Standard Model
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what is an elementary particle?
elementary particles are those with no underlying structure, meaning they are not composed of smaller particles
what is an antiparticle?
a particle with the same mass and opposite charge and/or spin to a corresponding particle, for example positron and electron. every particle in the standard model has an antiparticle.
what are the six types of quarks?
Up - down
charm - strange
top - bottom
what is a baryon?
composite subatomic particles made up of three quarks
what is a meson?
subatomic particles composed of one quark and one antiquark
what are the six types of leptons
Electron - Electron neutrino
Muon - Muon neutrino
Tau - Tau neutrino
what are the 4 gauge bosons?
gluon, photon, Z boson, W boson
describe the strong nuclear force in terms of gauge bosons
gluons are the force carriers in the strong nuclear force that hold quarks together tightly to form hadrons.
describe the weak nuclear force in terms of gauge bosons
W and Z bosons supply the weak nuclear force, which all quarks and leptons experience.
describe the electromagnetic force in terms of gauge bosons
photos supply the electromagnetic force that occurs between any charged particles, and has infinite range.
contrast the fundamental forces experienced by leptons and quarks
quarks experience all four fundamental forces, while leptons only experience electromagnetic, weak and gravitational forces, lacking interaction with the strong force due to their absence of colour charge.
what is a baryon number?
a conserved quantity representing the number of baryons in a system
what is a lepton number?
is a conserved quantity representing the number of leptons in a system
recall the conservation of lepton number and baryon number in particle interaction
In particle interactions, baryon number and lepton number are conserved. The total number of baryons and leptons (minus their antiparticles) remains unchanged before and after the reaction.
describe the significance of symmetry
the significance of symmetry appears to be that it can be used to predict other theoretical particle interactions.
what quarks form a proton?
up, up, down
what quarks form a neutron
up, down, down
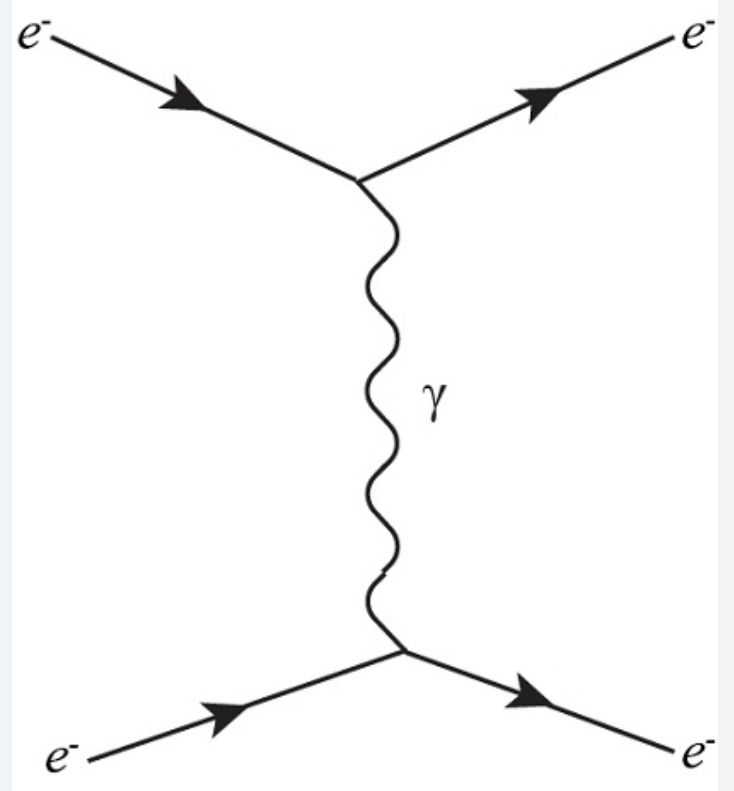
what is this process?
In electron–positron scattering, an electron and a positron approach each other and interact via the electromagnetic force by exchanging a virtual photon. This interaction causes them to scatter and move away in different directions.
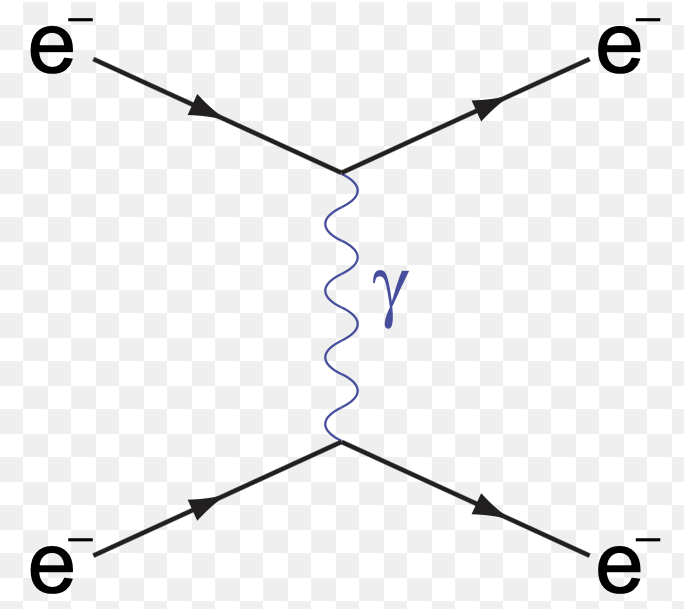
what is this process?
In electron–electron scattering, two electrons approach one another and interact via the electromagnetic force by exchanging a virtual photon. As a result of this interaction, they scatter and move away from each other.
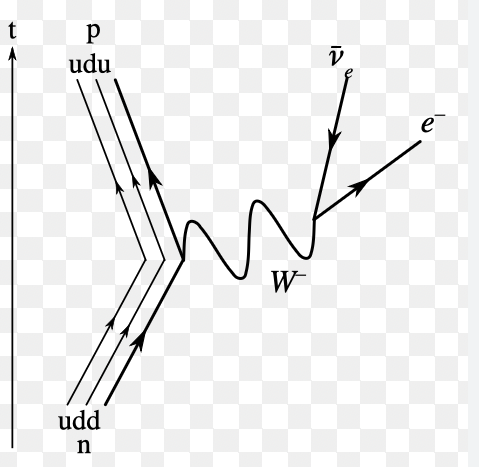
what is this process?
In beta minus decay, a down quark inside a neutron decays into an up quark, turning the neutron into a proton. This process emits a W−W− boson, which quickly decays into an electron and an electron antineutrino.
what are the charges of electrons, muons and tau?
-1
what is the charge of up, charm, top?
+2/3
what is the charge for down, strange, bottom?
-1/3
what are the charges of electron neutrino, muon neutrino, tau neutrino?
0
what is crossing symmetry?
Crossing symmetry means you can take a particle from before a collision and move it to after the collision — as its opposite (antiparticle) — and the reaction still follows the same rules.
what is time reversal symmetry?
just switching the products and reactants around
what is charge reversal symmetry?
where the charges of all charged particles are reversed or particles are switching between particles and antiparticles