Protozoa, Fungi, Helminths`
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Brief description of pathogenesis of pathogenic Coccidia (protozoa)
Damage to enterocytes following rupture of mature schizonts and merozoite release
Villus atrophy = malabsorption
Epithelial erosions and ulceration = exudative enteritis
Impaired intestinal barrier and permeability = diarrhoea
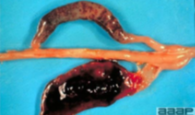
Name the causative agent
Eimeria tenella
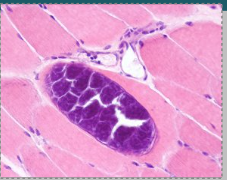
What is this?
Sarcocystis in skeletal muscle
Describe the pathogenicity of Sarcocystidae
Usually benign outside of the GIT
Forms cysts in muscle (including heart) but no inflammation
Disease occurs when
cysts rupture
dead/end host or nervous system infected (e.g. S. neurona in horses infects the spinal cord)

Causative agent
Trypanosoma spp.
What are the 2 major and 4 morphological forms of Trypanosoma and brief description
American (T.cruzi) and African (T. congolenese, vivax and brucei brucei)
Amastigotes (intracellular, T.cruzi only)
no flagellum
multiplies in mammalian cells
Trypomastigotes (blood form)
infective
does not multiply
Epimastigotes (intermediate form)
found in vector (fly), multiplies in midgut
Promastigotes
rapidly dividing stage
How do Trypanosoma evade immune system
Have antigenic variation in membrane surface glycoproteins
= host needs to constantly redevelop humoral immune response
= very hard to develop vaccine against it
What does chronic infection of T.cruzi cause
myocarditis
What does T. evansi cause in horses
meningoencephalitis = neurological signs
2 virulence factors of fungi
Capsule (yeast)
polysaccharide. impossible to effectively phagocytose
may contain melanin - antioxidant that inhibits lysosomal digestion
Constantly shedding surface antigens
= chronic inflammatory reaction = granulomatous inflammation
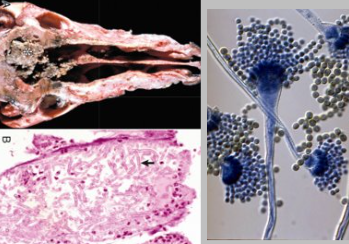
What is the causative agent?
Aspergillosis
3 virulence factors of aspergillosis
Gliotoxin = anti-inflammatory, apoptosis of phagocytes
Fumagillin and hevolic acid = antibiotics
Melanin = antioxidant
Pathophysiology of aspergillosis
Inhalation of conidia
Immunosuppression/disruption of phagocytosis = germination into hyphae. Secretion of enzymes that damage the epithelium, exposing the basal lamina and allowing easy colonisation and invasion.
Systemic spread via leukocyte trafficking, or rarely by angioinvasion
Gross appearance of aspergilosis in dogs
grey/black pseudomembraneous rhinitis/airways
Aspergillosis causes gross lesions on what organs of the cow
Lungs
Placenta
Udder
Gross appearance of fungal infections (2)
Fungal plaques (grey/red)
Haemorrhage (vasculogenic/brain, epistaxis)
4 examples of clinical signs caused by nematodes
Weight loss
Hypoalbuminaemia (PLE-causing)
Anaemia (Haemonchus contortus)
Diarrhoea

2 example nematodes that undergo hypobiosis and mass re-emergence
Cyathostomins (horse)
Ostertagia (cattle)
3 examples of nematodes that can cause death due to blood vessel damage
Strongylus vulgaris (horse = mesenteric vessels)
Angiostrongylus vasorum (dog = lungworm)
Haemonchus contortus (sheep = abomasal blood feeding)
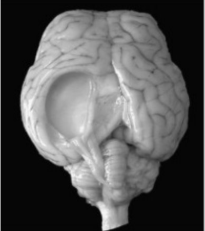
Causative agent in a sheep
GID - tapeworm cyst from Taenia multiceps (infects dog GIT)
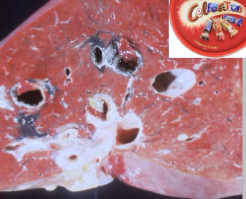
Causative agent
Trematode - liver fluke