BIOL 300: Principles of Genetics Discussion
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Gregor Mendel
Known as the Father of Modern Genetics he experimented on Pea Plants, and he was able to show that the Basic units of genetics are material elements

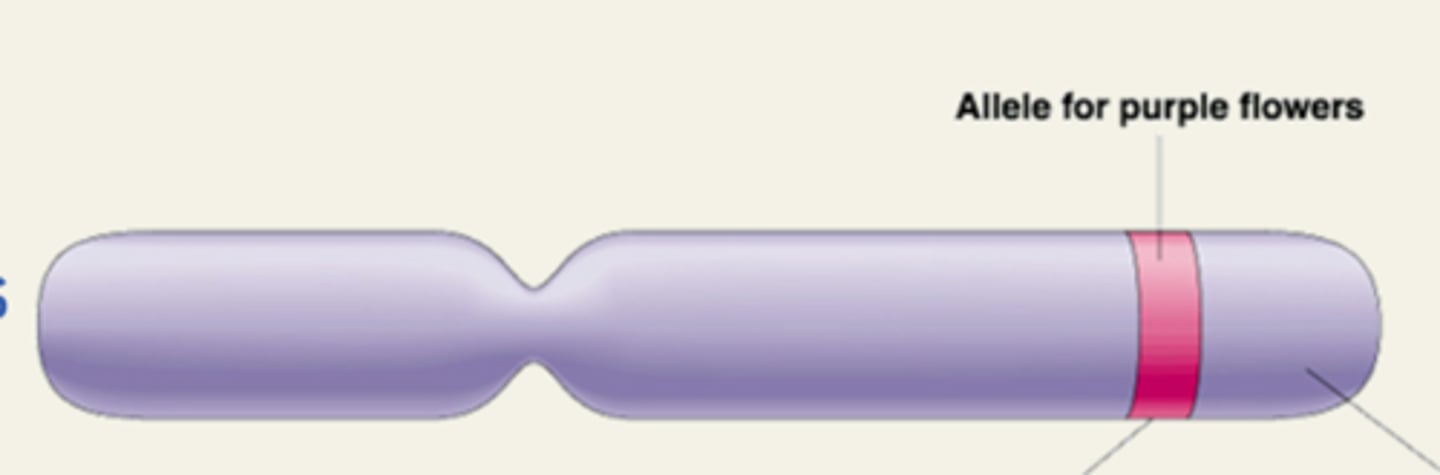
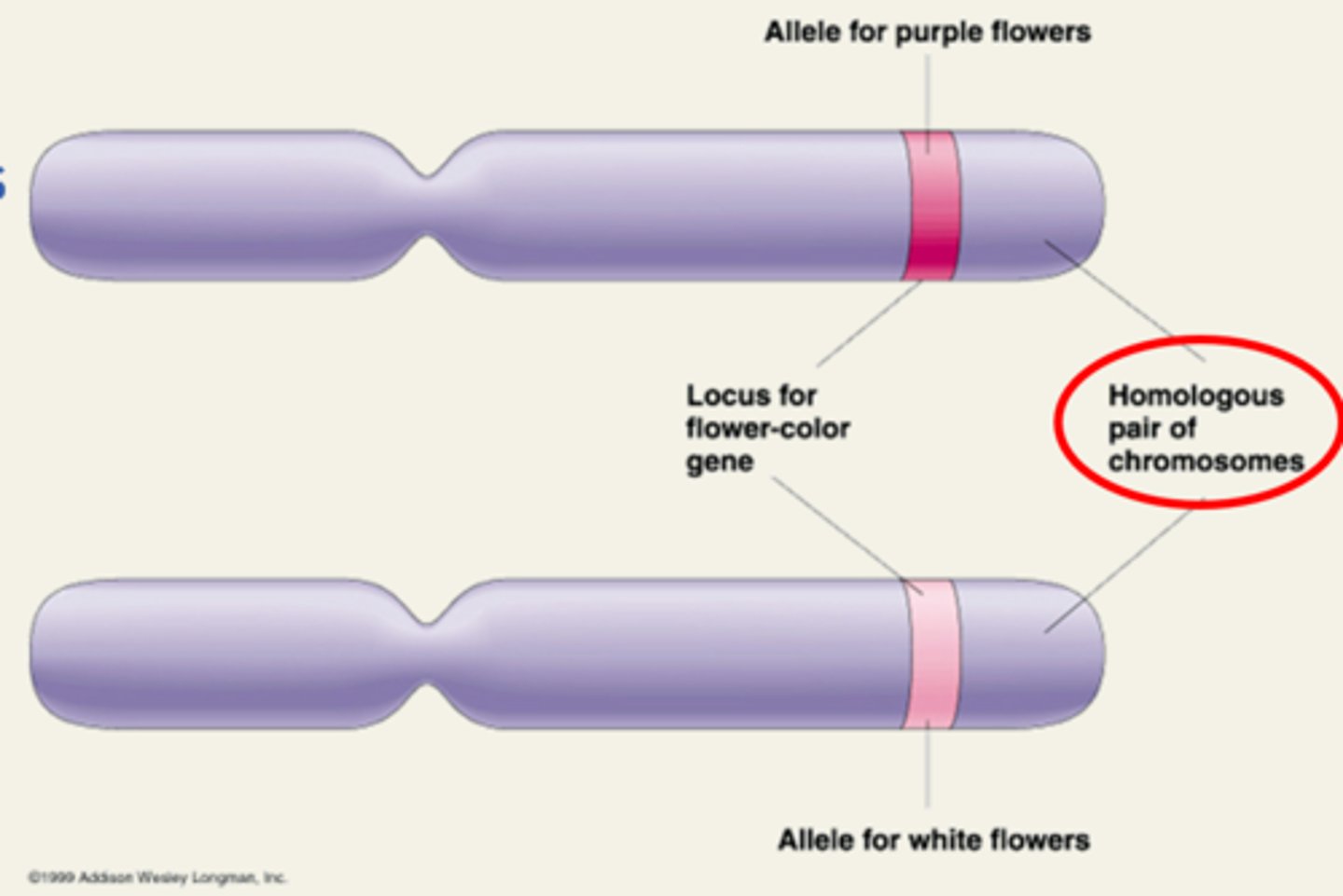
Locus
A specific location on DNA
Gene
