nutritional/obesity
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
When counseling a group of overweight individuals, the nurse should stress that during parties, the oxidation of alcohol provides how many kilocalorie/gram to one's diet?
A) 4 kcal/g
B) 5 kcal/g
C) 7 kcal/g
D) 9 kcal/g
C
Feedback: The oxidation of proteins provides 4 kcal/g; fats, 9 kcal/g; carbohydrates, 4 kcal/g; and alcohol, 7 kcal/g.
A dietitian is working with a morbidly obese client in an effort to facilitate weight loss. Which of the dietitian's following teaching points about the nature of adipose tissue should be included in the client education?
A) “Our ultimate goal is going to be eventually rid your body of adipose tissue or fat.”
B) “Your fat cells can be considered to be one large energy storage organ that also has a role in hormone production.”
C) “We ideally would like to maximize your levels of brown fat and minimize those of white fat.”
D) “Obesity is normally the result of the number of 'pre-fat' cells an individual is born with.”
B
Feedback: Fat cells are collectively considered a large body organ that is metabolically active in the uptake, synthesis, storage, and mobilization of lipids, which are the main source of stored fuel for the body; the role of adipose tissue as an endocrine organ has also been recently elucidated. It is neither a desirable nor reasonable goal to entirely rid the body of fat, given the key roles it plays in homeostasis, and brown fat is not common in postnatal life. Preadipocytes have been shown to play a role in obesity, but the condition is still primarily a consequence of energy intake exceeding output.
Which of the following statements most accurately captures an aspect of the basal metabolic rate (BMR)?
A) The resting BMR constitutes a small fraction of the total body energy needs.
B) Females tend to have a lower BMR than males due to a smaller skeletal muscle mass.
C) Variations in muscle mass account for much of the differences in the BMR that exist between individuals.
D) The BMR remains consistent throughout the life span.
C
Feedback: Body size and skeletal muscle mass account for most of the individual variations in BMR that exist between individuals. The resting BMR accounts for 50% to 70 % of the total body energy needs, and increased quantities of adipose tissue account for the lower average BMR in females as compared to males. BMR decreases with age.
Which of the following clients would be most reasonably expected to have the highest basal metabolic rate (BMR), assuming none is obese or malnourished?
A) A 22-year-old man, 69 inches tall, who has a sedentary lifestyle
B) A 47-year-old woman, 65 inches tall, who swims 1 mile four times a week
C) A 29-year-old woman, 61 inches tall, who is pregnant and on bed rest
D) A 60-year-old man, 72 inches tall, who is recovering from heart surgery
D
Feedback: Although age, sex, physical state, and pregnancy are contributing factors, variations in BMR among individuals are chiefly related to skeletal muscle mass and body size. Therefore, regardless of health and fitness status, the tallest and heaviest person in any sample will probably have the highest BMR.
When examining the types of energy expenditure, which of the following statements is accurate?
A) People who are more active and who fidget may have less fat gain than those with decreased nonexercise activity thermogenesis.
B) Parasympathetic stimulation will cause brown fat to generate more heat than other stimulations.
C) Recent research indicates that obese patients with persistent excess caloric intake have decreased sympathetic activity.
D) Carbohydrate intake increases the normal metabolic rate more significantly than other nutrients.
A
Feedback: Nonexercise activity thermogenesis includes the energy expended in maintaining posture and in activities such as fidgeting. People with increased NEAT may have less fat gain than those with decreased NEAT. Sympathetic stimulation causes brown fat to generate more heat. Research shows that obese patients with excess caloric intake have increased sympathetic activity. Proteins, not carbohydrates, increase metabolic rate more significantly
When explaining the role of protein and the nine essential amino acids' needs of the body to a group of students, the nurse should emphasis that which of the following foods are complete proteins (foods that provide the essential amino acids in adequate amounts)? Select all that apply.
A) Milk
B) Fish
C) Poultry
D) Nuts
E) Grains
A, B, C, D, E
Feedback: All of the foods listed are complete proteins from both animals and vegetable sources.
A 17-year-old female has announced to her family physician a desire to wholly eliminate fats from her diet. Which of the following aspects of the role of fats would underlie the physician's response to the client?
