Urinary System Flashcards
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary and concepts related to the urinary system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Kidneys
Produce urine, filtering water, ions, and soluble substances.
Ureters
Receive urine from the kidneys and carry it to the bladder via gravity and peristalsis.
Bladder
Receives and stores urine; contraction in its muscular wall leads to urination.
Urethra
Carries urine from the bladder to the external environment.
Functions of the Urinary System
Filters blood plasma
• Regulates concentrations of Na+/K +/Cl- ions (and others)
• Removal of drugs, toxins and waste products from the bloodstream
Conserves valuable nutrients
• Preventing nutrient loss via urine
Regulates blood volume and pressure
• Removing fluid (H2O) from blood → ↓ blood vol → ↓ blood pressure
Regulates blood pH, glucose levels
• Remove H+ ions and glucose from blood (maintain homeostasis)
Releases hormones (specialised endocrine cells)
• Erythropoietin – stimulates RBC formation
• Calcitriol – stimulates Ca 2+ absorption in the GIT
Location of the Kidneys
Paired organs that sit either side of the vertebral column
• Left kidney slightly superior to the right (due to the liver)
• Retroperitoneal: sit behind the peritoneum
(abdominal sac around the intestines)
• Protected by:
• 11 th and 12 th ribs
• Visceral organs (anteriorly)
• Fat
Connective Tissue Layers of the Kidney
Each kidney is protected and supported by
three connective tissue layers:
(1) Fibrous capsule
• The entire organ is covered by a capsule of
collagen fibres
(2) Perinephric/perirenal fat
• A thick, cushioning layer of adipose tissue
(3) Renal fascia
• A dense, fibrous outer layer that anchors the
kidney to surrounding structures
Hilum
Entry/exit point in the kidney for the renal artery, renal nerves, renal vein, and ureter.

Renal artery
Proportionally very large in diameter
Supplies kidney with ~20% resting cardiac output
(to be filtered)
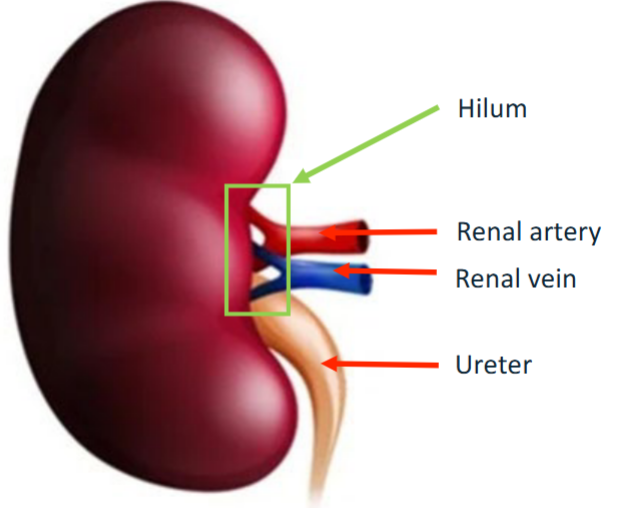
Renal vein
Takes blood out of the kidney
Ureter
Takes urine to the bladder
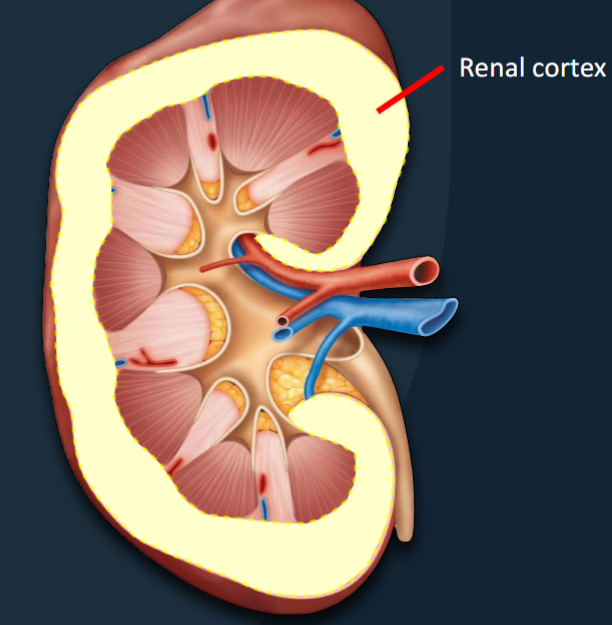
Renal Cortex
Outermost ~1cm of the kidney
• Where filtration and reabsorption occurs
• Waste products and H 2 O removed from blood
• Useful products (glucose, proteins, AA’s) are
reabsorbed from filtrate, back into the blood
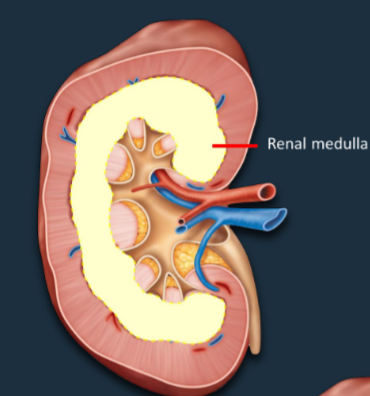
Renal Medulla
~2-3cm region below the cortex that regulates the concentration of urine.
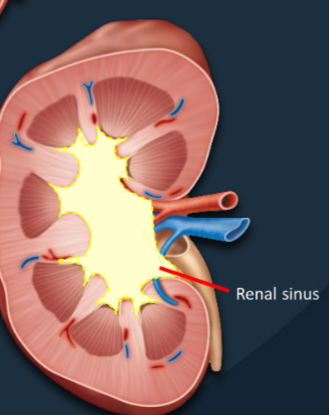
Renal Sinus
A central cavity containing the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, and fat.
Renal Pyramids
Conical structures that extend from the cortex to the renal sinus
• 8-18 per kidney (average)
• Transport urine from the cortex → sinus
• The apex (facing the sinus) = the renal papilla
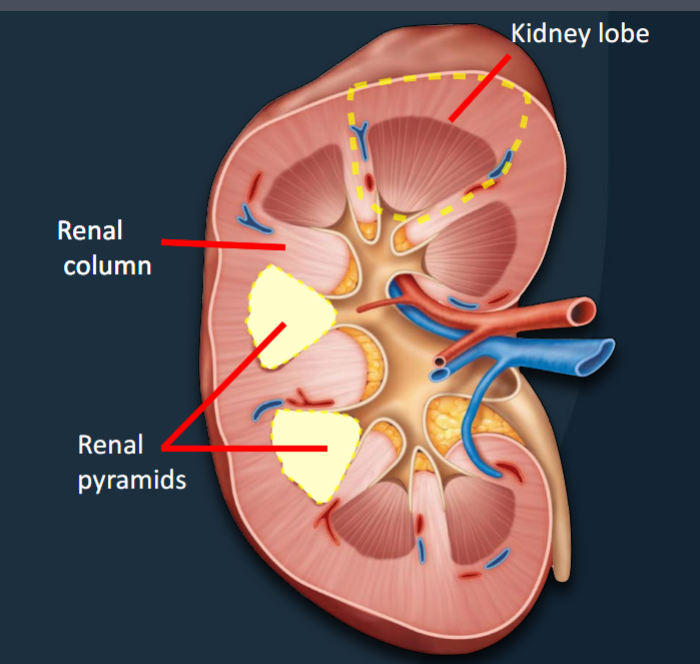
Renal Columns
Bands of tissue that separate adjacent renal pyramids.
