Age of Revolutions - World History
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
King Louis XVI
The king of France before the revolution who wanted to raise taxes to pay debts.

The First Estate
The clergy (Priests and Bishops). They paid no tax.

The Second Estate
The nobles of France. They were rich, landowners and paid no tax.

The Third Estate
Made up from all the workers in France; from merchants to poor farmers.

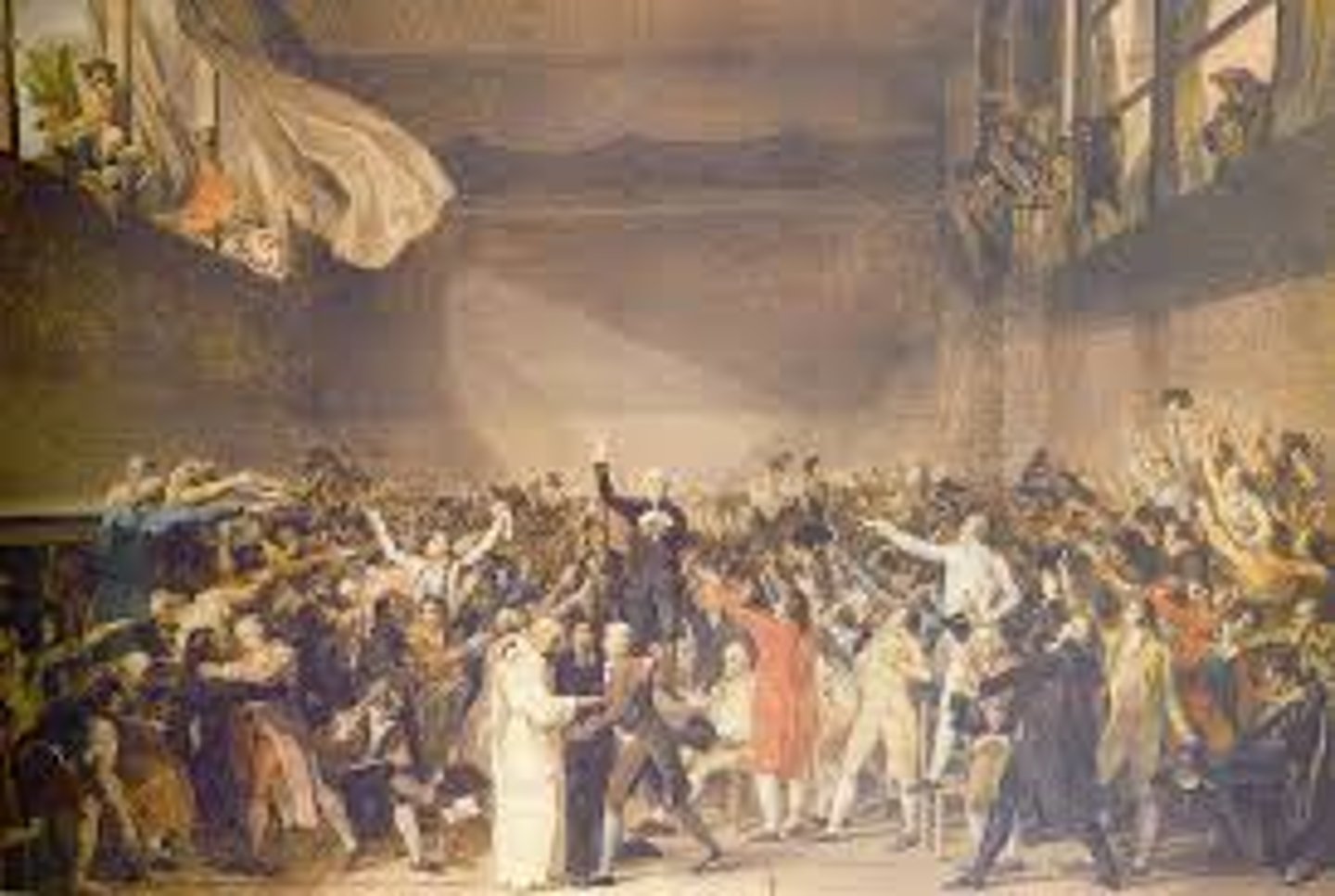
National Assembly
Group set up by the Third Estate at the Estates General because they thought they were being treated unfairly, and wanted more votes.

