Plant tissues: Scaling up: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Epidermal tissue
Tissue that covers and protects the plant
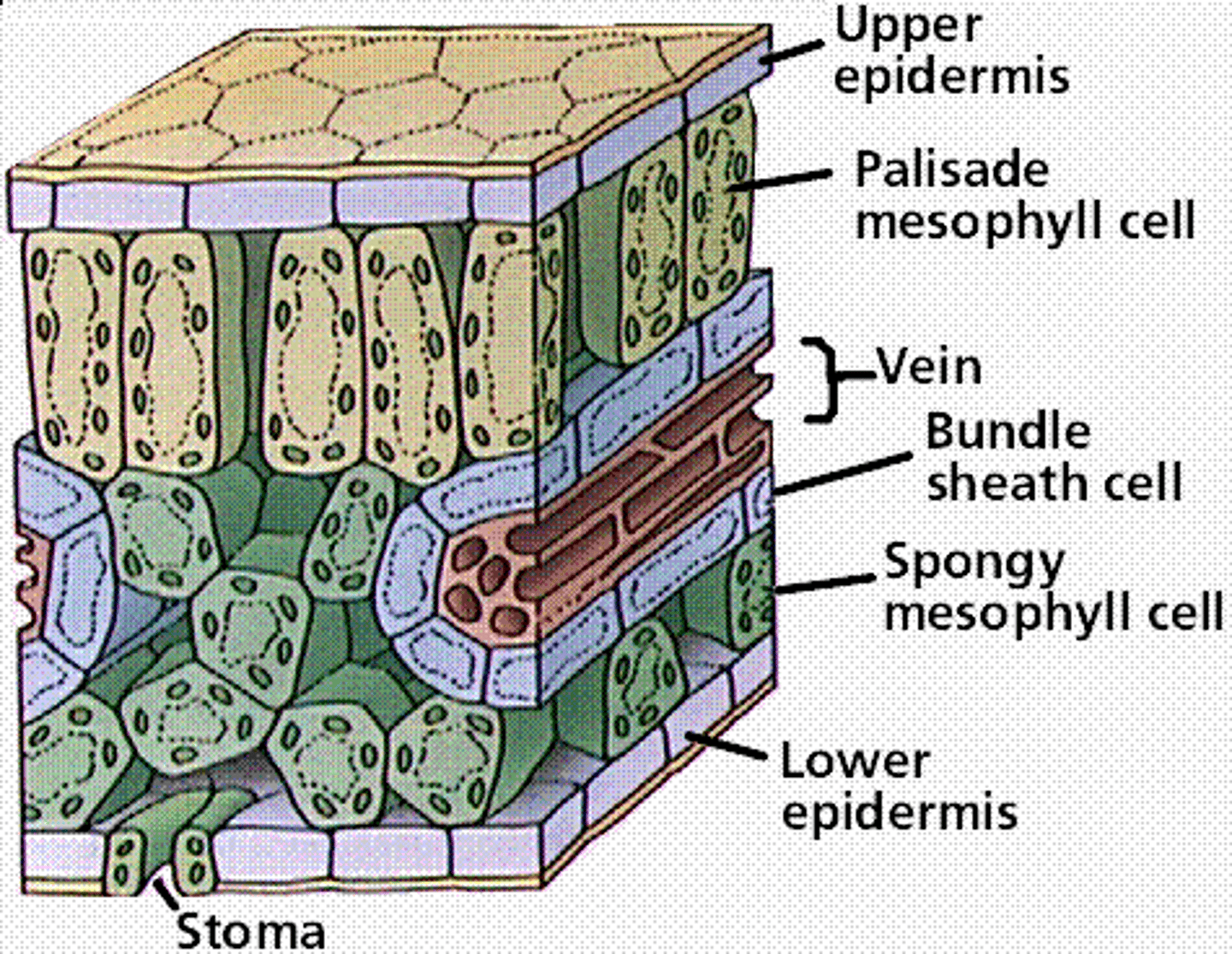
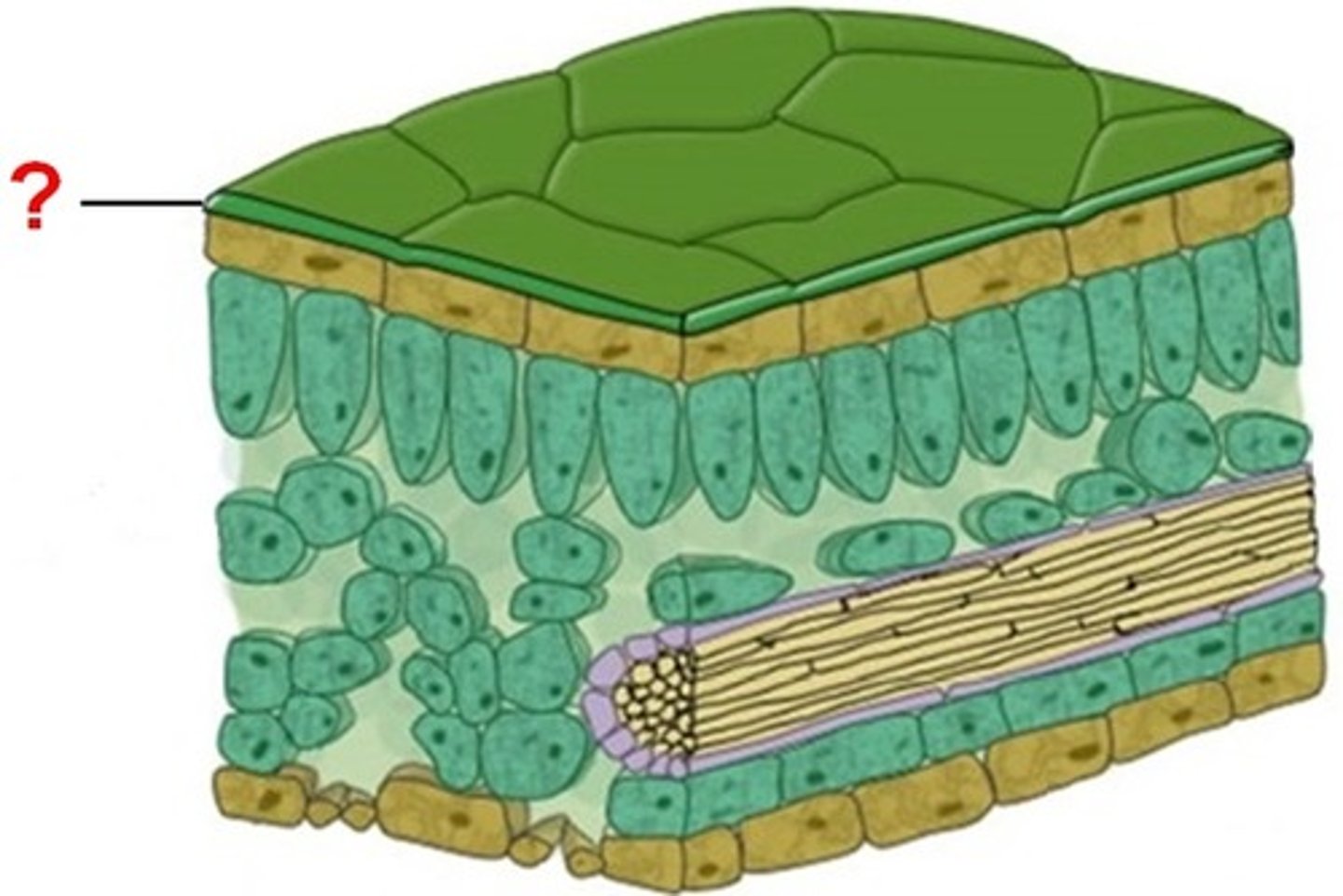
Waxy cuticle
A layer on the surface of the leaf which protects the plant and reduces water loss, thicker on the upper surface
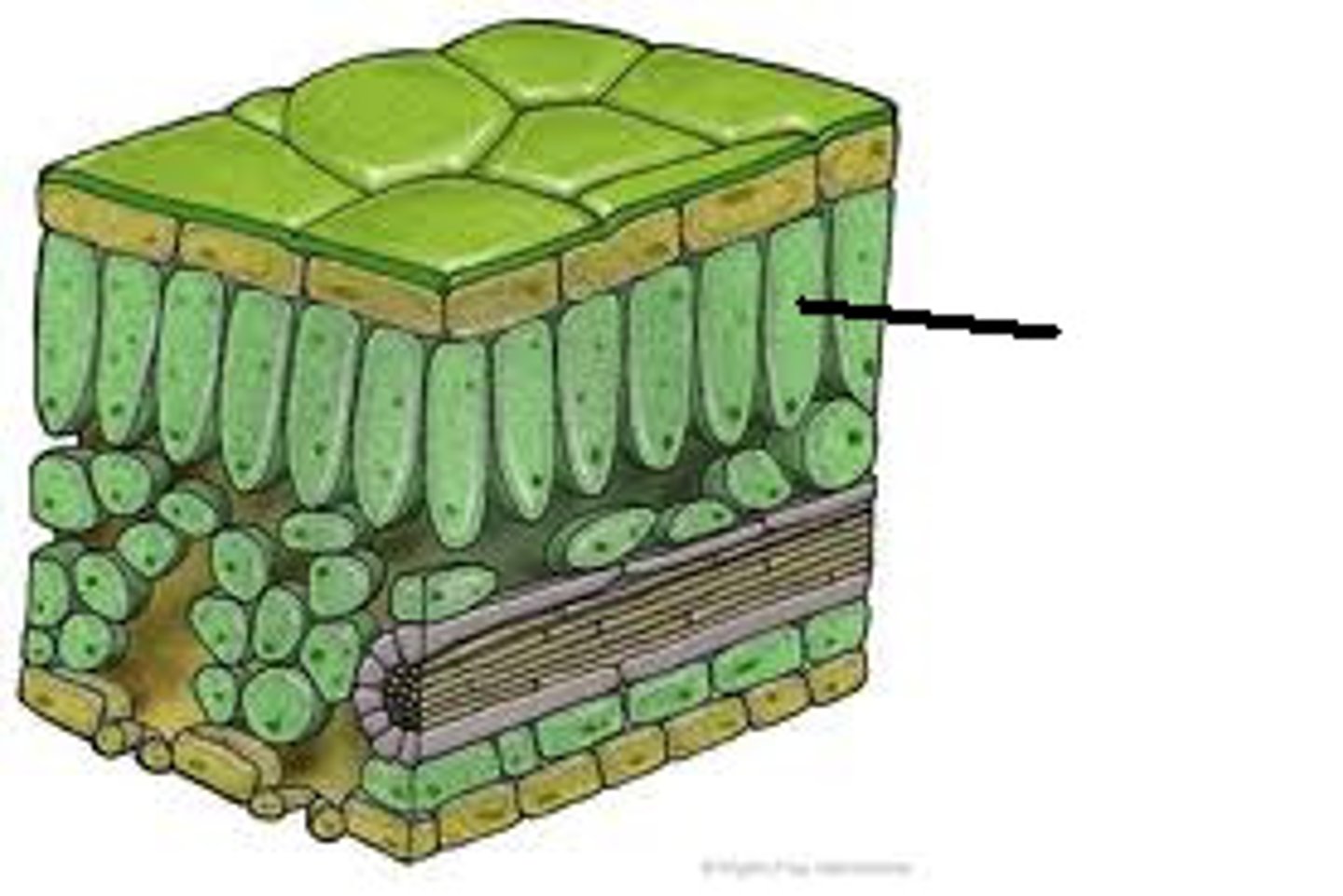