A) Apart from providing energy, fats are necessary as carriers of certain vitamins and are precursors to prostaglandins.
B) An extreme low-fat diet is associated with an increase in undesirable HDL cholesterol.
C) Fats are a key source of dietary nitrogen, and their elimination from the diet is associated with a negative nitrogen balance.
D) The total elimination of fat from the diet is associated with the development of ketosis.
A
Feedback: Far from being a completely undesirable component of the diet, dietary fats provide energy, function as carriers for the fat-soluble vitamins, serve as precursors of prostaglandins, and are a source of fatty acids. Low-fat diets tend to lower levels of HDL, which is a desirable form of cholesterol. Nitrogen balance is associated with protein, not fat, intake, and ketosis results from low-carbohydrate intake.
The physician has asked a newly diagnosed cardiac patient to begin taking omega-3 fatty acids to help prevent inflammation and blood clotting. The patient asks the nurse what types of food sources are high in omega-3 fatty acids. The nurse should educate the patient to increase his intake of which of the following items? Select all that apply.
A) Salmon
B) Walnuts
C) Seeds
D) Avocados
A, B, C
Feedback: All of the foods, except avocados, are rich with omega-3 fatty acids.
A 20-year-old male college student has recently finished a Thanksgiving dinner of heroic proportions while home for the holiday weekend. Which of the following phenomena would most likely have produced his sensation of satiety?
A) Stretch receptors in the stomach and small intestine signal the feeding center in the medulla.
B) Increased levels of leptin stimulate a decrease in appetite by way of the vagus nerve.
C) The breakdown of products of lipids such as ketoacids produces a decrease in appetite.
D) Cholecystokinin and glucagon-like peptide-1 suppress the hunger impulse.
D
Feedback: The presence of fat in the duodenum and nutrients in the small bowel results in the release of cholecystokinin and glucagon-like peptide-1, respectively, which suppress the feeding center located in the hypothalamus. Leptin and ketoacids are associated with the intermediate and long-term regulation of food intake rather than the short-term control that would signal the end of a meal or snack.
A 43-year-old male who is 5′10″ tall and weighs 216 lb has been informed by his nurse practitioner that his body mass index (BMI) is 31. Which of the following clinical conclusions based on these data would his nurse be most justified in rejecting?
A) Further investigation of his nutritional status is needed to supplement the BMI value.
B) The client faces an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and hyperlipidemia.
C) He is classified as being obese, likely as the result of the interplay of genetic and lifestyle factors.
D) The client is borderline obese but is not yet at the point of significantly increased risks to health.
D
Feedback: A BMI of 31 is classified as obese, and the client faces a risk of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and other health problems. While BMI is a valid instrument, other data sources are needed to supplement this value clinically. Obesity is considered to be an outcome of a variety of factors including heredity and lifestyle.
Which of the following statements about types of obesity is most accurate?
A) Upper body obesity is often referred to as being shaped like a “pear.”
B) A waist–hip ratio greater than 1.0 in men can be interpreted to mean upper body obesity.
C) Waist circumference is a measurement of subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue but not intra-abdominal adipose tissue.
D) A waist circumference of 40 inches or less in women is considered normal and therefore not associated with increased health risk.
B
Feedback: A waist–hip ratio greater than 1.0 in men and 0.8 in women indicates upper body or central (abdominal) obesity. Upper body obesity is referred to as being shaped like an apple. Waist circumference measures mostly subcutaneous and intra-abdominal adipose tissue. In males, a waist circumference greater than 40 inches (or 35 inches in females) is associated with increased health risk.
A 40-year-old female has been categorized as being obese, with a body mass index (BMI) of 33.2. Which of the following health problems place the client at a significantly increased risk for when compared with individuals with a BMI below 25? Select all that apply.
A) Cardiac arrhythmias
B) Osteoarthritis
C) Multiple sclerosis
D) Atelectasis
E) Gallbladder disease
F) Insulin resistance
B, E, F
Feedback: Obesity is associated with significantly increased risk for osteoarthritis due to bone and joint stress. Insulin resistance and gallbladder disease are also identified consequences of obesity. Cardiac arrhythmias are less likely to result directly from obesity, given their etiology rooted in electrical conductivity. Multiple sclerosis and other neurological effects are also unlikely, and atelectasis is not commonly a direct effect of high levels of body fat.
