Clinical Anatomy: Thorax Pt. 1 & some pt 2
1/264
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
265 Terms
Suprasternal notch
hollow U-shaped depression just above the sternum, in between the clavicles
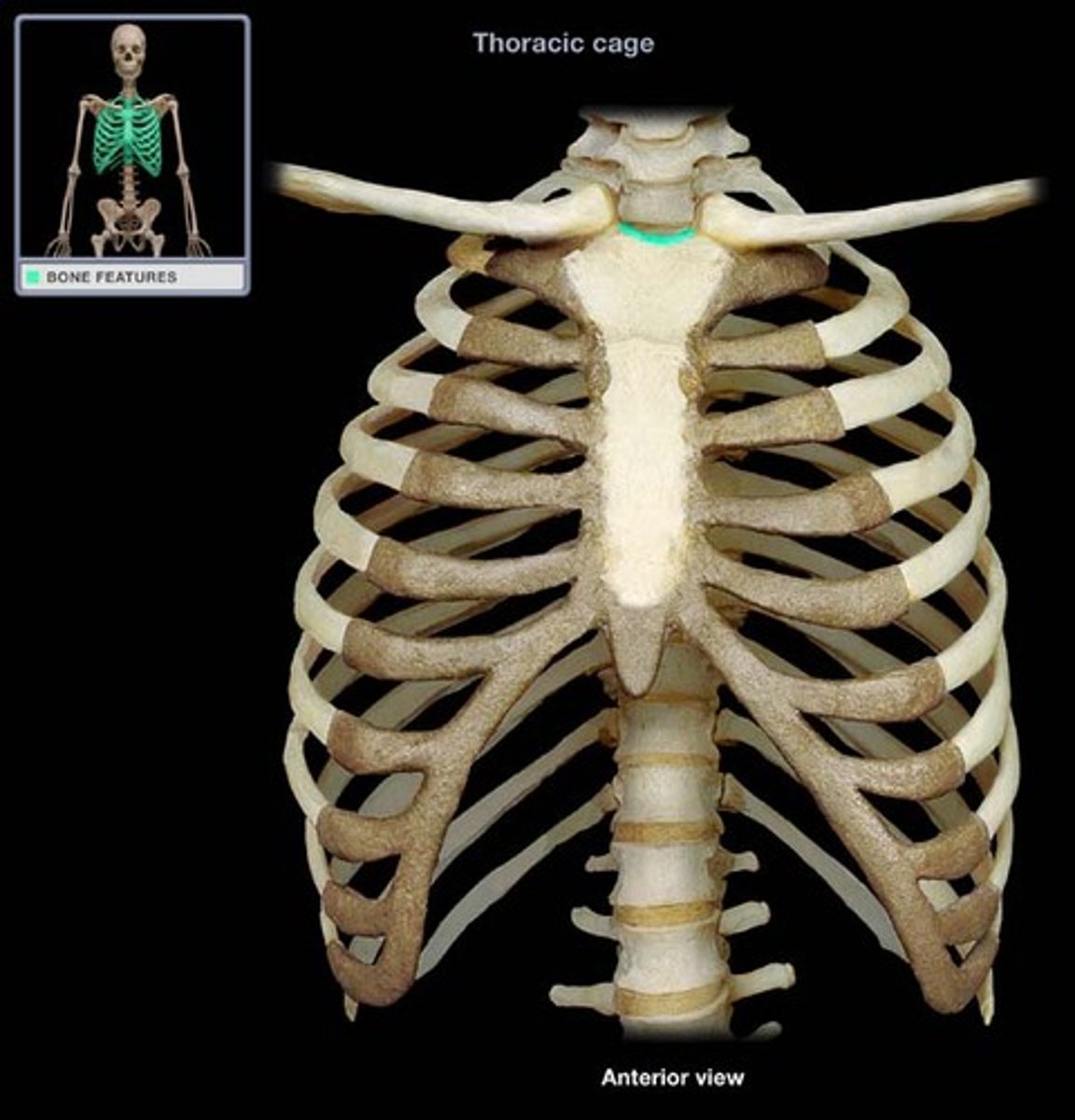
sternal angle (angle of Louis)
angle between the manubrium and the sternal body; lies opposite of the IV of 4th and 5th thoracic vertebrae; 2nd costal cartilage of 2nd rib
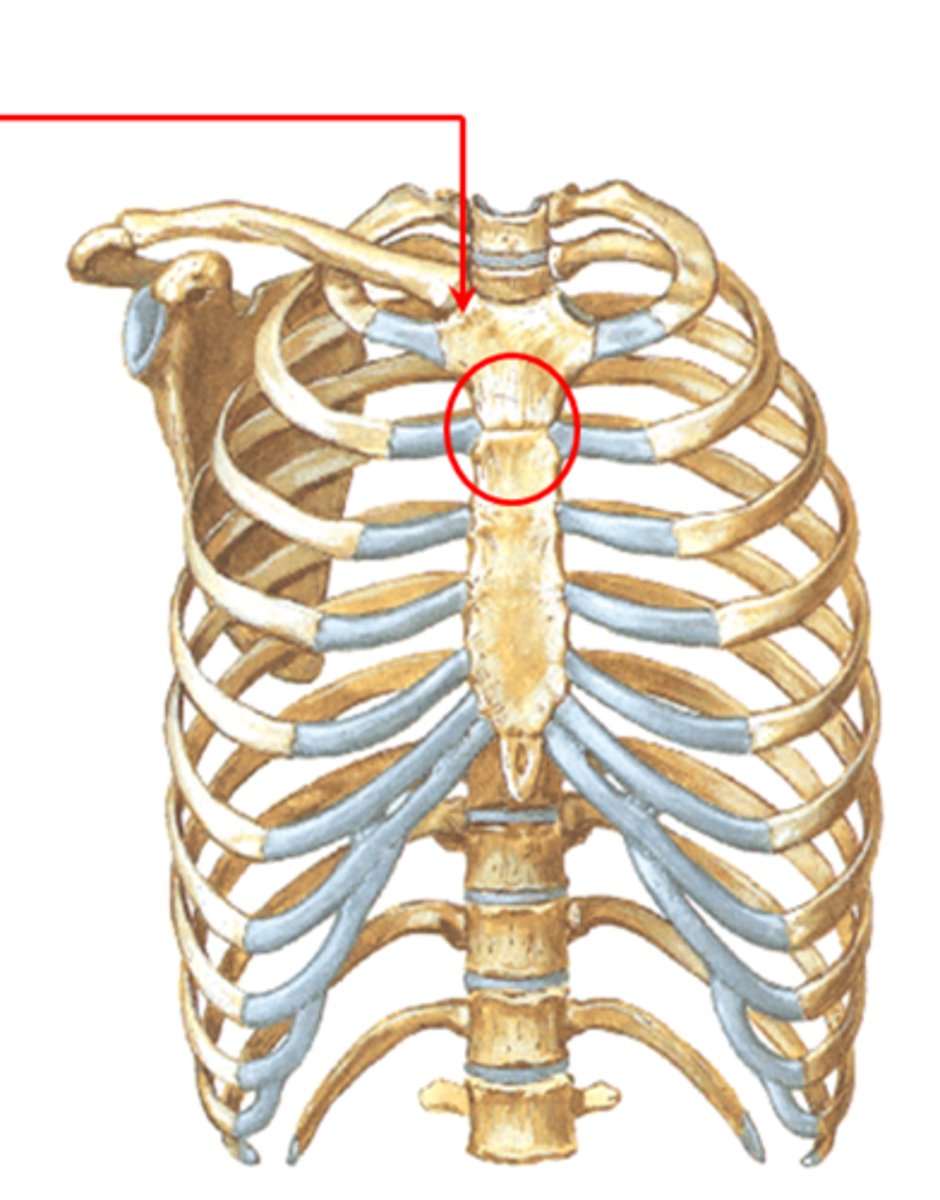
xiphisternal joint
joint between diploid and body of sternum
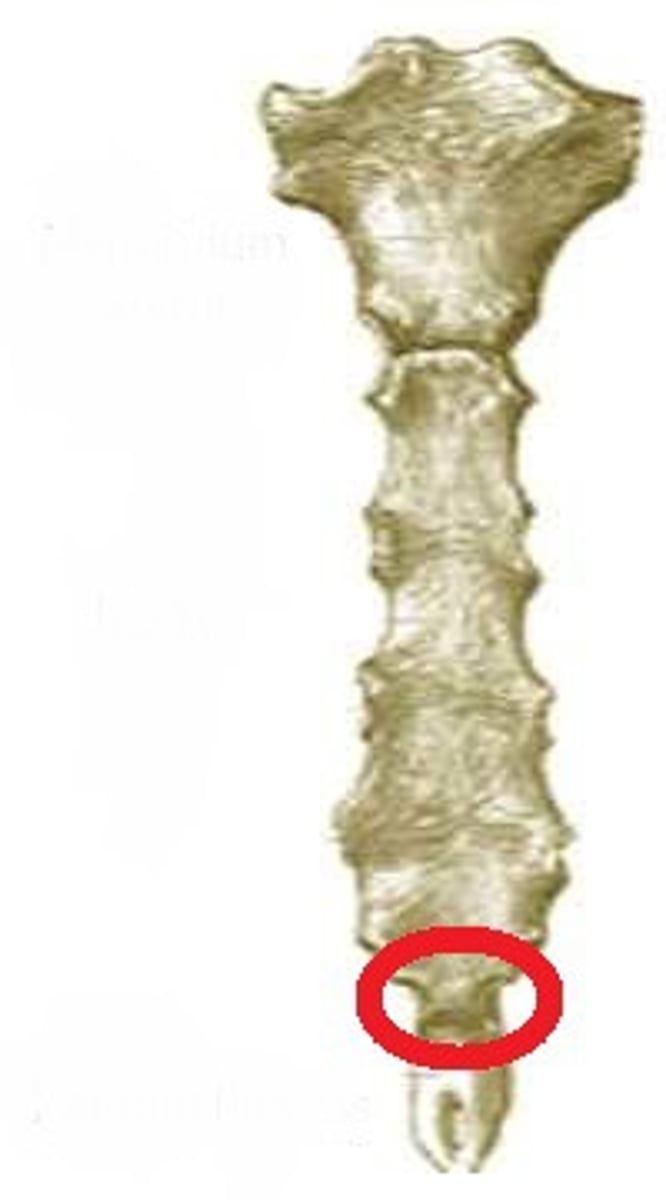
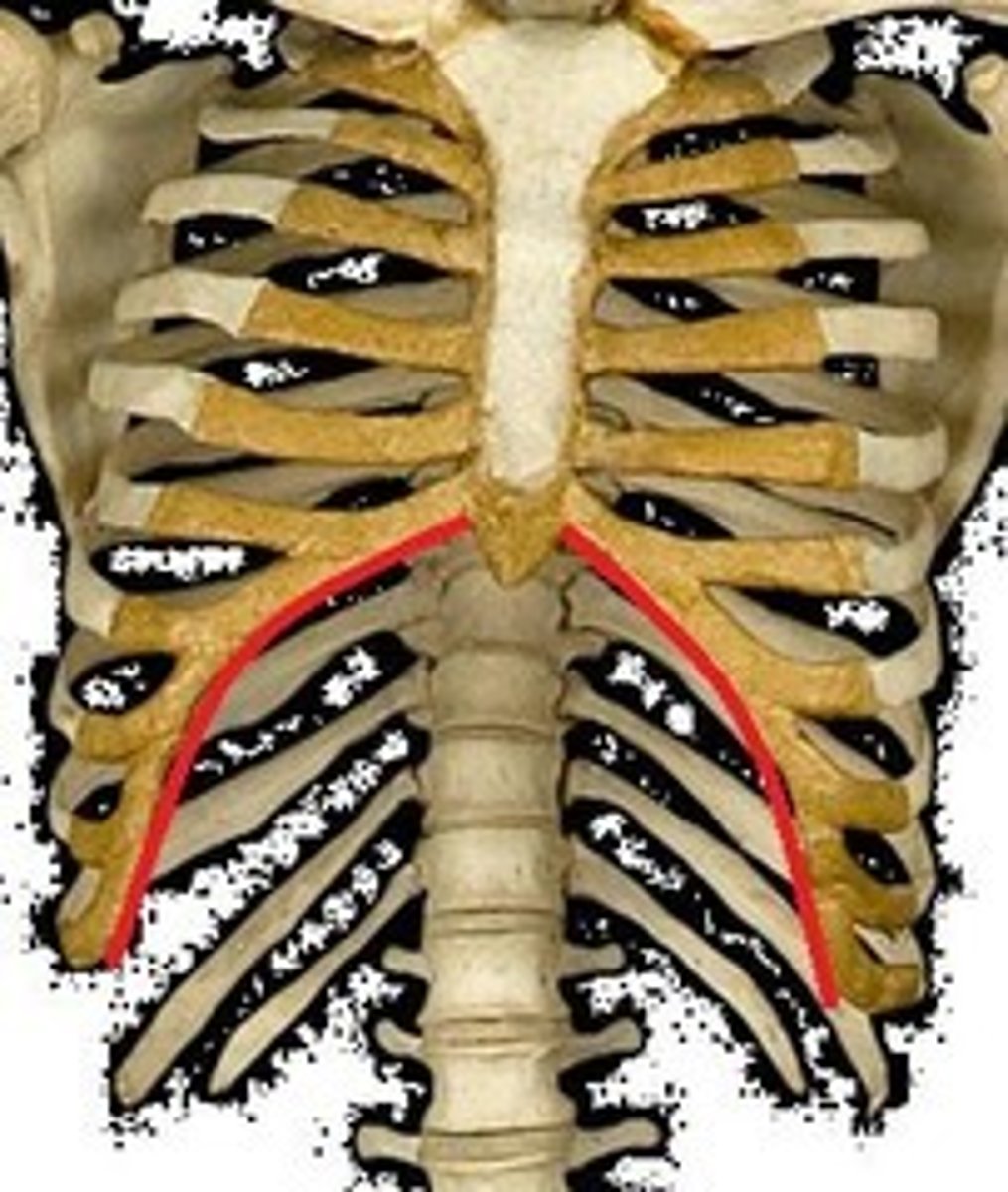
subcostal angle
inferior end of sternum, between sternal attachments from 7th costal cartilage
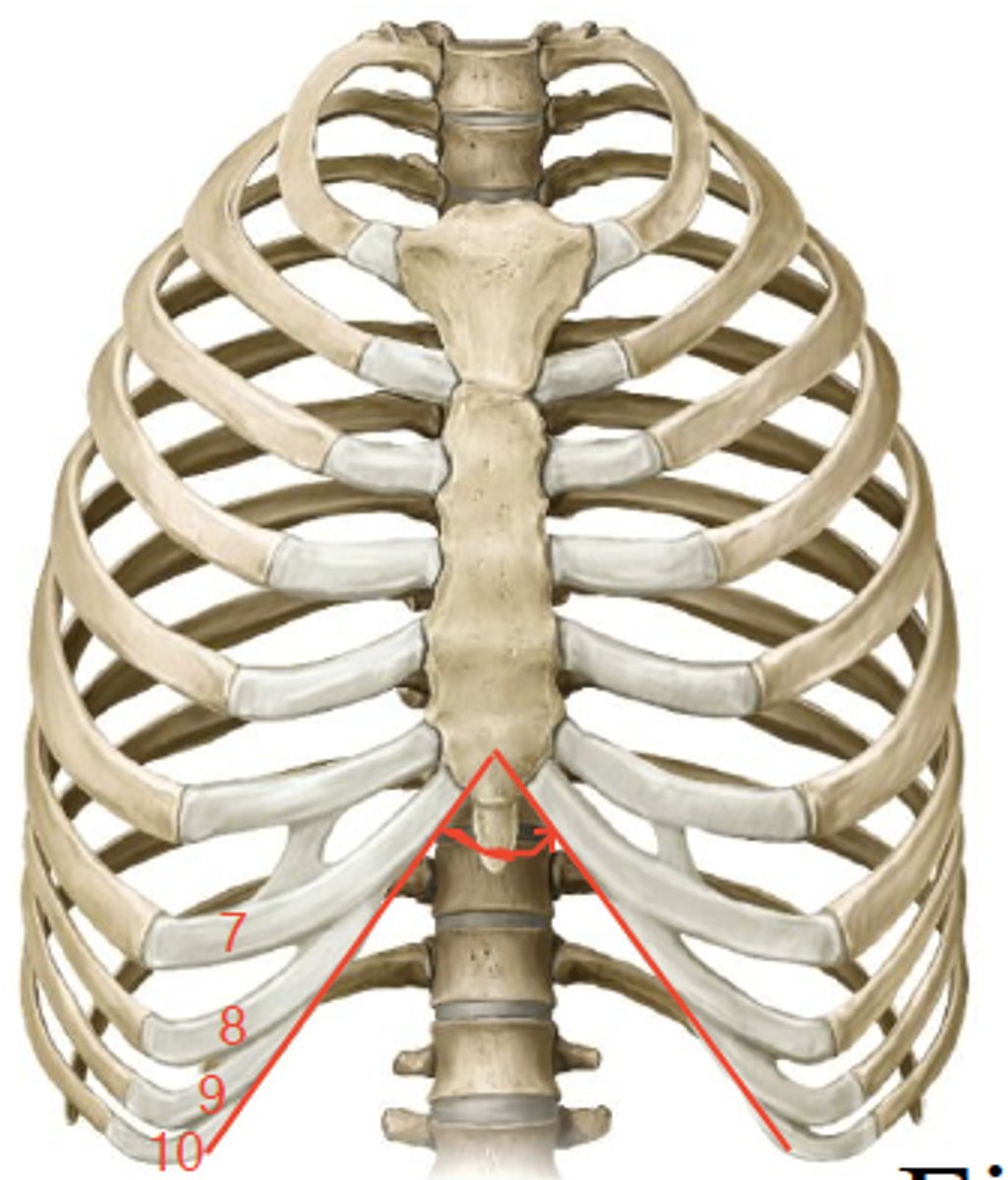
the sternal attachments of 7th costal cartilage
the subcostal angle is between...
