AP Psych Notes
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
what do behavior geneticists seek to understand?
the role of genetic heredity in humans
what does every cell in our body have?
our genetic code (genome)
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 (23 pairs)
are genomes different?
yes, but barely (0.1%). still create major differences in humans
genetic difference between humans and chimps
1.6%
what do we need to learn about the impact of heredity on human behavior?
case studies
important case studies on heredity?
*identical twins that shared identical genomes being raised in separate households.
can environmental factors fully explain differences in human behavior?
no, but play a large part.
are our genes destiny? example?
no, because of the role of our environmental factors.
*while intelligence is strongly hereditary, access to nutrition and a stable
home life decisively impacts it.
can you link behavior to genetic heritability?
no bc our genes and environment exist in a dynamic relationship.
what happens to our genes in reaction to our environment? what is this study called?
our genes change their behavior, or gene expression, in reaction to our environment. this is called epigenetics.
evolutionary psyschology
seeks to apply darwinian evolution to explain human behavior.
what is the most important principle in Darwinian's evolution?
natural selection
natural selection
principle that those traits which contribute to an organism's survival and reproduction are most likely to be passed on.
what do exolutionary psychologists use natural selection to explain?
Elements of human behavior that appear to be true cross-culturally.
ex: human sexual and reproductive behaviors
what do evolutionary psychologists think of male sex drives?
males have higher sex drive, initiate more sexual activity, perceive friendly non-sexual encounters as sexual interest.
What do evolutionary psychologists think of female sex drives?
lower sex drive, greater selectivity, impacted by hormone changes, bond emotionally (oxytocin)
what do critics of evolutionary psychology say?
*generalizes too much and imposes socially normative views on people who might not fit them
*untestable
neuron
the basic structure making possible the transmission of information between the mind and the outside world.
neuron structure?
1. Cell body (soma)
2. Dendrites
3. Axon
dendrites
(branching fibers, extending off the cell body) receive messages from other cells
Axons
(long "tails", extending from the cell body) send information to other cells.
how is information sent between neurons?
as electrical pulse called action potential.
how do neurons generate action potentials?
depolarization
what are the charges of the fluid around neurons?
the fluid INSIDE is negative, the fluid OUTSIDE is positive
resting potential
state when positively and negatively charged fluids in neurons are seperated.
what happens when a neuron is electrically stimulated?
gaps in the axon membrane open, commencing depolarization.
* the positive and negative ions come into contact, generating action potential ( moves from cell body to axon terminal
where does communication between neurons take place?
synapses junctions
synapses
tiny gaps where the axon terminal of one neuron comes into proximity with the dendrite of another.
What is sent between neurons synapses? who sends them?
chemical molecules called neurotransmitters are sent across this synaptic gap BY action potentials.
what do neurotransmitters do?
transmit signals between neurons by binding themselves to receptor sites on dendrites of other neurons.
reuptake process
returns excess neurotransmitter to the sending neuron for storage and future use. (neuron recycling)
myelin sheath
fatty material around the axon that aids in efficient neural communication with the body.
when does myelin stop being produced?
25
what disease means that your myelin is severely depleted
multiple sclerosis
what does your nervous system consist of?
1. central nervous system
2. peripheral nervous system
what is the central nervous system made up of?
brain and spinal cord only
how many neurons make up your brain?
tens of billions of neurons
what is the most complex part of the nervous system?
brain!
what does your spinal cord do?
it is a two-way information transmitter between your brain and peripheral nervous system (simpler than brain)
afferent neurons?
send sensory information up the brain
efferent neurons
send motor information down to muscles and glands
two components of the peripheral nervous system?
1. somatic nervous system
2. autonomic nervous system
somatic nervous system
enables control of skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system
controls glands and internal organs
*regulates involuntary processes (heartbeat, respiration, and digestion).
what are the exceptions to the autonomic ns?