Bastille
Prison in Paris captured by the gangs in Paris angry at the King. Took place on 14th June 1789- this date is still celebrated in France every year.
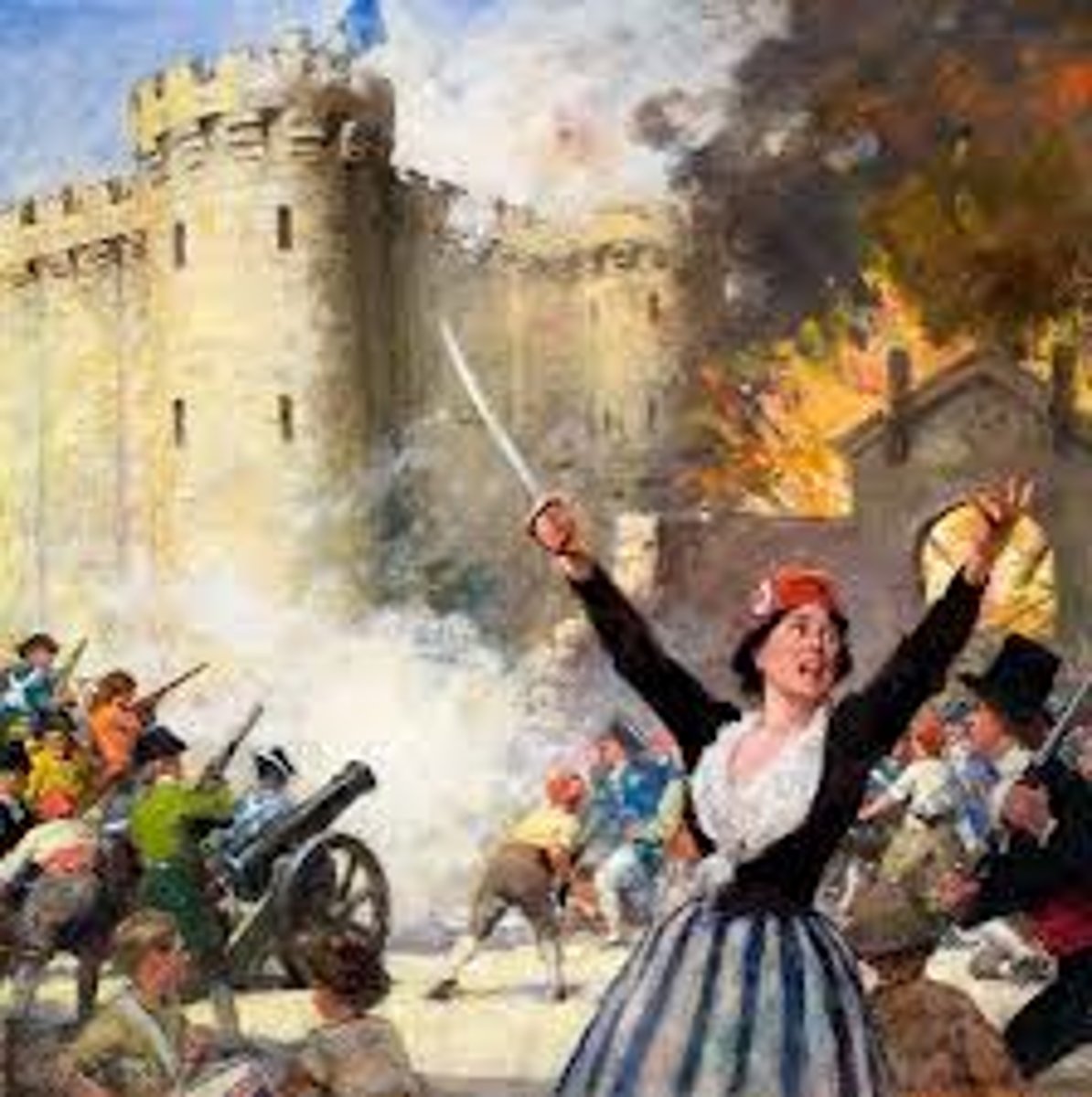

Republic
A type of government with no King or Queen. e.g. Ireland.