Frustrated with his inability to lose weight despite attempting numerous fad diets, a 42- year-old male who is 5′11″ and 270 lb has visited a clinic to gain tools to achieve longterm weight loss. Which of the following statements by the clinician is most accurate?
A) “Recent findings have determined that obesity is largely genetic and not preventable, but that doesn't mean we can't work together to help you lose weight and keep it off.”
B) “A combined approach of behavior therapy, changing your lifestyle habits, and increased physical activity gives the highest chance of long-term success.”
C) “By significantly changing the way you live your life, you could set and meet a goal of losing about 5% of your body weight each month.”
D) “Combined with regular exercise, a diet of taking in 500 to 1000 kcal/day will be the best approach.”
B
Feedback: A combined approach to weight loss including diet modification, exercise, and drug therapy has been shown to be successful in the treatment of obesity. In spite of a genetic component, obesity is still considered to be preventable. A reasonable rate of weight loss should be 5% to 10% of total body weight over a 6-month period. A reduction in food intake of between 500 and 1000 kcal, not a total food intake of 500 to 1000 kcal, is often necessary in the treatment of individuals with high BMIs. Pharmacotherapy and surgery are available as adjuncts.
The patient who has been consuming a very low-calorie diet (VLCD) of 450 kcal/day should be assessed for which of the following high-risk complications? Select all that apply.
A) Irregular heart rhythms
B) Bone/joint inflammation
C) Abdominal pain related to gallstones
D) Flank pain and spasm associated with kidney sludge
E) Elevated cholesterol levels
A, C
Feedback: VLCDs have higher risks, including abnormal heart rhythms and cholelithiasis. Anyone on this diet should be under direct supervision of a medical professional. Usually bone/joint pain/inflammation decreases with weight loss. Kidney sludge is usually related to the amount of water a person consumes.
Which of the following measures would likely be rejected as part of a first-line weight loss plan for a client with a BMI of 30.2, type 2 diabetes, and hypertension?
A) Prescription drug therapy
B) Gastric bypass
C) Calorie reduction by 500 to 1000 kcal/day
D) 30 minutes or more of moderate-intensity activity at least 3 days per week
B
Feedback: Weight loss surgery should be limited to individuals with a BMI greater than 40 or those with a BMI greater than 35 with comorbid conditions in whom medical therapy has failed. Calorie reduction is appropriate for anyone with a BMI of 25 to 29.9 plus two risk factors (in this case, type 2 diabetes and hypertension). Prescription drug therapy can be considered for those with a BMI of 30 or more, and increased physical activity, although it does not lead to significant weight loss, helps prevent further weight gain and reduces cardiovascular and diabetes risk beyond that achieved by weight loss alone.
During a humanitarian trip to an underdeveloped country, a medical student is assessing a 6-year-old male who has a protuberant abdomen, dry hair, and wrinkled skin. The child's heart rate is 59 beats/minute, blood pressure 89/50, and temperature 95.2°F (35.1°C). What is the most likely etiology of the child's health problems?
A) A diet lacking in fat-soluble vitamins
B) Fluid and electrolyte imbalances secondary to low -carbohydrate intake
C) A diet that is low or high in carbohydrates but low in fat
D) A diet deficient in both protein and calories
D
Feedback: The child's presentation is typical of marasmus, a diagnosis caused by deficiencies in protein and calorie intake.
A nurse who works on an oncology ward is providing care for a 68-year-old female patient with a diagnosis of lung cancer with bone metastases. The client is experiencing rapid weight loss and is exhibiting the signs and symptoms of malnutrition. The nurse would recognize that which of the following factors is most likely contributing to the client's malnutrition?
A) Autoimmune responses associated with acute illness are inhibiting anabolism.
B) Chronic hypoxia is precluding many of the aerobic processes required in body maintenance and repair.
C) Protein mass is being lost from the liver and other organs, and the liver is synthesizing fewer serum proteins.
D) Intestinal malabsorption is occurring as a result of tumor metastases.