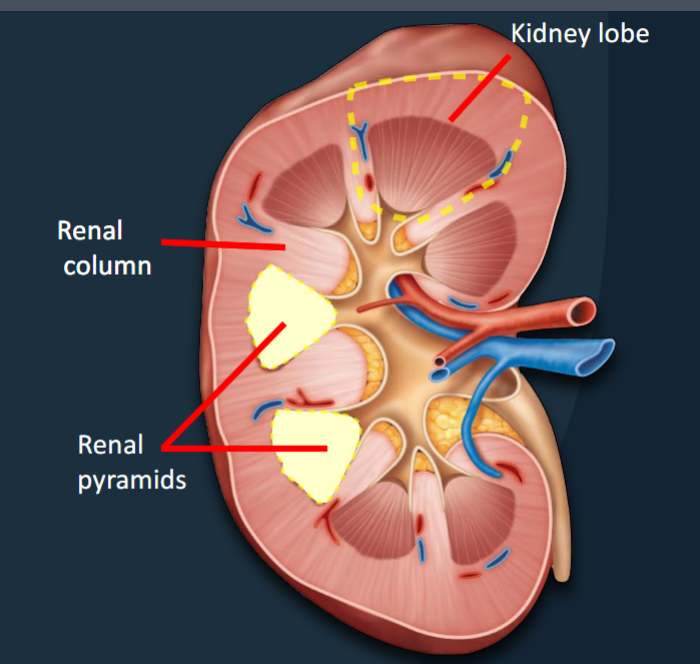
Kidney Lobes
Functional units consisting of a renal pyramid, overlying renal cortex, and adjacent tissues of the renal columns; where urine is produced.
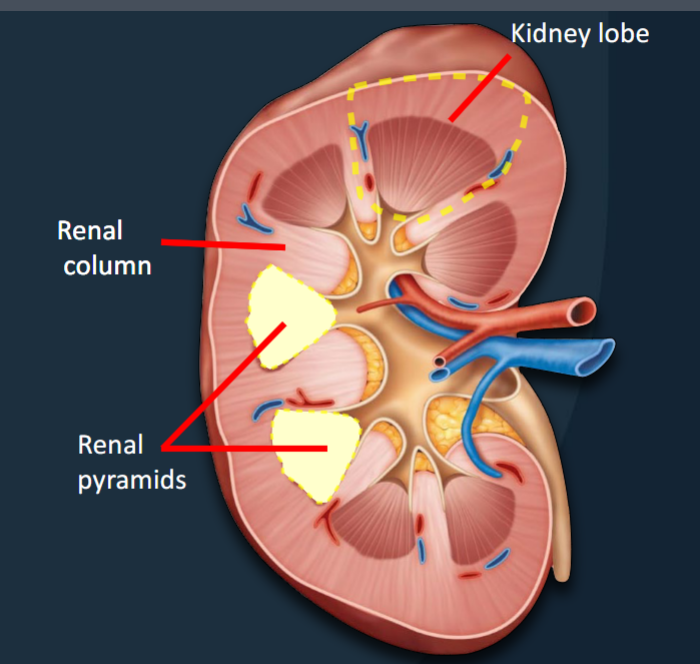
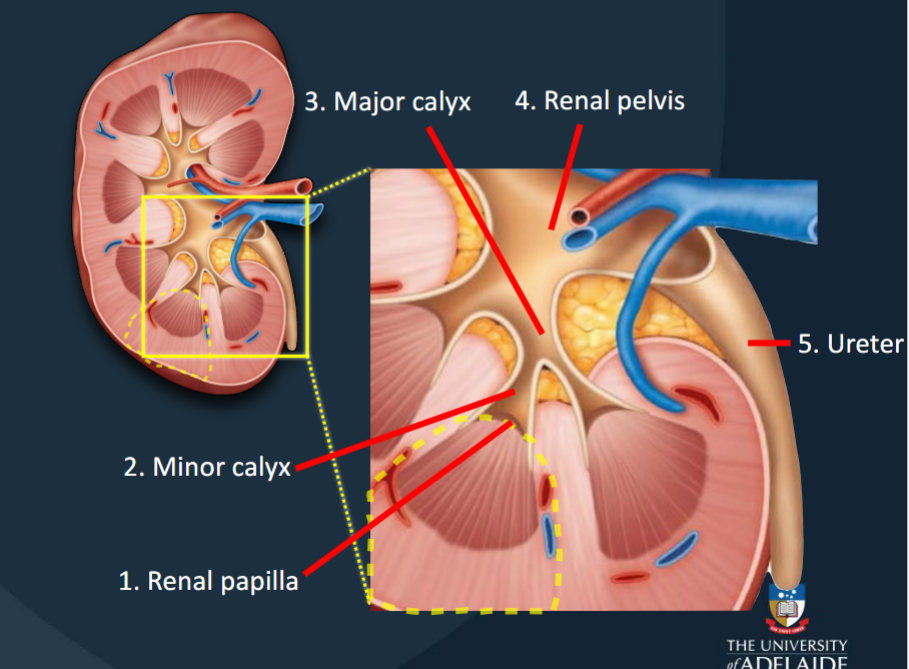
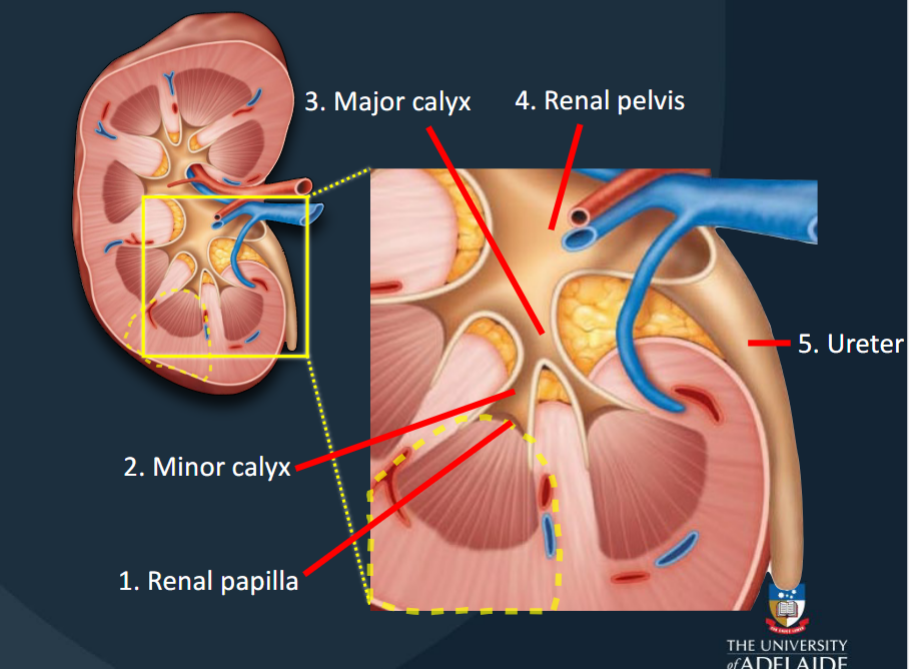
Urine produced in each kidney lobe is transported to the ureter via a series of structures
(1) Renal papilla
(2) Minor calyces
(3) Major calyces
(4) Renal pelvis
(5) Ureter
Renal Papilla
The location where filtrate passes from the renal pyramid to the renal sinus.
