Honors Bio Cell Membrane Quiz Study Guide
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms

Fluid Mosaic Model
how scientists describe what the cell membrane looks and functions like,
Cholesterol is also a key determinant of membrane fluidity
provide structure and support to the membrane
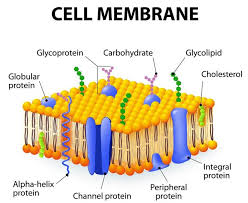
Structure of Cell Membrane
a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable
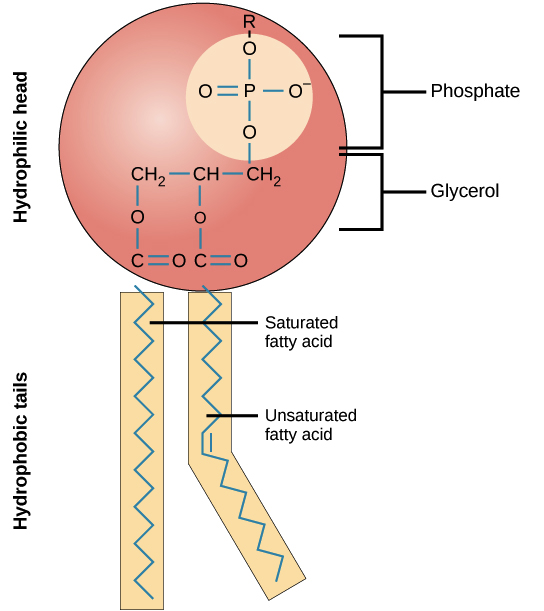
structure of a phospholipid
a polar phosphate head group and two nonpolar fatty acid tails joined by a glycerol backbone (tails hate water head loves it)
phospholipid bilayer
made of two layers of phospholipids. Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail. The two layers are arranged so that the tails face inward and the hydrophilic heads face outward toward the extracellular environment or the intracellular cytoplasm
Selective Permeability
some substances are able to pass through the membrane, while other substances are not able to pass through
passive transport
substances simply move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, which does not require the input of energy
types of passive transport
simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, filtration, and/or osmosis.
active transport
the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration—against the concentration gradient.
active transport types
ion pumps, exocytosis and endocytosis.
isotonic
wilting for plants and normal for animals
no change - equal amount of water in and out
hypotonic
animal cell will burst and normal for plants
water outside → goes inside
hypertonic
plasmolysis (kind of dies) for plants and animal is shriveled cell
water inside → goes outside
Diffusion
Diffusion refers to the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
Osmosis
Osmosis is a type of diffusion specifically for water molecules moving across a semi-permeable membrane.
Osmosis contrast to diffusion
Osmosis can only function in a liquid medium, but diffusion can occur in all three mediums (solid, liquid and gas).
