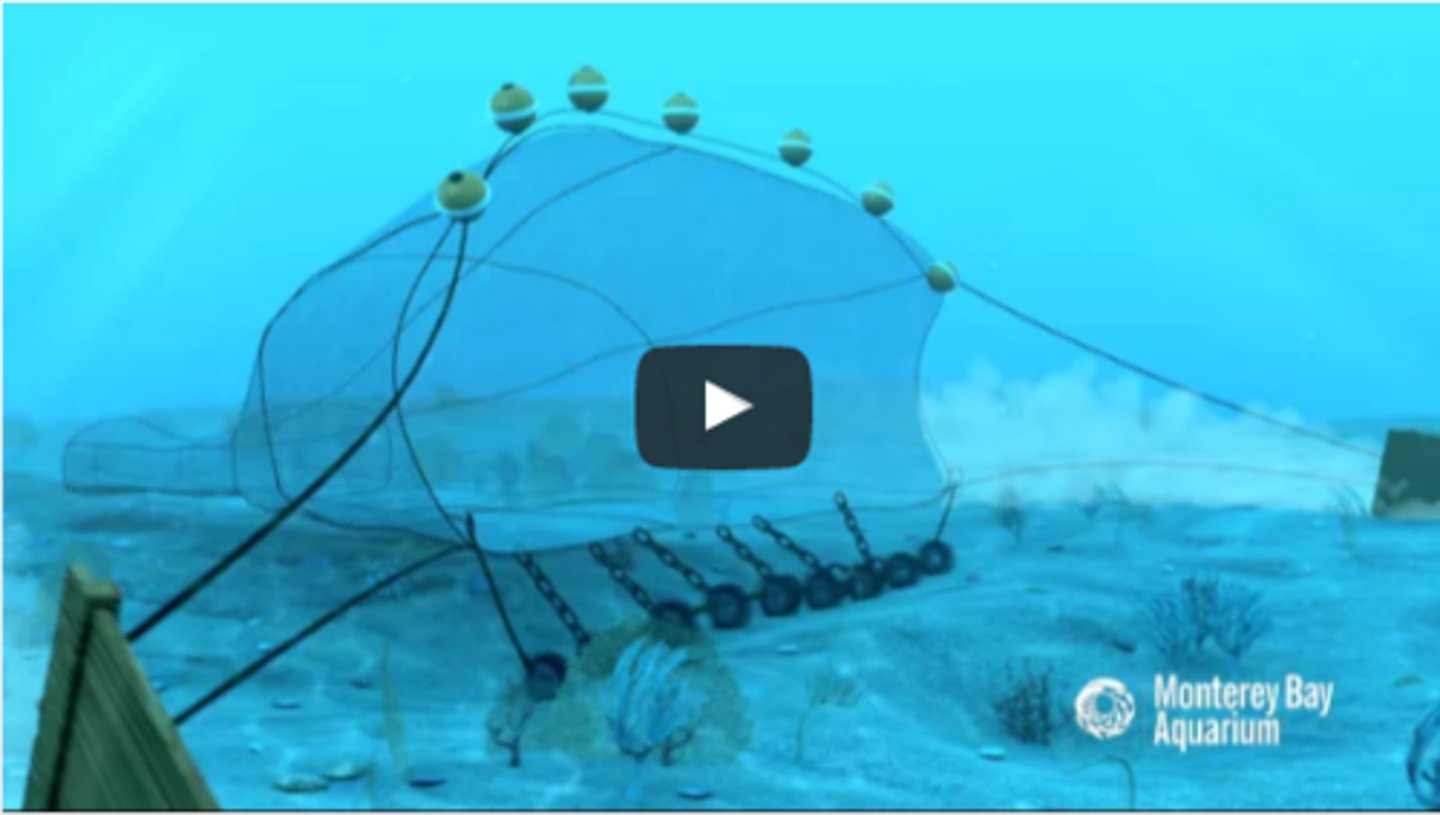
bottom trawling
a fishing technique in which the ocean floor is literally scraped by heavy nets that destroy the sea floor habitat

biopesticides
naturally occurring plants, bacteria, animals, and minerals
selective/narrow spectrum agents