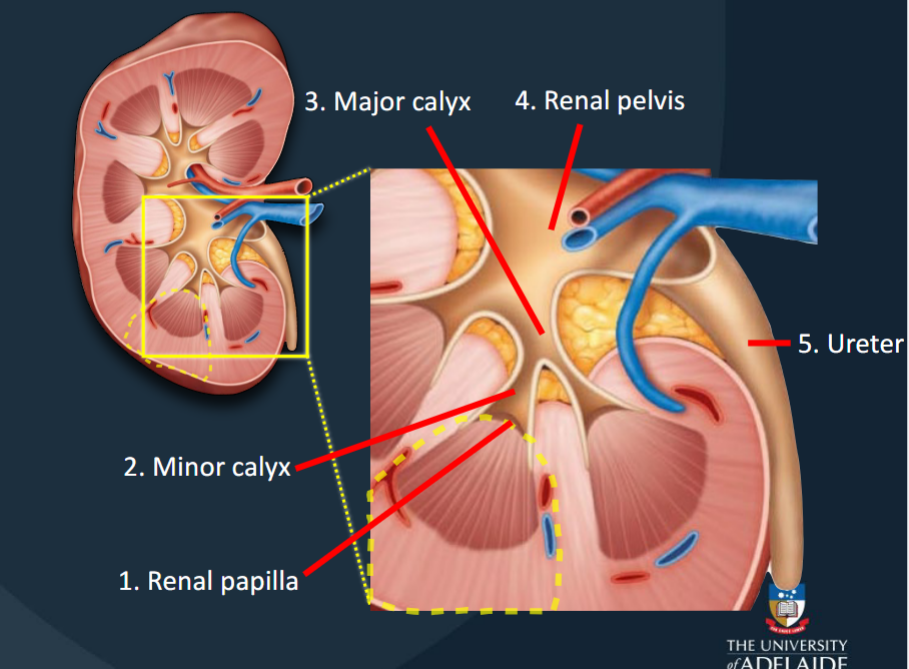
Minor Calyces
Collects urine produced by a single kidney lobe.
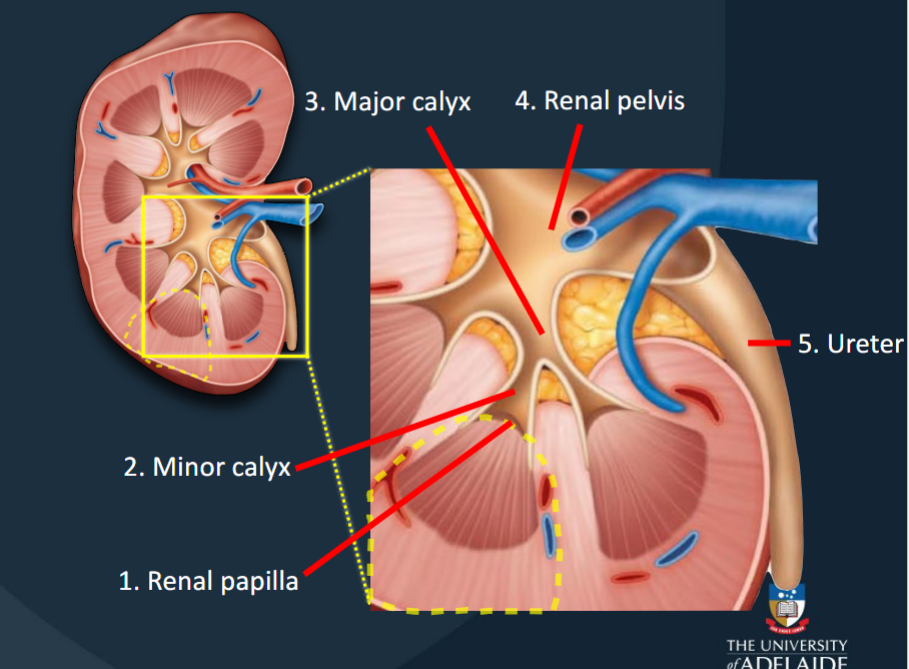
Major Calyces
Formed by the fusion of 4-5 minor calyces; collects urine from minor calyces.
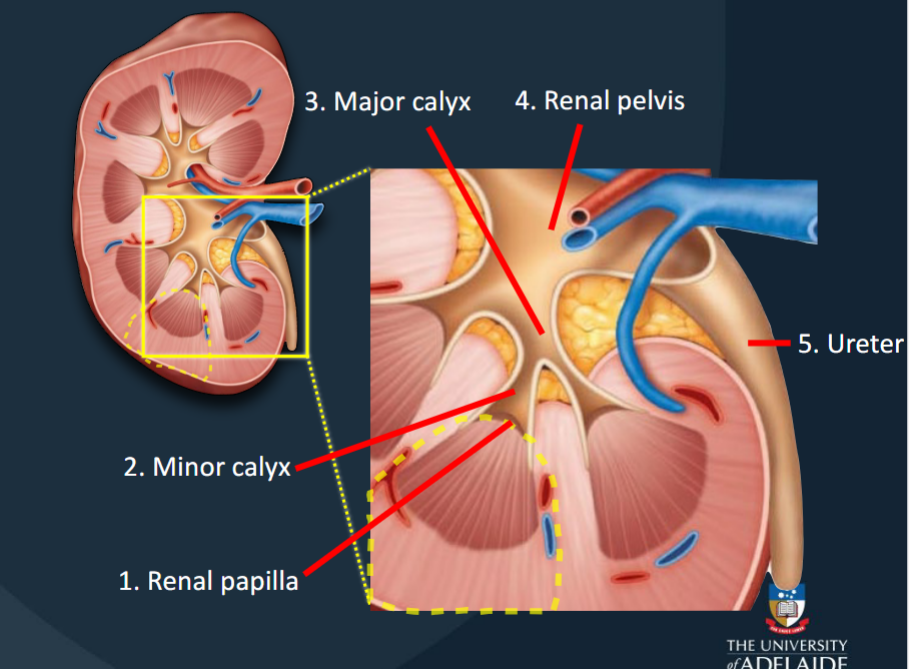
Renal Pelvis
Large funnel-shaped chamber continuous with the ureter.