C
Feedback: Ill individuals are prone to disruption in protein balance, in which protein breakdown exceeds protein rebuilding. Protein mass is lost from the liver, gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, and heart. As protein is lost from the liver, hepatic synthesis of serum proteins decreases and decreased levels of serum proteins are observed. Autoimmune processes, hypoxia, and malabsorption as a result of metastases are unlikely factors.
A 20-year-old male who is addicted to crystal methamphetamine has been admitted to a hospital with a diagnosis of protein–calorie malnutrition after many months of inadequate food intake. Which of the following treatment plans would the care team most likely favor?
A) Intravenous infusion of albumin coupled with vitamin supplementation
B) Total parenteral nutrition
C) Incrementally feeding combined with vitamin and mineral supplementation
D) Rapid administration of normal saline and carbohydrates
C
Feedback: Slow administration of protein and calories combined with mineral and vitamin supplementation is important in the treatment of protein–calorie malnutrition. Albumin transfusions and total parenteral feeding would likely not be necessary, and rapid administration of fluids and carbohydrates may precipitate congestive heart failure.
A teenage female has been admitted for complications resulting from bulimia nervosa. She has abused laxatives for many years and has been self-inducing vomiting since the age of 9. The nurse's admission assessment should pay close attention to which of the following complications that can arise from this disorder? Select all that apply. Assess for
A) dry, cracked lips and poor skin turgor.
B) missing tooth enamel and increased number of dental cavities.
C) painful swallowing and stomach cramping related to reflux and esophagitis.
D) fruity breath and labored, deep, gasping respirations.
E) jaundice of the skin and eyes.
A, B, C
Feedback: Distracters A, B, and C are associated with complications of bulimia nervosa. Answer choice A relates to dehydration/fluid volume deficit; answer choice B relates to dental abnormalities associated with high acid content of the vomitus; answer choice C relates to esophagitis. Answer choice D is indicative of DKA primarily caused by undiagnosed or undertreated diabetes. Jaundice of the skin and eyes is usually associated with liver disease.
As part of the intake protocol at an eating disorders clinic, an interview precedes a physical examination. Which of the following questions would a clinician be justified in excluding from an intake interview of a 16-year-old female referred by her pediatrician for the treatment of anorexia nervosa?
A) “Do you remember when your last menstrual period was?
B) “Have you noticed any new hair growth on your body in the last several months?”
C) “Have you had any episodes of shortness of breath in the recent past?”
D) “Can you tell me about some of the habits that you have related to food in your daily routine?”
C
Feedback: Respiratory complications are not a noted consequence of anorexia nervosa. Amenorrhea, development of lanugo, and complex and important rituals around food preparation are common.
A client informs the nurse that they do not want to take pills in order to increase the level of omega-3 acids. Which foods can the nurse encourage the client to eat that will provide adequate amounts of omega-3? Select all that apply.
Walnuts
Flaxseeds
Sunflower seeds
Salmon
Beef liver
1,2,4
Two types of obesity are recognized: upper body obesity and lower body obesity. How is the type of obesity determined?
Chest/hip circumference
Waist/hip circumference
Waist circumference/weight
Chest circumference/weight
2
The nurse assessing a client with obesity prioritizes recommending screening tests for which three conditions associated with obesity? Select THREE.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus
Dyslipidemia
Cholecystitis
Hypertension
Gastric reflux disease
Osteoarthritis
1,2,4
The health care provider reviews the waist–hip ratio of a male client. The ratio is 1.0. Which interpretation is most accurate for this result?
Upper body obesity
Gluteal–femoral obesity
Peripheral obesity
Lower body obesity
1
A client on a diet that is very low in carbohydrates and high in protein submitted a urine specimen for analysis. Which of the following does the nurse expect to see when the results come back?
Ketones
Glucose
Low specific gravity
Bacteria
1
A client with a body mass index of 32 would be classified as:
Class I obesity
Statistically healthy
Extremely obese
Underweight
1
Which response by the nurse best answers a client's question regarding the purpose of white fat?