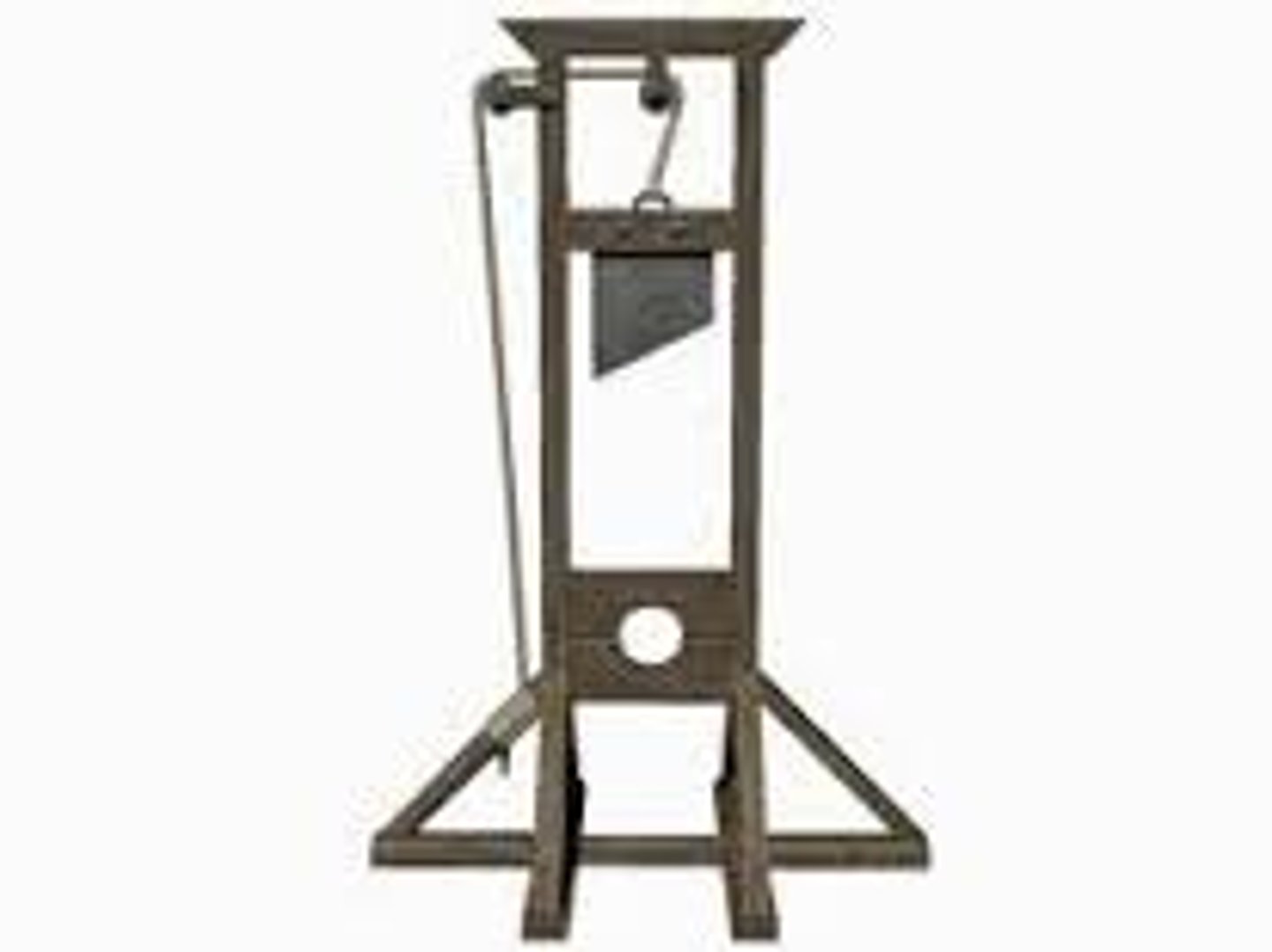
Guillotine
Machine widely used during The Reign of Terror to execute people.