costal margin
lower boundary of the thorax
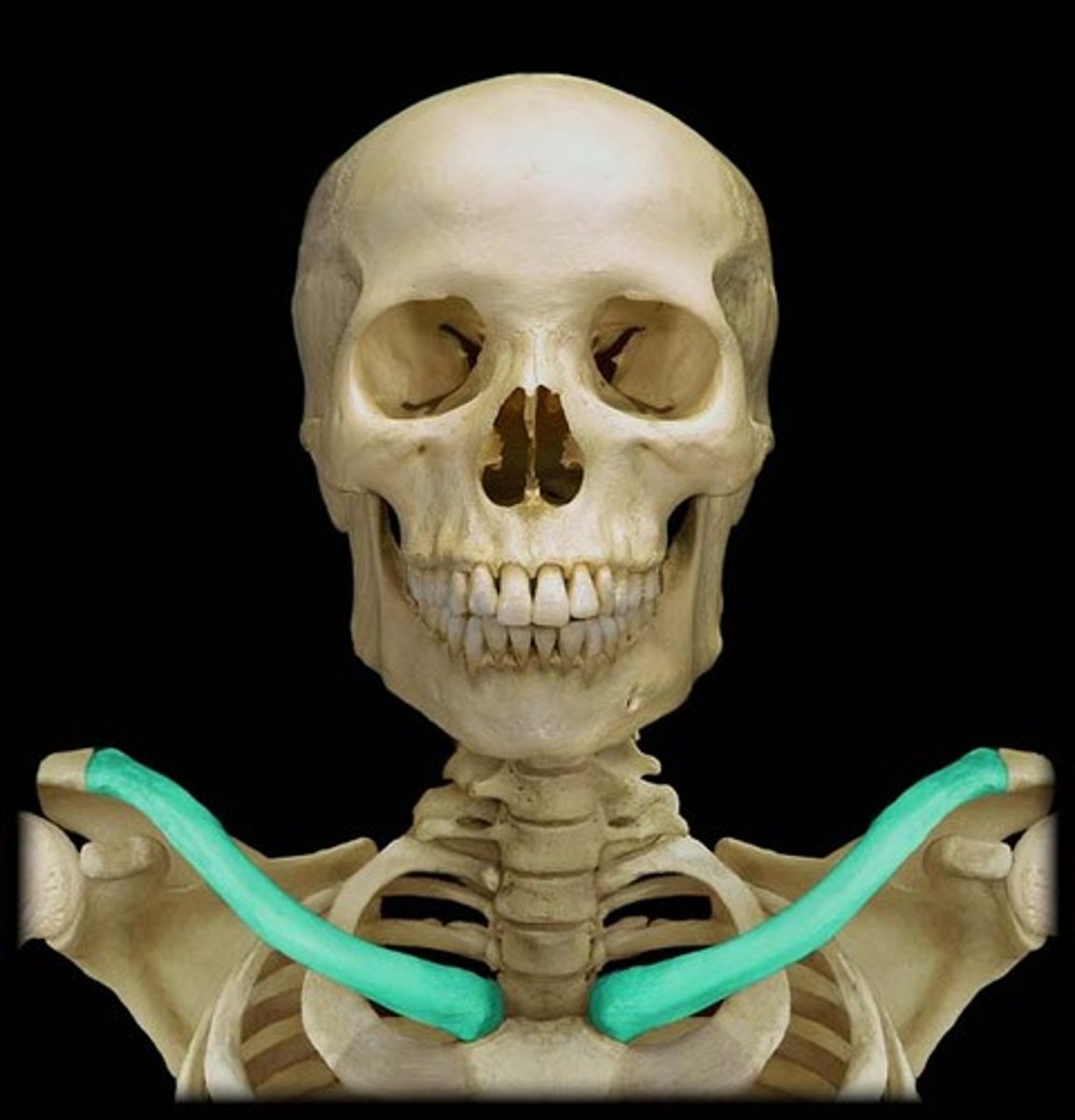
clavicle
collar bone
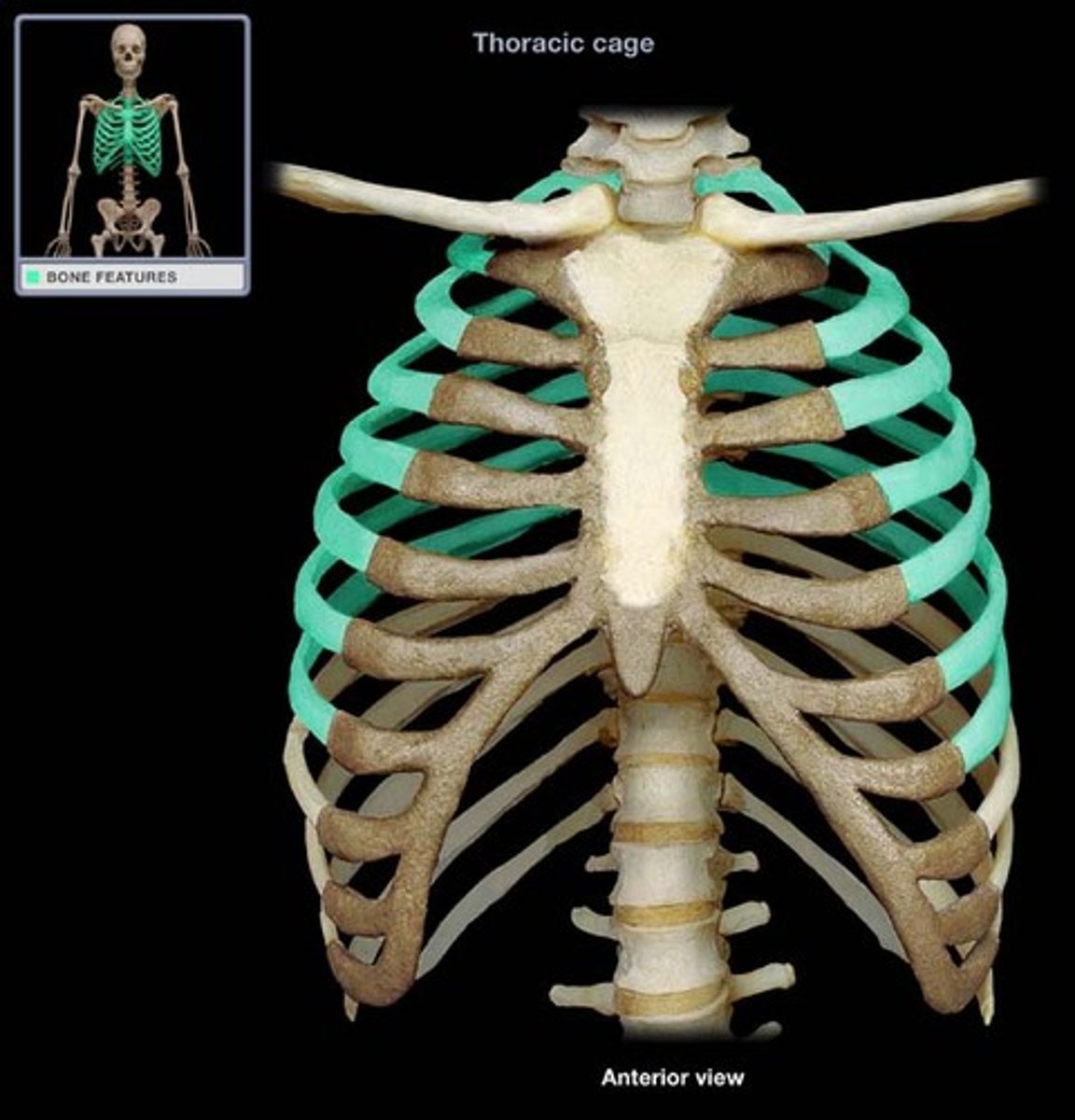
Ribs
The bones in the chest that protect the heart and lungs.
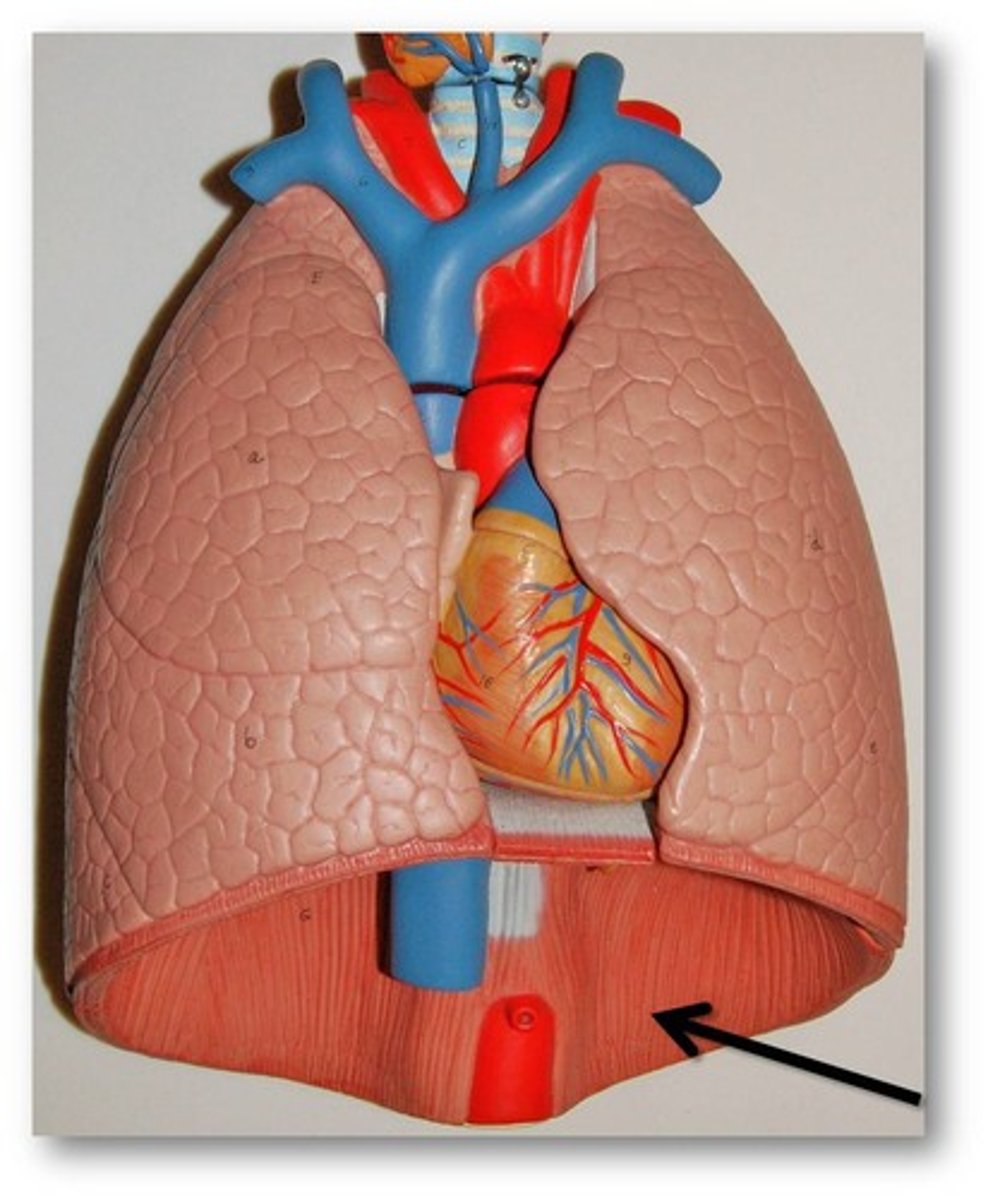
diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
xiphisternal joint
the central tendon of the diaphragm lies directly behind the...