You can choose to override involuntary functions (respiration) but can't do it for digestion etc.
two subsets of autonomic nervous system
1. sympathetic n.s (arouses body, expends energy)
2. parasympathetic n.s; (calms body, conserves energy)
what are reflexes?
somatic nervous system in response to sensory stimuli.
what is the neural process of our reflexes?
centered in a single neural pathways (reflex arc) made up of one afferent (sensory) neuron and one efferent (motor) neuron. Linked between an interneuron in the spinal cord (no brain needed).
where do neurotransmitters move?
throughout the brain and spinal cord (central n.s)
endorphins:
natural, opiatelike neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure.
agonist
a drug chemically-similar enough to a neurotransmitter that it can band to neural receptor sites and produce similar effects.
antagoinsts
drugs that are similar to neurotransmitters that band onto neural receptor sites, but not enough to produce effects.
real world example of antagonists
narcan/maloxone (blocks drugs from coming into contact with neurons).
adrenaline
fight or flight neurotransmitter (epinephrine)
nonadrenaline
concentration neurotransmitter (norepinephrine)
dopamine
pleasure (rewarding chemical) neurotransmitter.
ex: completing a task, doing self-care
serotonin
mood stabilizer neurotransmitter (sun exposure, meditating, running, sitting in nature)
gaba
calming neurotransmitter
glutamate
memory neurotransmitter
endorphin
painkiller neurotransmitter (laughing, exercising, dark chocolate, essential oils)
what else other than neurotransmitters affects human moods?
hormones from the endocrine system
endocrine system
composed of glands that secrete chemical hormones.
how do hormones travel?
through the bloodstream and influence our urges.
pineal gland
produces melatonin and is related to your circadian rhythm
hypothalamus
produces dopamine and is the brain's reward system
pituitary gland
produces oxytocin (love)
adrenal glands
produces adrenaline, noradrenaline, cortisol
gonads
produces testosterone and estrogen.
oxytocin
love hormone
what are the difference between hormones and neurotransmitters?
hormones go through your blood, neurotransmitters are through your neurons.
is the flow of hormones slower of faster than neurotransmitters
faster and long lasting
ex: hormones producing adrenaline (fight or flight) and its effects last after situation is over.
fMRI scans
(functional magnetic resonance imahine)
- allows us to better understand the anatomy of the brain
what is the innermost and most primitive part of the brain?
brainstem
brainstem
located at the top of the spinal cord and is responsible for regulating our
automatic survival functions
two parts of the brain stem?
1. medulla: controls heartbeat and breathing
2. Pons: helps coordinate movement
where is the thalamus and what does it do?
above the top of the brainstem, or midbrain.
* functions as the brain's information hub.
what extends from the thalamus and send signals to the rest of the brain stem?
nerve fibers extend from the thalamus.
reticular formation
nerve network that extends throughout the brainstem to the thalamus. Helps control arousal, alertness, and wakefullness
cerebellum
extends from the rear of the brainstem (the little brain) and coordinates movement and balance.
Also: plays a role in emotional regulation and nonverbal learning and memory
what do the brainstem and cerebellum consist of?
the hindbrain
where does the limbic system lie?
between the brain's oldest and youngest regions!
what makes up the limbic system?
hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus, and basal ganglia.
what is the limbic system associated with?
emotions and long-term memory
what are both amygdala's linked to?
aggression and fear
flashback memories
when the intense feelings of aggression and fear create crystal clear memories
hypothalamus location?
below the thalamus
what does the hypothalamus do?
maintains homeostasis (body temp) and basic drives (hunger, thirst and sex drive)
ALSO: activates the pituitary gland (endocrine)
what is the hypothalamus known as?
the reward center, because it produces dopamine when stimulates —> leads to addictive behaviors.
what is the youngest part of the brain?
cerebrum
how is the cerebrum divided and what is it responsible for?
Right and left hemispheres. Responsible for higher level mental functions (speech, perceptions, conscious thoughts).
cerebral cortex
thin layer of gray matter that covers the cerebrum.
*control and information processing center
the larger the cerebral cortex, the more ______ the animal.
intelligent
what does the cortex contain?
neurons and glial cells.
glial cells
found in the cortex and provide nutrients and oxygen to neurons. (support neurotransmission)
Neurogenesis
generation of new neurons.
