Human rights
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Civil society
. NGO's working to support peoples human rights (non governmental agencies)
Human rights norms
Statements set out by the UDHR - moral principles that form the basis of global laws - protected by international low
Geopolitics
Global political power + international relations - dominated by AC's
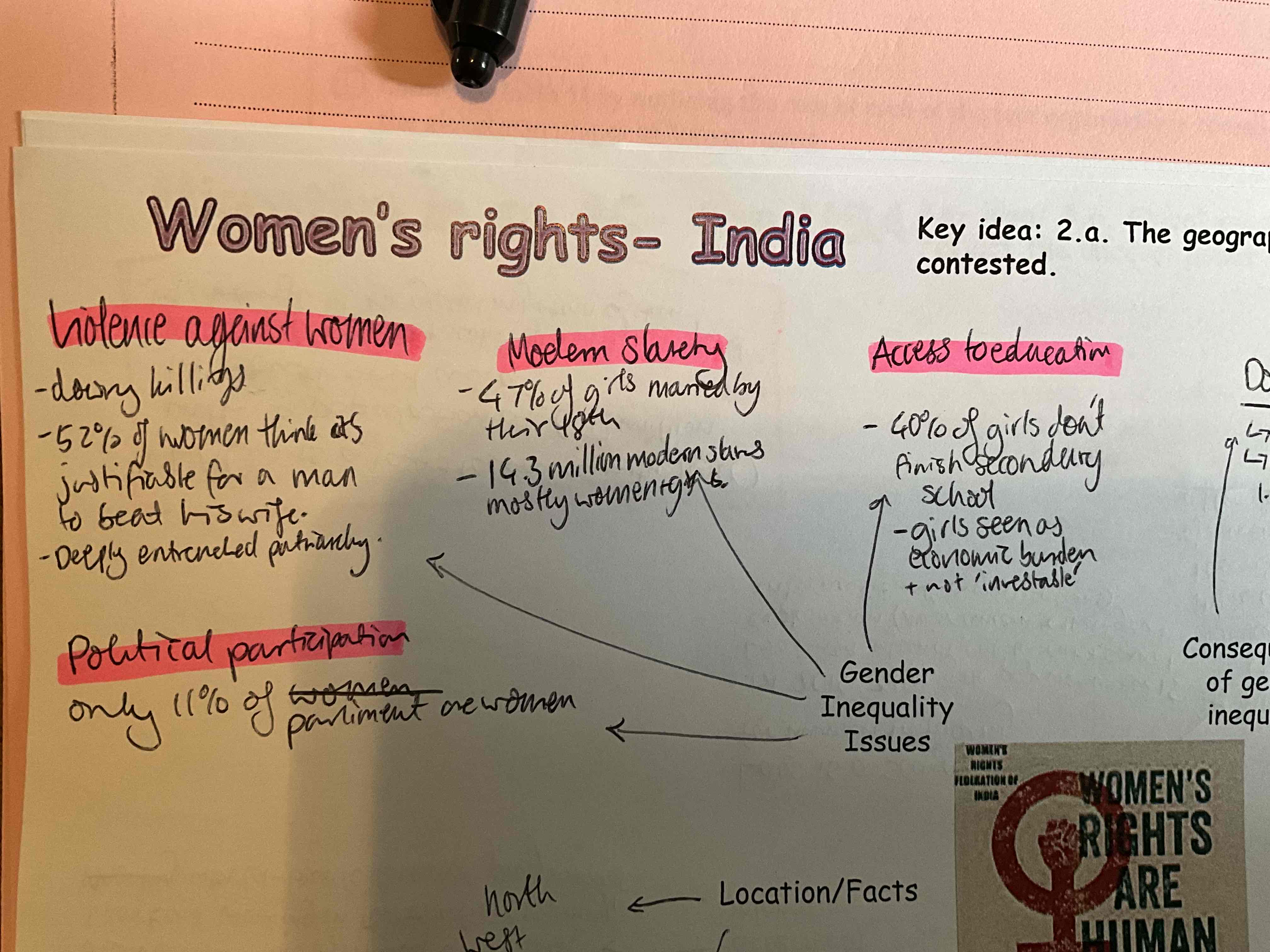
give examples of Gender inequality issues in India
For example violence against women 52% of women think it’s justifiable for a man to be his wife additionally there are many dowry killings. It’s worse in northern India with 1.4 deaths per 100,000 women due to dowry deaths.