4th
nipples are located in the ____ intercostal space
Apex beat of the heart
lower portion of the left ventricle; 5th ICS/MCL
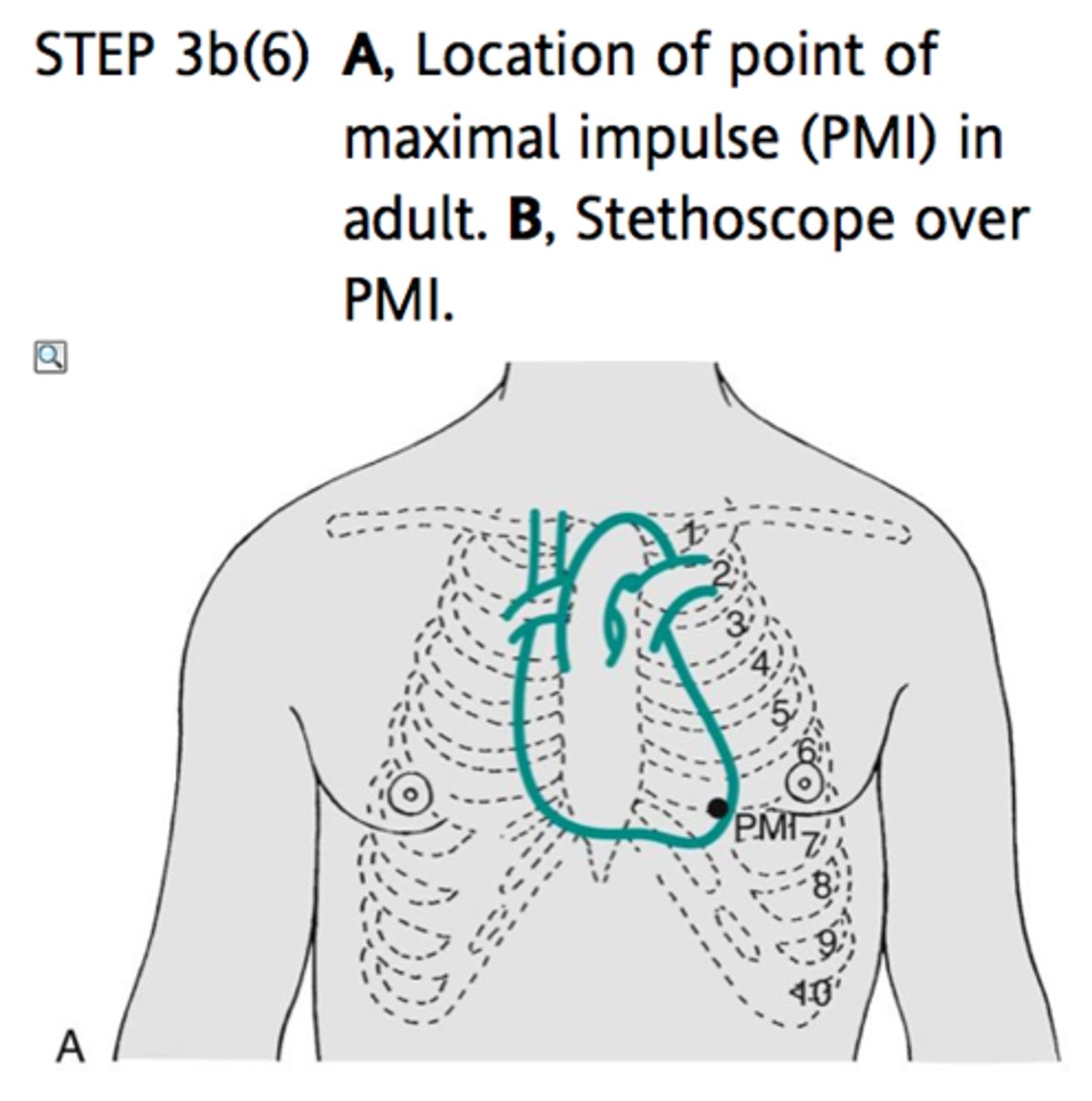
5th ICS
the apex beat of the heart is found in...
lower border of the pectoralis major muscle
the anterior axillary fold is made up of...
tendon of the latissimus dorsi muscle as it passes around the lower border of the teres major muscle
the posterior axillary fold is made up of...
spinous processes
Project backwards from each vertebra; also serve as attachment sites for skeletal muscles
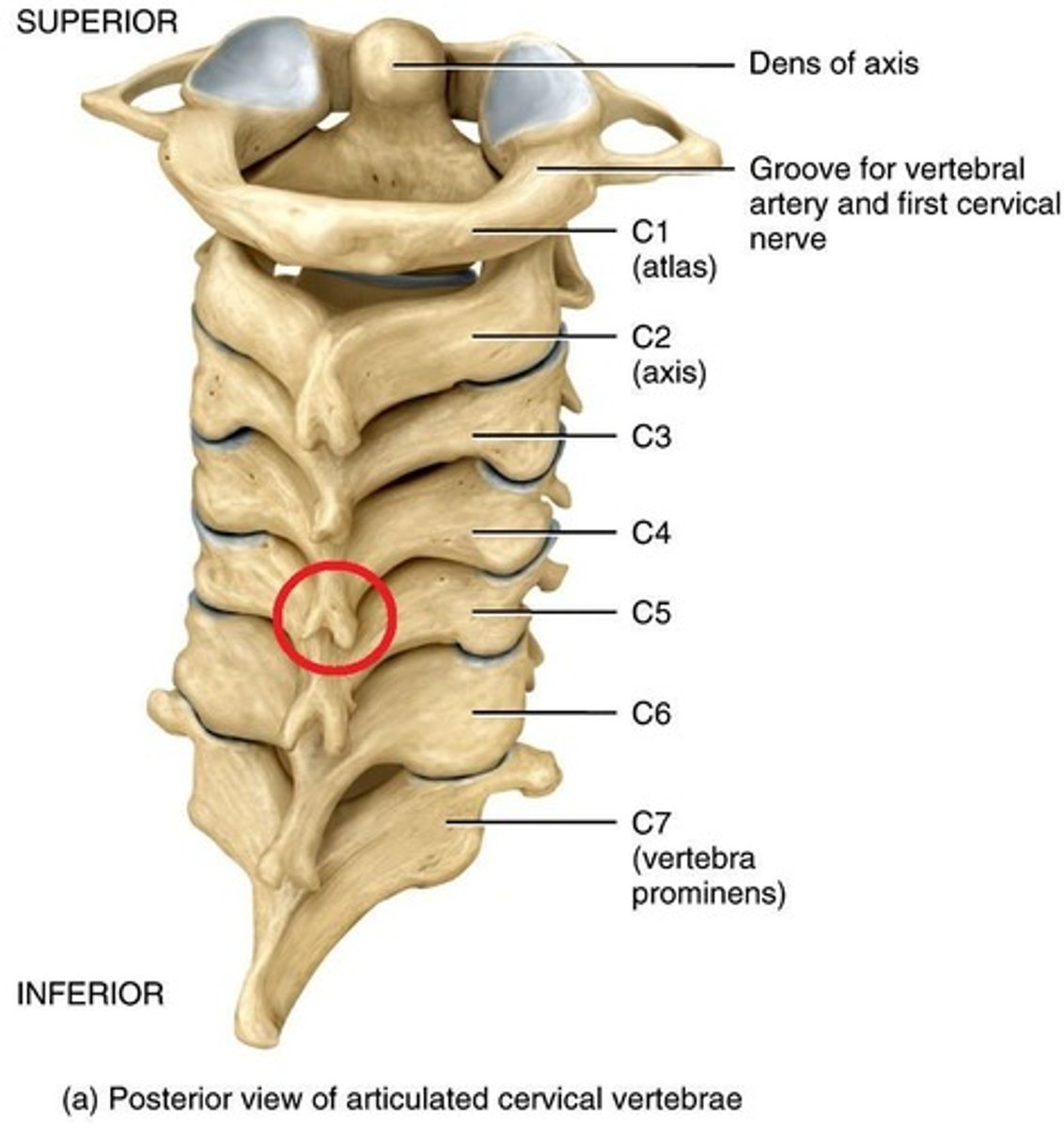
Vertebra prominens
spinous process of C7
Ligamentum Nuchae
an elastic ligament that connects the vertebrae of the neck to the skull
C1-C6
ligamentum niche runs from the spinous processes of...
Superior angle of the scapula
part of scapula that is opposite of spinous process of 2nd thoracic vertebrae
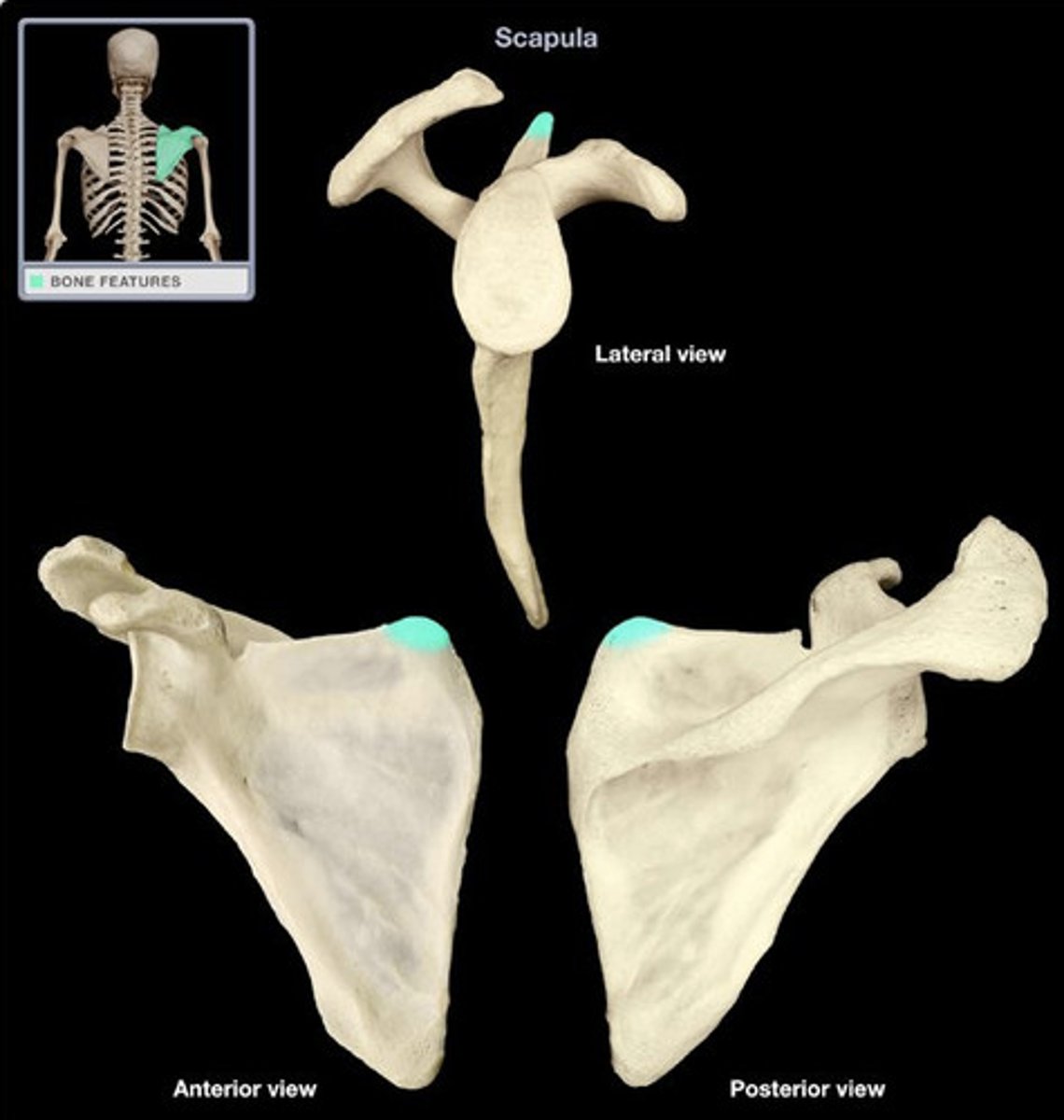
2nd