utterer
Drains the urine from kidney → bladder
Every ~30 sec, a peristaltic wave sweeps along the ureter
The Ureters and its layers
A pair of muscular tubes that extend from the kidneys to the urinary bladder (posterior wall)
• ~25-30 cm long and retroperitoneal
• Firmly attached to the posterior abdominal wall
1. Mucosa:
• Consists of transitional epithelium
• Stratified epithelium (cuboidal squamous)
• Allows for expansion of ureter diameter
2. Muscularis:
• Facilitates peristalsis (movement of urine)
• Upper 2/3: Two layers of smooth muscle
• Inner longitudinal, outer circular
• Lower 1/3: Three layers of smooth muscle
• Inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer longitudinal
The Urethra
Transports urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body
• ~20-25 cm in males and ~4cm in females
• In females: Transports urine only
• In males: Transports urine and semen
1. Mucosa:
• Epithelium varies along the length of the urethra*
• Proximal end: Transitional
• Distal end: Stratified squamous
2. Muscularis:
• Facilitates expulsion of urine
• Two layers of smooth muscle (inner longitudinal, outer circular
Internal Urethral Sphincter
Involuntary sphincter that controls urine flow from the bladder.
External Urethral Sphincter
Voluntary sphincter that controls urine flow from the bladder.
Micturition (Urination)
Urine reaches the bladder by peristaltic contractions of the ureters
• When the bladder is full, stretch receptors in the bladder wall trigger the micturition reflex
• The urge to urinate generally appears when the
bladder contains ~200mL
• If ignored, urine will continue to accumulate in the
bladder
• At ~500 mL, muscle contractions force the internal
urethral sphincter open
Micturition Reflex
Receptors detect stretch and reporting to spinal cord, which triggers the Micturition Reflex
sent to brain for evaluation, bladder contracts, and the internal sphincter relaxes
The brain sends instructions
external sphincter relaxes/contracts
Micturition (Urination) for babies and elderly
If neurological pathway for control of external
urethral sphincter has not yet been established,
urination will occur involuntarily, e.g. infants
• At 2-3 years the brain is mature enough to execute
voluntary control of external urethral sphincter
• If external urethral sphincter is not powerful
enough to prevent it, urination will occur
involuntarily, e.g. elderly
Cortical Nephrons
Nephrons located almost entirely within the renal cortex, important for excreting waste products in urine (~85%).
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Nephrons with long nephron loops that extend deep into the renal medulla, essential for producing concentrated urine (~15%).
The nephron: Renal corpuscle:
Where water and dissolved solutes are pushed out of the blood and into the renal tubule
• Site of blood filtration
The nephron: renal corpuscle: Glomerulus
Capillary network within the renal corpuscle where blood filtration occurs.
• Afferent arterioles – going in
• Efferent arterioles – going out
• Efferent are smaller diameter = ↑
glomerular pressure
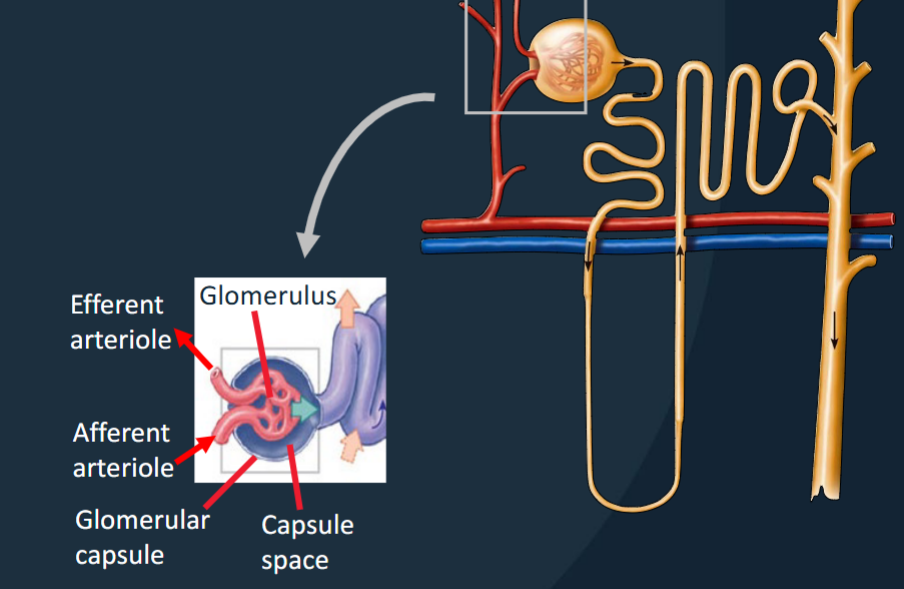
The Nephron: renal corpuscle: Glomerular Capsule (Bowman’s Capsule)
• Blood pressure forces water/solutes out of the glomerular capillaries into the capsule space and then into the renal tubule.
• Filtration of blood from the glomerulus into the glomerular capsule via filtration membrane.

Afferent Arteriole
Arteriole that carries blood into the glomerulus.
Efferent Arteriole
Arteriole that carries blood out of the glomerulus to the peritubular capillaries.