A sequence at a particular locus that codes for a protein
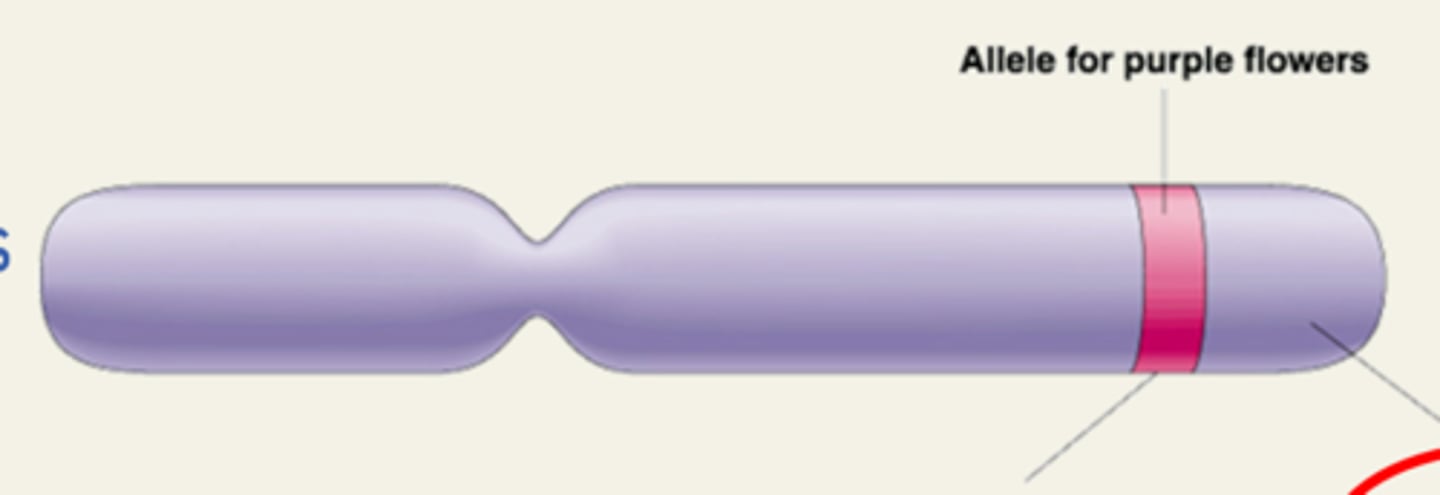
Allele
An alternate form of a gene (multiple)
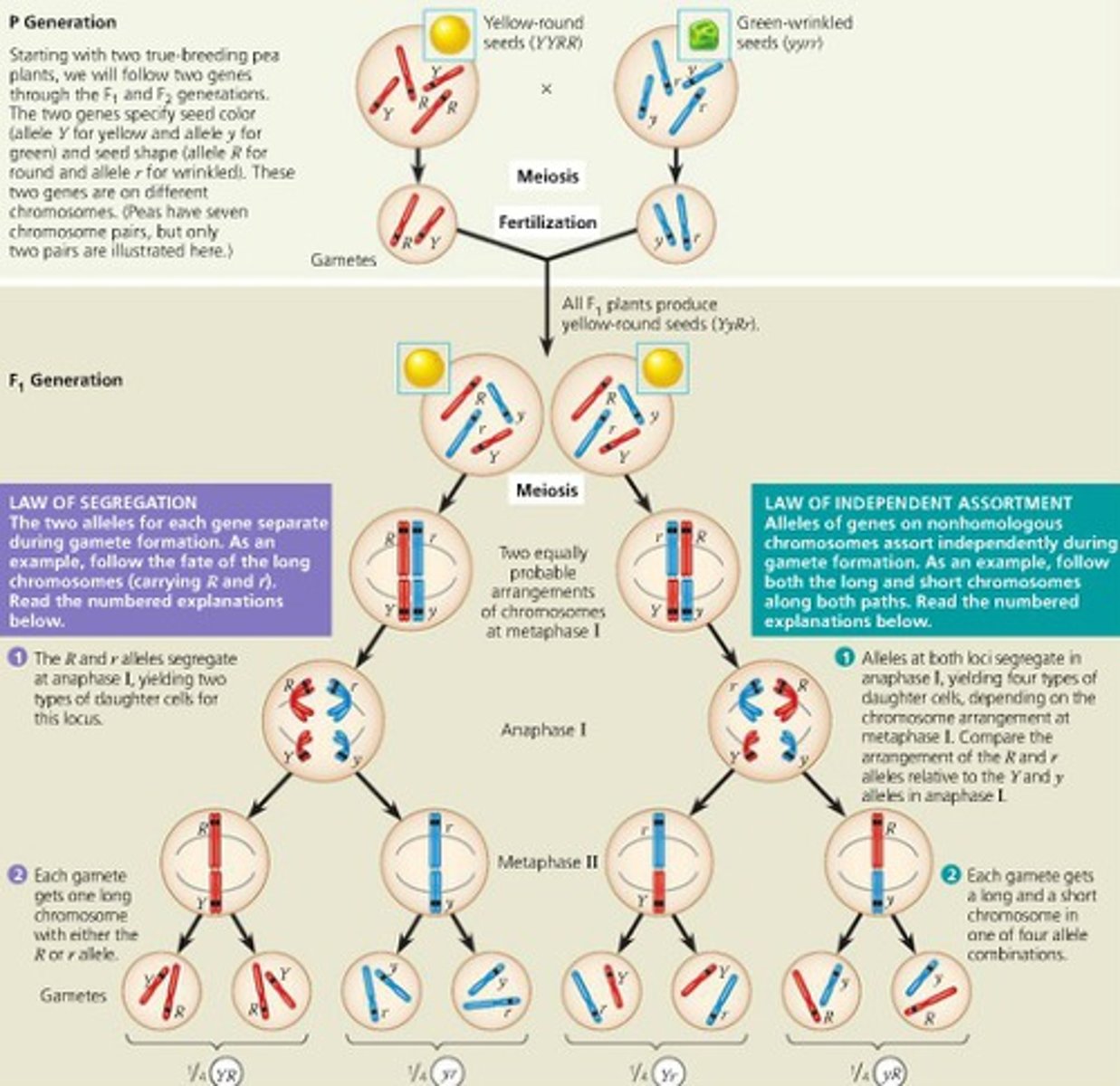
Law of Segregation
Alleles of the same gene will separate from each other during meiosis.
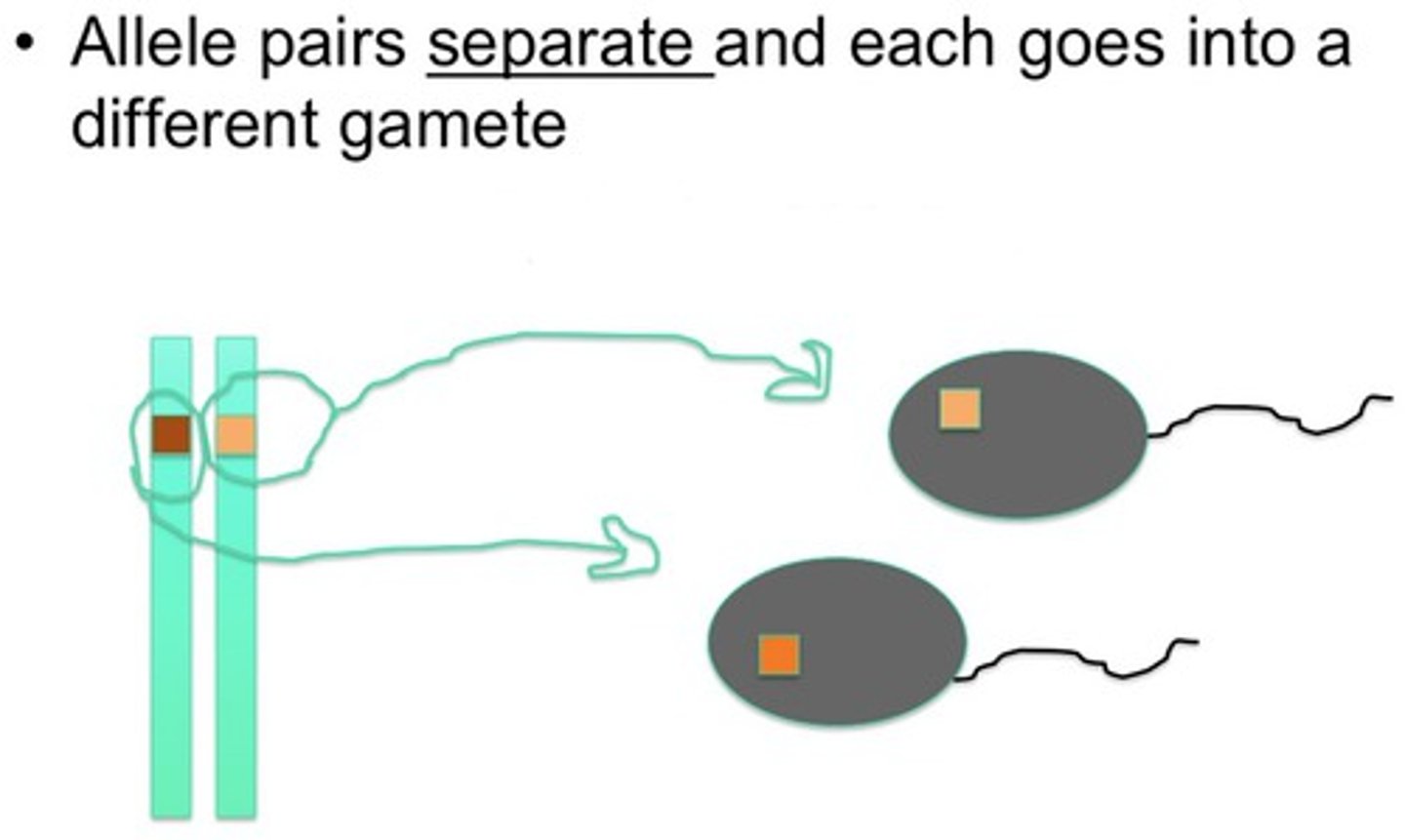
What process leads to many combinations of alleles in gametes?