Active transport
against gradient, energy required
Passive transport
no energy required, moves with gradient
passive and active contrast
active - energy + against
passive - no energy + with
Phagocytosis
engulf and destroy foreign substances, such as bacteria, and remove dead cells
Pinocytosis
a process by which the cell takes in the fluids along with dissolved small molecules
Glycolipid
consist of a lipid molecule with a carbohydrate attached
glycoprotein
simply proteins with a sugar attached to them
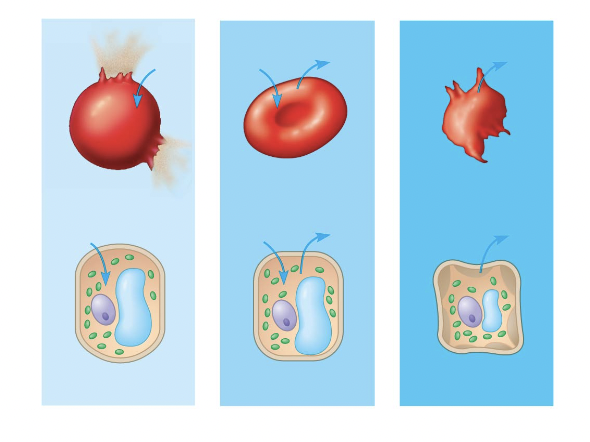
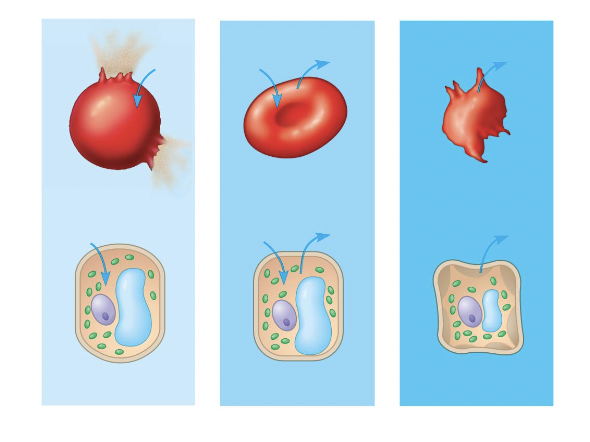
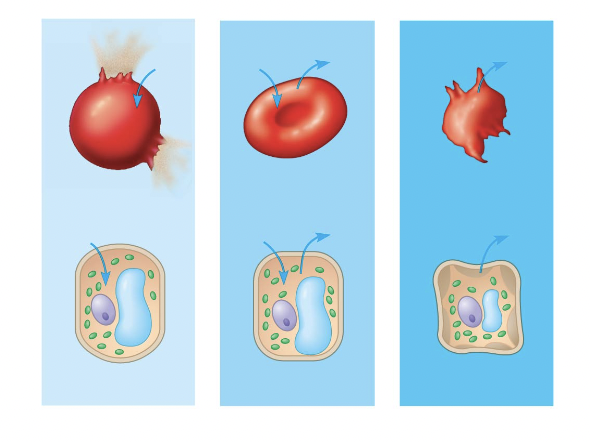
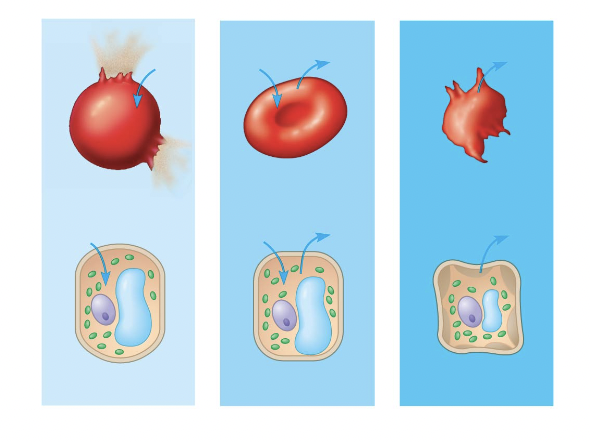
red blood cell 1
hypotonic red blood cell
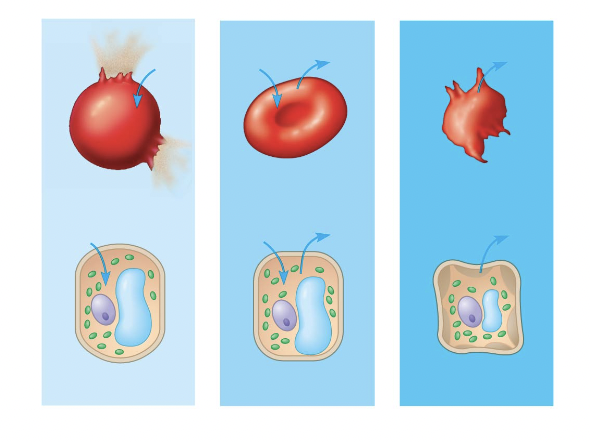
red blood cell 2
isotonic red blood cell
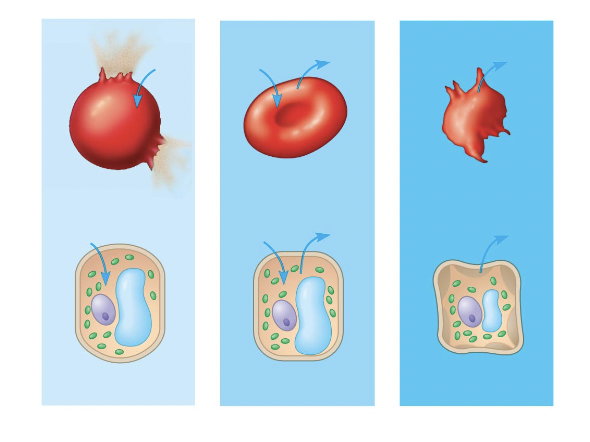
red blood cell 3
hypertonic red blood cell
plant cell 1 turgid
normal for plants ;
plant cell 2 flaccid
wilting for plants ;
plant cell 3 plasmolysis
, lose turgor pressure
