Lecture 17 - accessory structures and fxns
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
why would threshold for sweating onset be shifted forward if the blood osmolarity is high?
to prevent further water loss
the kidneys will also try to hold on to urine as well
what factors would cause sweating to begin at a lower mean body tempurature?
training
heat acclimation
increased skin temperature
What are the three types of interindividual variation in sweat rate?
bigger gland = higher sweat rate
“poor” sweater
moderate sweater
heavy sweater
what is the physiological significance of sweat?
thermoregulation via heat dissipation
skin health
epidermal barrier homeostasis → delivery of water, amino acids, NaCl, etc.
micronutrient balance
heat acclimation → conversation of NaCl, bicarb, trace minerals
sweat-induced deficiencies (NaCl)
prolonged sweating (>8 hrs)
excretion of environmental contaminants
excretion of ethanol → not supported
excretion of metabolic waste (ex: urea)
limited evidence
Sebaceous Glands - types, location, and structure
types:
attached to hair follicles
not attached to hair follicles (eyelids, nipples, genitals)
location:
mid-dermis throughout skin EXCEPT palms/soles
outlet either into follicular canal or skin surface
structure:
grape-like clusters of specialized epithelial cells
sebaceous glands functions
lubrication of skin and hair
anti-desiccant for epidermis (prevent water loss)
androgen processing
cholesterol → testosterone
wound healing “keeping them sealed”
secretion of sebum largely regulated by androgens → teen acne
what is a special function of sebaceous glands
vernix - birth stuff
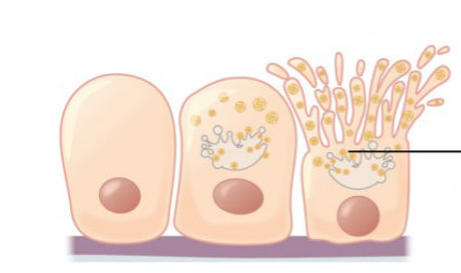
what is the mechanism of sebaceous glands
mature cell dies and becomes secretory product
holocrine = wHOLe cell breaks down
ceruminous glands
specialized apocrine sweat glands; merocrine secretion → exocytosis
location:
subcutaneous layer of the external auditory canal
function:
produces earwax!
mix of gland secretion + sebum + dead epidermal cells
earwax functions:
pliability of eardrum
lubrication
antimicrobial/acidic
particle barrier
mammary glands
present in all humans to some extent
development arrests at the end of puberty in females; differentiation and growth completes during lactation
clinical relevance
location
breasts, connected via many ducts to the nipples
function
secrete milk
mammary glands - method of secretion
apocrine secretion
pinched off portion of cell is the secretion
APocrine = APex of cell breaks off