the superior angle of the scapula goes across from the ___ thoracic vertebra
Spine of the scapula
sharp ridge located on posterior side of the scapula; root lies on T3 level
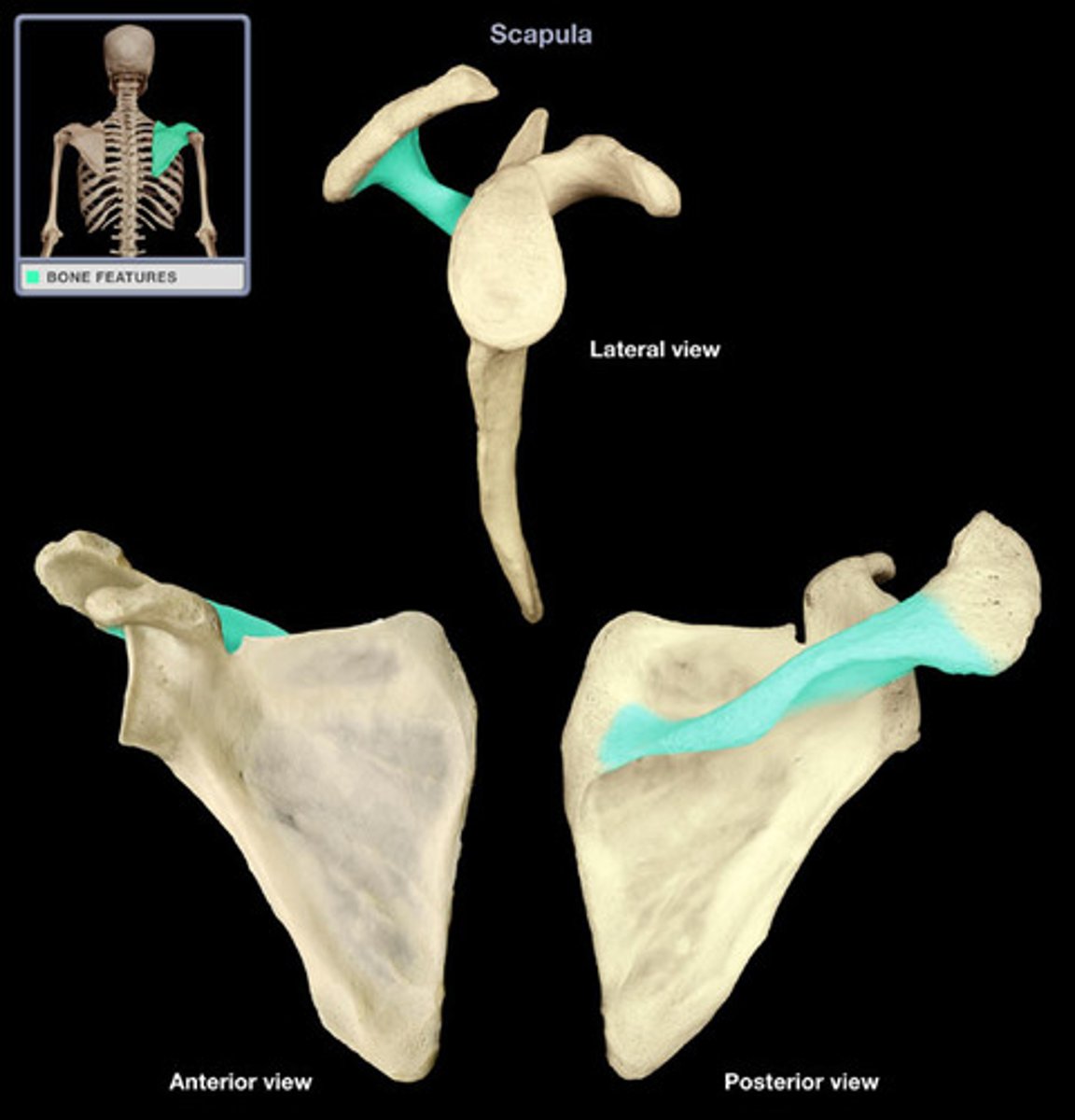
3rd
the spine of the scapula goes across from the ___ thoracic vertebra
inferior angle of scapula
bottom point of scapula (T7)
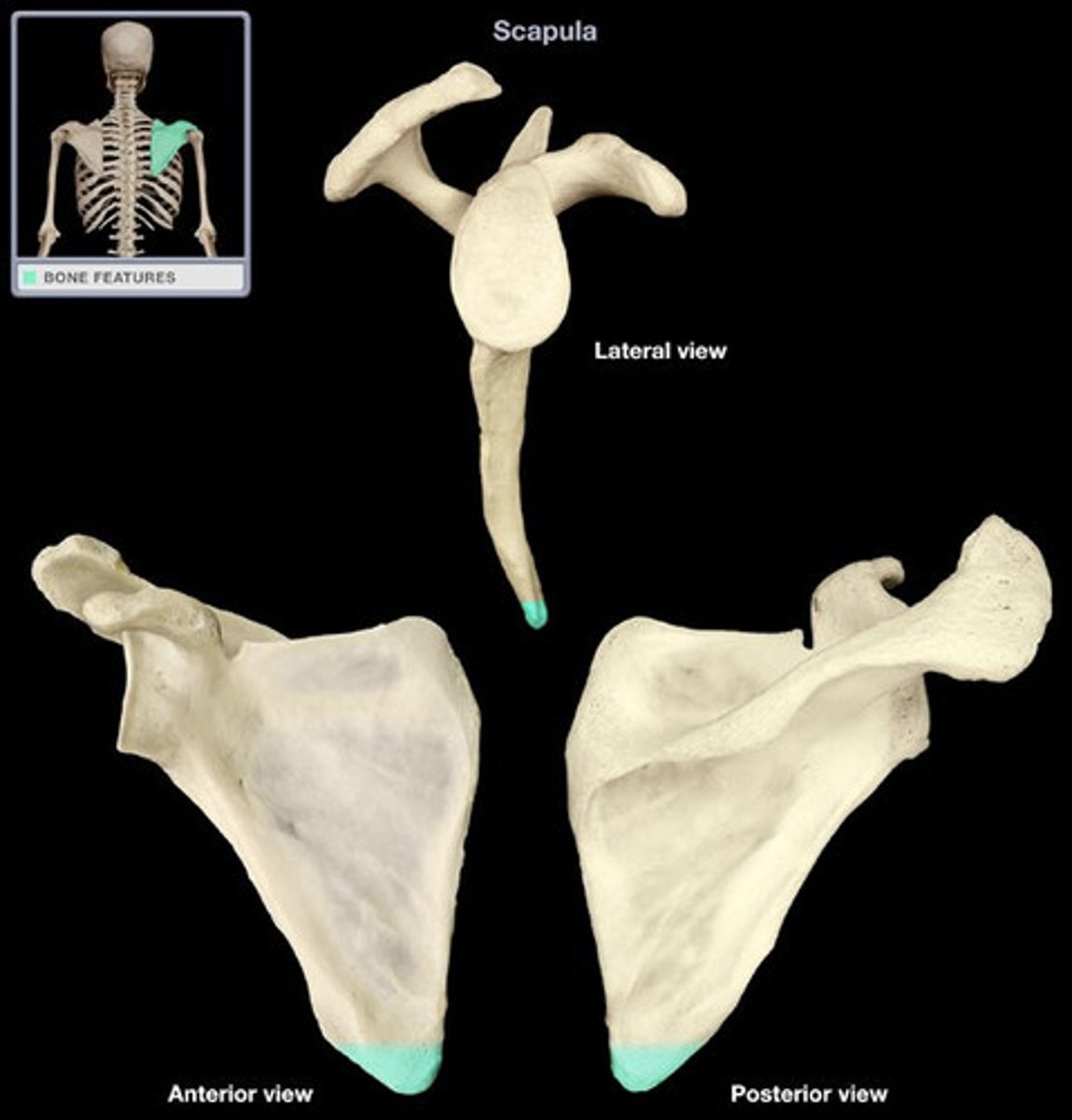
7th
the inferior angle of the scapula goes across from the ___ thoracic vertebra
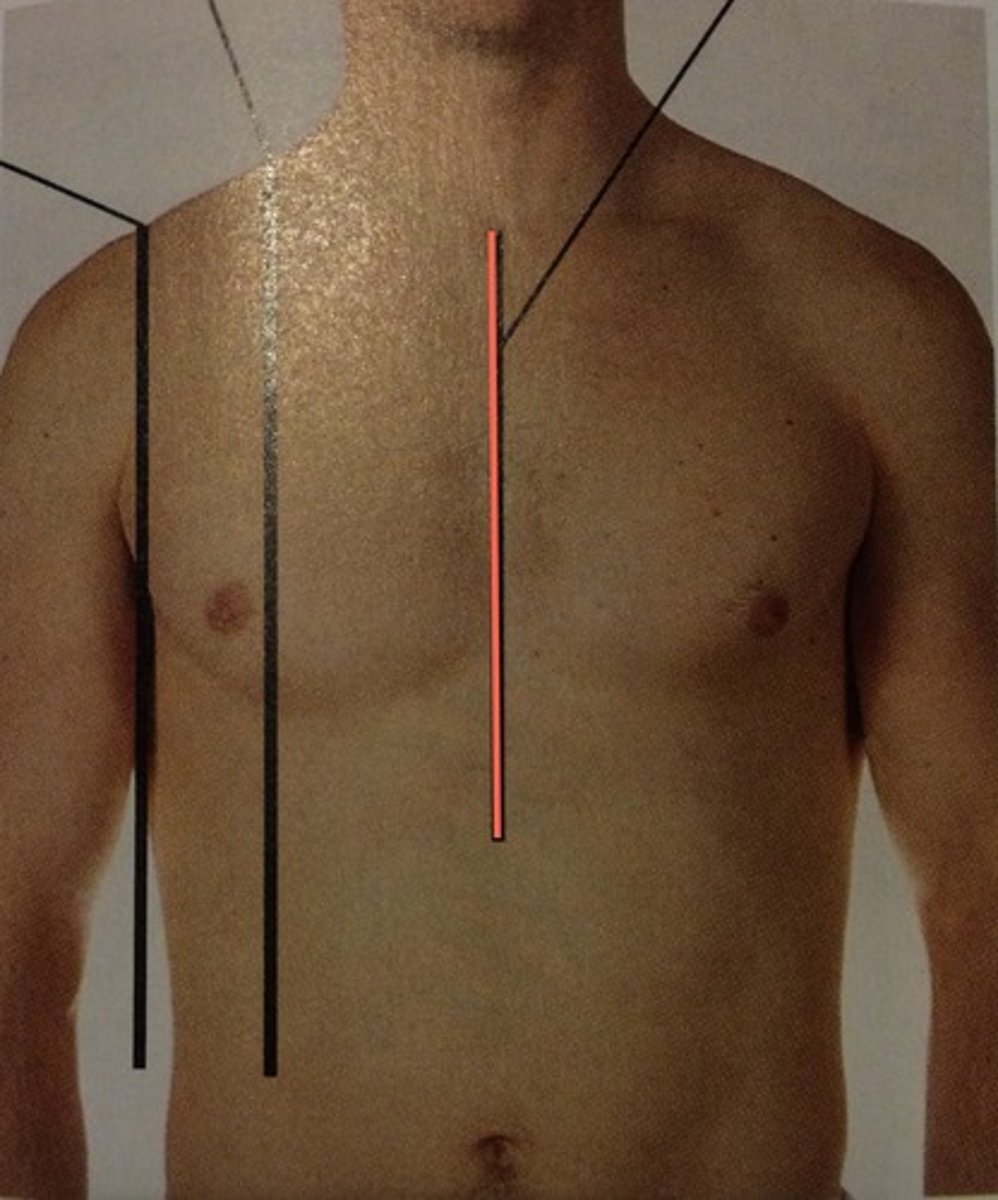
Midsternal line
a vertical line down the middle of the sternum
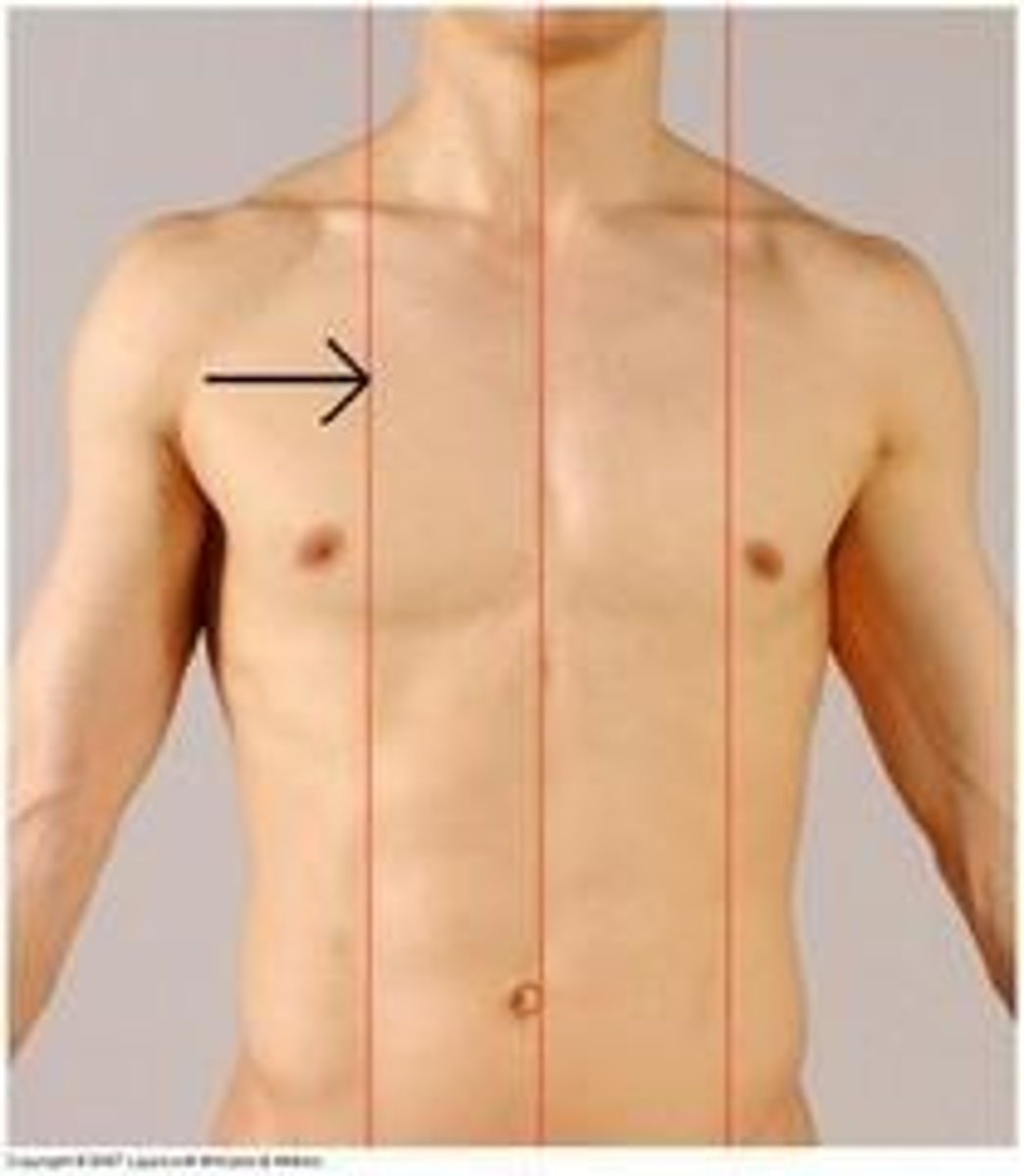
Midclavicular line
imaginary vertical line that runs vertically downward from the midpoint of the clavicle
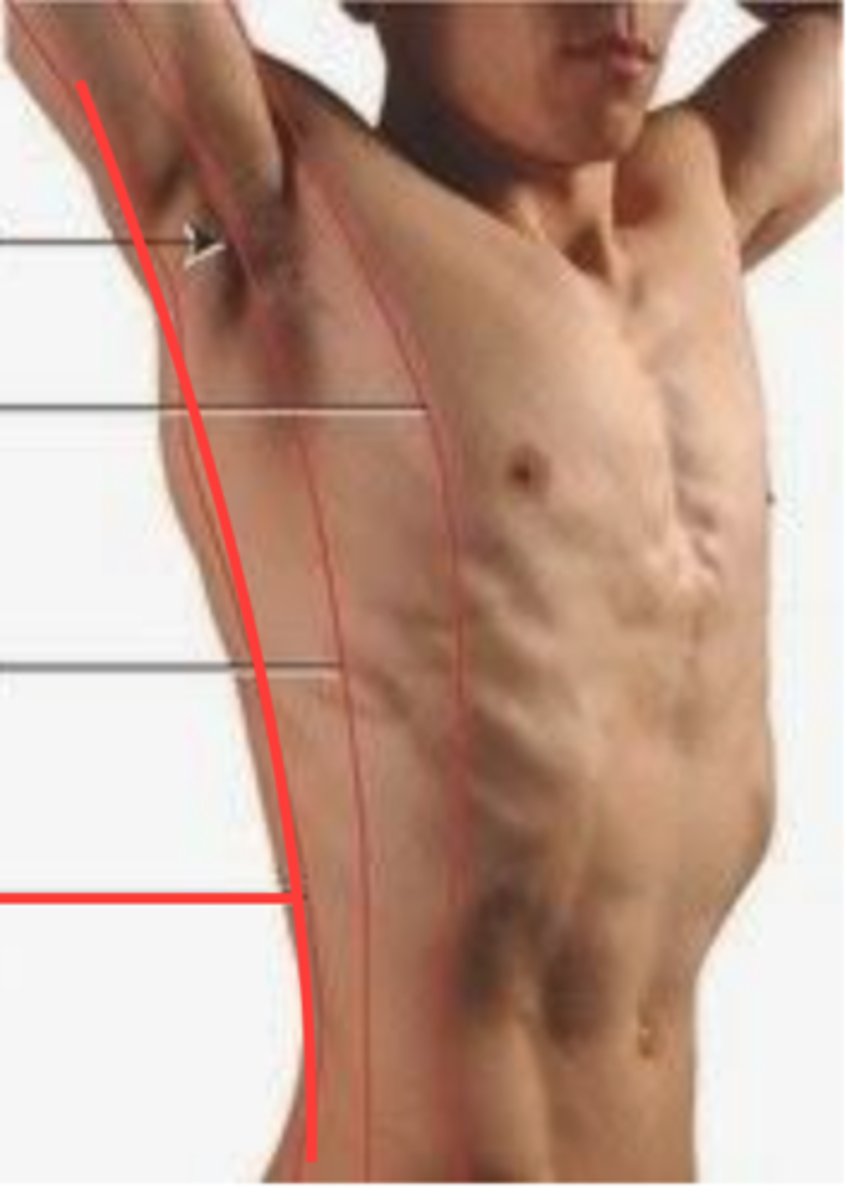
Anterior axillary line
imaginary line that runs vertically downward from the anterior axillary fold
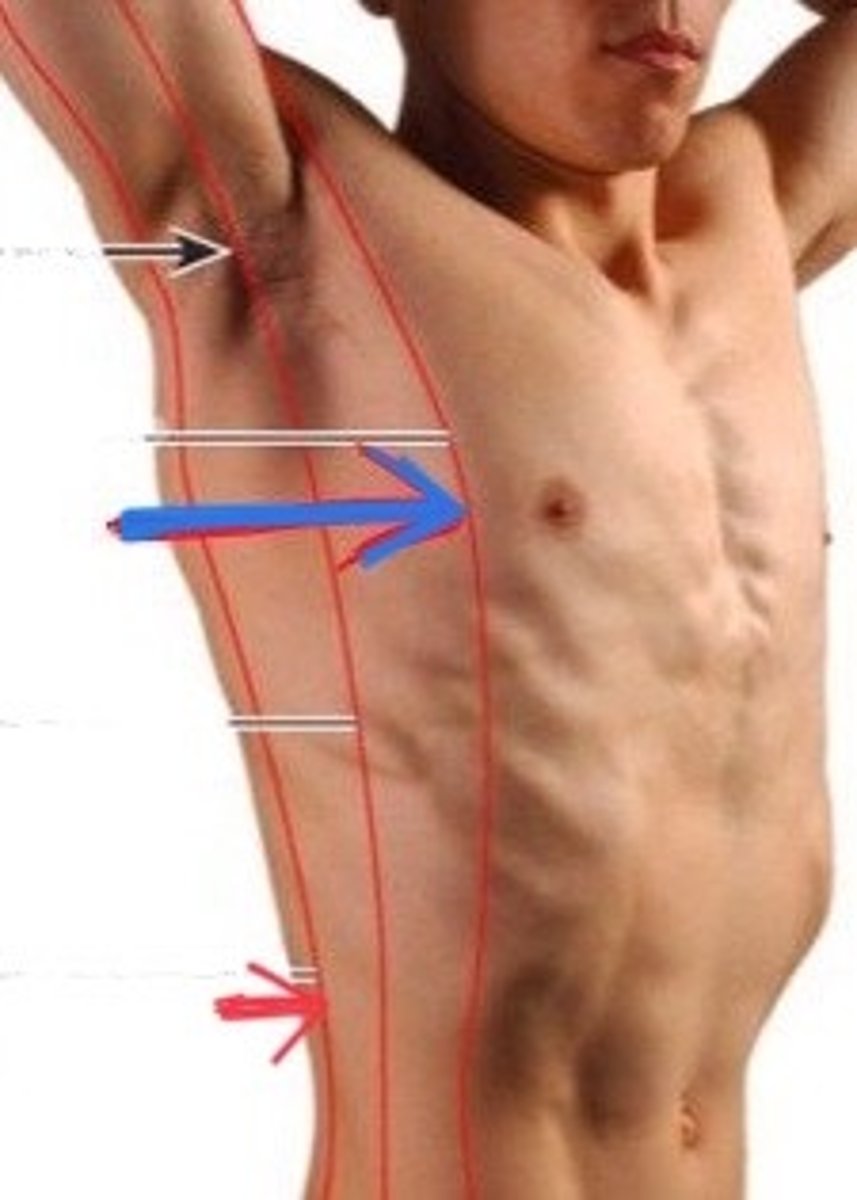
Posterior axillary line
imaginary line that runs vertically downward from the posterior axillary fold
