🌱BIO153 Animals
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Eumetazoa
non-sponge animals that have “true tissue” such as muscles and nerves
What type of symmetry does the basal group of Eumetazoa have?
radial symmetry
What is animalia also known as?
Metazoa
What are the closest living relatives to animals?
Choanoflagellates, a type of unicellular protist
How are choanoflagellates used to determine the origin of multicellular organisms?
they have proteins that stick onto other cells, forming a colony
What were the first group of animals to diverge from the rest of animalia?
Porifera (sponges)
What are the three major clades of Bilateria?
Lophotrochozoa, Ecdysozoa, Deuterostomia
Radial symmetry
body can be divided into two equal halves by any plane passing through the center
eg. jellyfish, sea stars, corals, sea anemones
Bilateral symmetry
body can be divided symmetrically into a “left side” and “right side”
eg. humans, fish, birds, insects
What are three specific traits that vertebrates have?
backbone, hinged jaws, limbs with digits
How does a zygote divide?
by cleavage
Cleavage (division)
mitotic cell division not accompanied by cell growth
What does the zygote form after multiple cleavages?
a blastula
Blastula
a single layer of cell covering a hollow space
Blastocoel
the hollow space inside the blastula
Gastrulation
one end of the blastula’s surface internalizes, allowing the blastula to become a gastrula
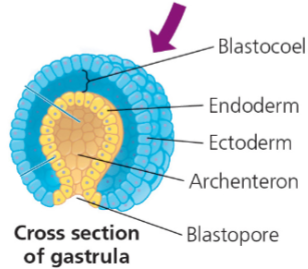
What does gastrulation lead to?
the beginning of cell differentiation, where different cell layers develop into different tissues and organs
What two surfaces is the gastrula composed of?
Archenteron and Blastopore
Archenteron
cavity inside the gastrula
Blastopore
opening into the cavity where both the mouth and anus form
Deuterostomes
organisms that form the anus before the mouth in embryonic development
Ecto-
outside
Endo-
inside
Ectoderm
cell layer that forms skin, hair, teeth, nervous system, germ cells, etc.
Endoderm
cell layer that forms epithelial surfaces of digestive, respiratory, excretory and reproductive tracts, etc.
Mesoderm
cell layer that forms skeleton, muscle, circulatory system, etc. (not all animals have this)
Incomplete Metamorphosis
gradual growth of larva into adult via multiple molts (nymphs)
Complete Metamorphosis
growth of larvae into adult via a pupal stage
What are the two main classes of deuterostomes?
Echinoderms and Chordates
Echinoderms
invertebrates such as sea stars, sea urchins
Chordates
vertebrates such as fish, reptiles, mammals, (and some invertebrates)
What are the four major derived traits of chordates?
Notochord, hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail
NNGT (notochord, nerve cord, gills, tail)
Notochord
A flexible rod found between the digestive tube and nerve cord. In vertebrates, the backbone develops around the embryotic notochord.
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
The nerve cord that develops from the neural plate in the ectoderm into a neural tube.
What does the neural tube form in vertebrates?
the spinal cord
Pharyngeal slits
Pharyngeal clefts that develop into pharyngeal gills in some chordates. In humans, pharyngeal clefts differentiate into other tissues in utero
What is distinctive about early diverged vertebrates such as lampreys?
They lack jaws and have a cartilage skeleton. The cartilage skeleton can be mineralized with calcium for added support.
What is special about lancelets?
they have all the features of a chordate, however they do not have a backbone.
What qualifies some invertebrates to be members of Chordata?
they have all four derived traits of Chordata at some stage in their life, even if they usually disappear by adulthood.
Ray-finned fishes
Fins are made of bony rays connected with webs without muscular structure
Lobe-finned fish
Pectoral and pelvic fins have a thick muscle supporting the bony fin, usually seen in extinct species or living fossils such as coelacanths.
Tetrapods
Gnathostomes that have limbs with digits, a four-footed animal
Amniotes
Tetrapods with terrestrially adapted eggs
Amnion
encloses the amniotic fluid that the embryo floats in
Ectothermic
“cold-blooded”
Endothermic
“warm blooded,” less energy efficient than ectothermic but able to withstand harsh conditions
What covers the archenteron?
the endoderm and then the ectoderm
Where does the mesoderm form in gastrulation?
between the ectoderm and endoderm
Monozygotic twins
occur when a egg fertilized by a single sperm is split into two
Dizygotic twins
occur when two eggs are fertilized simultaneously by two different sperm
What is the sponge body made up of?
two cell layers filled in by mesohyl (“middle matter”) that provides good access to water, hence the lack of need for a circulatory system
What does a sedentary suspension feeder do?
they draw in water from their side-pores and out from the central cavity, filtering out food particles suspended in water
Choanoflagellate cells look very similar to what?
the collar cells of sponges
Lophophore
crown of ciliated tentacles for feeding
Trochophore
larval form of the group of invertebrates Lophotrochozoa
Where does the clade Ecdysozoa get its name from?
from “ecdysis,” the molting of the exoskeleton that a lot of organisms partake in
What does the visceral mass in mollusks do?
it contains most of the inner organs
What does the mantle in mollusks do?
covers the visceral mass and secretes the shell
the mantle may extend beyond the visceral mass to create mantle cavity
What does the mantle cavity in mollusks contain?
the gills, anus, excretory organs, etc.
What is the difference between the mantle in cephalopods and in mollusks?
the mantle in on the outside and the shell is minimized or lost in cephalopods
Siphon
an organ found in cephalopods and mollusks that expels water
Which group of animals contains more species than any other eukaryote?
Ecdysozoans
What composes the segmented body of insects?
head, thorax (“torso” where legs are), post-genital region
What happens to the notochord in humans?
the embryotic notochord reduces and becomes part of the intervertebral disc in the spinal column
What happens to the nerve cord in humans?
it develops into the spinal cord
What are tunicates and what are they closely related to?
An invertebrate animal whose larvae present all four Chordate traits. They are more closely related to vertebrates than lancelets.
Gnathostomes
jawed vertebrates, includes cartilage-skeleton fish such as sharks and rays
What is the sister group to tetrapods?
Lung fish that adapted to life on land, with the fins evolving into limbs with digits.
What is another term for placental mammals?
Eutherians
How are carnivore stomachs adapted to their diets?
they have large, expandable stomachs since they go long intervals between feeding and need to eat large quantities when they can
How are herbivore and omnivore stomachs adapted to their diets?
they have longer digestive tracts since vegetation is harder to digest
Why is beneficial gut bacteria important for herbivores?
the bacteria can break down cellulose walls in vegetation that are otherwise unable to be digested
What group of primates were the first to diverge from the common ancestor?
The clade that includes lemurs, lorises, bush babies, and tarsiers
Anthropoids
all primates including monkeys, apes, and humans
Hominins
extinct species more closely related to humans than other apes