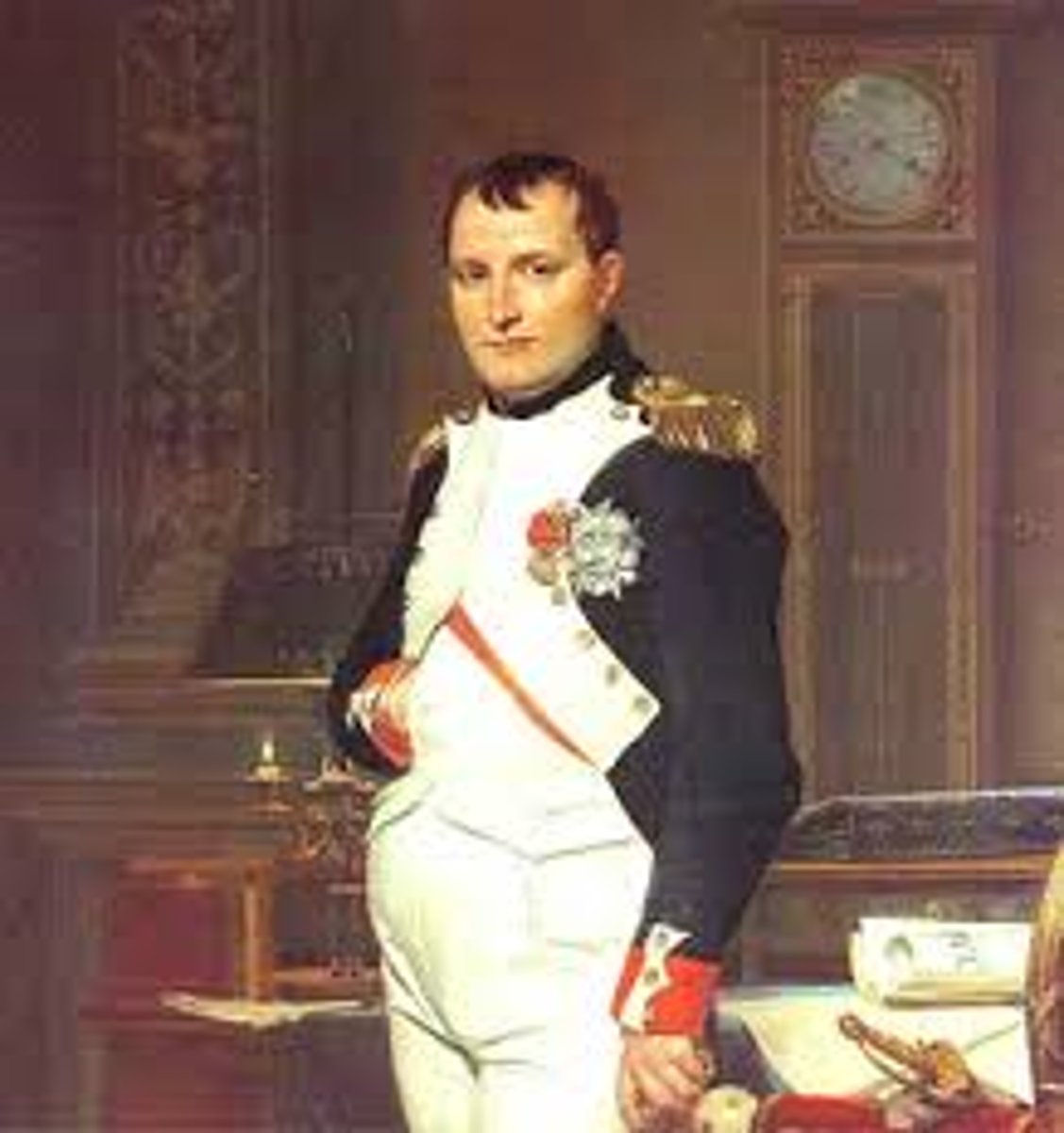
Napoleon Bonaparte
Army general who eventually became emperor of France after the Revolution.

Latin America
Areas south of the United States: Mexico, Central America, the West Indies (Caribbean), and South America.

peninsulares
Spanish-born people (born in Spain), who came to Latin America to live and rule. They were the highest social class.
creoles
People who had Spanish or Portuguese parents but were born in Latin America.

Simon Bolivar
1783-1830, Venezuelan nobility: leader of revolt of South American colonies against Spanish rule. Known as the "Liberator".