midaxillary line
An imaginary vertical line that starts at the middle of the axilla (armpit) and extends down the side of the chest.
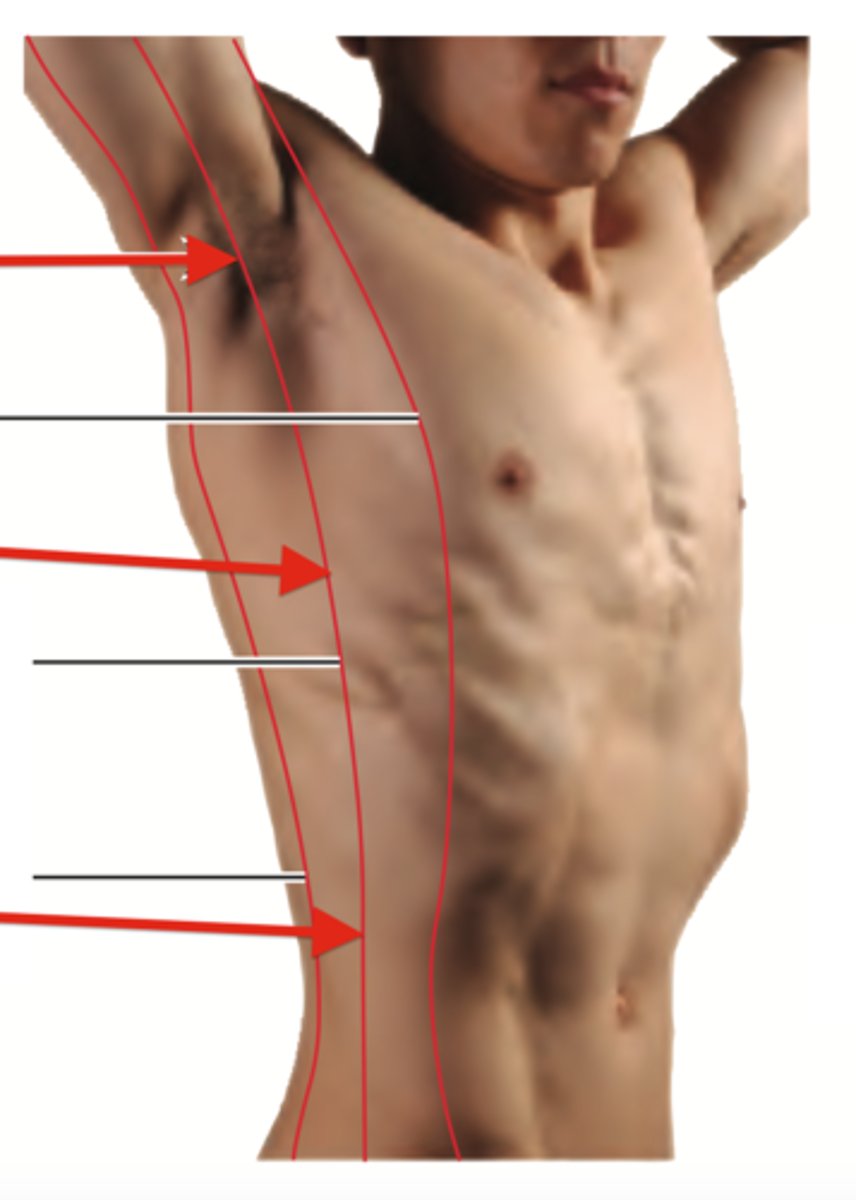
Scapular line
imaginary line that runs vertically downward on the posterior wall of the thorax, passing through the inferior angle of the scapula while the arms at at the side.
Trachea
a large membranous tube reinforced by rings of cartilage, extending from the larynx to the bronchial tubes and conveying air to and from the lungs; the windpipe.
lower border of the cricoid cartilage
the trachea begins from the...
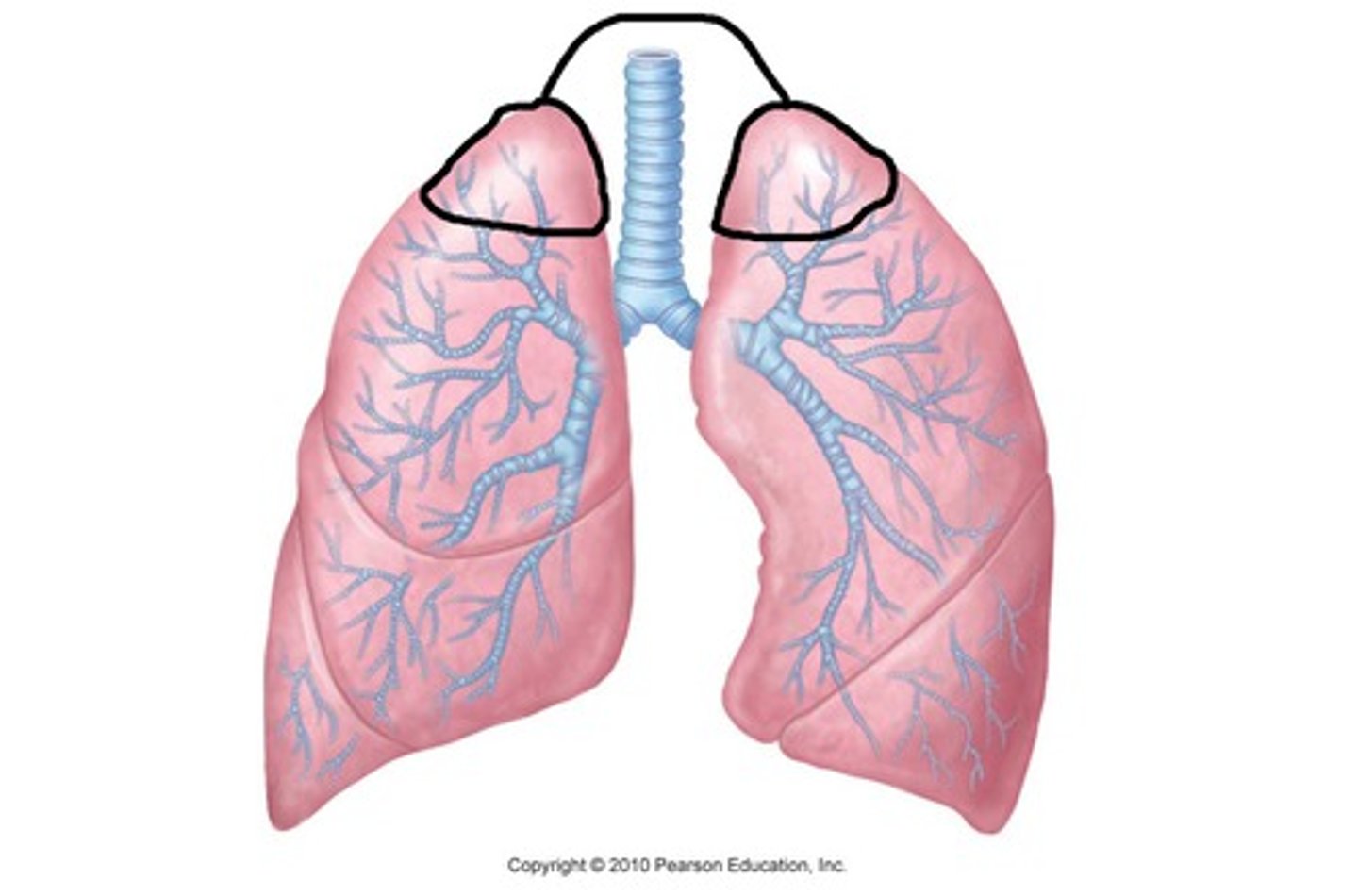
Apex of the lung
tip or uppermost portion of the lung.; projects into the neck
Anterior border of the right lung
Behind the sternoclavicular joint and runs downward almost reaching the midline behind the sternal angle, it then continues downward until it reaches the xiphisternal joint
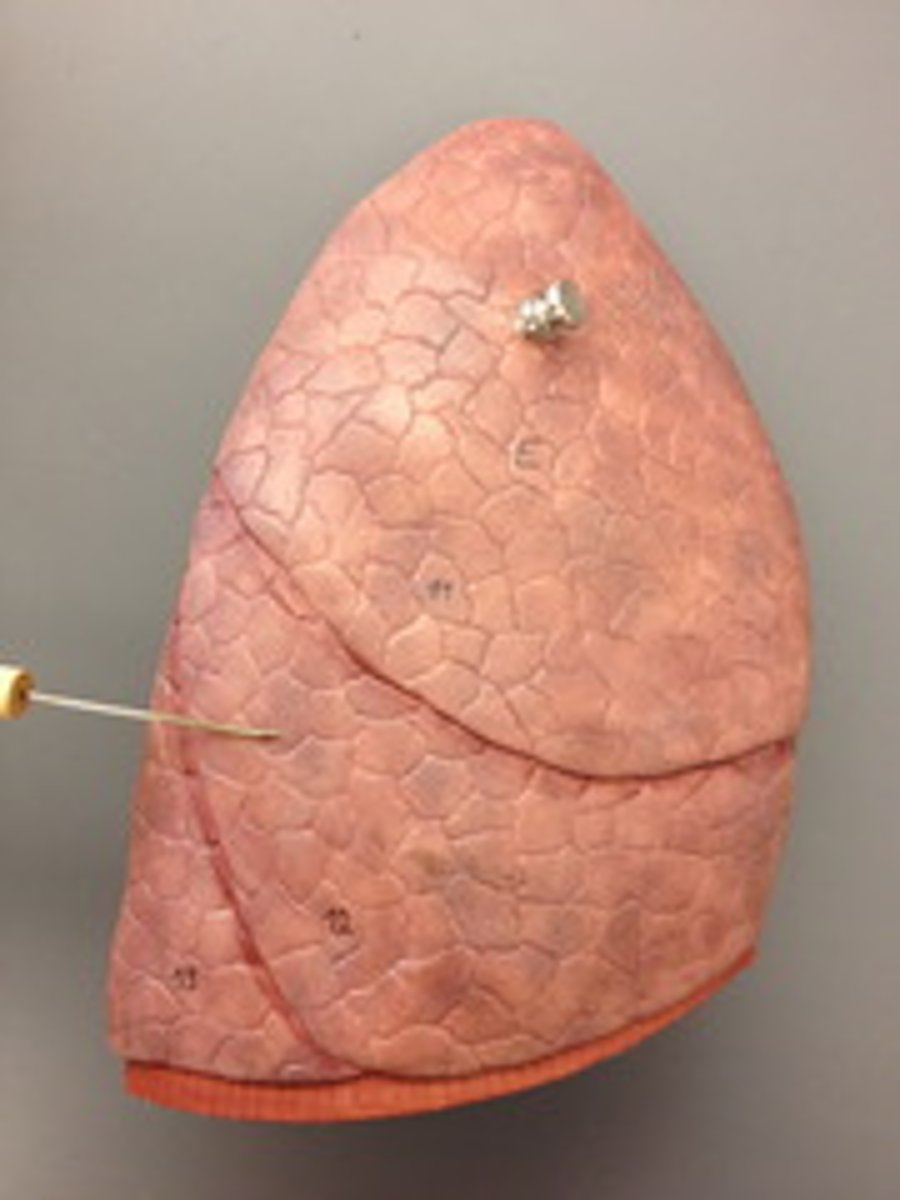