Heat production
Energy storage
Blood sugar regulation
Gluconeogenesis
2
A client asks the nurse what the body's primary source of immediate energy is. The best response would be:
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
Triglycerides
1
The nurse is assessing a client who is in the clinic for a routine physical. The client is female and has upper body obesity. How would the nurse describe the body type of this client?
Apple shaped
Rotund
Gynecoid shaped
Pear shaped
1
The nurse is caring for a group of hospitalized clients who require dietary prescriptions for their conditions. For which of these does the nurse encourage a diet with increased caloric intake? Select all that apply.
Fever
Burn injury
Pregnant client
Hypothyroidism
Postoperative
1,2,3,5
After receiving laboratory results indicating that a client has elevated cholesterol levels, a nurse is to instruct the client about dietary restrictions. The nurse should tell the client that the daily cholesterol intake should be restricted to:
Less than 200 mg
Less than 400 mg
Less than 300 mg
Less than 100 mg
3
A female client with a waist–hip ratio of 1.2 is beginning a weight loss program. Which teaching point(s) will the nurse prioritize providing the client as most relevant?
Select three (3).
"Based on your waist–hip ratio, you have developed gynoid obesity."
"Loss of visceral fat will be more rapid than loss of subcutaneous fat."
"Reducing your waist–hip ratio will reduce the risk for joint degeneration."
"A reduction in your waist–hip ratio will reduce the risk for heart disease."
"Weight loss will greatly reduce the risk for varicose veins in the legs."
"Correcting this form of obesity can reduce the risk for type 2 diabetes."
2,4,6
The nurse is considering targeting a risk group for preventive education. Which group would benefit most from this education?
Obese clients age 20–40
Clients with lupus erythematosus
Clients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Clients with anorexia nervosa
1
Which individualized plan does the nurse understand will be included in the initial plan of treatment for the client who seeks treatment for obesity? Select all that apply.
Increased physical activity
Reduced-calorie diet
Surgery
Medications
Lifestyle modification with behavioral therapy
1,2,5
During a humanitarian trip to an underdeveloped country a senior nursing student is assessing a 6-year-old child who has a protuberant abdomen, dry hair, and wrinkled skin. The child's heart rate is 59 beats/min, blood pressure 89/50 mm Hg, and temperature 95.1°F (35.1°C). For which should the student assess the child?
diet deficient in both protein and calories
fluid and electrolyte imbalances secondary to low carbohydrate intake
diet lacking in fat-soluble vitamins
diet that is high in carbohydrates but low in fat
1
A client in high school is brought to the emergency department after fainting at school. Assessment findings reveal severe indigestion, tooth erosion, enlarged parotid gland, and an irregular heartbeat. What diagnosis should the nurse suspect, given this age population?
Bulimia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa
Eating disorder not otherwise specified
Binge-eating disorder
1
The nurse is assessing an adolescent who has a body mass index (BMI) that places them in the 96th percentile. Which assessment does the nurse prioritize as most important related to identifying possible complications of the client's BMI?
Heart rate and rhythm
Kidney function tests
Waist circumference
Fasting blood glucose level
4
A client diagnosed with a binge-eating disorder has made a goal to establish a regular, healthy eating pattern. Select the interventions the client should implement. Select all that apply.
Exercising regularly
Increasing consumption of sugar
Keeping a daily food intake report
Making a meal plan
Avoiding alcohol
Eating six small meals a day
1,3,4,5
In collecting assessment data on the school-aged population, which factor could be the most significant predictor of childhood obesity?
Low self-esteem
Low socioeconomic status
Having parents who are obese
Living in a rural neighborhood
3
A nurse observes a client moving restlessly in the hospital bed. Which type of energy expenditure can be affected by this activity?
Environmentally related thermogenesis
Diet- and exercise-induced thermogenesis
Resting energy equivalent
Nonexercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT)
4
An obese client informs the nurse that they are pregnant and is concerned about their baby's health because they realize that they are obese. Which risk factor does the nurse understand may occur regarding the parent's obesity?
Cardiac arrhythmias
Congenital anomalies
High birth weight leading to cesarean birth
Peripheral vascular disease
3
When educating a client recently diagnosed with the metabolic syndrome, the nurse begins by explaining how adipose tissue secretes which substance that regulates sensitivity to insulin?