Palisade mesophyll
Photosynthetic tissue below the epidermis in a leaf, palisade cells contain high concentrations of chlorophyll and high quantities of chloroplasts for photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll
Layer of tissue found beneath the palisade mesophyll that is packed loosely for efficient gas exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen

Xylem
Non-living vascular tissue that carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots of a plant to its leaves, the xylem is hollow and nearby cells are lignified or dead so water can move continuously
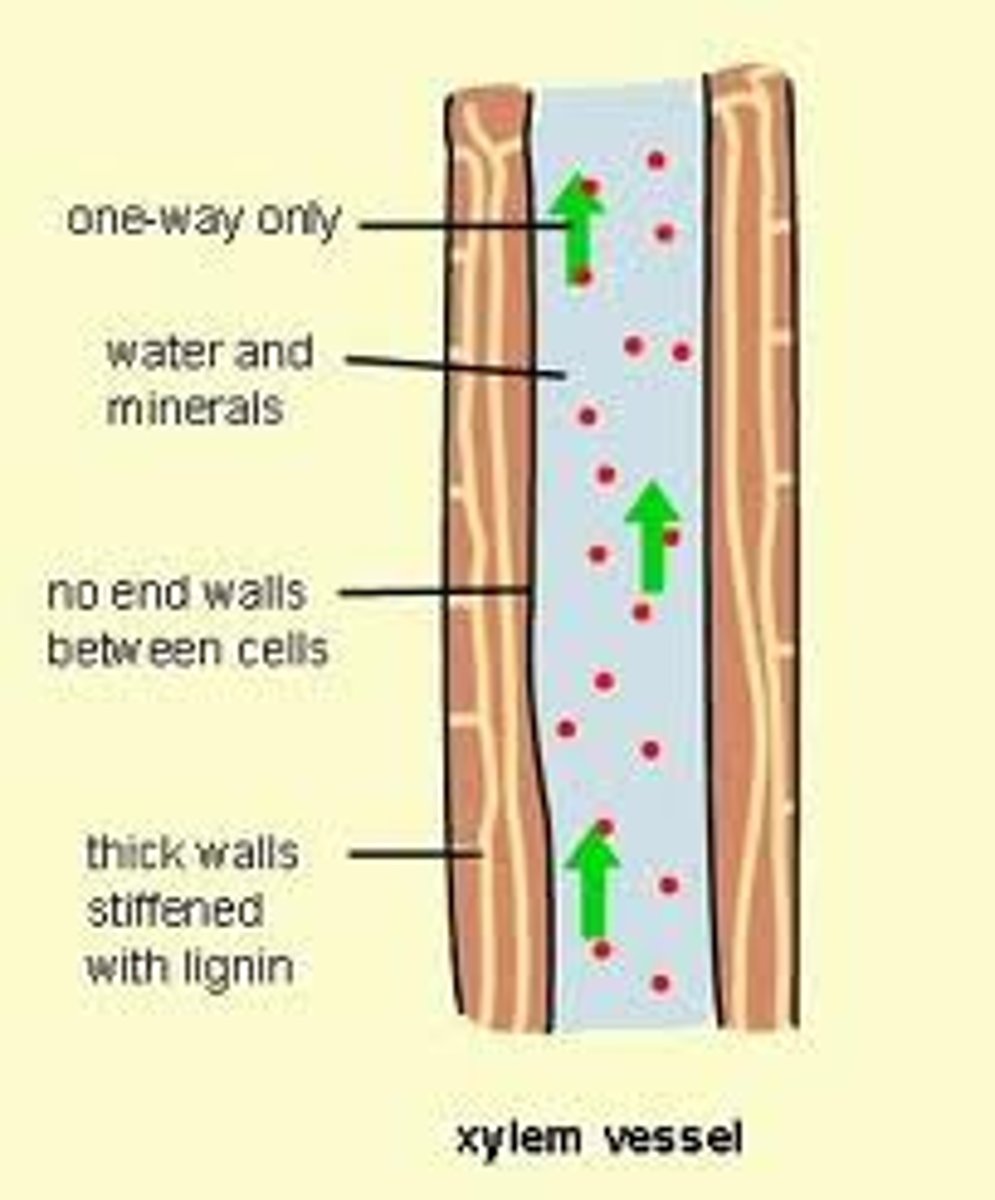
Lignin
A chemical that provides support to xylem cells and prevents the unwanted movement of water into nearby cells