The Law of Segregation leads to many combination of alleles
Law of Independent Assortment
Alleles of different genes will separate independently from one another, inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of another trait
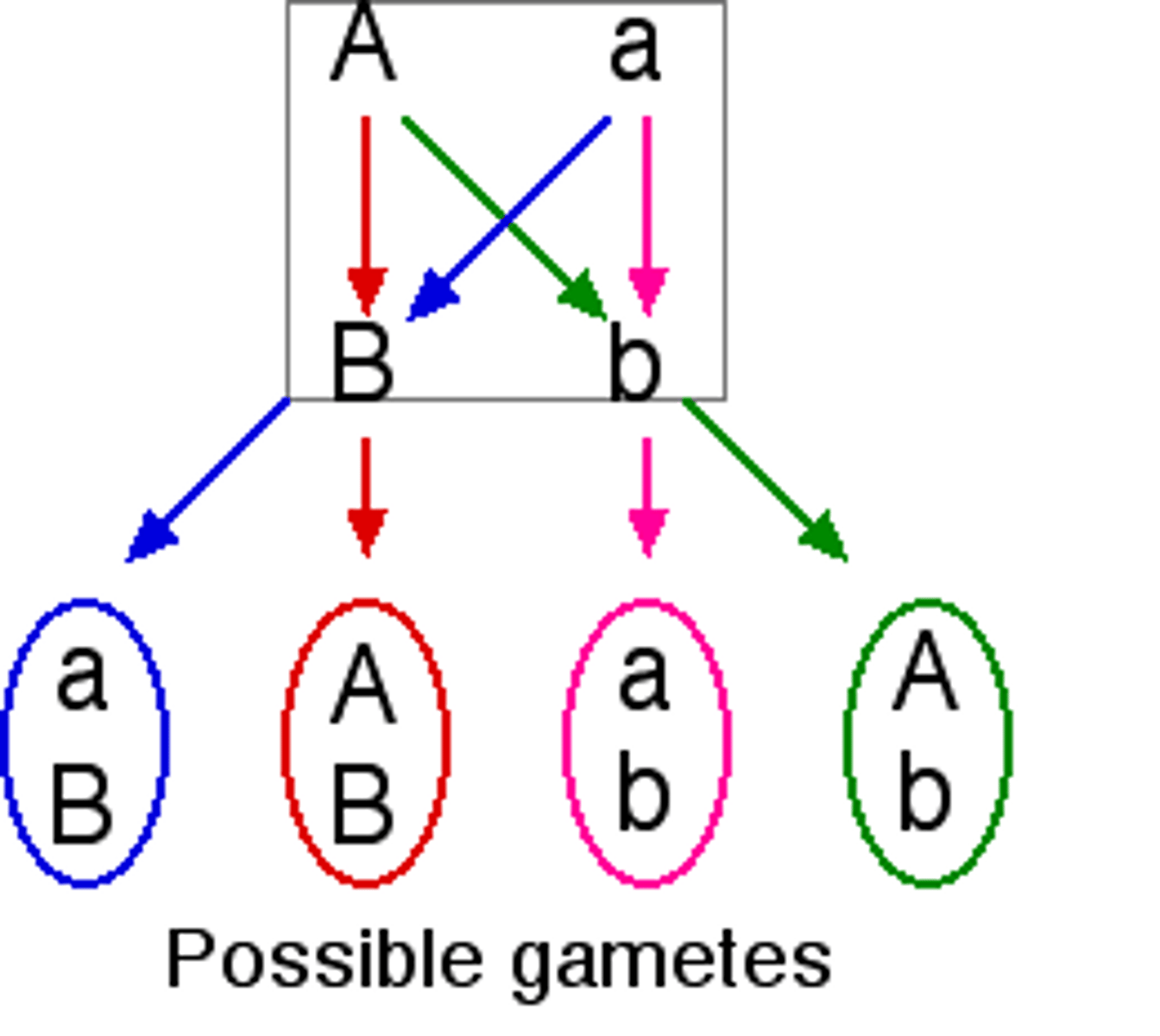
Mendel's Laws
Law of Segregation and the Law of Independant Assortment
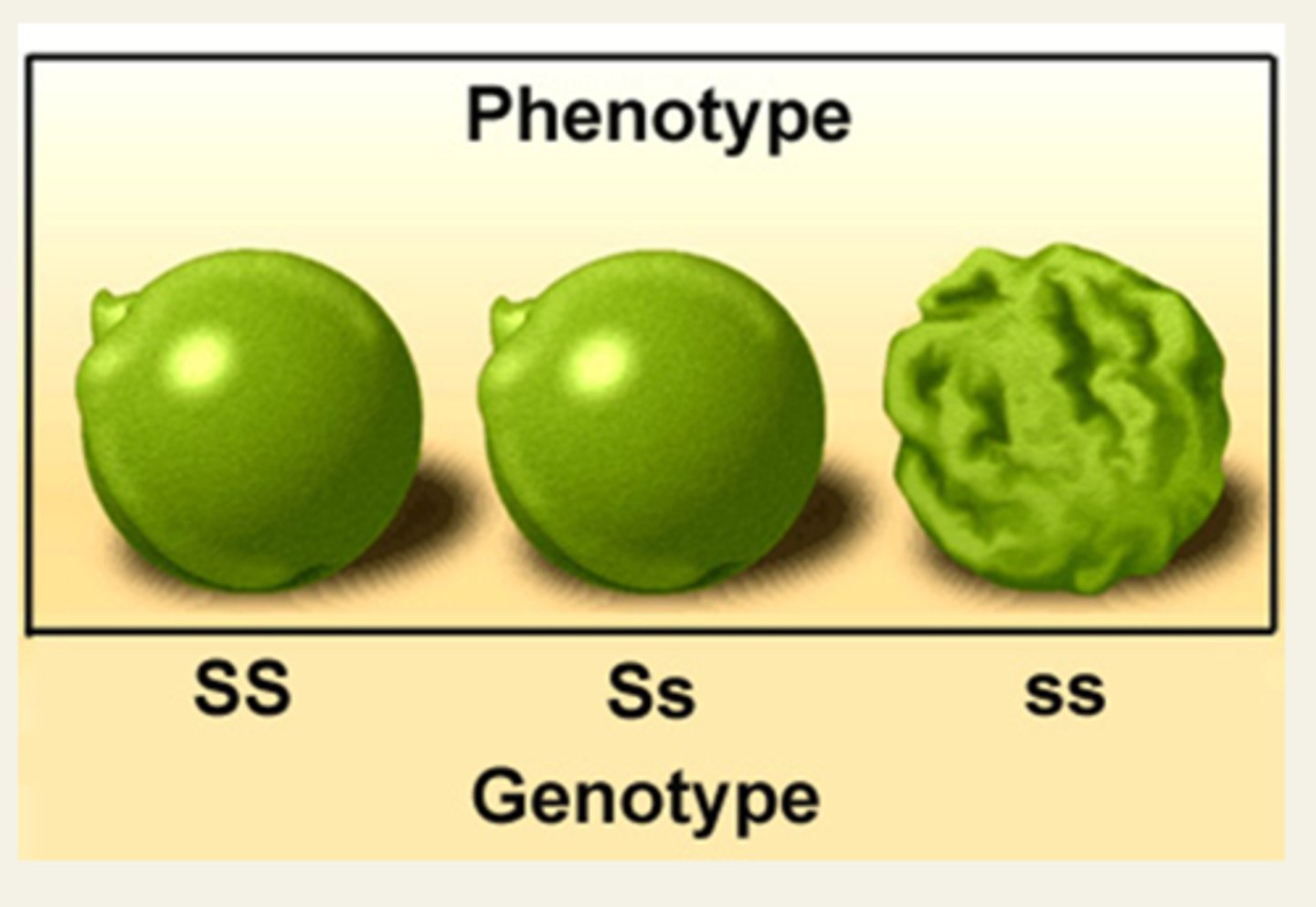
Genotype