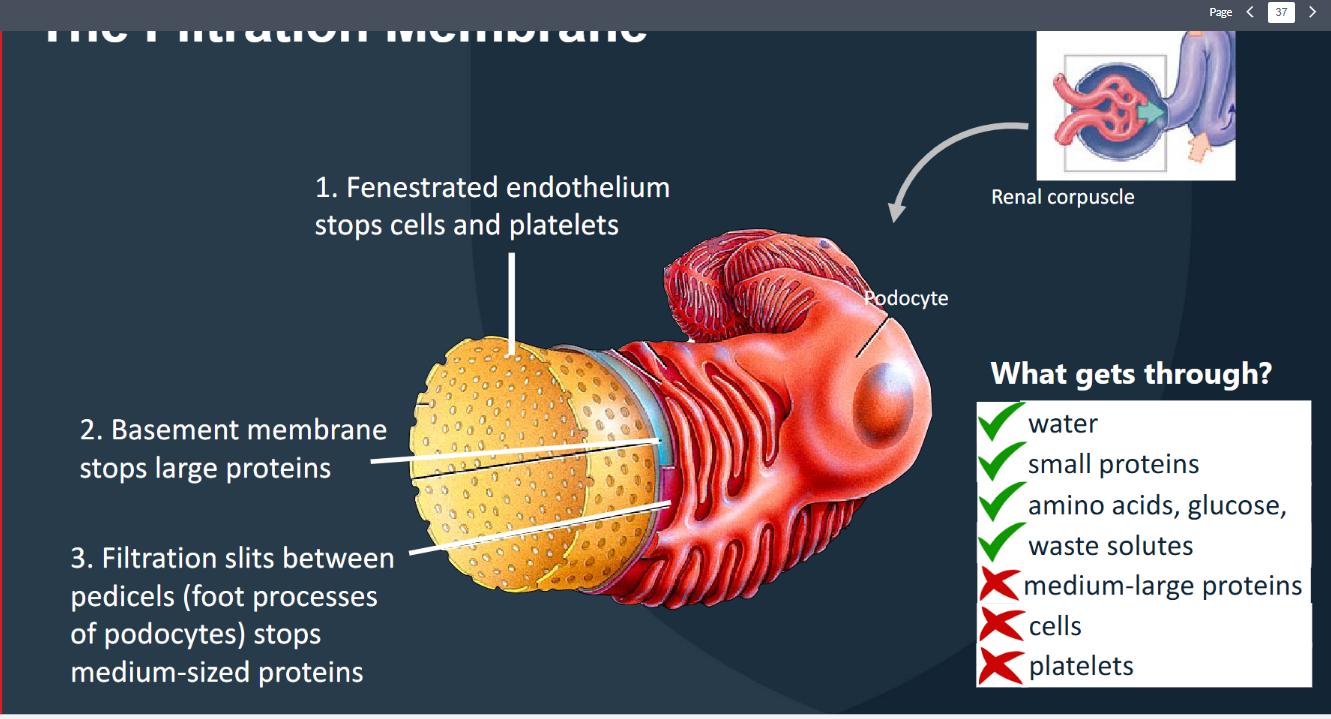
The Nephron: Renal corpuscle Membrane layers
Blood enters the glomerulus (via afferent arteriole)
→ filterable blood components move into the
capsular space (= filtrate)
→ nonfilterable components exit the glomerulus
(via efferent arteriole)
(1) Glomerular capillary endothelium is fenestrated
(blocks cells)
(2) Underlying basement membrane (blocks
large/charged proteins)
(3) Filtration slits - gaps between adjacent pedicels –
(blocks medium-sized proteins)
• ~20% of blood pumped by the heart each minute will
undergo filtration
The Nephron: Renal Tubule
Where the components of the filtrate are altered (via secretion and absorption)
• Site of filtrate modification
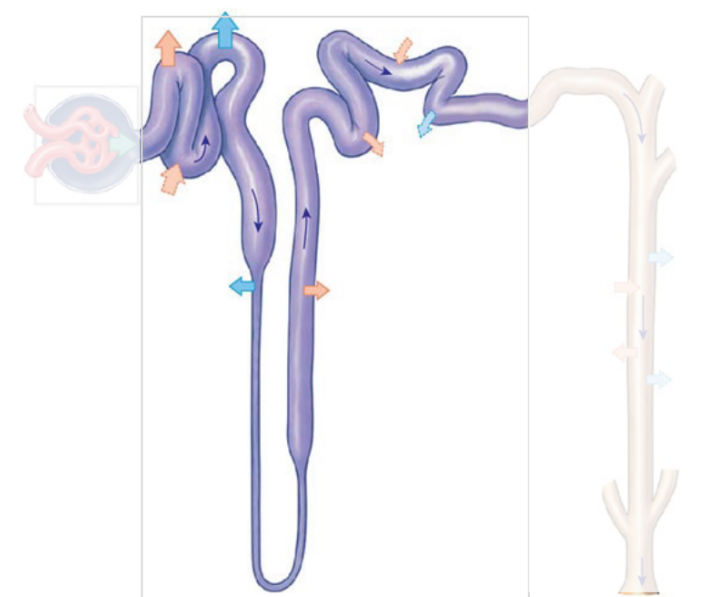
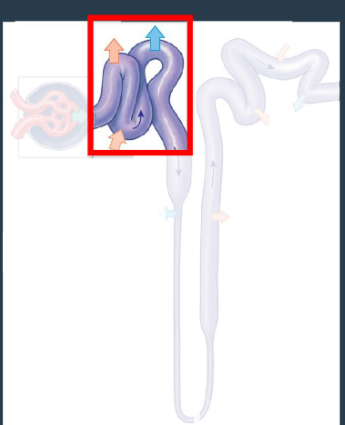
The Nephron: Renal Tubule: Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Beginning of the renal tubule where reabsorption of essential substances from the filtrate back into the blood occurs.
Cells have microvilli to aid reabsorption
The Nephron: Renal Tubule: Nephron Loop (Loop of Henle)
Middle segment of the renal tubule with descending and ascending portions for water and ion reabsorption.
• Descending = reabsorption of water
• Ascending = reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- from the filtrate
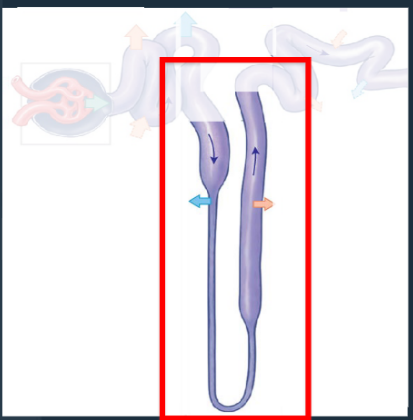
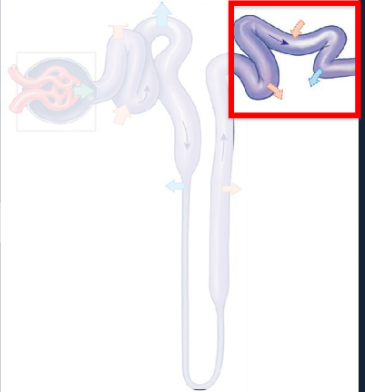
The Nephron: Renal Tubule: Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Last segment of the renal tubule where filtrate composition is adjusted via reabsorption and secretion.