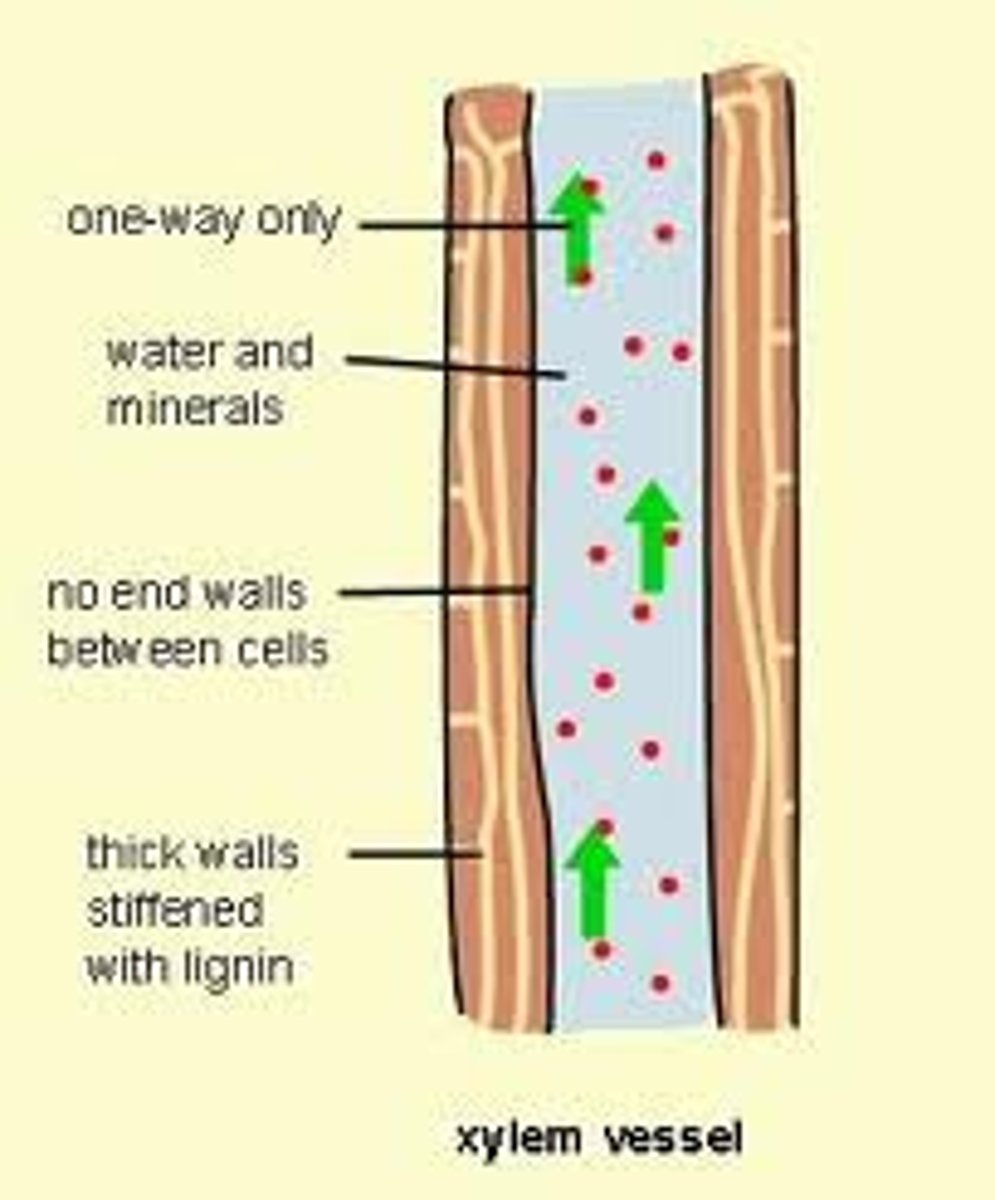
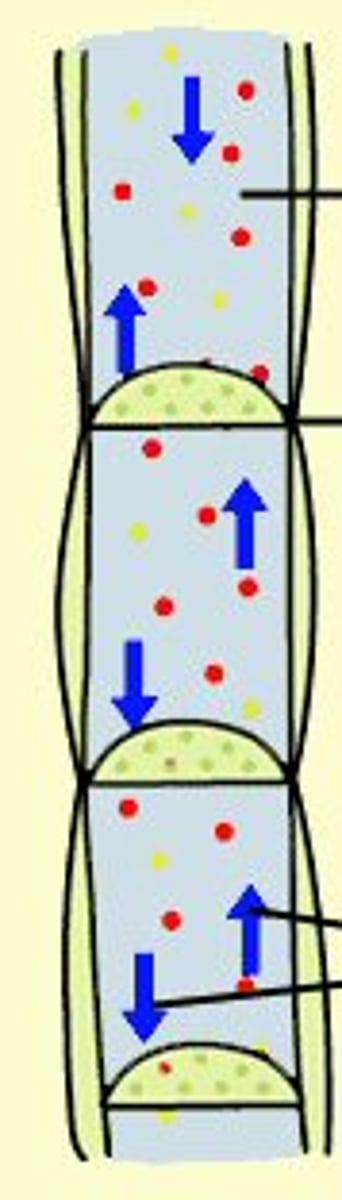
Phloem
Living and elongated vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant, the phloem has sieve plates that act as pores to allow molecules to diffuse between cells
Meristem
Undifferentiated plant tissue from which new cells are formed, found in the shoots and roots