Adiponectin
C-reactive protein
Inflammatory mediators
Leptin
1
Which statement is true concerning energy requirements across the lifespan?
A pregnant client needs an additional 500 kcal/ day.
A newborn requires more kcal/kg of body weight than a 10-year-old.
Regardless of sex, adolescents require 50 kcal/kg of body weight.
Growth spurts require additional protein but no additional kcal.
2
A client has a mineral deficiency that inhibits glucose absorption in the small intestine. Which mineral would the nurse assess for deficiency?
Calcium
Sodium
Magnesium
Potassium
2
A large, high-calorie meal has resulted in the intake of far more energy than a person requires. What will the individual's body do with the excess carbohydrates provided by this meal?
Excrete most of the excess polysaccharides through the kidneys
Create structural proteins from some of the carbohydrates and store the remainder as triglycerides
Convert the carbohydrates into amino acids in preparation for long-term storage
Convert them into glucose and store them in the liver and muscles
4
How does the full-term newborn help to regulate its body temperature?
Shivering
Brown fat
Decreased sweat
Peripheral vascular constriction
2
A client is having difficulty with a weight loss plan and asks the nurse, "What is wrong with me? Why can't I lose this weight?" Which rationale might the nurse offer to this client?
"Obesity ultimately results from an energy imbalance of eating too many calories and not getting enough exercise."
"Obesity ultimately results from a metabolic disorder causing a decrease in the metabolic rate."
"Obesity ultimately results from a person's inability to control themself when around food."
"Obesity ultimately results from a psychological disorder that causes low self-esteem."
1
The body mass index (BMI) is the measurement used to determine a person’s healthy weight. A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered the lowest health risk in relation to the weight of a person. How is the BMI calculated?
BMI = weight [pounds]/height [meter2]
BMI = weight [kg]/height [meter2]
BMI = weight [pounds]/height [feet2]
BMI = weight [kg]/height [feet2]
2
The nurse is assessing a client who has bulimia nervosa. The nurse would expect the assessment data to include that the client:
engages in binge eating.
weighs less than 85% of normal weight for height.
reports constipation, cold intolerance, and bradycardia.
engages in alcohol and substance use.
1
A client presents to the clinic with severe edema. Which type of deficiency should be suspected in this client?
Protein
Fats
Water
Carbohydrates
1
Which condition does the school nurse know is of highest health concern for school-aged children?
Childhood obesity
Gastrointestinal disorders
Dental caries
Diseases affecting the immune system
1
An older adult client is frail and has been diagnosed with severe protein–energy malnutrition. Which laboratory value is correlated with this diagnosis?
Low prealbumin
High C-reactive protein
Low fasting blood sugar
High bilirubin
1
A 20-year-old client who is addicted to methamphetamines has been admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of protein–calorie malnutrition after many months of inadequate food intake. Which treatment plan would the care team most likely favor?
Total parenteral nutrition
Rapid administration of normal saline and carbohydrates
Intravenous infusion of albumin coupled with vitamin supplementation
Incremental feeding combined with vitamin and mineral supplementation
4
A child asks about the purpose (function) of "white" fat. Which responses by the nurse are best? Select all that apply.
It releases protein to generate heat in the skeletal muscles.
It stores energy for the body to use.
It makes everyone unique by proportioning fat in various body parts.
It regulates temperature through insulation.
It cushions vital organs of the body.
2,4,5
Which assessment should be the priority when caring for a client with anorexia nervosa?
Serum electrolyte levels
Blood pressure monitoring
Chest auscultation
White blood cell count with differential
1
The nurse is teaching a client newly prescribed the thiazolidinedione medication pioglitazone. Which information will the nurse include? Select all that apply.
You should follow a prescribed diet as part of the treatment plan.
This medication is associated with an increase in weight gain.
Lipodystrophy is a potential complication of this medication.
This drug increases glucose uptake into your adipose cells.
Pioglitazone increases the amount of insulin released.