• Only 15-20% of initial filtrate volume reaches the DCT
The nephron: Collecting system:
• Tubular fluid (urine) from each nephron empties into the
collecting system (→ minor calyces)
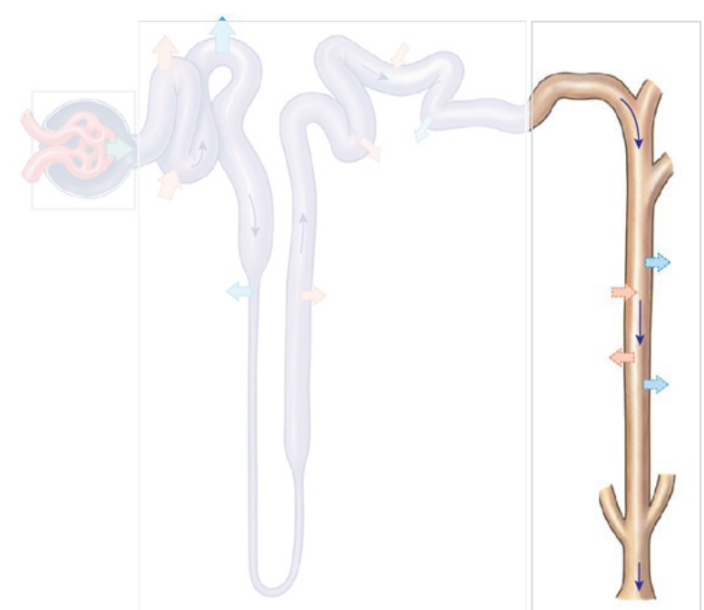
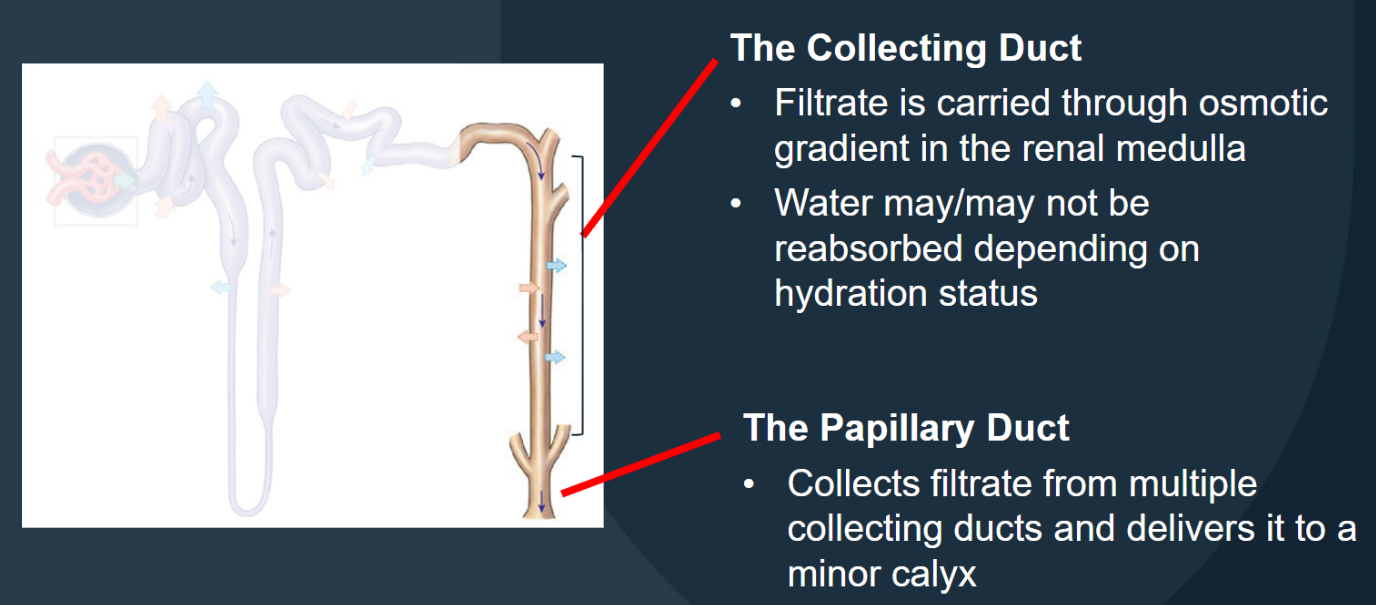
The nephron: Collecting system: Collecting Duct
Carries filtrate through the osmotic gradient in the renal medulla; water may/may not be reabsorbed depending on hydration status
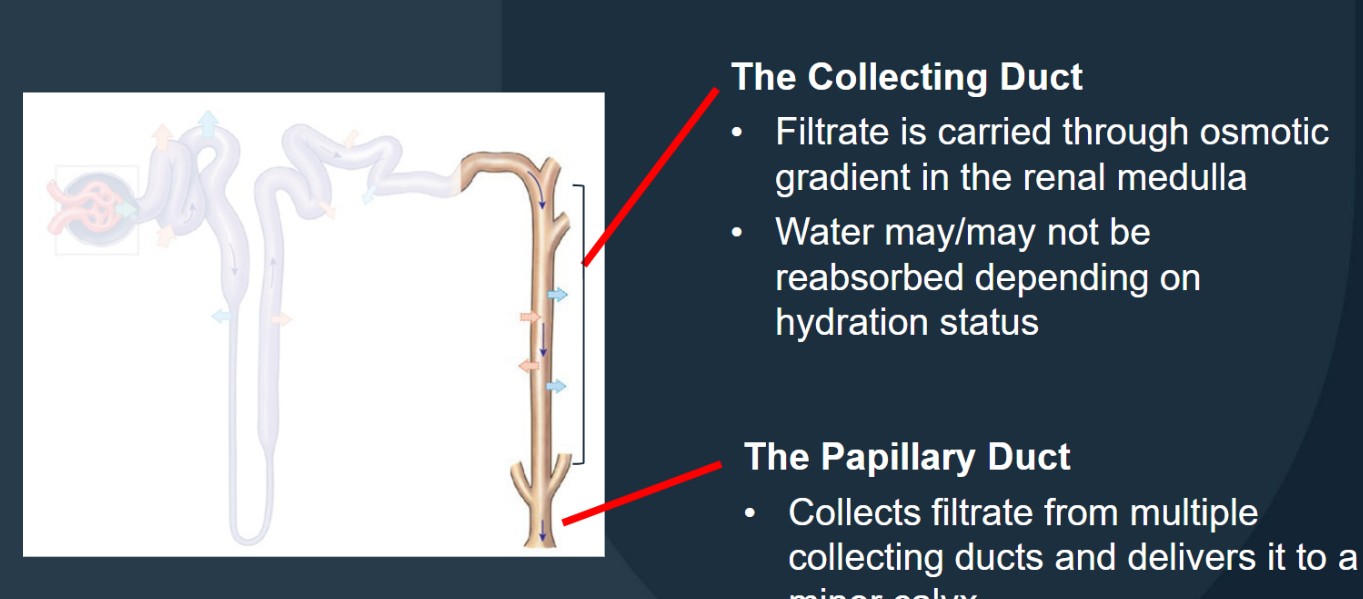
The nephron: Collecting system: Papillary Duct
Collects filtrate from multiple collecting ducts and delivers it to a minor calyx.
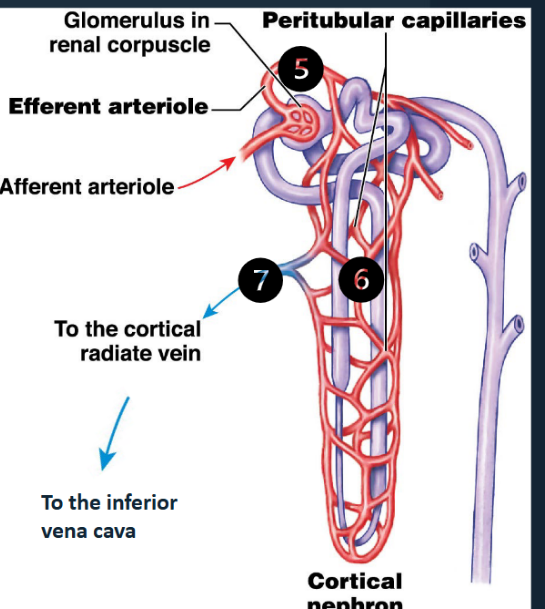
Blood Flow Through the Kidney (steps 1-4)
About 20% of the blood pumped by the heart each minute is sent to the kidneys for filtration. The remaining 80% goes to the rest of the body for gas exchange.