Shoots
The aerial portion of a plant body consisting of stems, leaves and flowers

Roots
Underground plant organs that absorb water and minerals

Stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen, carbon dioxide and water can move
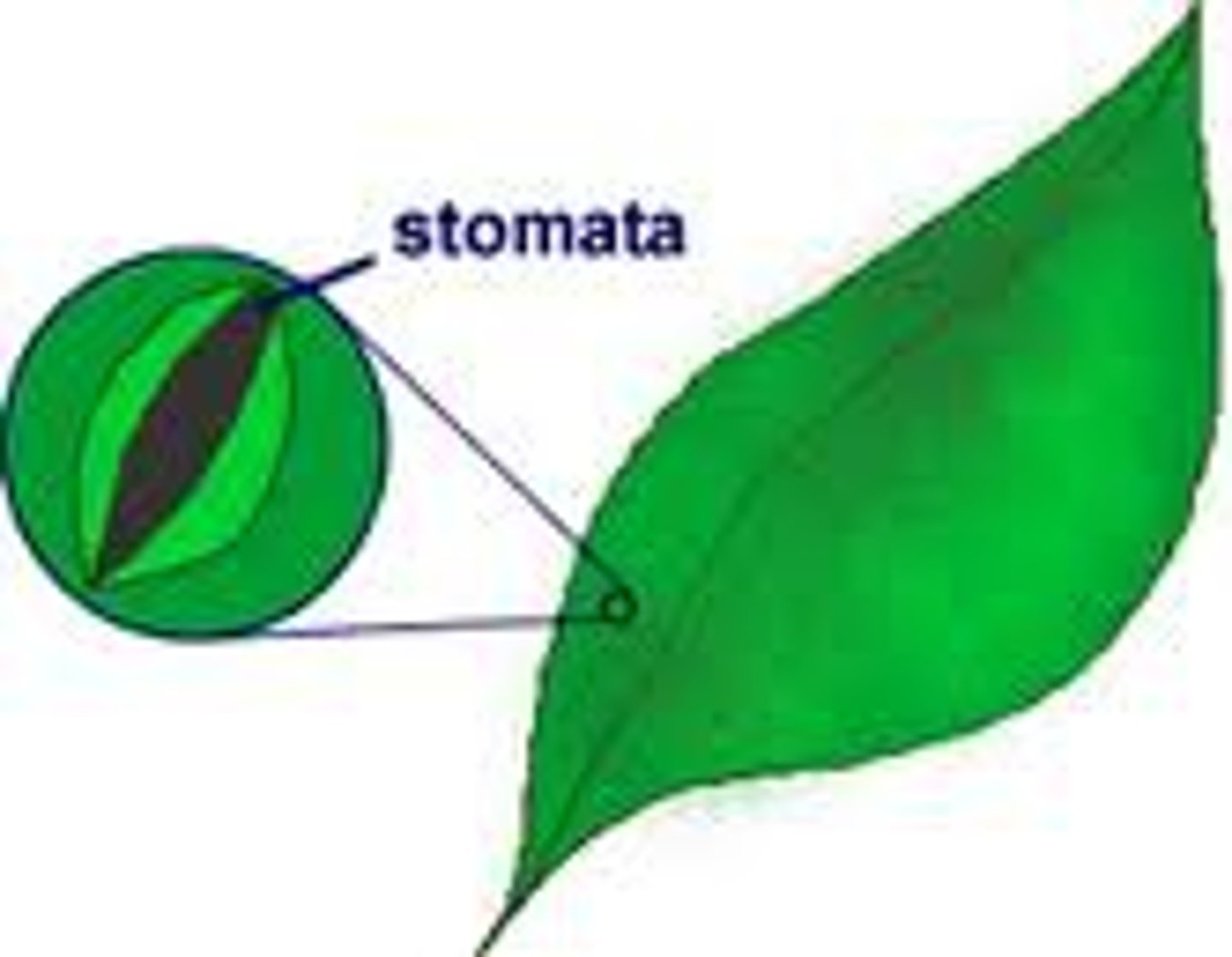
Guard cells
Pairs of cells that surround the stomata and control their opening and closing to optimise gas exchange and reduce water loss