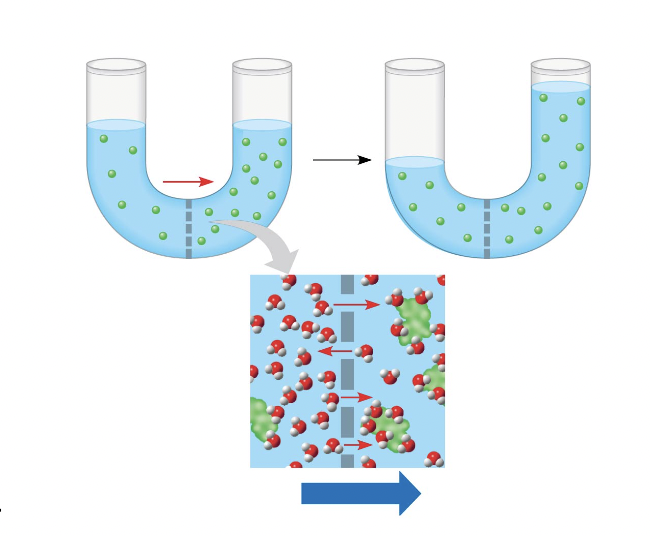
Why is the water going up?
Less concentration on the right so water goes to the right and goes up
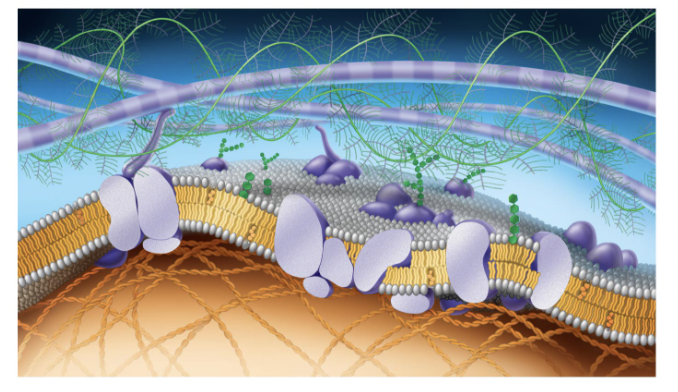
purple long tubes at top
ana-hypholic fatty acid tails
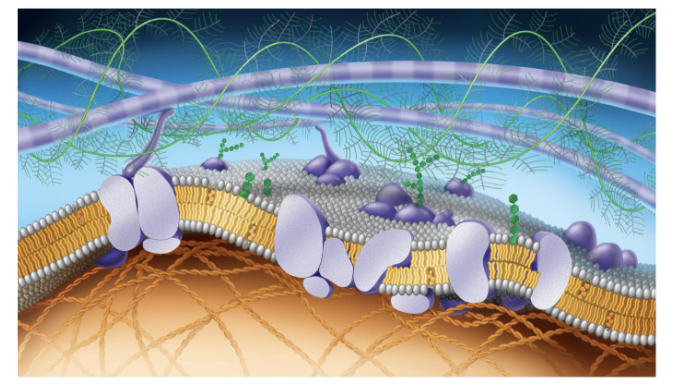
green fern things
fivers of ELM
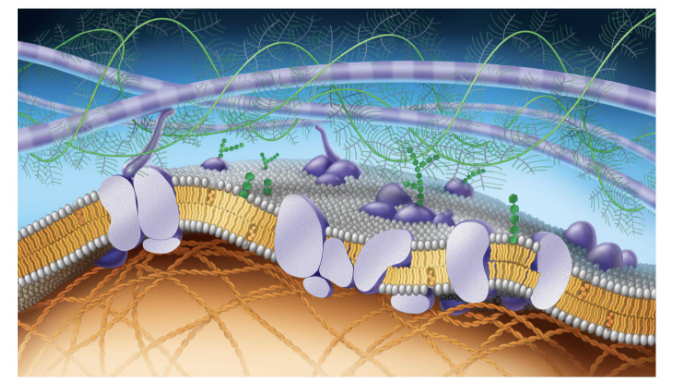
green things (hexegon)
carbohydrates
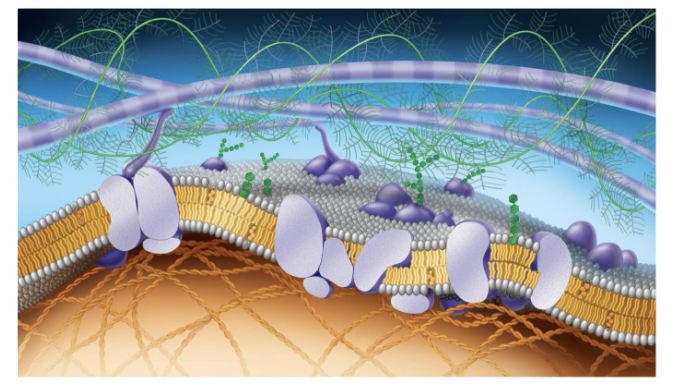
purple potatoe in half
transport proteins (trans intergal protein)