1) O 2-rich blood from the heart arrives via the renal artery
(2) The renal artery divides into segmental arteries in the renal sinus
(3) The segmental arteries branch into interlobar arteries, which run within the renal columns
(4) Interlobar arteries continue to branch into smaller and smaller vessels, culminating in the afferent arterioles that supply each nephron (i.e.the blood vessel entering the glomerulus)
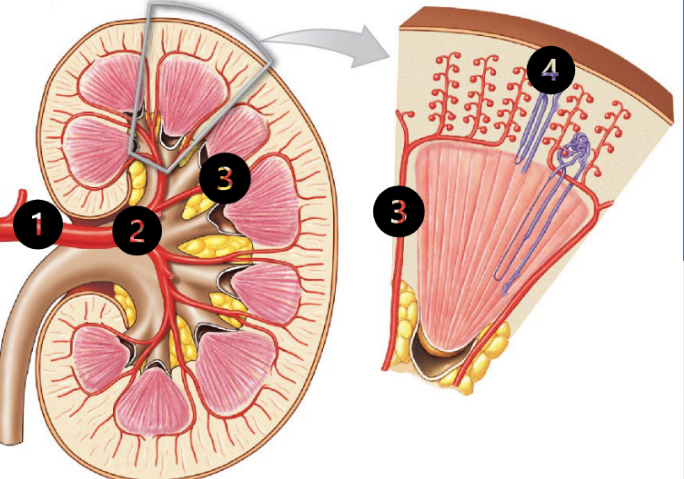
Blood Flow Through the Kidney (steps 5-7)
After entering the glomerulus via the afferent
arteriole:
(5) The efferent arteriole carries blood from the glomerulus to the peritubular capillaries
(6) The peritubular capillaries surround the entire renal tubule
• Collect water and solutes absorbed by the nephron.
• Deliver other solutes to the nephron for secretion
(7) The peritubular capillaries drain into cortical veins,
which carry filtered blood back to the inferior vena cava
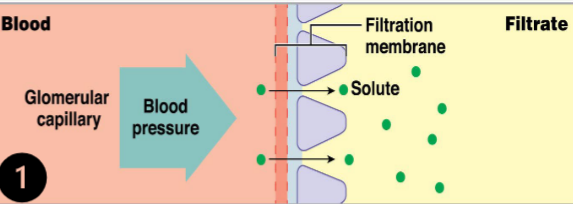
The kidneys maintain homeostasis by regulating
the volume and composition of blood: (1) Filtration
a renal physiology process that occurs in the renal corpuscle of the nephron where solutes within the blood passes through the filtration membrane and into the nephron
The kidneys maintain homeostasis by regulating
the volume and composition of blood: (2) Reabsorption
a renal physiology process that involves the transport of water and solutes from the tubular fluid (i.e. filtrate) into the peritubular fluid (→ bloodstream).
The kidneys maintain homeostasis by regulating
the volume and composition of blood: (3) Secretion
a renal physiology process that involves the transport of solutes from the peritubular fluid into the tubular fluid (i.e. filtrate).
Glomerular Filtration at the Renal Corpuscle
Driven by blood pressure
• ~180 L/day filtrate enters the glomerular capsules
• ~178-179 L/day is reabsorbed back into the blood
• ~ 900mL – 2L of urine is produced
• Filtration is enhanced by:
• Thinness of the filtration membrane
• Large surface area of glomerular capillaries
• High glomerular BP (due to ↓ size efferent arteriole)
• Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
• Formula based on creatinine levels (waste product), age
and gender
• Roughly equates to kidney function
• E.g. GFR 60 = kidneys working at ~60%
Reabsorption at the Proximal Convoluted Tubule
Reabsorption of essential substances from the
filtrate back into the blood via channels, pumps,
and co-transporters:
• Water
• Glucose
• Ions
• Small proteins
• Organic nutrients
• >99% of glucose, amino acids and other
organic nutrients are reabsorbed – water follows along with it
• Cells have microvilli to aid reabsorption
Reabsorption at the Nephron Loop (Loop of Henle)
Descending Loop of Henle
• Further reabsorption of water from the filtrate
• Filtrate becomes more concentrated (saltier)
• Osmolarity: 400 → 1200 mOsm/L
Ascending Loop of Henle
• Reabsorption of Na+ and Cl - from the filtrate
• Impermeable to water
• Filtrate becomes more dilute (less salty)
• Osmolarity: 1200 → 100 mOsm/L
Secretion and Reabsorption at the Distal Convoluted Tubule
Only 15-20% of initial filtrate volume reaches the DCT
• Adjusts filtrate composition via reabsorption and secretion
• Secretion of substances into the filtrate via exchange pumps and carrier proteins
• Ions (Na + reabsorbed in exchange for K+)
• Acids (H+ secreted in exchange for Na+)
• Drugs and toxins – via carrier proteins
• Variable reabsorption of:
• Water (hormonally controlled)
• Na + & Ca ++
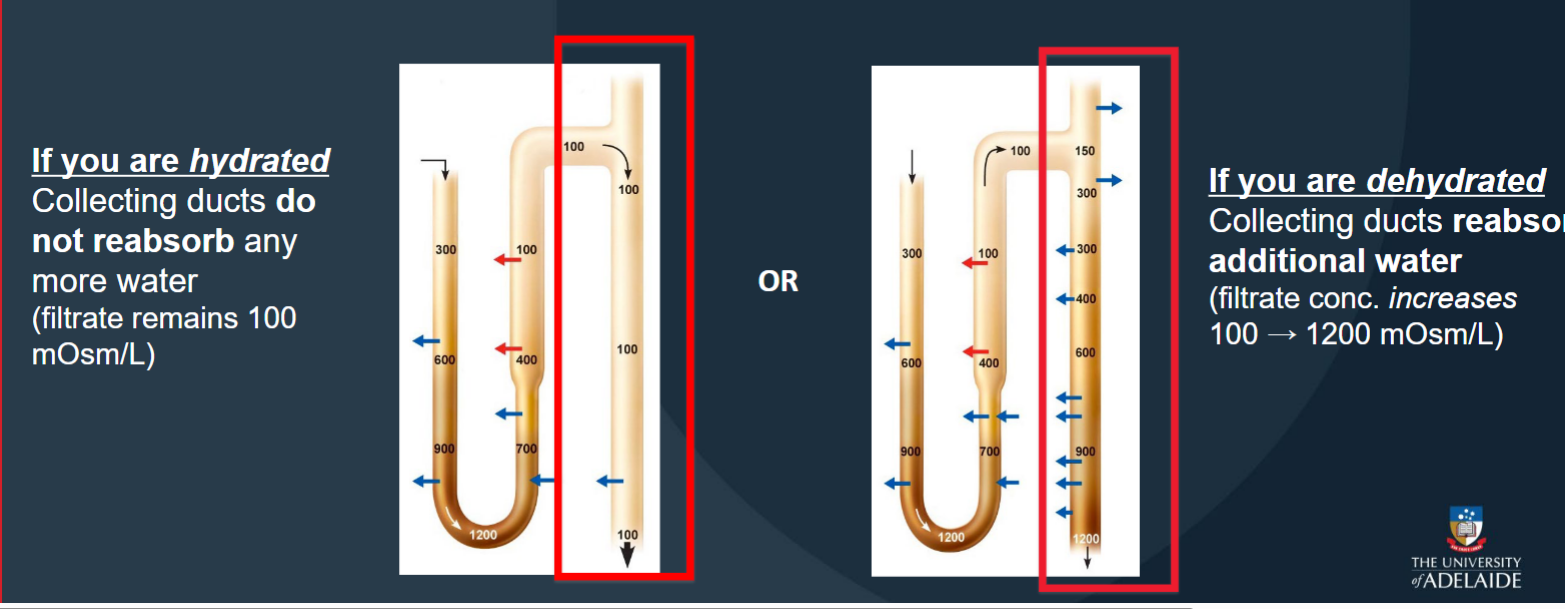
Reabsorption at the Collecting Ducts
Where filtrate from each nephron empties into the collecting system (carried through the renal medulla → minor calyces).