pesticides that target a particular type or family of pests
endocrine disruptors
chemicals that interfere with the normal functioning of hormones in an animal's body

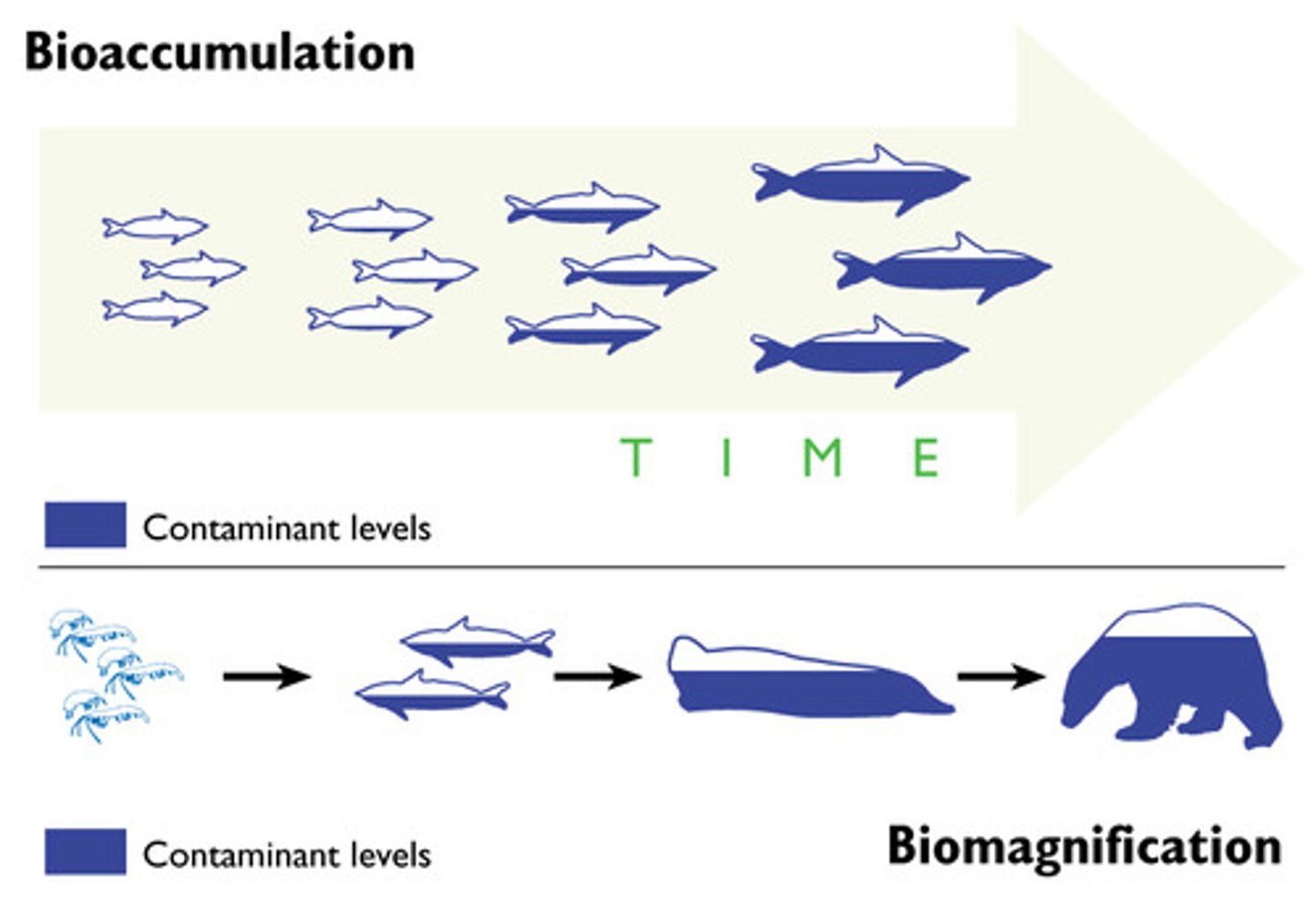
bioaccumulation
an increased concentration of a chemical within an organism over time