Anterior border of the left lung
similar to its counterpart, but at the level of the 4th costal cartilage, it deviates laterally and extends for a variable distance beyond the lateral margin of the sternum to form the cardiac notch
Cardiac notch
a concave space on the left lung in which the heart lies
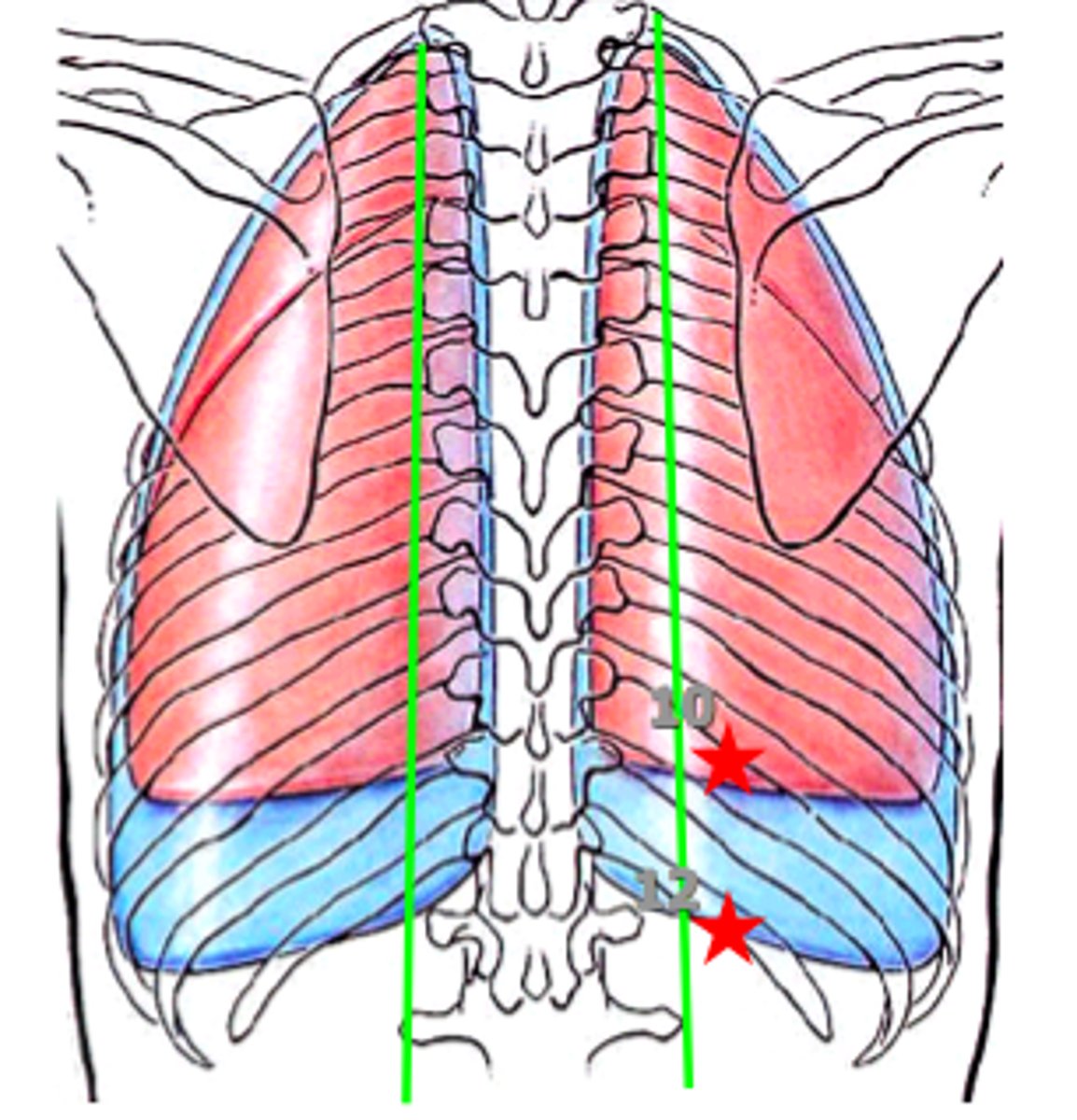
6th, 8th, and 10th ribs
the lower border of the lung extends into the...
Posterior border of the lung
where costal and mediastinal surfaces meet posteriorly
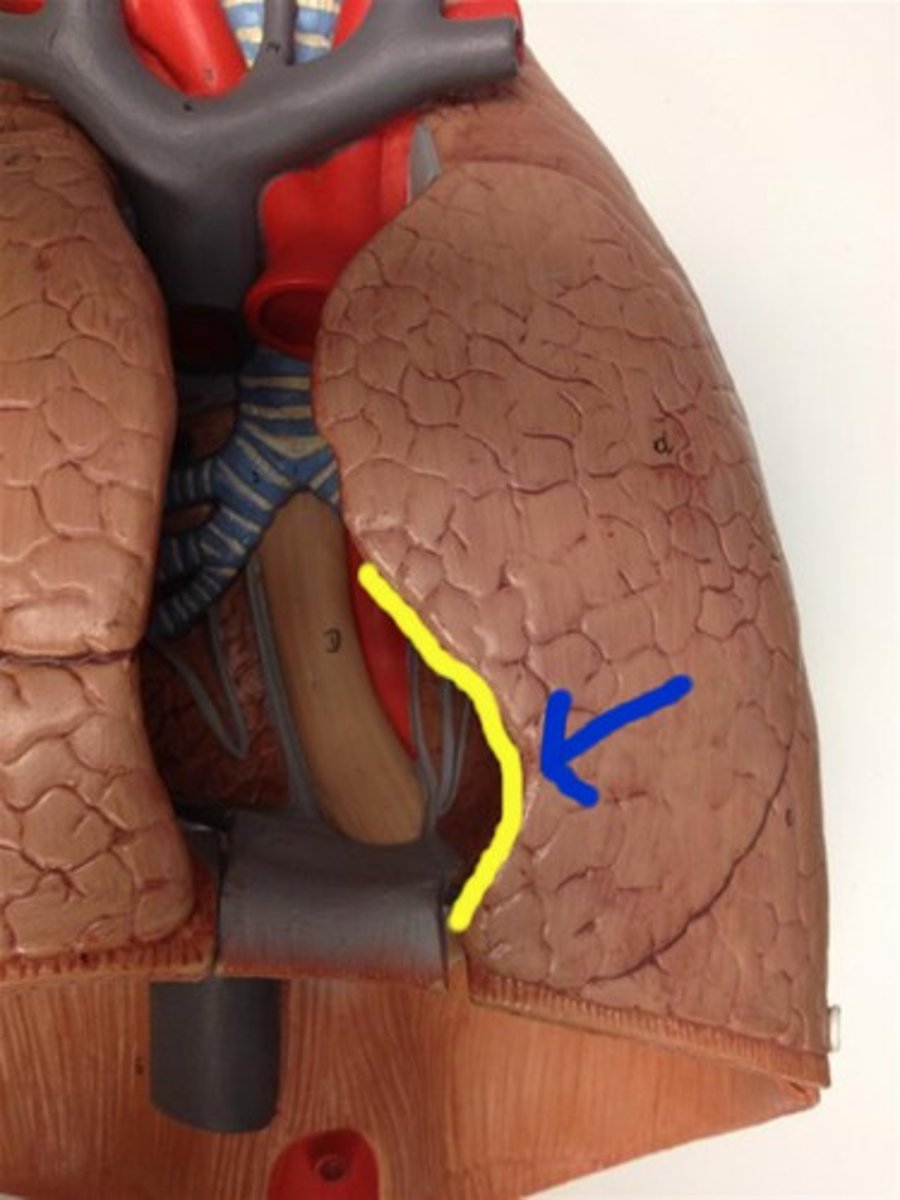
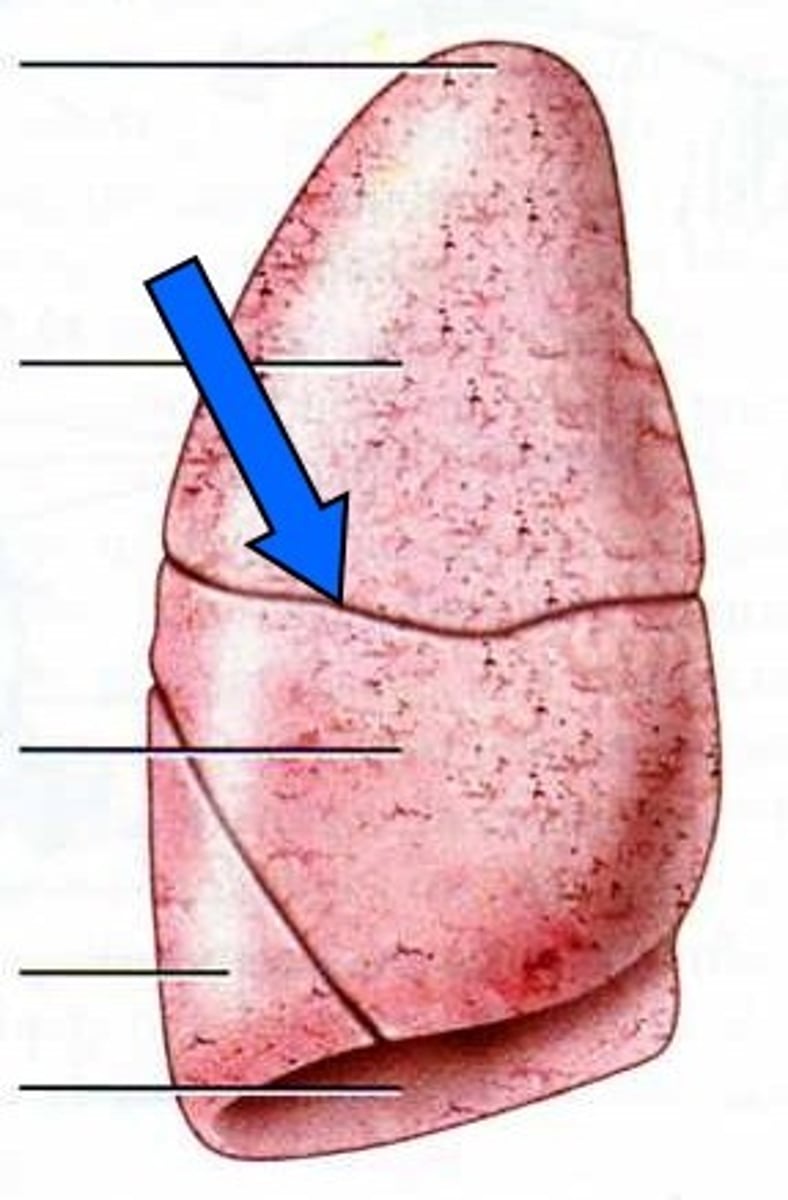
oblique fissure
separates superior and inferior lobes of the R/L lungs
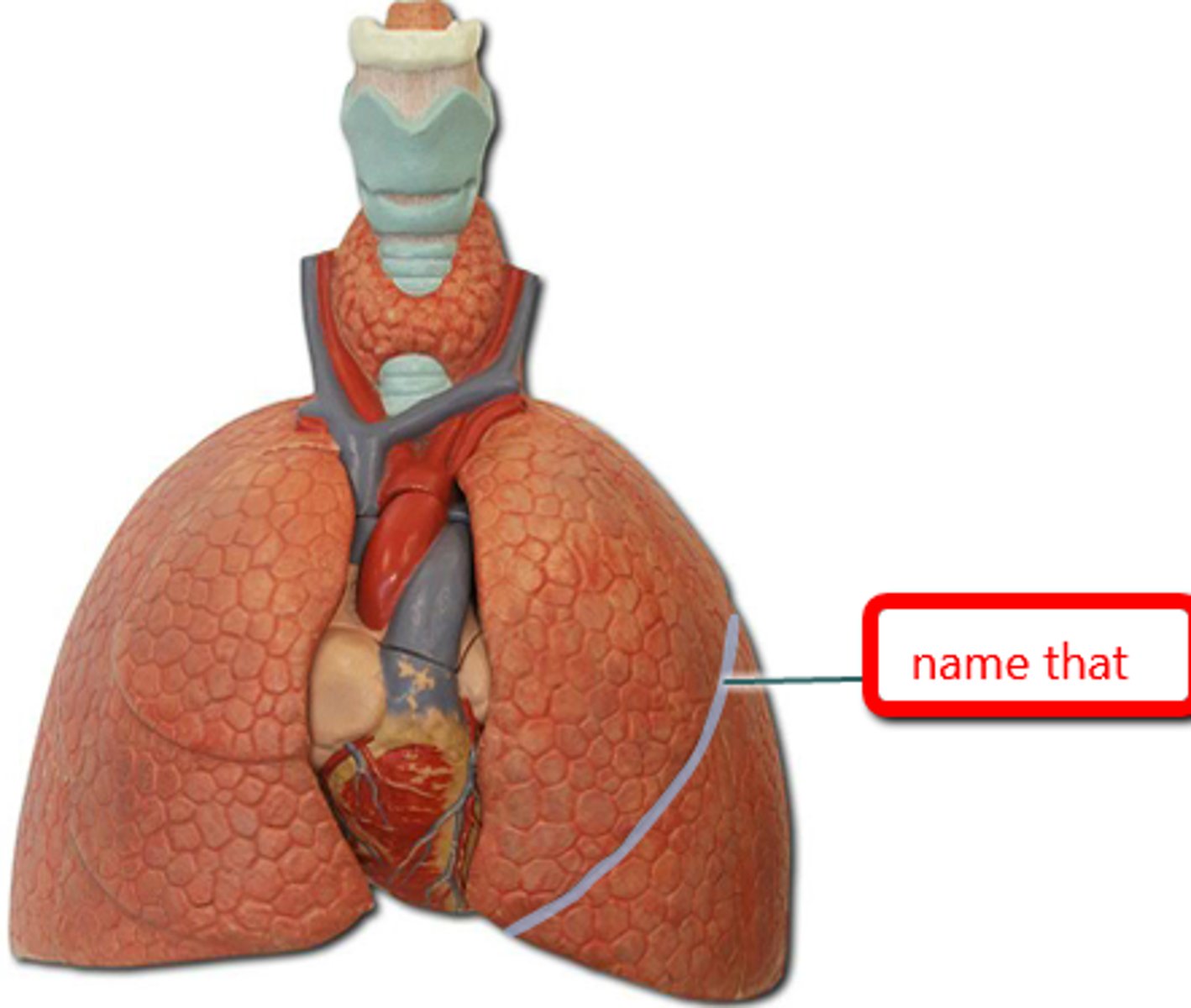
Horizontal fissure
separates the superior and middle lobes of the right lung
so the heart can fit into the the cardiac notch
why does the right lung have 3 lobes while the left only has 2?
lateral border of sternum to midaxillary line
the female breasts extend from...