_____ percent of humans are right brain dominant.
90
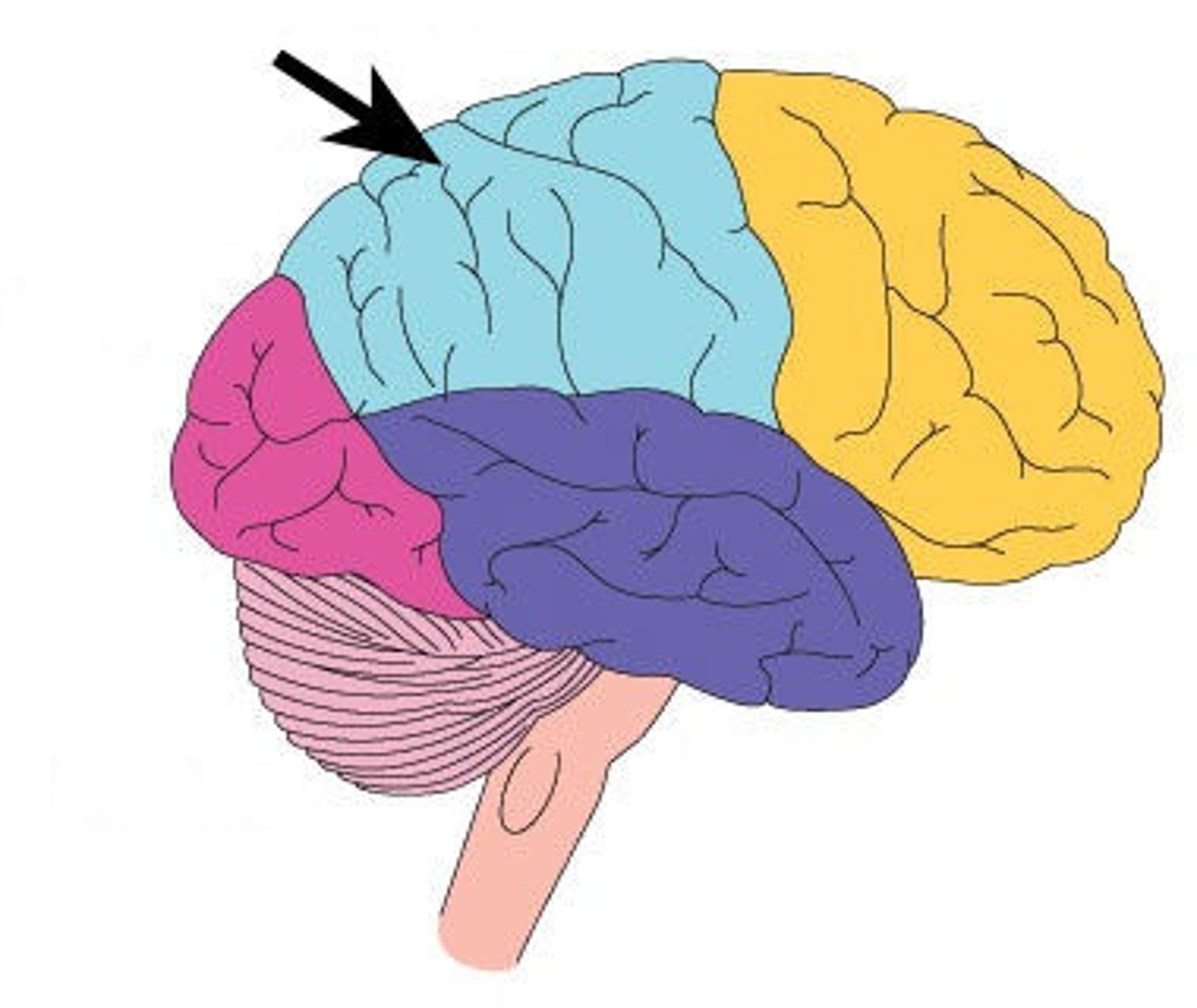
how many lobes is the cerebral cortex divided into?
4!