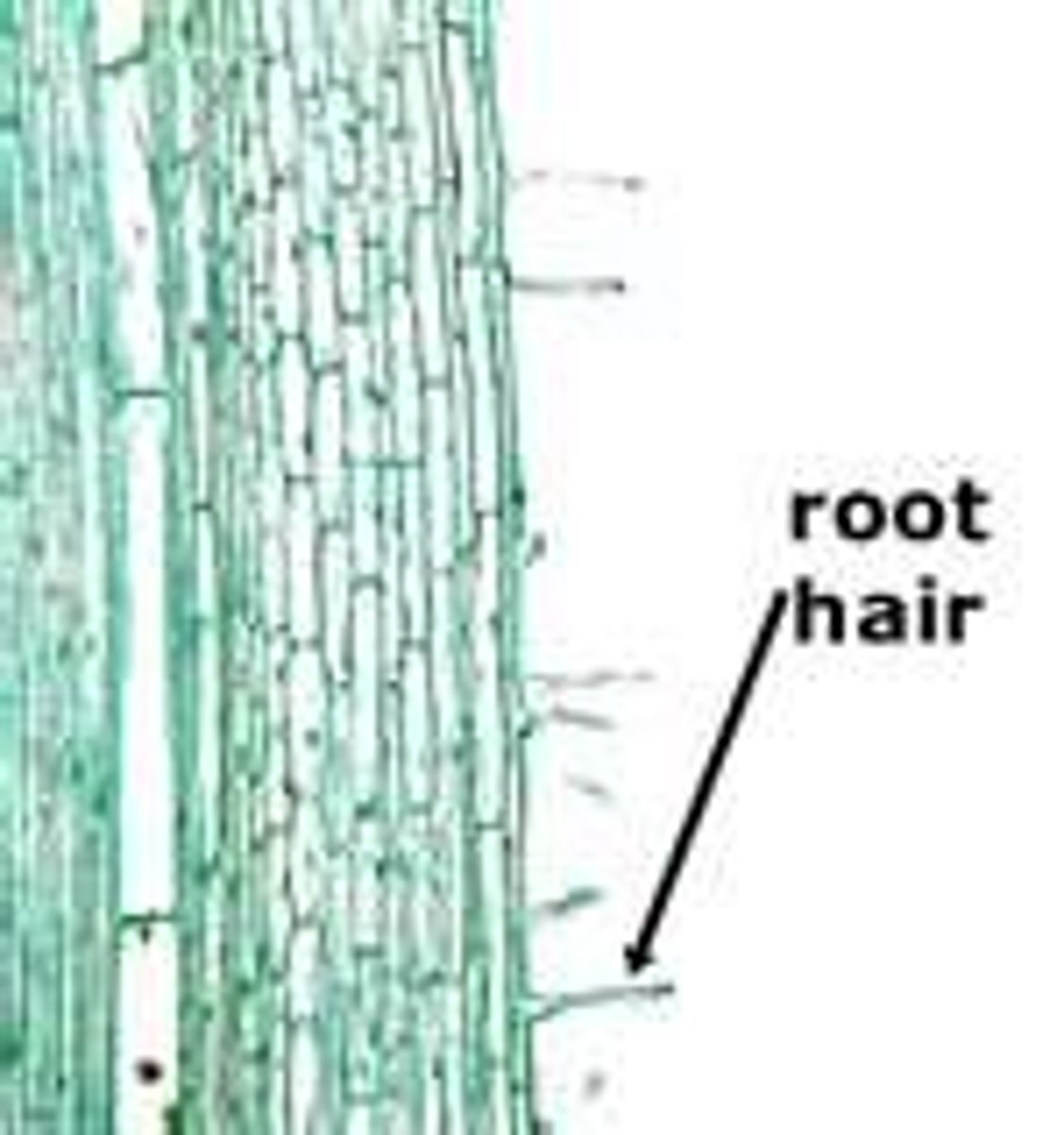
Root hair cell
Cells that absorb water and mineral ions from the soil, via diffusion, osmosis or active transport using structures with a large surface area
Transpiration
The process of the movement of water through a plant and the loss of water from a plant through its leaves