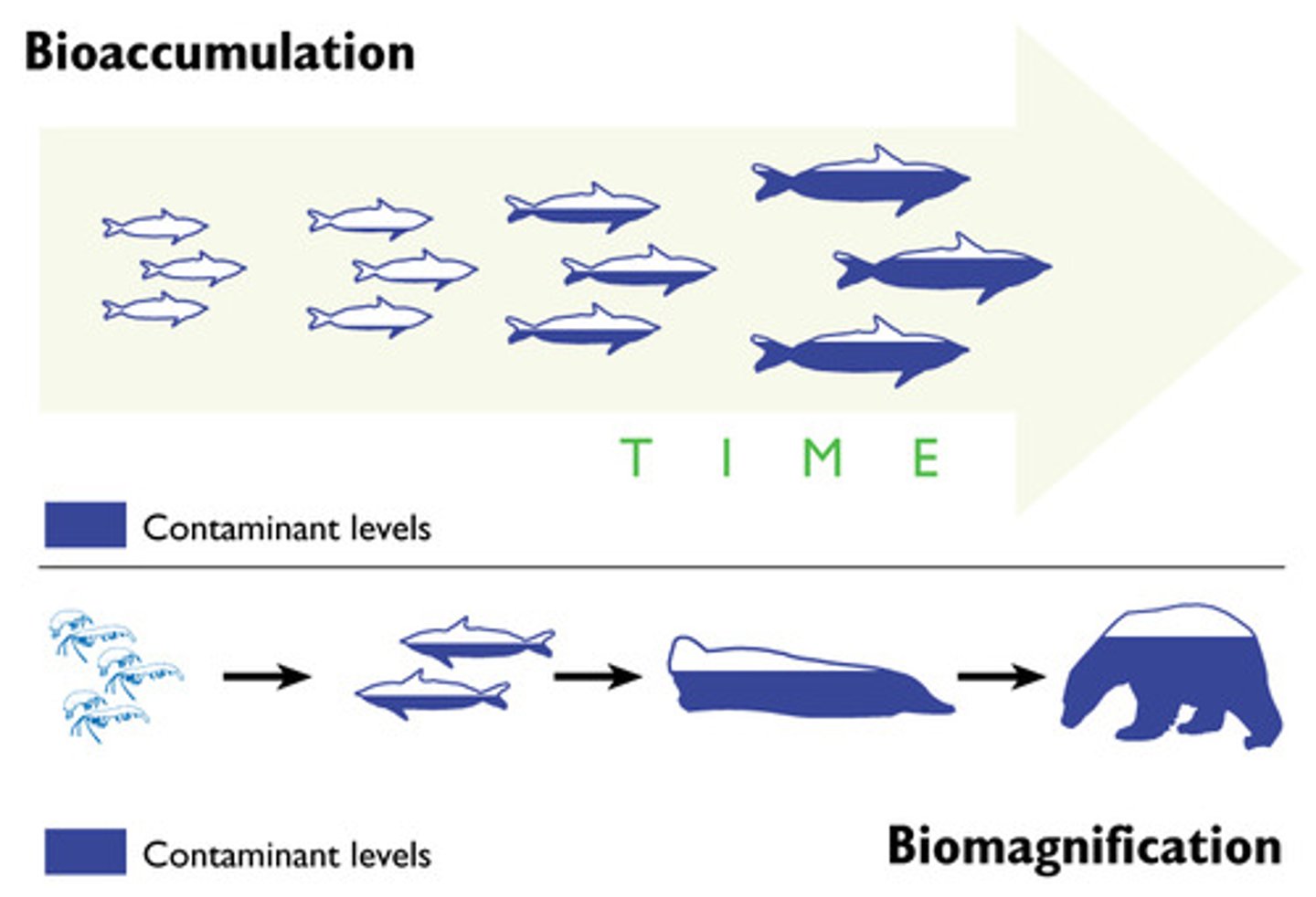
biomagnification
accumulation of pollutants at successive levels of the food chain
O horizon
the uppermost horizon of soil. It is primarily made up of organic material, including waste from organisms, the bodies of decomposing organisms, and live organisms.