1,2,4
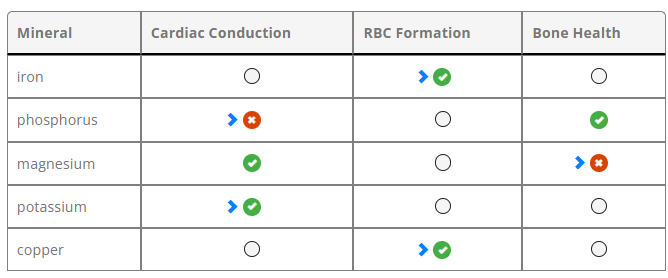
The nurse is assessing a client with malnutrition.
For each of the listed minerals, click to specify if a deficit in this mineral would most likely affect cardiac conduction, red blood cell (RBC) formation, or bone health.
A client is taking highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). While the client is taking these medications, what should the client be carefully monitored for relative to the loss of fat cells?
Constipation
Vomiting
Lipodystrophy
Seizures
3
While educating a class about adipose tissue, the faculty will emphasize that adipocyte cells serve as storage sites but also perform which other function?
Synthesize triglycerides
Degrade fat-soluble vitamins
Increase glucagon release
Produce linolenic fatty acid
1
A school nurse has identified a student with noticeable loss of lean tissues and muscle mass likely due to protein-calorie malnutrition. The nurse should assess for which clinical manifestation to help confirm a diagnosis?
Excessive blood cell production
Diarrhea
Increased cardiac contractility
Respiratory muscle stimulation
2
The nurse is concerned about a pregnant client whose weight gain has not increased during the last weeks of the pregnancy. How many extra calories above their usual requirement should the client be consuming?
300 kcal/day
200 kcal/kg
105 kcal/kg
500 kcal/day
1
The nurse is aware that psychological factors may be related to a client's problem with obesity. For this client, eating could be a response to:
Select all that apply.
Anger
Boredom
Stress
Anxiety
Pain
2,3,4
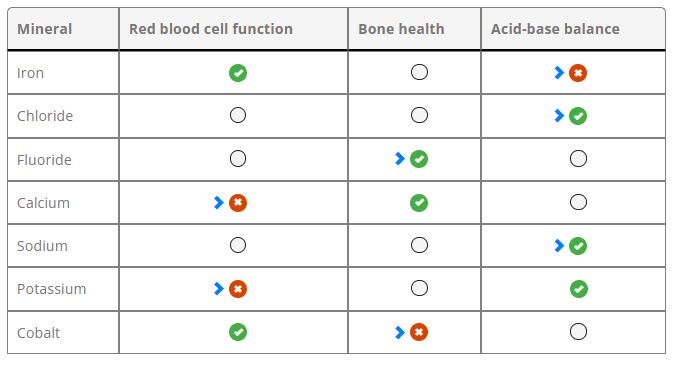
The nurse is teaching a group of school-age children about the function of minerals in the body.
For each mineral, click to specify if the primary function of the mineral is related to red blood cell function, bone health, or acid-base balance.
A 2-year-old child who has been neglected is admitted to the hospital. The child presents with systemic edema, flaky skin, oddly white-and-brown-colored hair, and extremely low body weight. The nurse should anticipate what intervention?
Incremental increases of a high-calorie, low-protein diet
A bolus of Lactated Ringer's followed by enteral feeing
Aggressive diuresis to resolve dependent edema
Administration of protein and calorie supplements
4
A client tells the nurse that "if my cholesterol is high, I guess I should try and eliminate all cholesterol in my diet." Which information should the nurse inform the client regarding the role of cholesterol within the body? Select all that apply.
Maintain normal blood clotting
Produce hormones
Maintain normal hemoglobin levels
Maintain cell permeability
Metabolize many vitamins
2,4,5
While assessing a teenage child suspected of having bulimia nervosa, the health care provider may find which clinical manifestation that would confirm the diagnosis? Select all that apply.
Skin with lanugo
Eroded tooth enamel leading to sensitive teeth
Painless parotid gland enlargement
Large number of teeth with dental caries
Kyphosis
2,3,4
When caring for a client in the medical clinic who has tried to lose weight multiple times, the client asks the nurse if they should try a high-protein, very low-calorie restricted diet. The nurse encourages them to seek guidance from the health care provider as these diets may cause which complication?