The actual alleles that are inherited such as Ss, SS, or ss (Genetic Makeup)
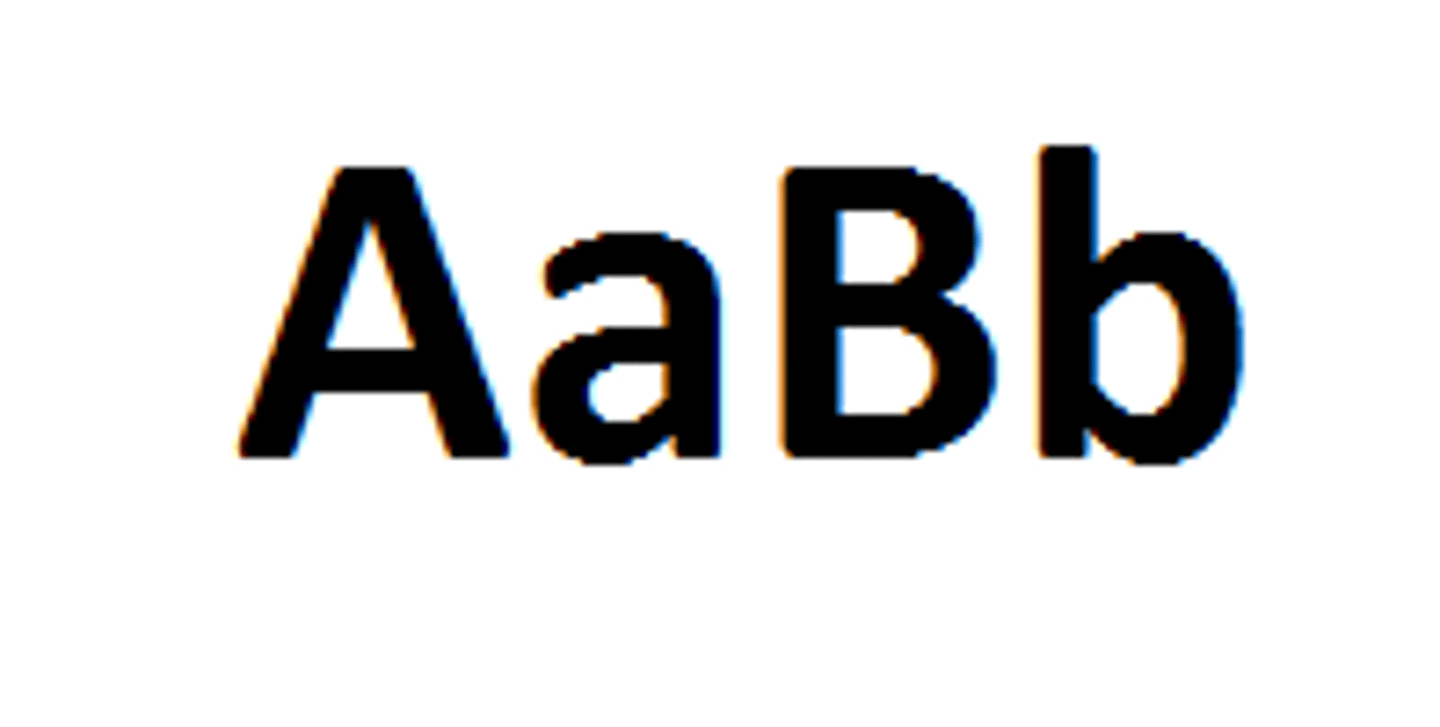
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits according to the Genotype
Homozygous
The two alleles in an individual are the same
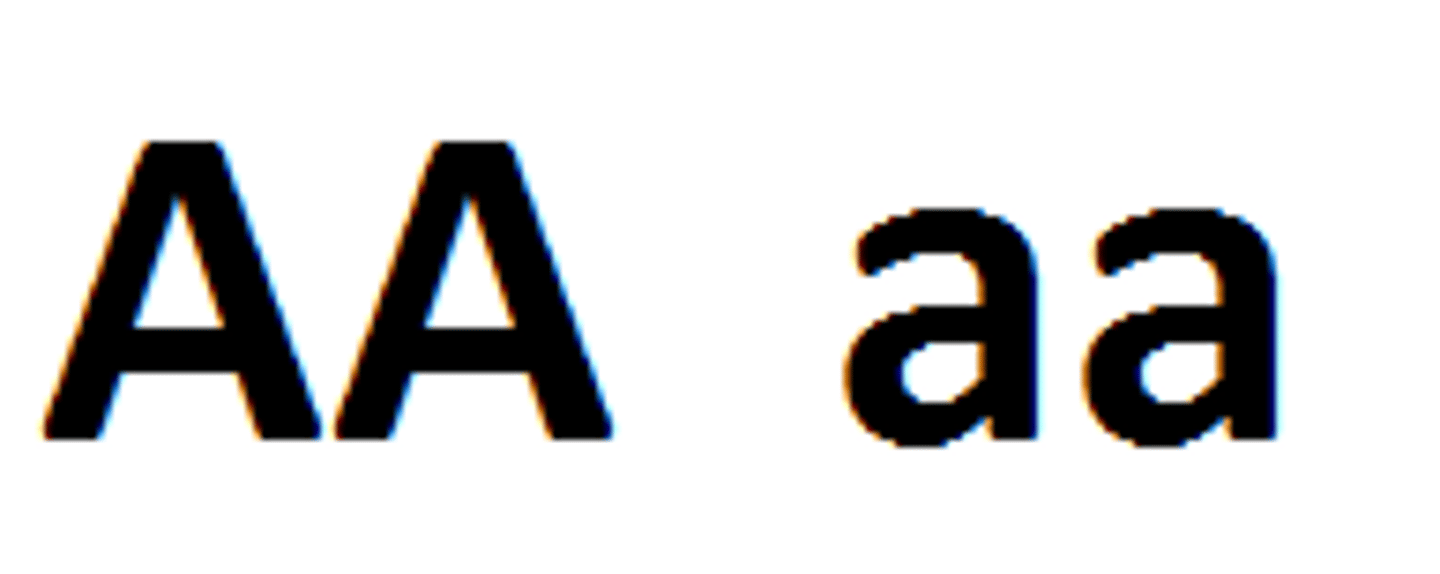
Homozygous Dominant
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and dominant (AA)

Homozygous Recessive