2nd, 6th
the female breasts span from the ___ to ____ ribs
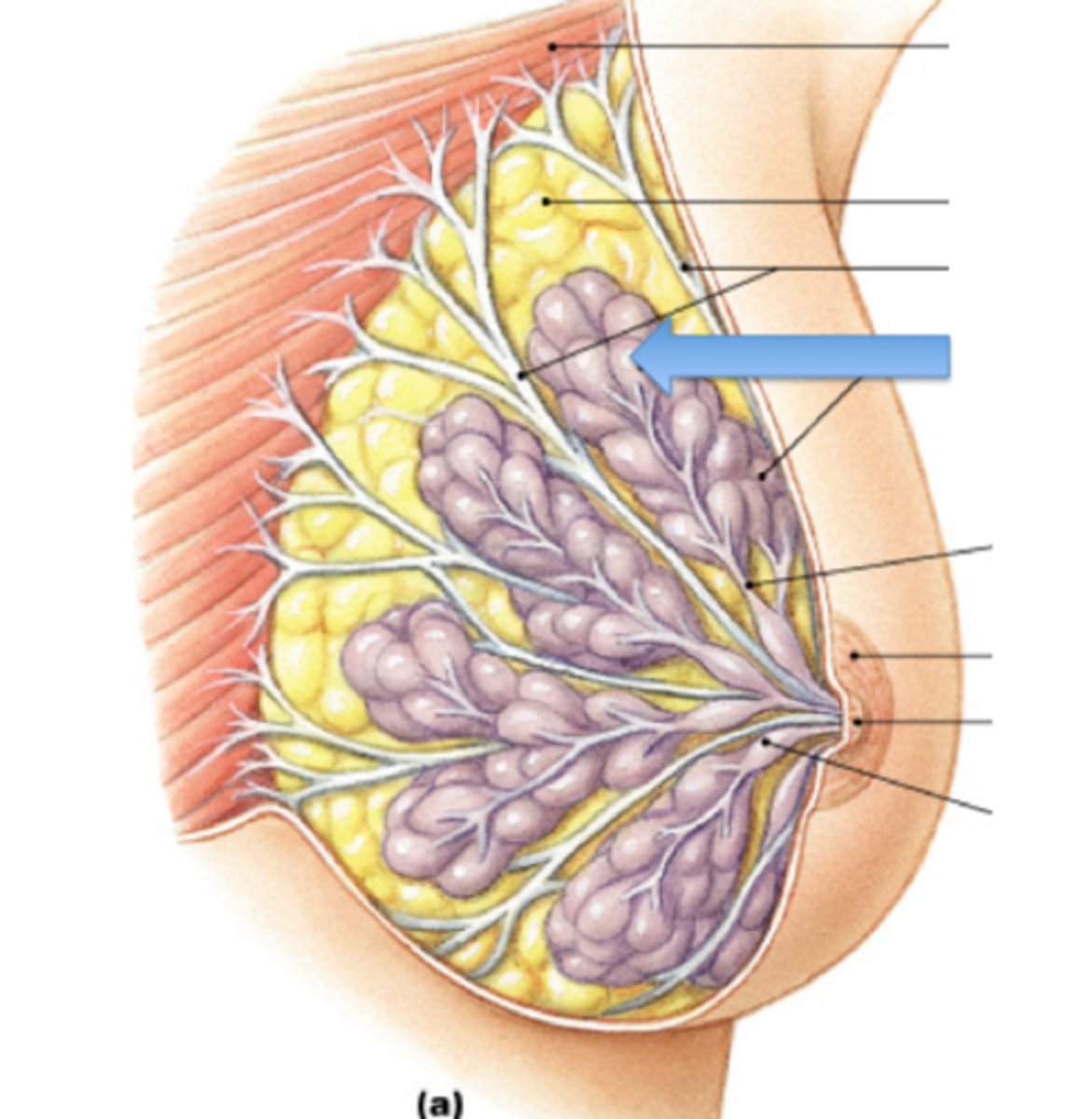
axillary tail of spence
superior lateral corner of breast tissue, projects up and laterally into axilla
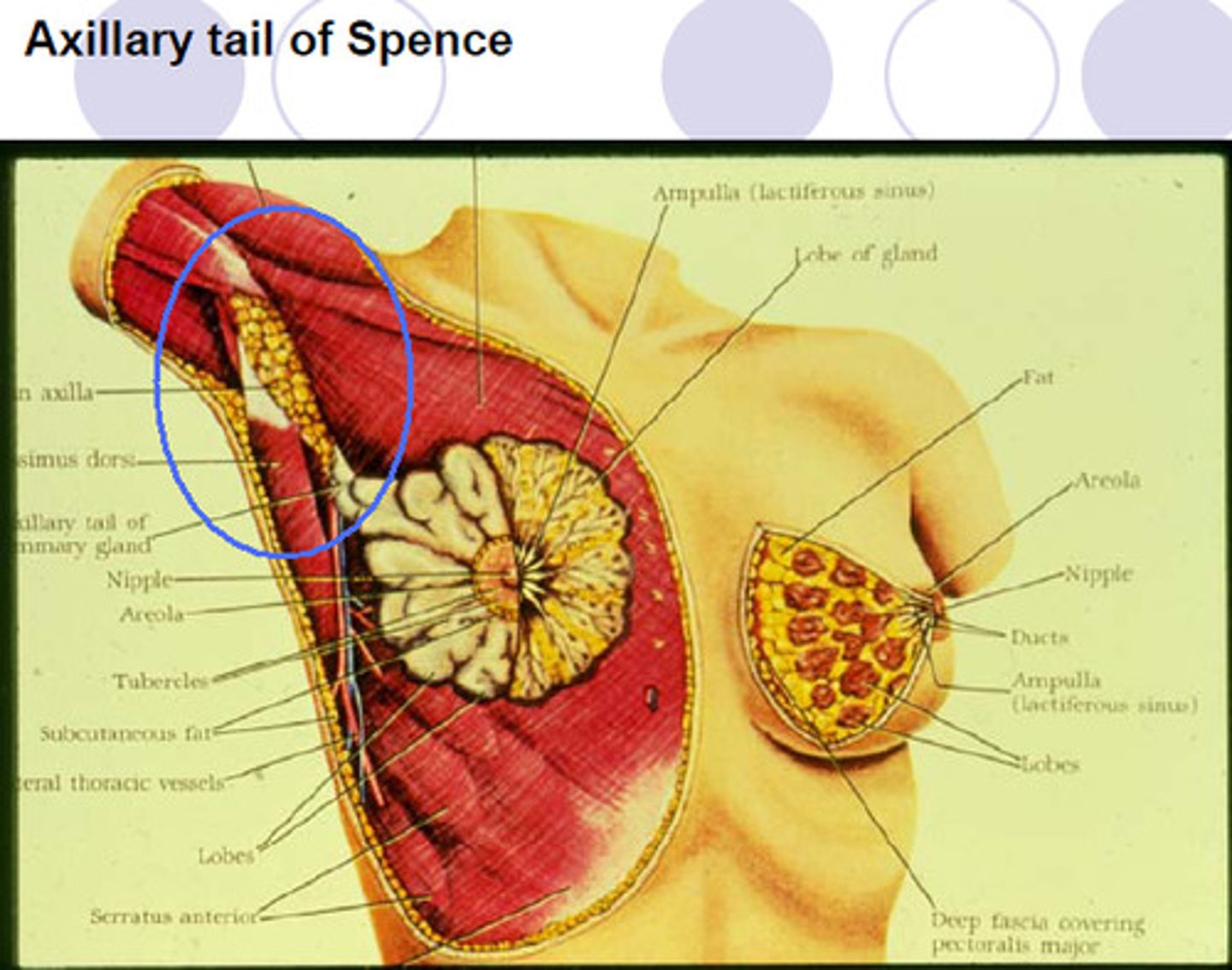
deep pectoral fascia overlying the pectoralis major
2/3 of the breast rests on the...
fascia covering serratus anterior
1/3 of the breast rests on the...
Retromammary space
potential space between breast tissue and pectoralis major; allows for movement of breast on pectoral fascia
allows for movement of breast on pectoral fascia
function of retromamary space
suspensory ligaments of breast
attach breast to underlying muscle
Breast lobules
gland in the breast that makes milk; have 15-20
Lactiferous ducts
drains each boule, opens independently of nipple
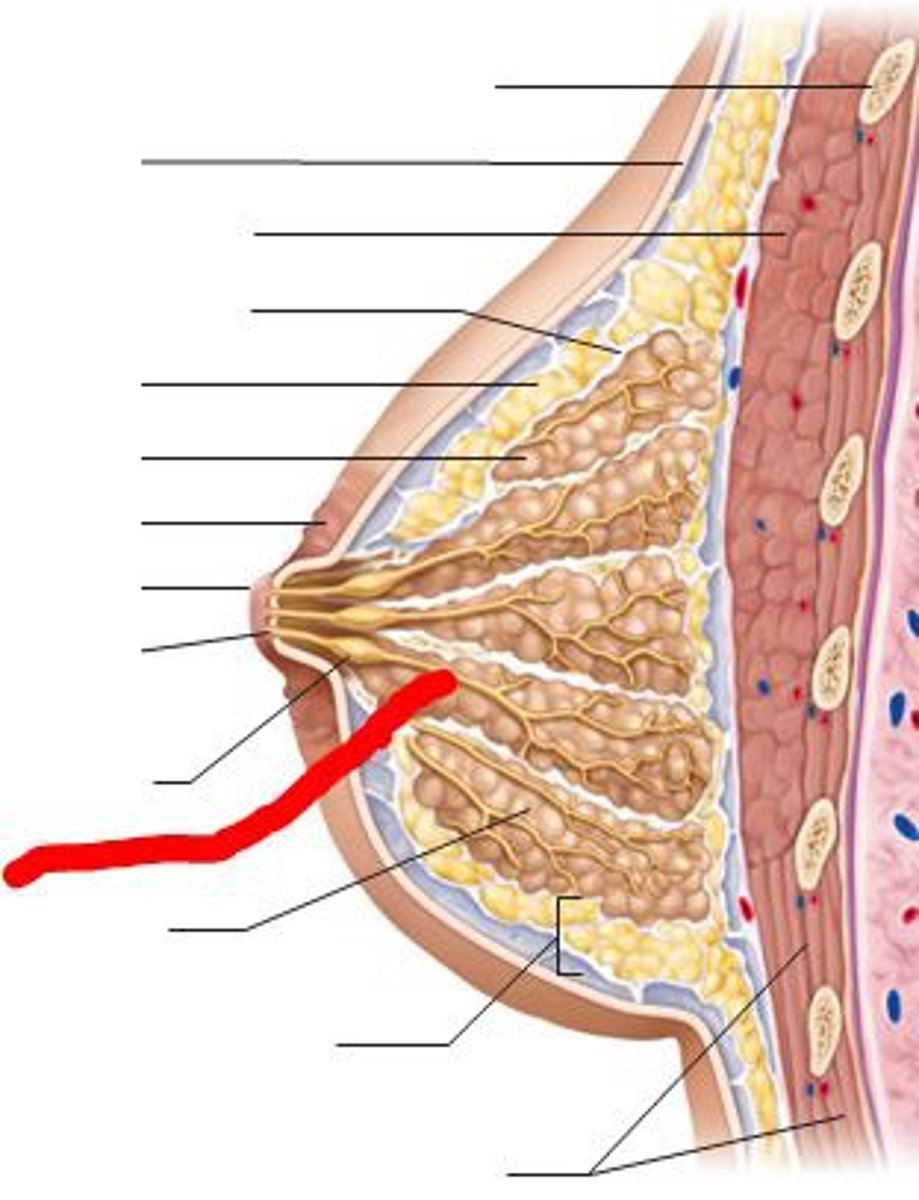
Lactiferous sinus
under areola; dilated reservoir for milk during lactation
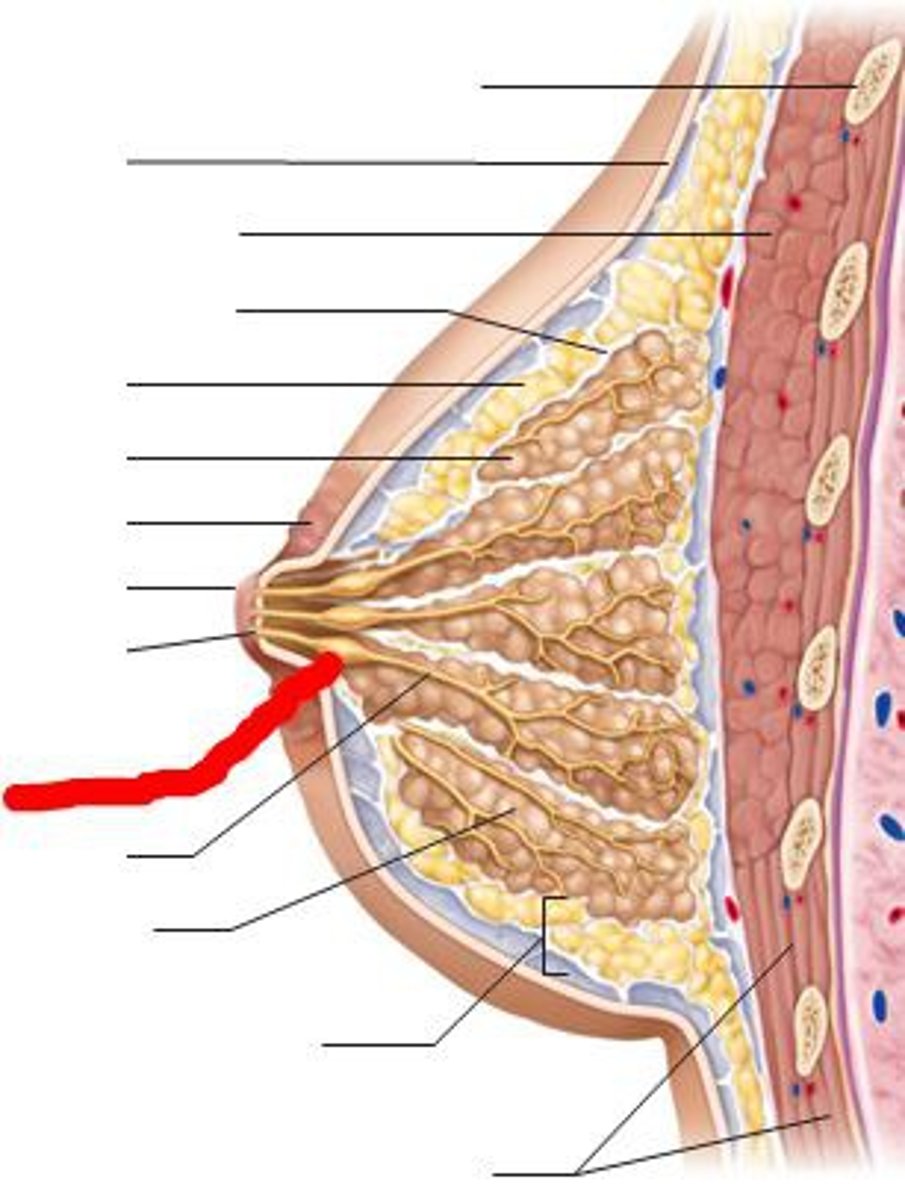
Let down reflex
the reflex that forces milk to the front of the breast when the infant begins to nurse; infant compresses areola and the lactiferous sinus and a droplet of milk will come out; encourages infant to continue to suckle on breast; actual reflex occurs when milk is secreted into the baby's mouth
Montgomery glands/tubercles
"small bumps" located around areola that secrete an oily substance during pregnancy and lactation; a lubricant
Mammary glands
accessory glands of the skin that are capable of secreting milk
yes; in the male and immature female, the breast are similar in structure
are mammary glands present in both sexes?