A horizon
topsoil
B horizon
A soil horizon composed primarily of mineral material with very little organic matter
bedrock
The solid layer of rock beneath the soil
C horizon
weathered parent material
R horizon
bedrock
soil properties
color, texture, structure, consistence, porosity, moisture
soil texture triangle
a chart used to classify the makeup of various soils
mechanical erosion
physically breaking down of rock by wind and water
splash erosion
the impact of falling raindrops breaking up the clumpy structure of the topsoil
sheet erosion
Peeling off thin layers of soil from the land surface; accomplished primarily by wind and water
rill erosion
erosion in which water running down the side of a slope carves a small stream channel
gully erosion
removal of layers of soil, creating channels or ravines too large to be removed by normal tillage operations
wind erosion
when the wind picks up dirt and dust and moves it from one place to another
contour plowing
plowing fields along the curves of a slope to prevent soil loss
strip cropping
Planting regular crops and close-growing plants, such as hay or nitrogen-fixing legumes, in alternating rows or bands to help reduce depletion of soil nutrients.
Terracing Techniques
farming that builds platforms on hills to reduce erosion.
geology
Study of the earth
Earth Core
Middle of the earth that is iron with nickel part is molten then the next part is solid. The iron ball sloshes around in the center in the dynamo effect which creates a magnetic field.
Earth Mantle
Just below the crust. It is around 1800 miles thick and made mostly of solid rock. It is very hot, around 5400 degrees
earth crust
earth's outermost layer of rock made up of both dry land and ocean floor
Minerals
Naturally occurring compound that exists as a crystalline solid & is inorganic
Rock
A naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals or organic matter
rock cycle
A series of processes on the surface and inside Earth that slowly changes rocks from one kind to another
plate tectonics
A theory stating that the earth's surface is broken into plates that move.
convergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other.
divergent boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other.
transform boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions
earthquake
The shaking that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface.
Rickter scale
Assigns numbers to describe the magnitude of an earthquake
Tsunami
A giant wave usually caused by an earthquake beneath the ocean floor.
volcano
A weak spot in the crust where magma has come to the surface
surface mining
cheaper and can remove more minerals; less hazardous to workers
open pit mining
A mining technique that uses a large pit or hole in the ground, visible from the surface of Earth.
strip mining
involves the removal of the Earth's surface all the way down to the level of the mineral seam.
mountain top removal
a mining technique in which the entire top of a mountain is removed with explosives
placer mining
the process of looking for minerals, metals, and precious stones in river sediments
Dredging
Type of surface mining in which chain buckets and draglines scrape up sand, gravel, and other surface deposits covered with water. It is also used to remove sediment from streams and harbors to maintain shipping channels.
subsurface mining
The extraction of mineral and energy resources from deep underground deposits.
black lung disease
Black lung disease is a common name for any lung disease that develops from inhaling coal dust. This name comes from the fact that those with the disease have lungs that look black instead of pink. Medically, it is a type of pneumoconiosis called coal workers' pneumoconiosis (CWP).
hydraulic fracturing
the forcing open of fissures in subterranean rocks by introducing liquid at high pressure, especially to extract oil or gas.