Hypothyroidism
Pulmonary embolism
Cardiac arrhythmias
Spontaneous fractures
3
A client who is overweight has been sent to have their basal metabolic rate (BMR) measured by their health care provider. Which statement most accurately describes an aspect of the BMR?
BMR tends to remain consistent throughout the lifespan.
The resting BMR constitutes a small fraction of total body energy needs.
Female client's tend to have a lower BMR than male client's due to a smaller skeletal muscle mass.
Variations in body mass account for many differences in BMR between individuals.
4
Which client has the greatest caloric needs?
Client who gave birth 1 month ago and is breastfeeding
82-year-old client with diabetes
Female client with no known disorders
Pregnant client at 8 weeks' gestation
1
An obese client is being seen in the clinic for treatment of a weight problem. The client states that they have been on multiple dietary regimens without success. In which situation is treatment indicated? Select all that apply.
The client weighs 150 pounds
There is a large waist circumference with a BMI of 25–29
There is a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher
The client requests help
There are two or more risk factors and BMI between 25-29
2,3,5
A client with liver disease is unable to emulsify fats efficiently due to an underproduction of bile and bile salts. The nurse monitors the client for evidence of deficiency in which vitamins? Select all that apply.
E
B12
K
Biotin
Thiamine
1,3
The health care provider will be assessing the nutrition status of a new client. Which assessment measures would they utilize? Select all that apply.
Height and weight
Skinfold thickness
Age
Dietary intake
Socioeconomic status
Body mass index
1,2,4,6
For a client with a vitamin A deficiency, which item on the menu should the nurse encourage the client to choose for supper?
Ground beef patty with broccoli and an apple
Grilled beef liver with carrots and cantaloupe
Fish cakes with pinto beans and cake
Grilled chicken breast with mashed potatoes with a dinner roll
2
The parish nurse is serving in a third-world country where protein calorie malnutrition is common. When assessing the children, which of these does the nurse anticipate will be present in the children with marasmus? Select all that apply.
Infections
Diarrhea
Small stature
Fine, smooth skin
Tachycardia
1,2,3
The nutritionist counsels a client to maintain a daily intake of alpha-linolenic acid to provide essential fatty acids. The client is encouraged to eat which food sources? Select all that apply.
Walnuts
Soybeans
Blueberries
Green, leafy vegetables
Red, beefy tomatoes
1,2,4
The nurse is caring for a client diagnosed with marasmus. The nurse would expect the client to manifest:
muscle wasting, “flaky paint” lesions of the skin.
loss of subcutaneous tissue, stunted growth, protuberant abdomen.
changes in hair texture or color, hypoalbuminemia.
growth failure, normal subcutaneous fat, hepatomegaly.
2
The nurse is teaching an extremely obese client scheduled for bariatric surgery about the benefits related to weight-loss surgery. What should the nurse include when discussing the priority benefit to the client?
The client's self-esteem will improve.
The client will look nice in new clothing.
The client's mobility will improve.
There will be a resolution of comorbid disease states.
4
An older adult client informs the nurse that although they are eating the same foods as usual and walking daily, there has been a weight gain. What does the nurse understand is related to a progressive decline in the basal metabolic rate (BMR)?
There is a decrease in muscle mass and replacement with adipose tissue.
As the body ages, leptin levels increase, causing weight gain.
As the body ages, the metabolic rate increases and weight loss occurs, and thus the client should be screened for illness.
The older adult has an increase in brown fat.
1
Similarities between clients with anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa include which clinical manifestation?
Low estrogen level
Electrolyte imbalances
Periodontal disease
Enlarged parotid gland
2
A nurse is caring for a client who is being treated for anorexia nervosa. Which personality traits are associated with this eating disorder?
Aggressive and extroverted
Introverted and shy
Easily angered and paranoid
Perfectionist and compulsive
4
The health care provider needs to assess a client for protein–calorie malnutrition. The best diagnostic measure would be:
Body circumference
Serum potassium level
Skinfold thickness
Prealbumin
4
A client arrives at the clinic and informs the nurse that there is an "itchy rash" on their face. Which type of deficiency should the nurse suspect that may have caused dermatitis in this client?
Hemoglobin
Alpha-linolenic acid
Linolenic acid
Folic acid
3