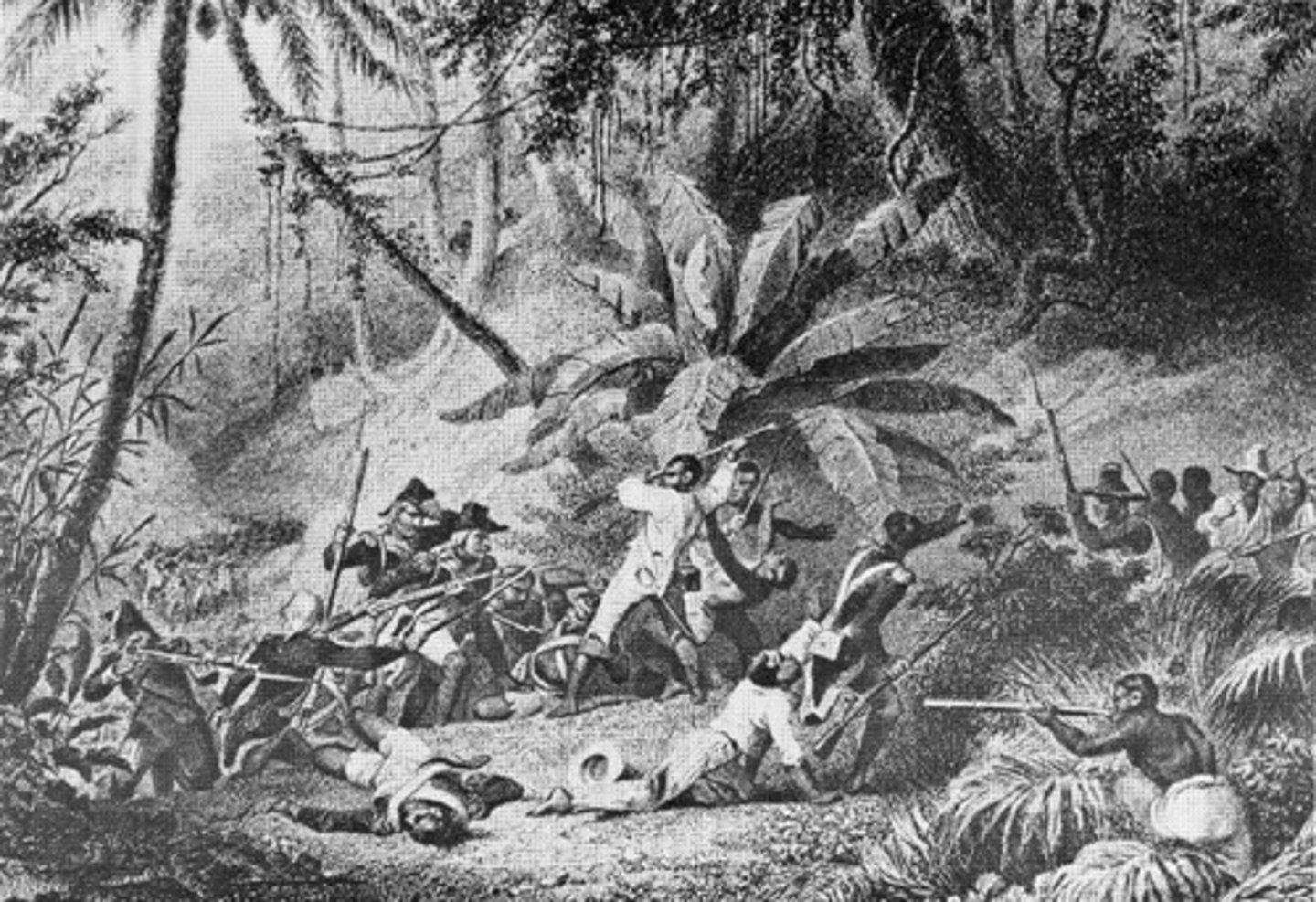
Haiti
A French colony on Hispainola which had a slave revolution (1794) to gain independence. The revolution was led by Toussaint L'Ouverture.
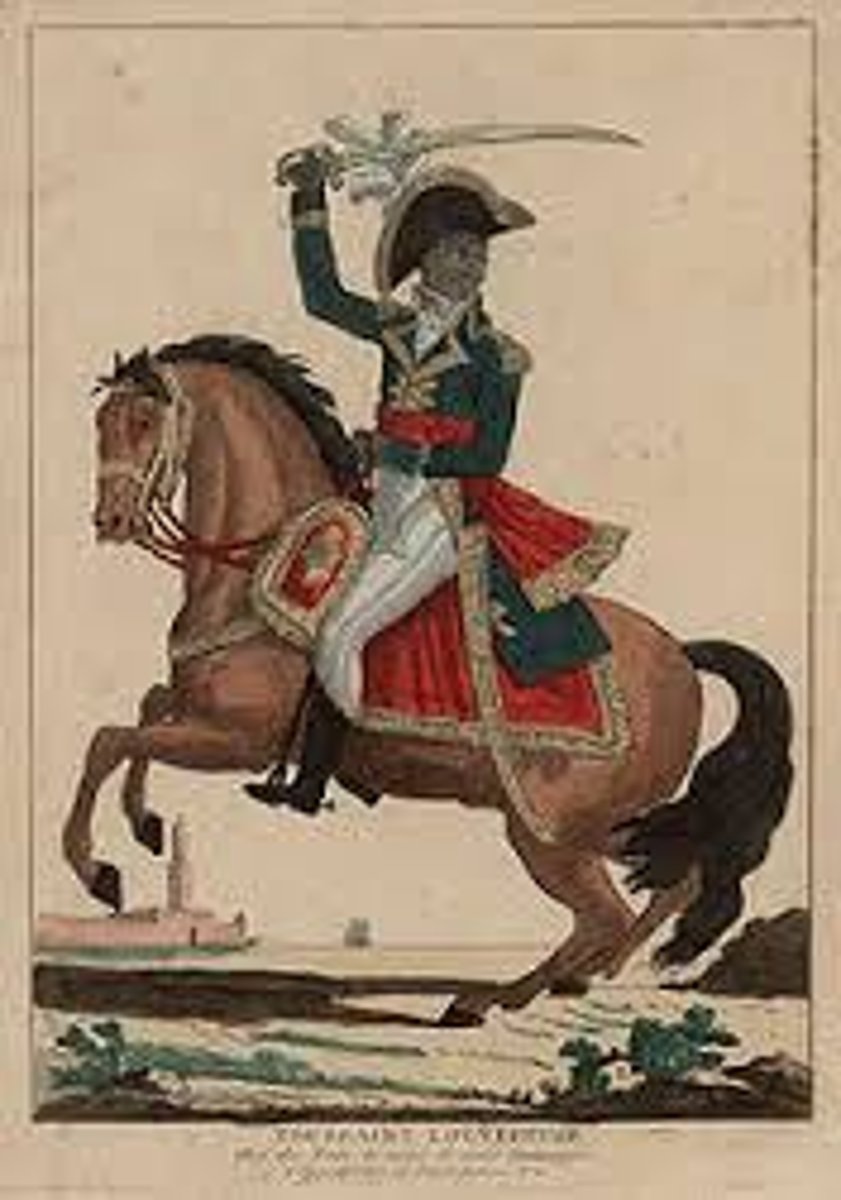
Toussaint L'Ouverture
A former slave in Saint-Domingue who started a revolution to overthrow the French colonial rule. The former slaves fought for 10 years for independence and then created Haiti.