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and recessive (aa)
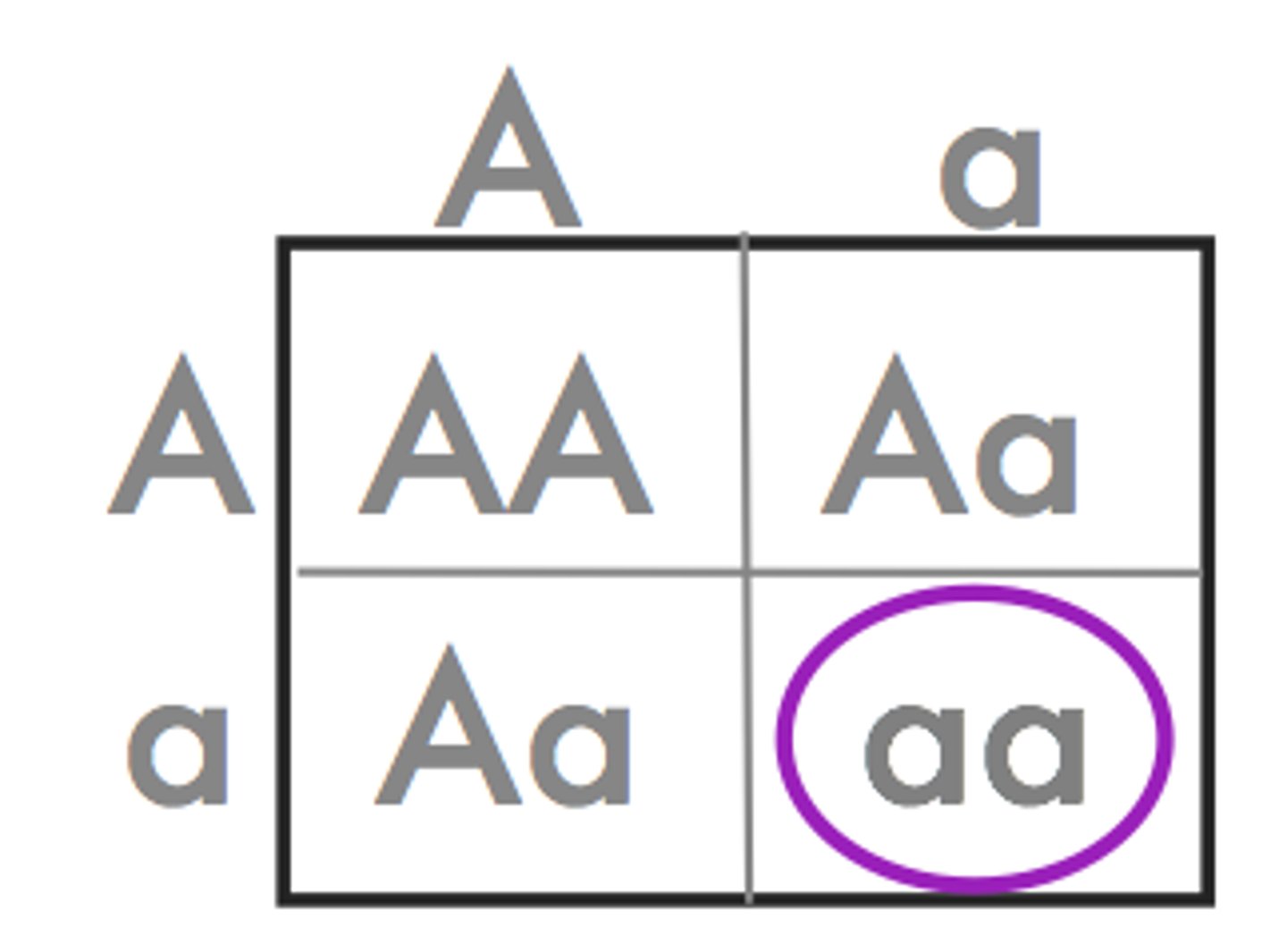
Heterozygous
The two alleles an individual has for a gene are different

Expression of the Dominant Trait
When the individual is either Heterozygous for an allele or Homozygous Dominant for an allele
Expression of the Recessive Trait
When the individual is Homozygous Recessive for an allele