(each lobe has its own processes and functions)
frontal lobe
* located behind forehead
* involved in active thinking and judgement
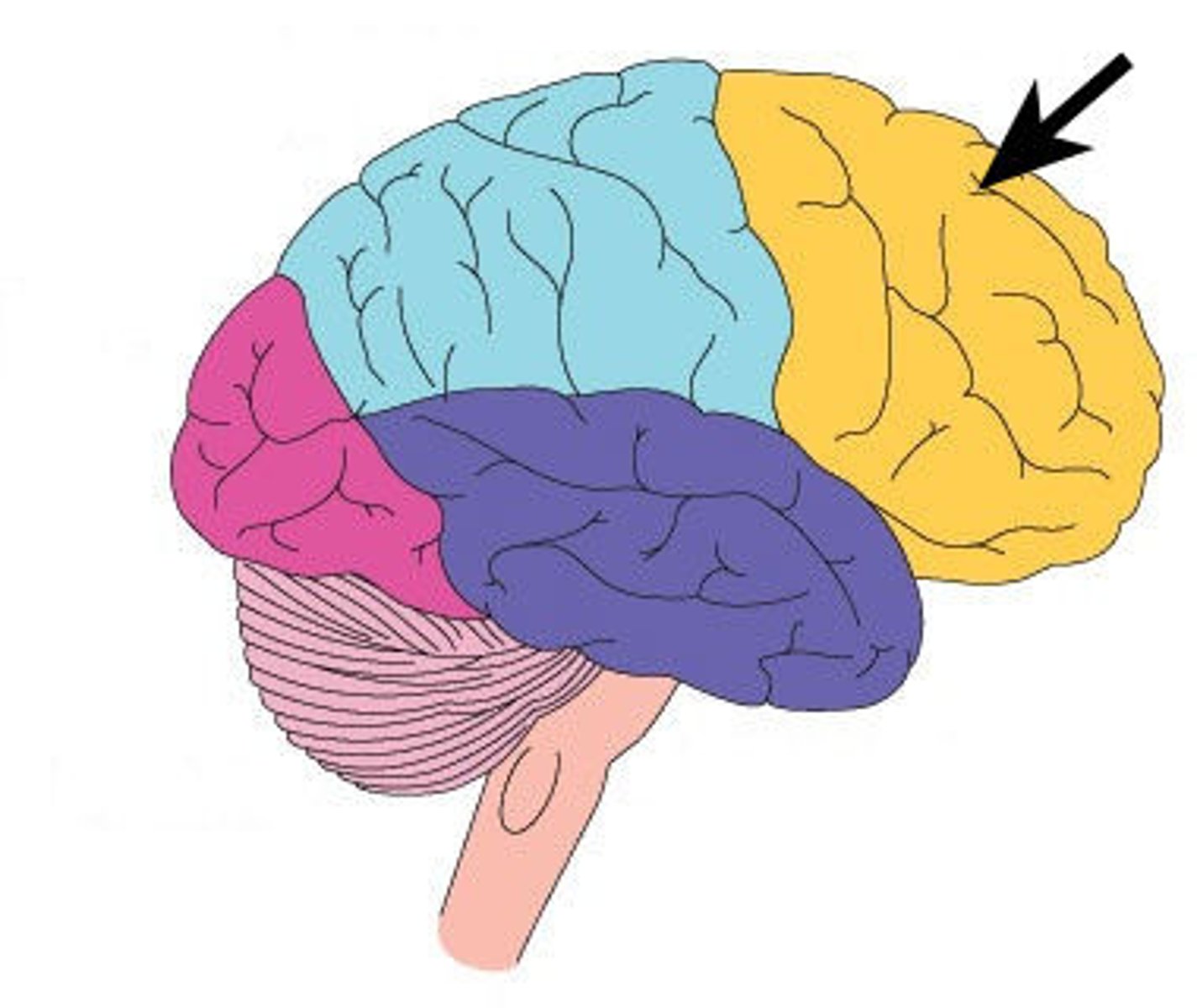
parietal lobe
located at the top and rear of head.
* receives sensory input for touch and body position