areola
dark-pigmented area surrounding the breast nipple
connective tissues
ducts are embedded in...
capsule or sheath
mammary glands are modified sweat glands, meaning they have no...
fat lobules
most of the breast is composed of...
new glandular tissue will form
breasts will enlarge during pregnancy because...
Alveoli
milk-secreting grape like clusters
FSH/LH increase; secondary to gonadotropin hormones
breasts enlarge slightly during menstrual cycles due to...
Colostrum
premium fluid that is secreted from the breast during the last trimester of pregnancy and at the beginning of nursing; rich in protein, growth factors, and helps the infant's intestines
large and pendulous
in multiparous women, the breast often become...
the decrease in fat and atrophy of glandular tissue
why do breasts become small/wrinkled in elderly women?
4
the breasts are divided into ___ quadrants; they are used to document masses or physical findings on examination
location, size, consistency, mobility, and delimitation of the mass
if one finds a mass on a breast exam, one must note the...
upper outer quadrant
breast masses are mostly found in the...
internal thoracic (mammary) artery, lateral thoracic artery, thoracoacromial arteries, posterior intercostal arteries
arterial supply of the breast
axillary vein
main venous drainage of the breast
internal thoracic vein, posterior intercostal veins
other routes of venous drainage for the breast
they drain into the azygos and hemiazygos system of veins alongside the bodies of the vertebrae -- this can be a route in which cancer cells can spread from the breast to the vertebrae and from there to the skull and brain
why are the posterior intercostal veins important clinically?
axillary lymph nodes, pectoral (anterior) does, parasternal nodes, phrenic nodes
lymphatic drainage of the breast
axillary lymph nodes, initially to the anterior nodes
most lymph from the breast drains to the...
parasternal nodes
the remaining lymph goes to the ______ after the axillary nodes
supraclavicular/infraclavicular, subclavian lymphatic trunk
lymph from the axillary nodes goes to the ______ and _______ nodes and then into ________.
bronchomediastinal
lymph form the parasternal nodes travels to the _______ trunk
abdominal nodes (phrenic)
lymph form the lower breast quadrants pass deep to the...
4th-6th intercostal nerves
the nerves of the breast derive from anterior and lateral cutaneous branches of the...
Breast cancer
the most common cancer in women and the 2nd leading cause of cancer death (after lung) in women in the US; 1 in 8 American women affected; 2/3 of cases occur in postmenopausal women
adenocarcinoma
most common cell type for breast cancer
skin retraction/skin dimpling, nipple retraction, mass, palpable nodes
clinical signs of breast cancer
dimpling of skin over carcinoma is caused by involvement and retraction of Cooper's ligaments
what causes dimpling of the skin in breast cancer?
cancer involvement of mammary ducts may cause duct shortening and retraction of inversion of the nipple
what causes nipple retraction in breast cancer?
axillary nodes
what nodes are the most common site of breast cancer metastasis?
Peau d'orange
orange peel appearance of breast due to interference with lymphatic drainage of the breast by cancer; skin is puffy and has prominent pores that give it an orange peel appearance
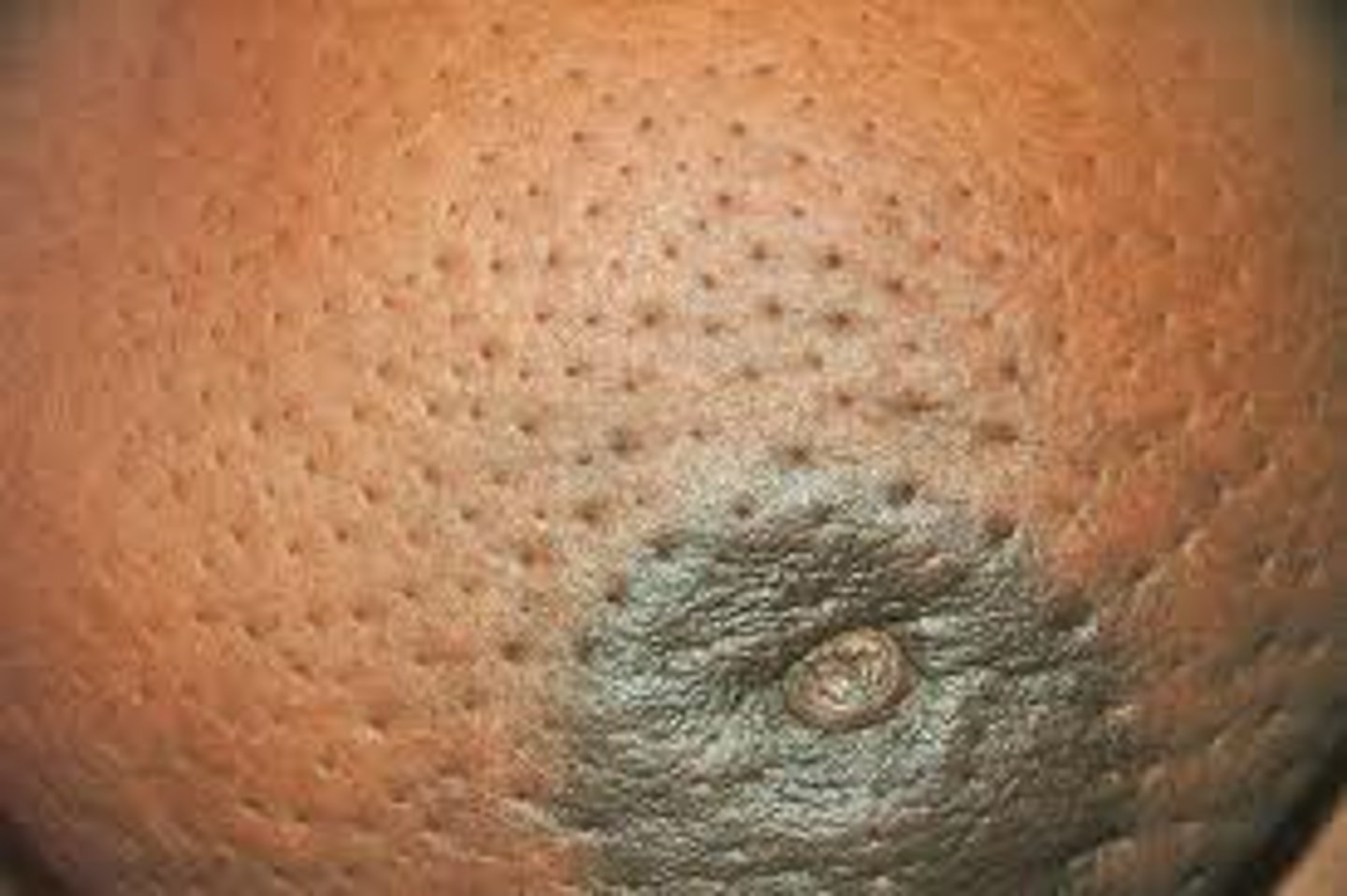
subareolar breast cancer
nipple inversion can occur from...
stereotactic biopsy
needle biopsy using a computer-guided imaging system to locate suspicious tissue and remove samples for study
lumpectomy
excision of a small primary breast tumor and some of the normal tissue that surrounds it
sentinel lymph node biopsy
injection of blue dye and/or radioactive isotope used to identify the sentinel lymph nodes
Simple mastectomy
removal of an entire breast but with the underlying muscle and axillary lymph nodes left intact; breast removed down to retromammary space
radial mastectomy
the surgical removal of an entire breast and many of the surrounding tissues such as pectoral muscles, fat, fascia, lymph nodes, in axillary and pectoral region
Supernumerary breasts
extra breasts that may appear anywhere along a line extending from the axilla to the groin (Milk line)
Milk line
the location of the embryonic mammary ridge from which the breast develops
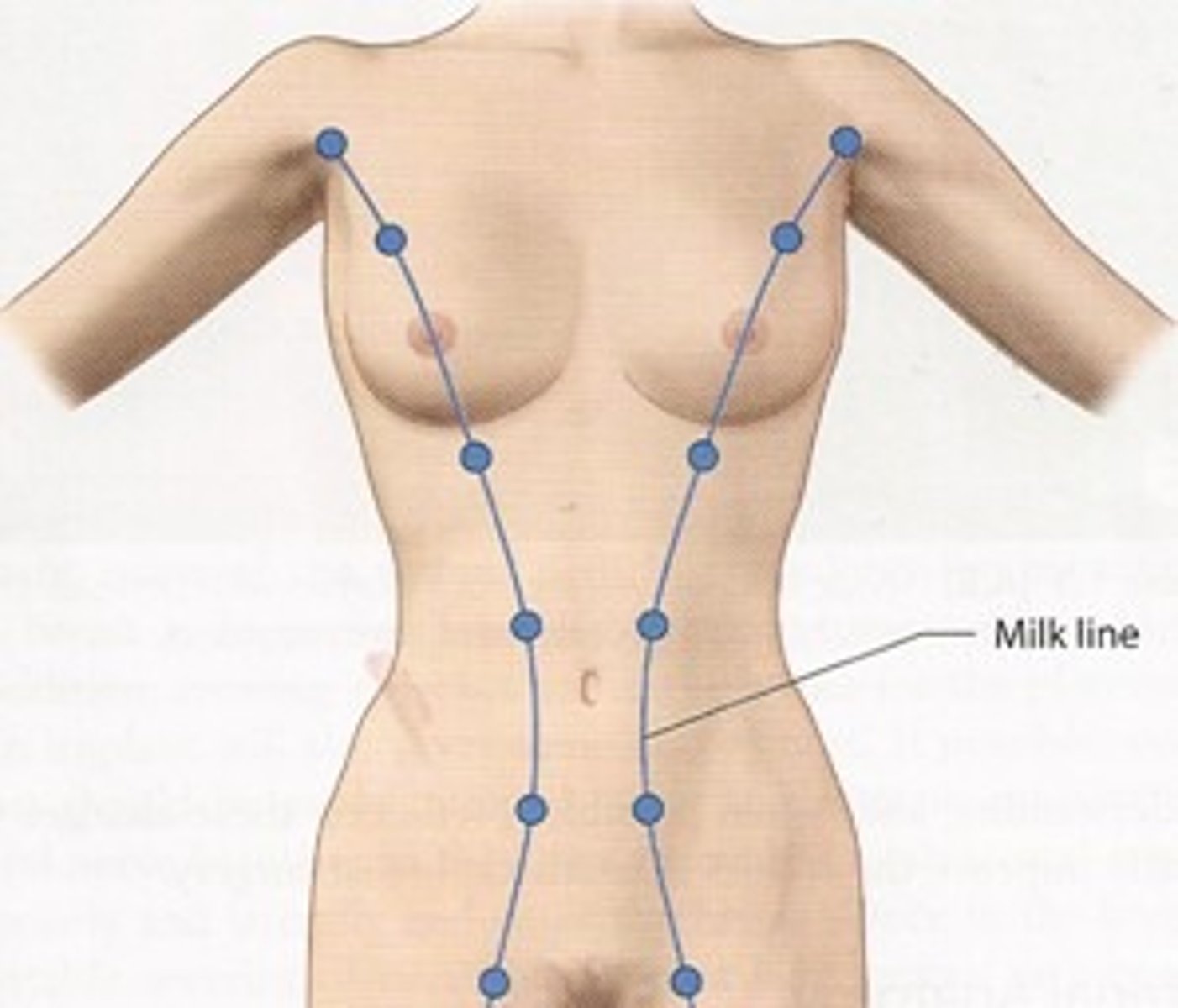
Polymastia
presence of more than two breasts
Polythelia
extra nipples
Gynecomastia
enlargement of one or both breasts in men
puberty, aging, drug-related (antihypertensives, estrogen), medical conditions (cirrhosis of liver, testicualr tumors, pituitary adenoma)
what can cause gynecomastia?