revolution
An attempt to overthrow the existing political structure and put another type of government in its place.

Colony
A territory owned and run by another country.
No Taxation without Representation
Slogan shouted by Americans angry at the British as they had to pay tax but had no say in how the country was run.
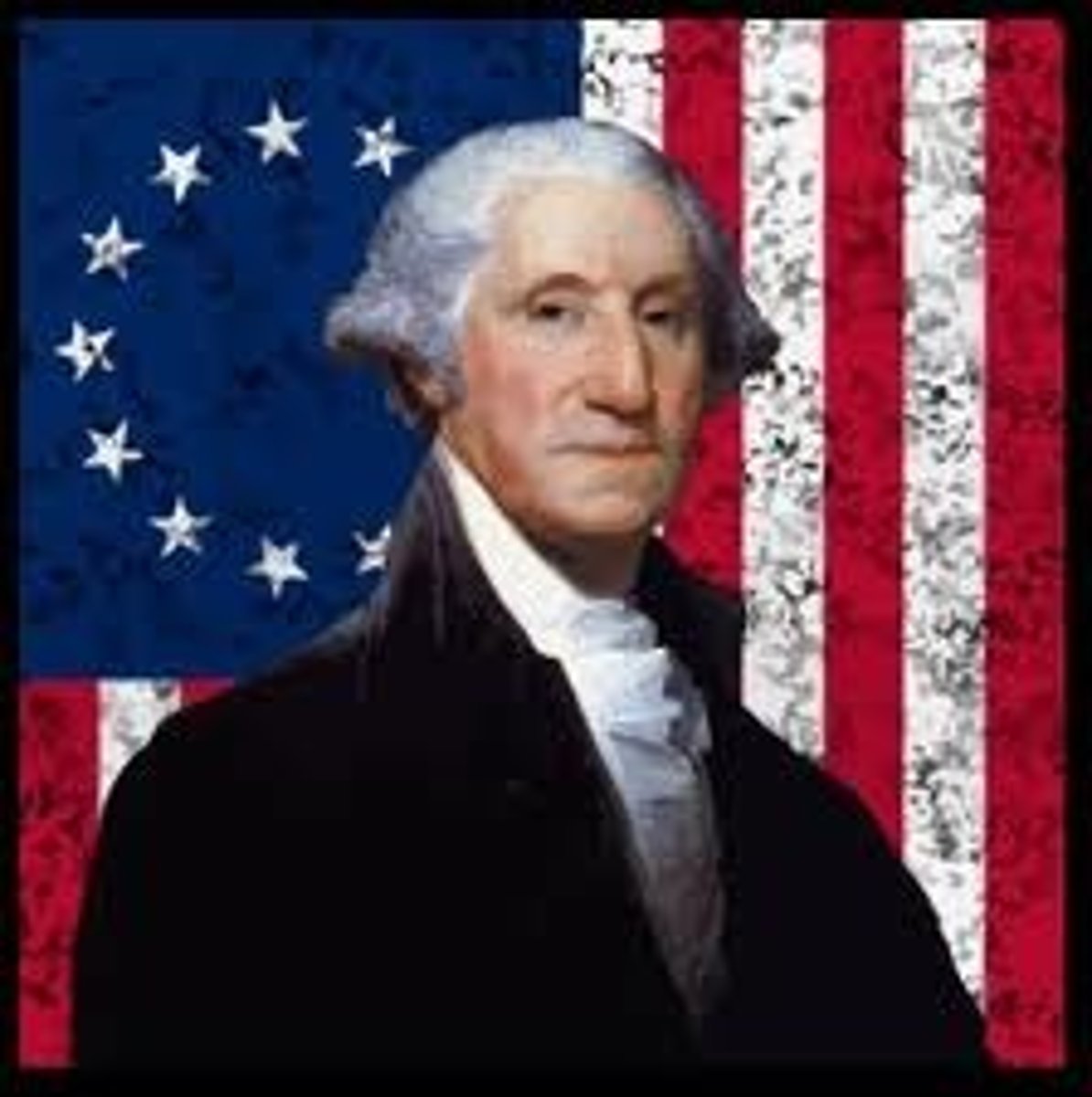
George Washington
Commander of the American Continental Army and first president of the USA.