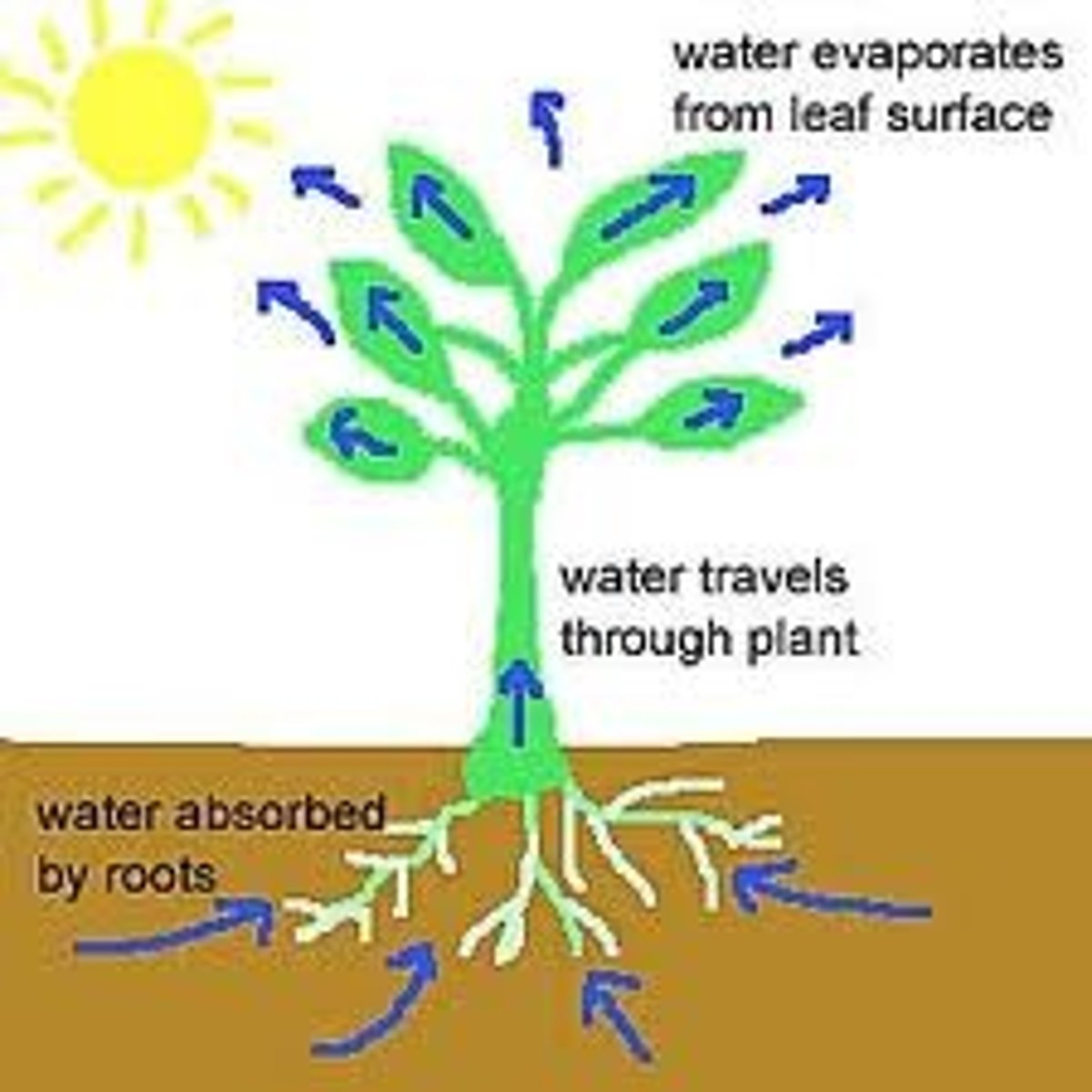
Factors affecting transpiration
Changing temperature, humidity, air movement and light intensity
Rate of transpiration
The rate of water loss from a plant
Effects of factors affecting transpiration
Light, wind and heat will increase the rate of transpiration, humidity will decrease the rate of transpiration
Potometer
A device used for measuring the rate of water uptake of a plant due to photosynthesis and transpiration, a bubble of water will move along the potometer to indicate the rate of transpiration

Translocation
The transportation of sugars and amino acids around the plant via phloem tissue, sugars are prone to translocation as they are made in the leaves and needs to be transported around the plant