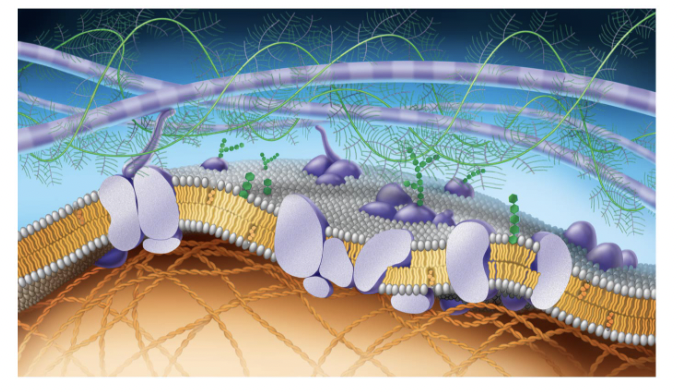
small cirlcular purple potatoe in half
perphial proteins
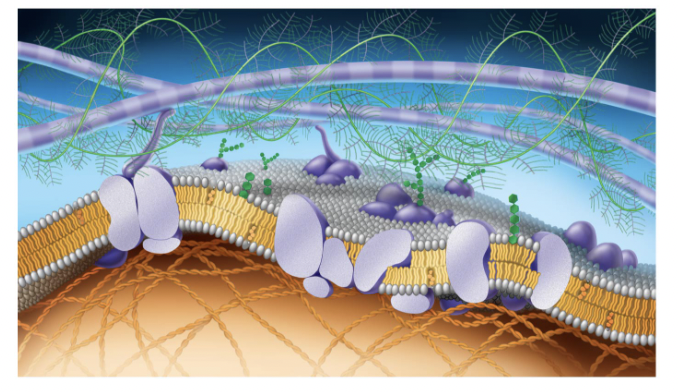
straight green hexagon
gylco lipid
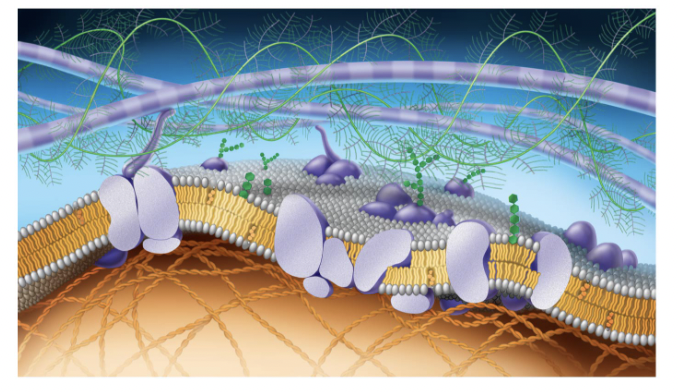
white egg layer
extracellular side of membrane
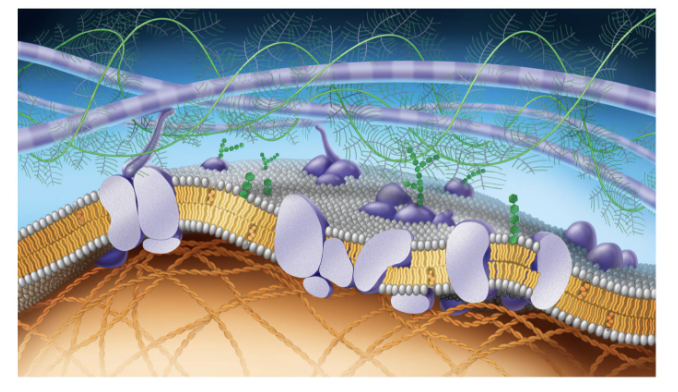
orange hexagons
cholesteral
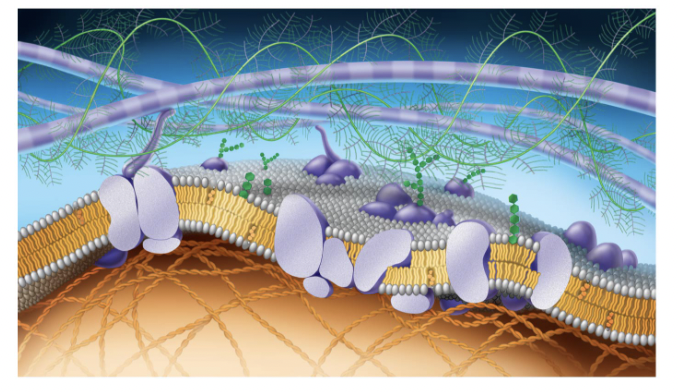
bottom layer of eggs
cytoplasmic side of membrane
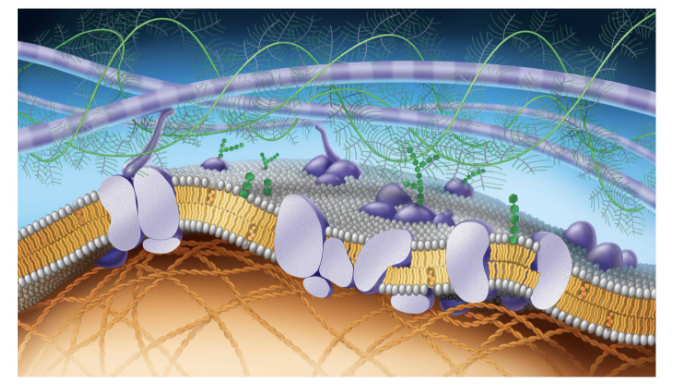
orange cords at bottom
figments of cytoskeleton