If you are hydrated: Collecting ducts do not reabsorb any more water (filtrate remains 100mOsm/L)
If you are dehydrated:Collecting ducts reabsor additional water (filtrate conc. increases100 → 1200 mOsm/L)
Metabolic Waste Products: 1.Urea
Most abundant metabolic waste product; a by-product of amino acid breakdown in the liver.
Metabolic Waste Products: 2. Creatinine
Metabolic waste product generated in skeletal muscle tissue through the breakdown of creatine phosphate.
Metabolic Waste Products: 3. Uric Acid
Metabolic waste product; a by-product of recycling the nitrogenous bases of RNA molecules.
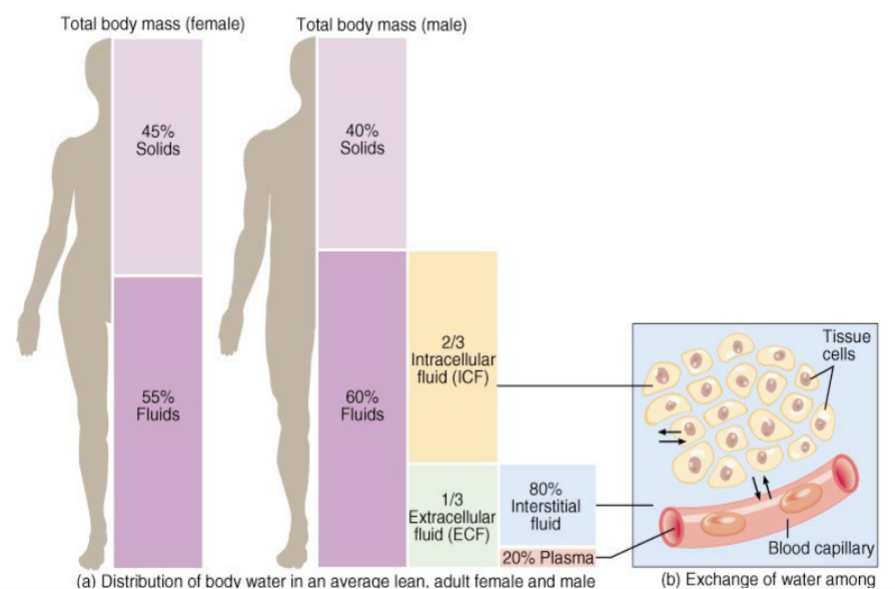
Body Fluid
Represents 55-60% of body mass
• Declines with age (as fat increases)
• Locations:
• Intracellular fluid (ICF)
• Extracellular fluid (ECF)
• Exchange occurs across:
• Cell membranes: ICF ECF
• Capillary walls: ECF blood plasma
Body Fluid - Location
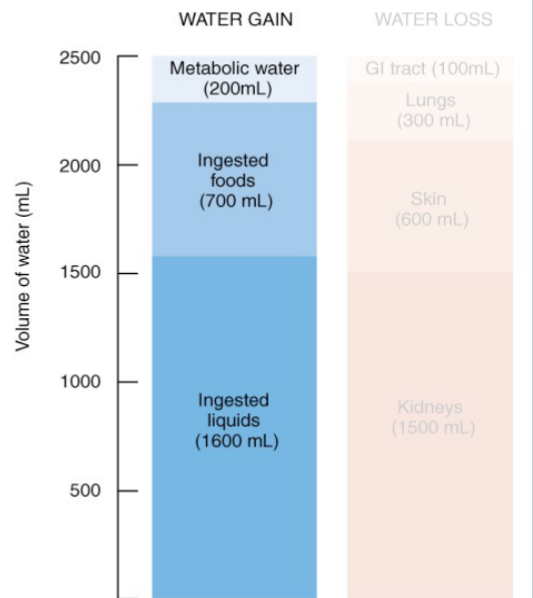
Water Gain
Metabolic water
• Generated in reactions
• NOT regulated
Ingested foods
Ingested liquids
Regulated in hypothalamus
• Triggered by drop in blood
pressure/blood volume
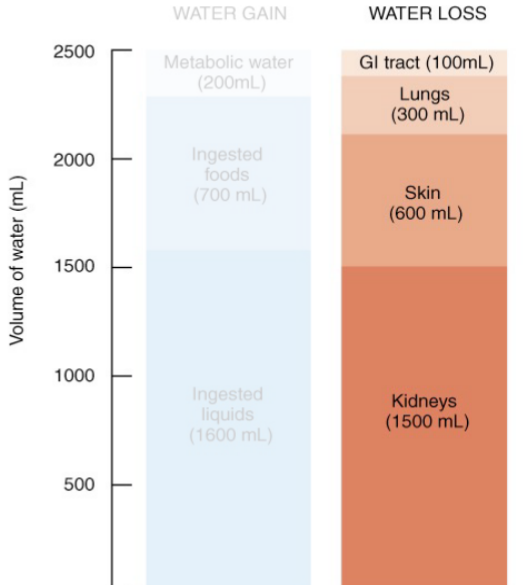
Water Loss
• Through the kidneys
• The body’s fluid volume is determined
by the extent of salt loss through urine
• Water ‘follows’ salt out (osmosis)
• Depends on dietary salt levels
• Evaporation from skin
• Exhaled from lungs
• Component of faeces
Electrolytes
Charged ions in solution involved in multiple crucial functions: control osmosis, Maintain acid-base balance, Carry electrical currents.