Econ 10; Error & Types of Error
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is the Error formula?
yi = ŷ + ϵ

What does yi mean?
your observed outcome
What does ŷ mean?
your prediction
What is formula for ŷ?
â + B̂ * (x)
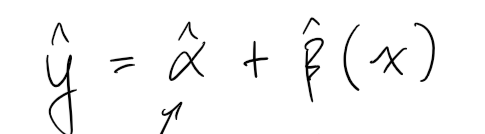
What doe â mean?
the intercept
what does B̂ mean?
the slope
How may systemic sources of Error are there?
6
Sampling error occurs:
any time our sample data does not represent the population we’re trying to represent
All polls suffer from which type of error?
Sampling error
What is the solution to Sampling Error?
Simple Random Sampling with replacement
What is the solution to Measurement Error?
anonymize collective data
Soulution for Measurement Error (social science)
rounding
Solution for Measurement Error (physical science) drift in measures
better instrumentation
Randomization Error
anytime the treatment and the control differ from each other in any way other than the treatment
For Randomization Error, error can occur before, during, or after
True
What is the solution to Randomization Error?
Double blind test
Types of Modeling / Perceptual Error
Reverse Casualty, Omitted Variable, & Spurious Correlation
Reverse Casualty
Using the model in the wrong way. Not the way it was meant to be use
Example of Reverse Casualty
college application scandal ($ gives you a place at the table)
Omitted Variable
a third variable that affects both x and y, but is left out of the model
Example of Omitted Variable
A study ignores the number of hours worked when comparing income level and level of education
Spurious Correlation
when data moves together, but not causally
Examples of Spurious Correlation
Vaccines cause Autism
Solution for all types of Modeling / Perceptual Error
Peer Review
Random Error
small positive or negative variation in the data
Solution for Random Error
Get more data