L8: dividing up deep time and clocks in rocks
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
radiometric dating suggests earth is 4.5 billion yrs old
absolute dating and relative dating
uniformitarianism
concept that geological features today formed in ways that we can observe and understand today
stratigraphy
a branch of geology which explores rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification)
principles of stratigraphy
principles of original horizontality
layers of sediment are usually deposited horizontally under the action of gravity
principle of superposition
in series of stratified sedimentary rocks, the lowest stratum is the oldest
principle of cross-cutting relationships
if it is no longer horizontal the deformation occurred subsequently
if a rock is cut by a feature, it must be older than the feature that cuts it
law of inclusions
if one rock contains parts of another rock, those other rocks must be older
what if time goes missing?
unconformity
is a stratigraphic gap in the geologic record
disconformity
is when upper sedimentary sequences overlies an erosional surface
angular unconformity
upper beds overlie lower beds that have been folded by tectonic processes then eroded to an even plane
what else can we see?
we know different organisms have come and gone
biostratigraphy
correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them
geological division
eon
us: phanerozoic (541-0 Ma)
era
us: cenozoic (6-0 6Mya)
period
us: quaternary (2.6Mya)
epoch
holocene (0.01 Ma)
radiometric dating
method of dating geological specimens by determining the relative proportions of particular radioactive isotopes
isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element that have a different mass
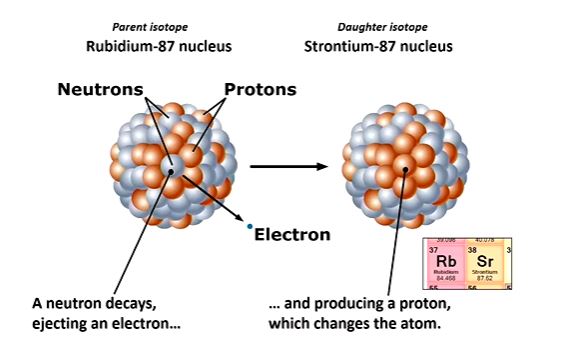
radioactive isotopes
atoms that breakdown into another stable or radioactive atom by radioactive decay
half-life
the time it takes for one-half of the atoms of a radioactive material to disintegrate
decay times (various carbon isotopes as an example)
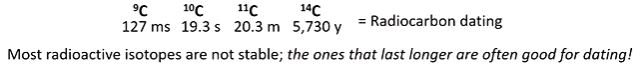
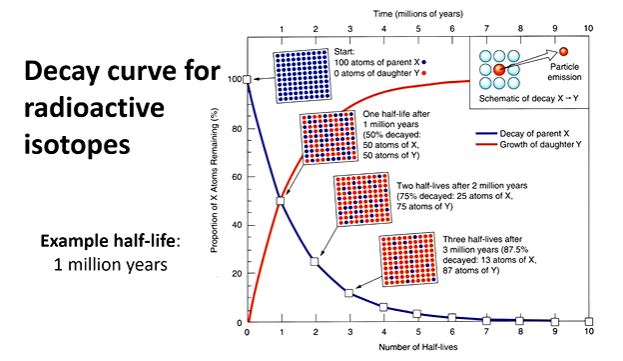
decay curve for radioactive isotopes
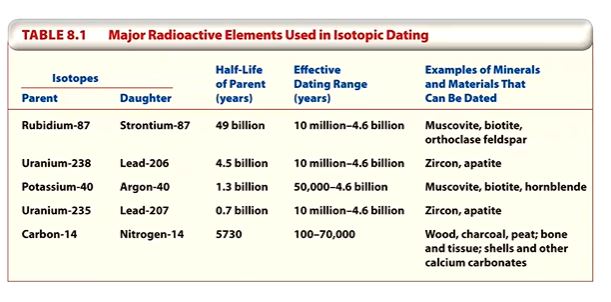
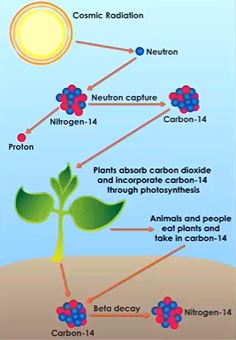
radiocarbon dating
we have cosmic radiation that is firing neutrons into the atmosphere which is dominated by nitrogen. neutrons are slamming into the nitrogen and shooting off the proton. carbon is in the tissues of plants
fission track (another dating method)
where you have nuclear fission within some unstable radioactive elements. splitting atoms to create energy, when they split they can create light so photons or physical damage if it takes place in minerals (e.g. creates physical scars in zircon)
age = number of track + need to know how much uranium
dating window up to several billions of years
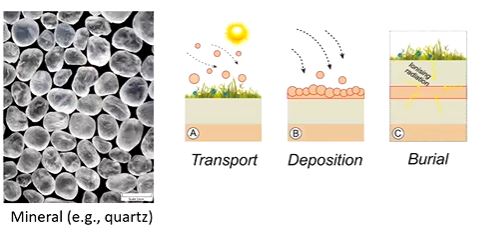
luminescence dating
can pick up radioactive elements