Incomplete Dominance
Situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele, AKA Intermediate Phenotypes
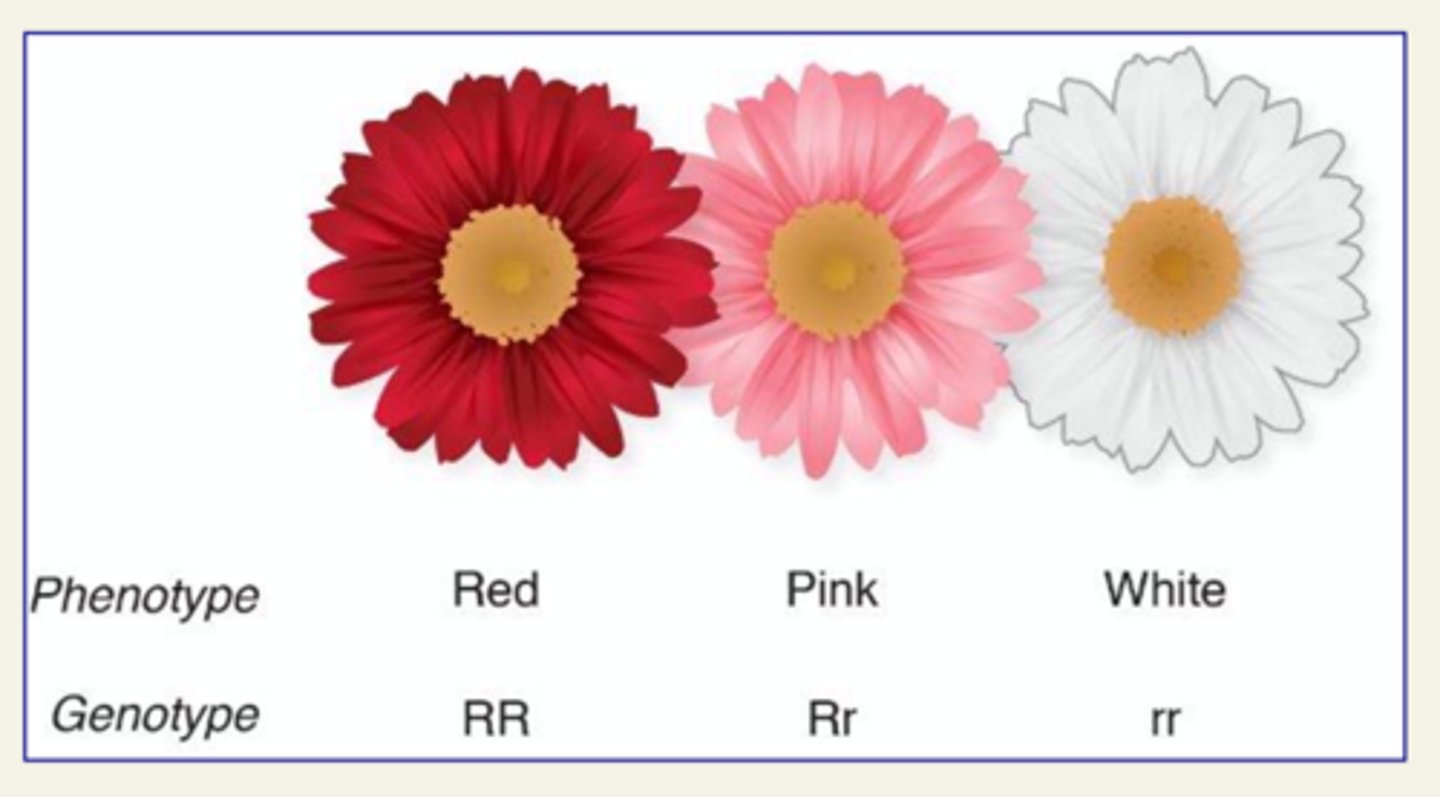

Codominance
When both alleles are expressed in the phenotype

Punnet Square
A diagram that shows the possible genotypes of a particular cross between two individuals
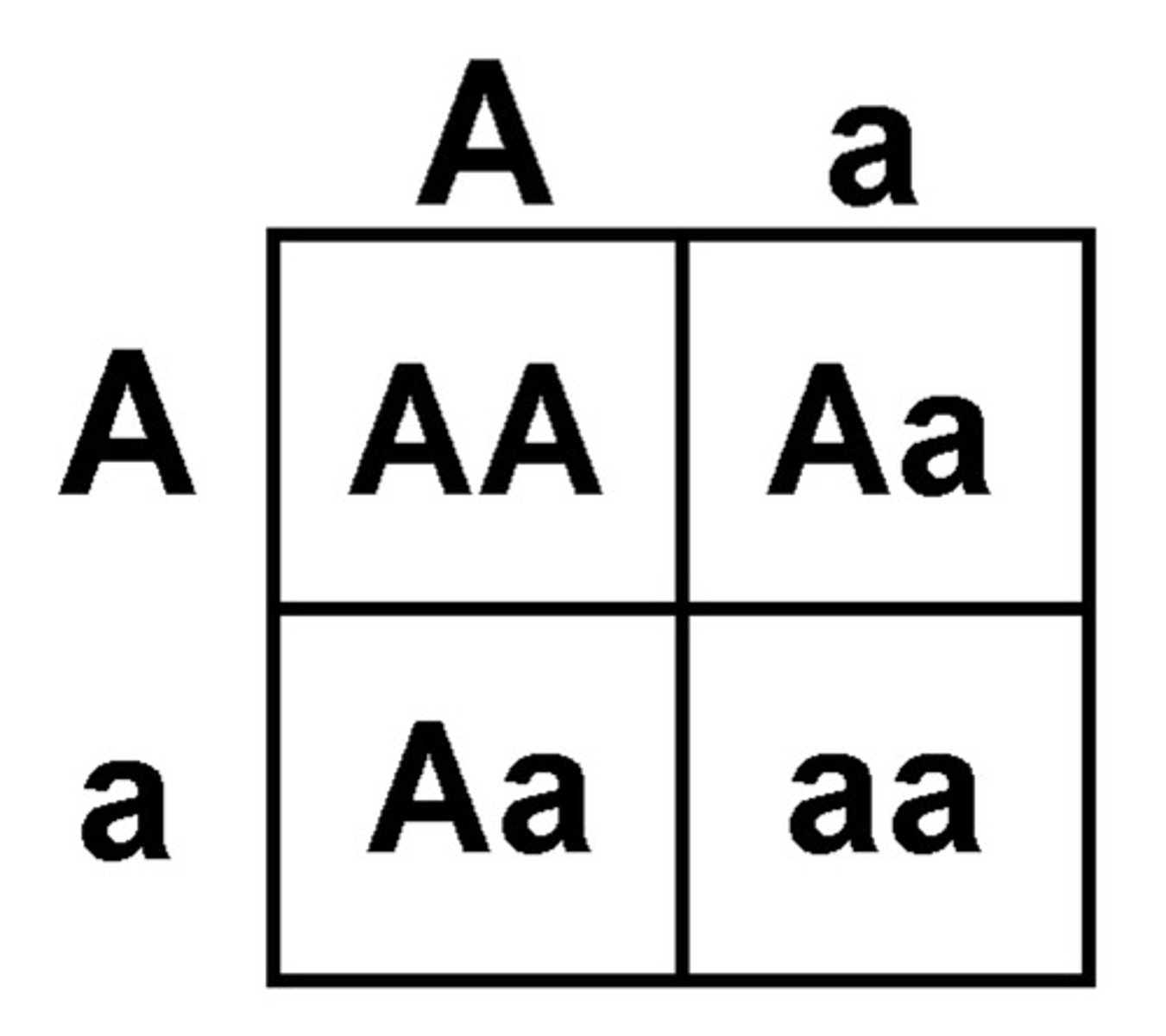
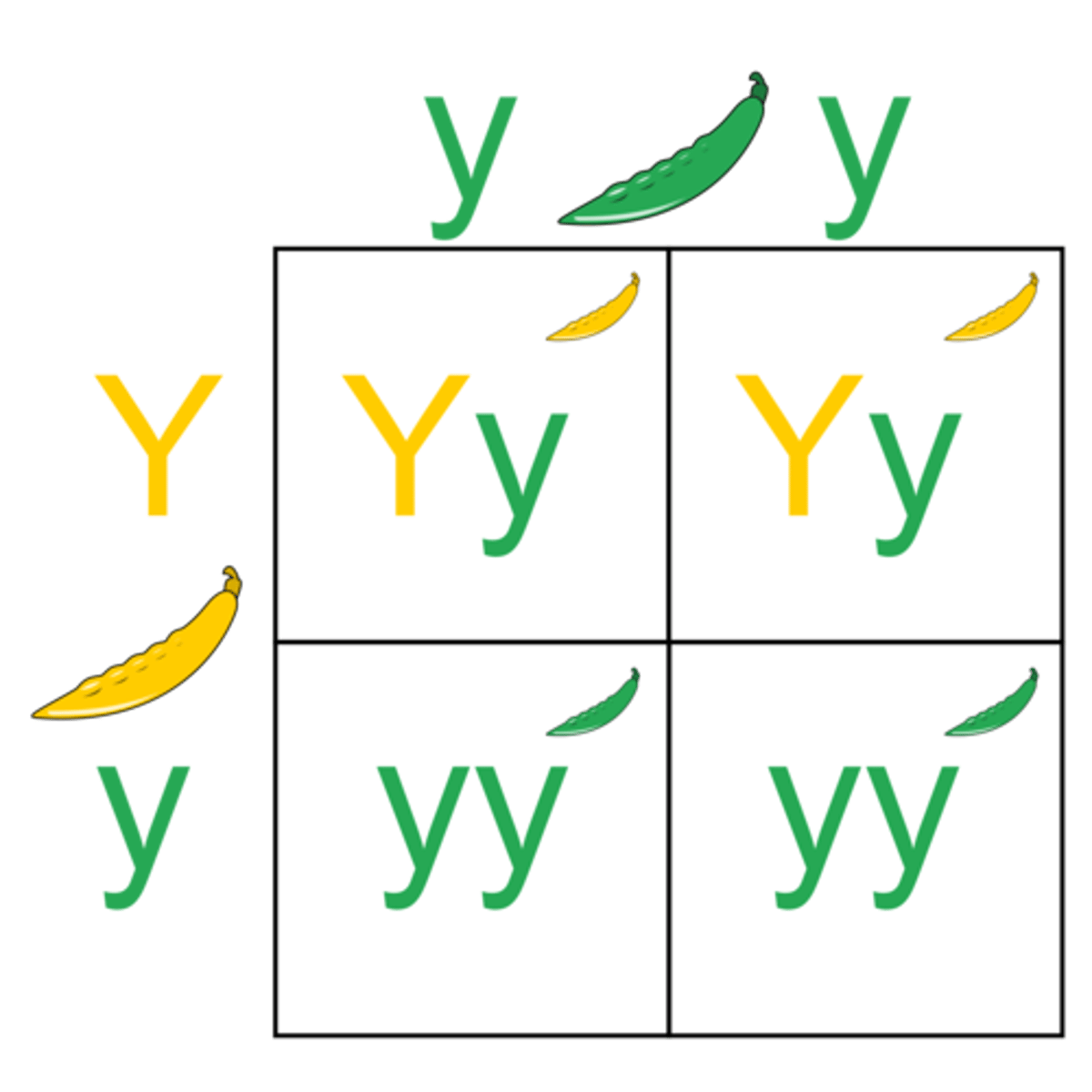