Only 11% of the parliament are woman so women have lack of political participation
47% of girls are married by the 18th birthday 14 million people are in modern slavery with most being women and girls
40% of girls don’t finish secondary school and are seen as an economic burden.
Consequences of gender inequality in india
1.4 dowry deaths per 100,000 women
Honour killing has grown by 796% and just one year from 2014 to 2015
Mortality maternal rate is high and women are subject to sex selective abortions

What are the strategies to fight against gender inequality in India?
‘Our daughters, our wealth scheme’ Cash incentives for families who enroll their daughters at birth the rule is they must remain unmarried until at least 18 however only 32% use the cash to put the girl into education so it’s not as successful as hoped however still reduces childhood marriage
Bejing Platform for action in 1995 - commitments were made under 12 areas of concern for example violence against women. This caused India to release a new policy for empowerment of women.
SABLA empowerment scheme aiming to improve nutritional health in girls and has reached 50,000 girls out of school.

What norms are changing in India regarding gender inequality?
There is an aim to be eliminating violence against women. There’s better health for girls and aim for reduction in child marriage.
What’s India’s average GDP PER person?
$1900
What are the positive consequences for rural areas of Afghanistan because of global governance?
Women are more integrated into society and a local democracy has been introduced. NGOs also improve agriculture technique by working with communities.
What is the negative consequences for rule areas because of global governance in Afghanistan?
Poverty leading to families having to sell their livestock. Basic human rights being neglected due to conflict for example article 26 limited access to education additionally the place is a geographically in hospitable and politically hostile due to this conflict.
What is the rural area studied for Afghanistan?
Ghor province
What is the urban area studied for Afghanistan?
Kabul
What are the positive consequences for urban areas because of global governance in Afghanistan?
The UN are working to coordinate the Afghan government. There is funding from Japan to upgrade neighbourhoods which is targeted 2500 residence.
they’re working to improve engagement of woman in projects and community development Councils aim to upgrade : housing, infrastructure, schools and healthcare.
What are the negative consequences for urban areas because of governments in Afghanistan?
Denial of basic human rights due to urbanisation. It led to deprivation because of stress on services due to an increased population
What is the role of multinational corporations in global governance of human rights?
Focus mainly on protection of human rights in the workplace for example working conditions and equality between men and women
What is the role of ngos in Global governance of human rights?
They campaign to raise awareness of human rights issues make presentations and can lobby governments to change and develop their laws
What is the international criminal court (ICC)?
The investigate try and prosecute serious crimes within the international community for example genocide
What are the opportunities for stability growth and development in Afghanistan?
Large opportunity in agriculture/trade.
Encouraging women to develop skills and engage in projects means more job opportunities.
Security of Land tenure inform housing allows people to focus on their personal development as they are stable in their shelter.
How are the opportunities for Stability growth and development in Afghanistan being promoted or developed?
Training and disease resistance seeds for farmers to increase their profit as well as vets or veterinary training to help save livestock.
Road infrastructure have been improved to provide crucial training links.
Teaching sanitation household in Kabul for example reduces disease allowing people to be more healthy allowing them to work.
Women have been encouraged to develop skills and engaging projects.
What are the challenges of inequality and injustice in Afghanistan?
for Injustice, Afghanistan is controlled by the Taliban (they took over in 2021). This means that there has been lots of human rights violations making it hard for people to develop. For example, article 3 the right to life liberty and security has been broken as there are many More civilian casualties.
For inequality, People living in current poor living conditions leads to a cycle of deprivation as they may become too unwell to work and earn more money.
Not everyone has access to the aid that is being provided by these NGO and governments.
For opium trade people may be relying on the profits to live. Additionally, Exploitation and corruption happen easily within this trade and it is hard to control. When more opium is grown, there is less land available for food growth which can lead to shortages for people throughout the country further adding to deprivation and poverty.
What articles of human rights are being broken in Afghanistan with statistics?
Article 25 the right to adequate standard of living including food- 2.4 million farmers are involved in OPM production as the income for opium is US$4600 per hectare whereas Wheat is only US$1600 per hector
Article 3 write to life liberty and stability - In 2011 there were 11,000 civilian casualties. Double that of 2009.,