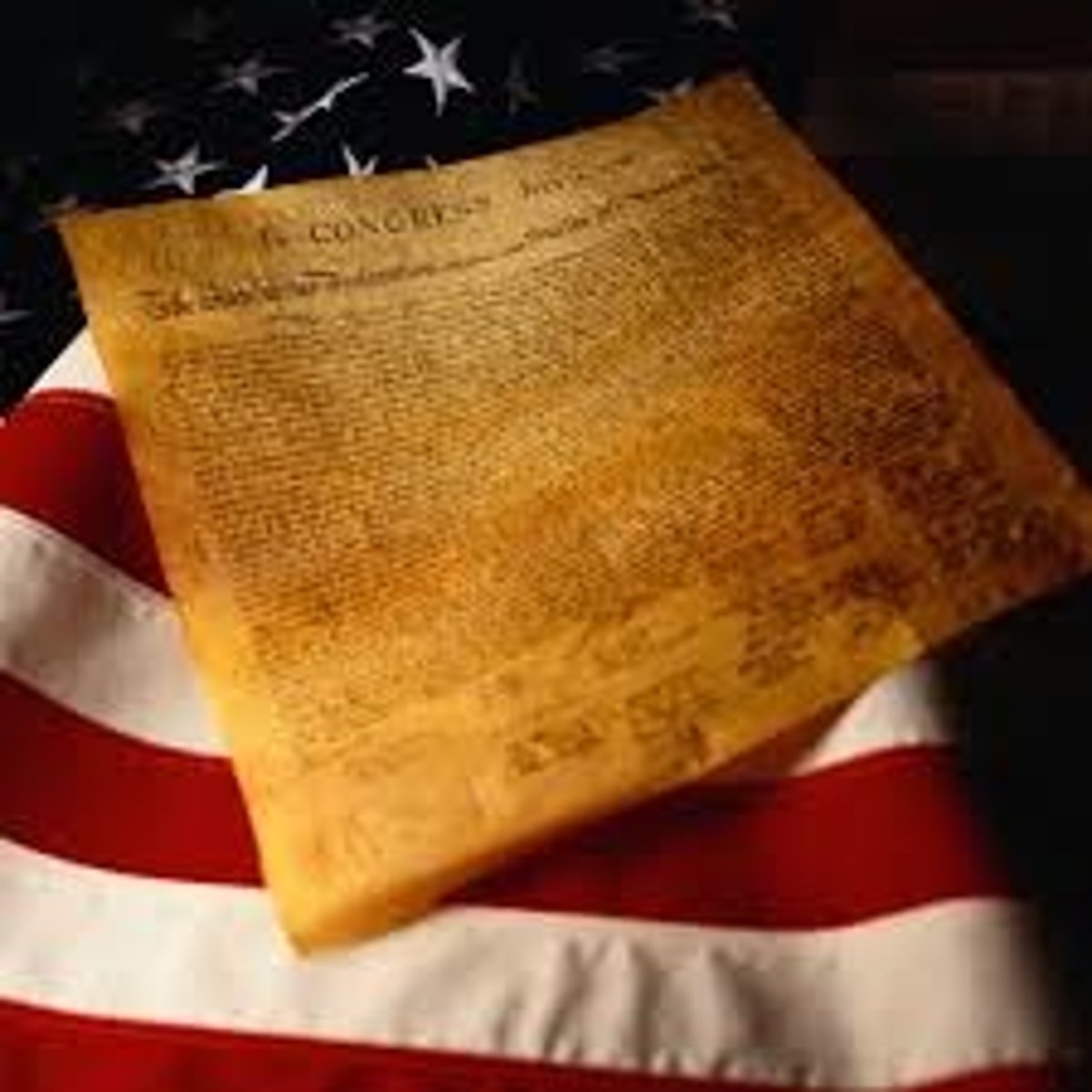
Declaration of Independence
Document in which the Americans set out their beliefs and aims for independence.

what were the primary causes of the French Revolution
enlightenment ideas,
American revolution,
Old regime,
privileges of the 1st and 2nd estates,
financial crisis( impeding bankruptcy)
why did king Louis XVI call for a meeting of the Estates general in 1789
he wanted to agree on new taxes to be applied to the first and second estates
what was the significance of the tennis court oath
instead of the 3rd estate leaving they promised to write the constitution for france first
what was the storming of bastille and its significance
bastille was a prison
it symbolizes the institution of the monarchy:
huge mobs surrounded it and took over to free the prisoners
THEY STOLE WEAPONS
what was the significance of the declaration of the rights of man and citizen
it stayed that all people were equal before the law
GRANTED FREEDOM OF SPEECH,RELIGION, PRESS, AND SPEECH
protected them against arbitrary imprisonment and arrest
what happened to Louis XVI during the republic
tried, convicted and beheaded for treason by radicals
what was the reign of terror
when they hunted down traitors and corner revolutionaries and turned them over the revolutionary tribunal
who led the reign of terror
Radicals
Robespierre
how does the reign of terror end
when robespierre is sent to guillotine
Bismarck
(1815-1898) Prussian chancellor who engineered the unification of Germany under his rule. Delivers "blood and iron" speech.
Realpolitik
realistic politics based on the needs of the state
Franco-Prussian War
This was a major war between the French and the Germans in 1871 that brought about the unification of Germany. It was caused by Otto Von Bismarck altering a telegram from the Prussian King to provoke the French into attacking Prussia, thus hoping to get the independent German states to unify with Prussia (which they did, thus creating Germany).
Charles I of England
English King during the English Civil War is executed by Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell
Led the parliamentarians (Roundheads) in the English Civil War
William and Mary
These people were the king and queen of England after the Glorious Revolution that recognized the supremacy of the English Parliament
Louverture, Toussaint
First leader of the Haitian Revolution, a former slave (1743-1803) who wrote the first constitution of Haiti and served as the first governor of the newly independent state.
Bolivar
Led revolutions all over Latin America
Giuseppe Garibaldi
United Southern Italy
Count Cavour
Unified Northern Italy
Glorious Revolution
A reference to the political events of 1688-1689, when James II abdicated his throne and was replaced by his daughter Mary and her husband, Prince William of Orange.
English Civil War
civil war in England between the Parliamentarians and the Royalists under Charles I