Monohybrid Cross
Crosses ONE gene
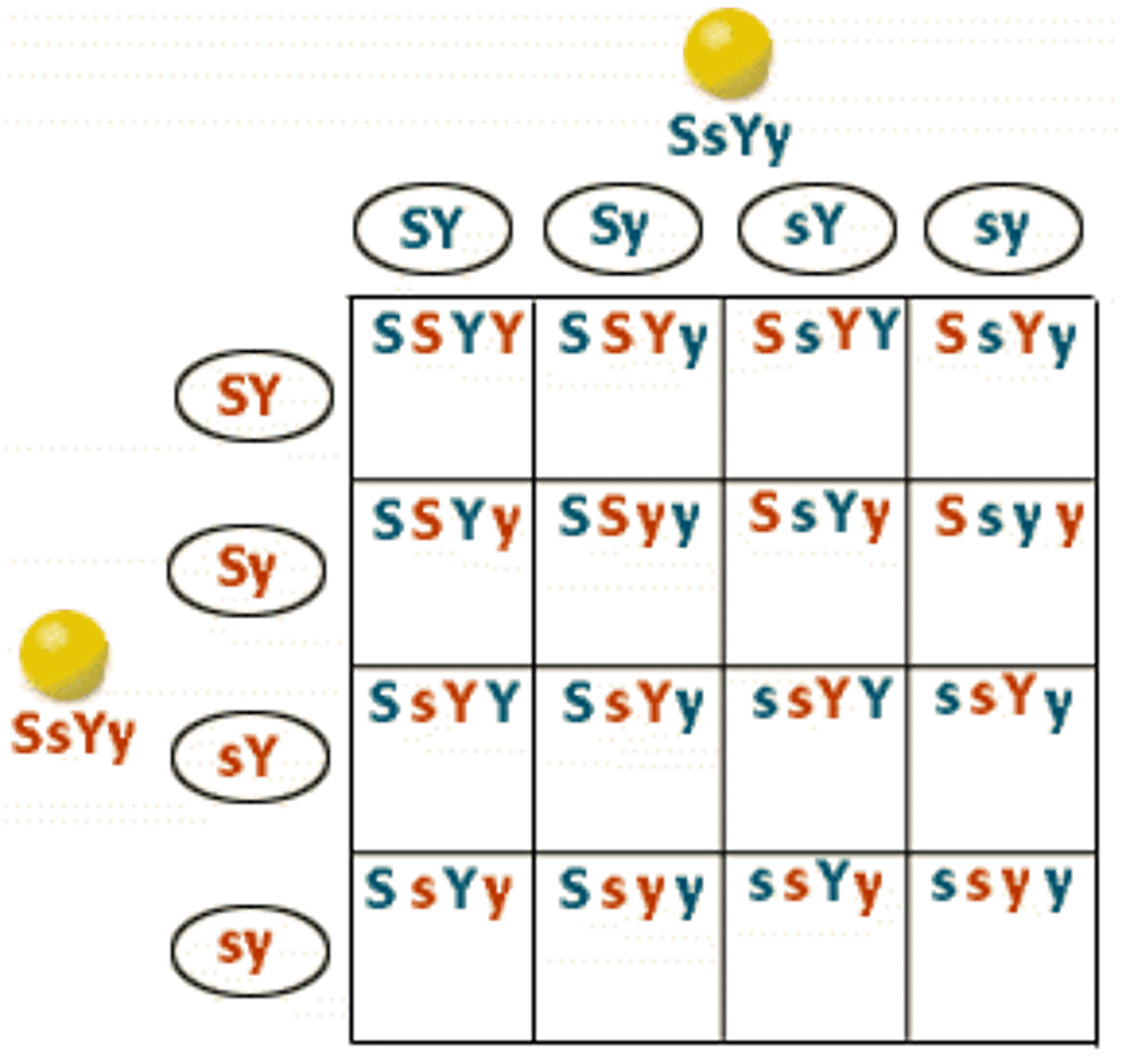
Dihybrid Cross
Crosses TWO genes
Linked Genes
Genes located on the same chromosome that tend to be inherited together in genetic crosses.
Katrina Pinili
The Instructor
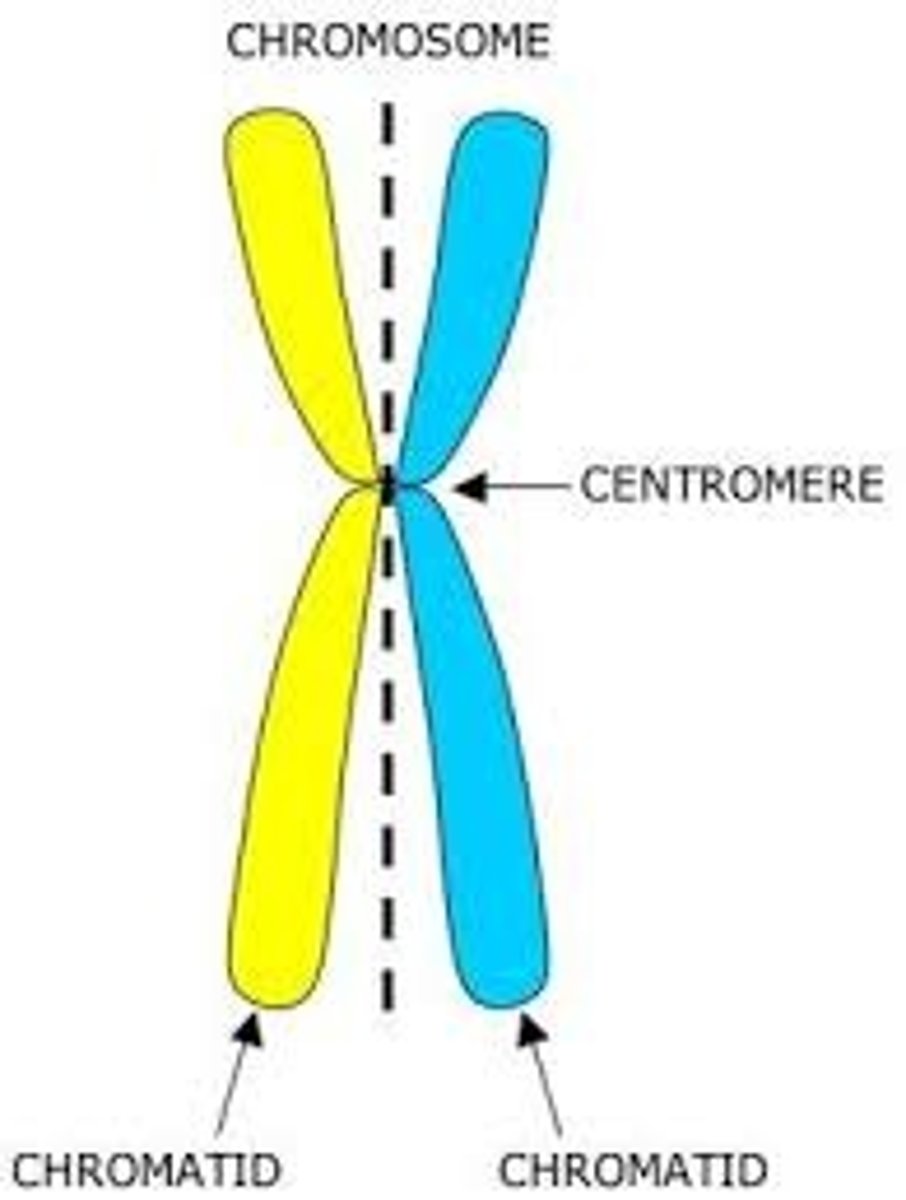
Sister Chromatids
Replicated forms of a chromosome joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis or meiosis II.
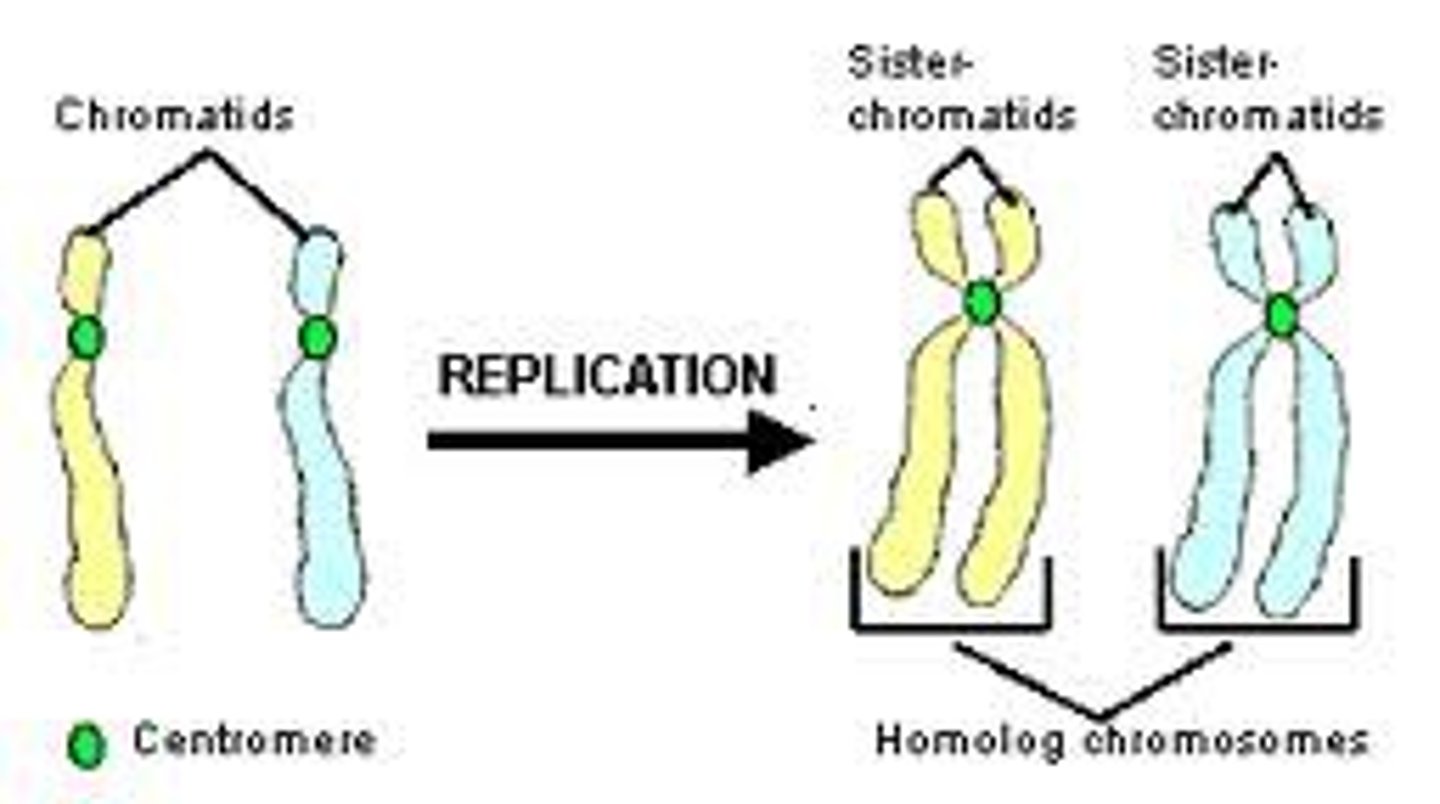
Non-Sister Chromatids
chromatids from different homologs in a pair
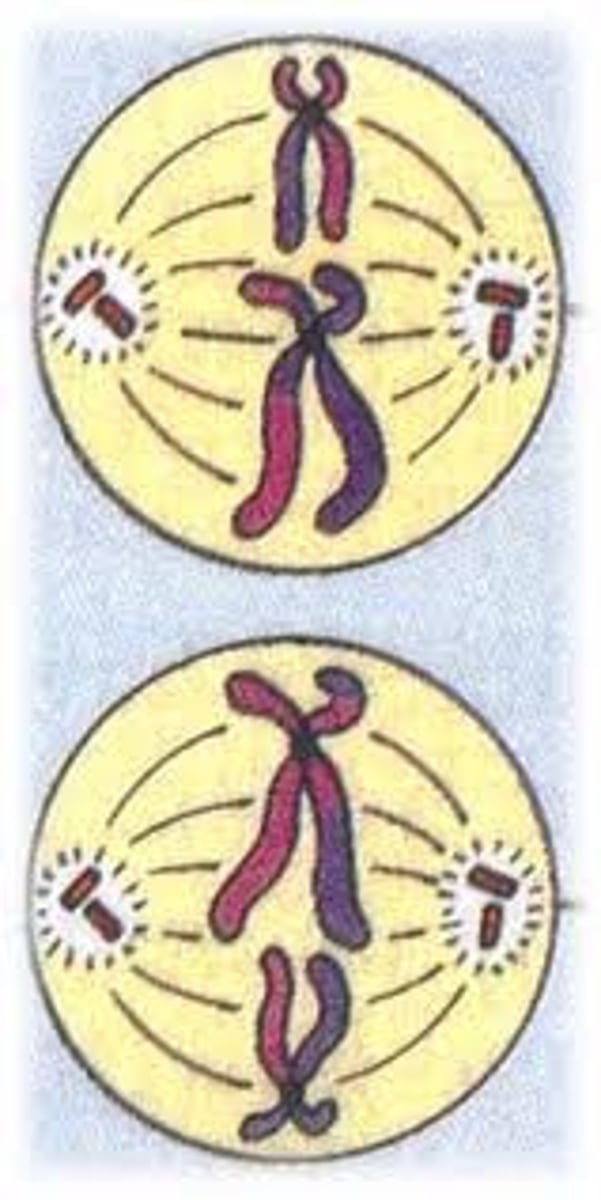
Meiosis 1
Separation of Homologous Chromosomes
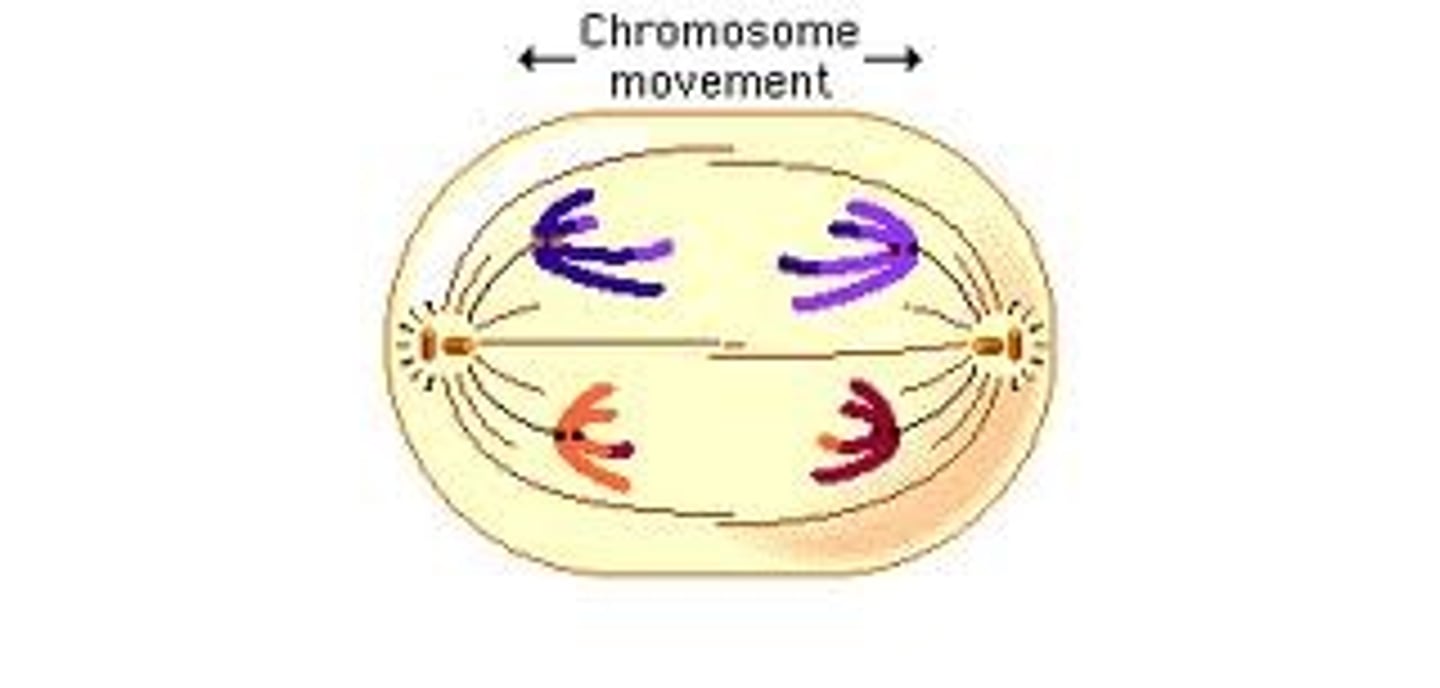
Meiosis 2
Separation of Sister Chromatids