IB biology: topic 2/7: DNA VS RNA
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:33 PM on 1/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
what does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
2
New cards
what is DNA?
the genetic material in all living organisms
3
New cards
what does the DNA code do?
tells the cell what to do and what proteins to make.
4
New cards
where is DNA found in eukaryotes?
DNA is found mainly in the nucleus but there is also some in chloroplasts and mitochondria.
5
New cards
where is DNA found in prokaryotes?
DNA is not enclosed in a membranous envelope
6
New cards
what is RNA?
a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule
7
New cards
what is the function of RNA?
mostly involved in synthesising proteins
8
New cards
what is the role of mRNA?
transfers genetic information to the rest of the cell and later to make proteins
9
New cards
how are ribosomes formed?
from RNA and proteins
10
New cards
what is the function of nucleic acid?
carry the cell's genetic code (instructions for the function of the cell).
11
New cards
what are DNA and RNA made up of?
nucleotides
12
New cards
what are examples of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
13
New cards
what are nucleic acids made up of?
polynucleotides
14
New cards
what is an important role of nucleic acids?
important for passing on information from generation to generation.
15
New cards
what type of bonds connect the two strands of DNA?
hydrogen bonds
16
New cards
what is a DNA nucleotide made up of?
a deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group and an organic base (A,C,G,T)
17
New cards
what is a RNA nucleotide made up of?
a ribose sugar, a phosphate group and an organic base (A,C,G,U)
18
New cards
what type of reaction joins bonds between the two nucleotides?
a condensation reaction (between sugar of one nucleotide and phosphate group of different nucleotide)
19
New cards
how many hydrogen bonds does A-T form?
2
20
New cards
how many hydrogen bonds does C-G form?
3
21
New cards
what are the two forms of nucleic acids?
pyrimidines and purines
22
New cards
what are pyrimidines?
single-ringed molecules - cytosine, thymine and uracil
23
New cards
what are purines?
double-ringed molecules - guanine and adenine
24
New cards
what is the difference between uracil and thymine?
thymine is present in DNA, while uracil is used in RNA
25
New cards
what is the monomer of DNA and RNA?
nucleotides
26
New cards
what are polynucleotides?
nucleotides joined together to make up nucleic acids (e.g DNA or RNA)
27
New cards
what is the structure of nucleotides?
formed from a pentose sugar, a nitrogen-containing organic base and a phosphate group.
28
New cards
what is the structure of deoxyribose?
the carbon 2 hydroxyl group loses its oxygen, leaving a hydrogen atom
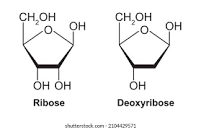
29
New cards
what is the structure of ribose?
the carbon 2 hydroxyl group keeps its oxygen, leaving an OH group
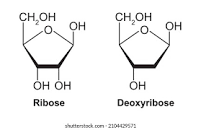
30
New cards
what is the genome?
the complete set of genes in an individual's DNA.
31
New cards
what do the genes in the genome do?
encode the different proteins a cell needs
32
New cards
what is the proteome?
the full range of proteins an individual can produce.
33
New cards
what is a codon?
a specific sequence of **three** bases
The order of the bases on the DNA tells us the order for combining amino acids to create particular proteins.
The order of the bases on the DNA tells us the order for combining amino acids to create particular proteins.
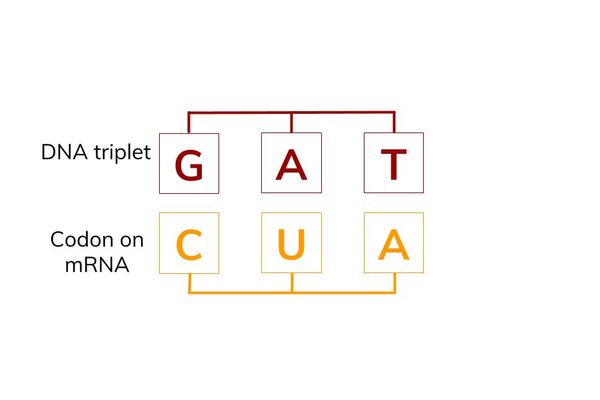
34
New cards
how is an amino acid encoded?
a specific sequence of three bases (codon) encodes a specific amino acid
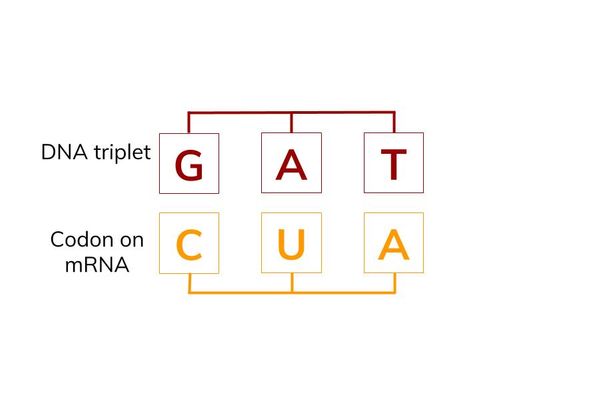
35
New cards
what is RNA usually made up of?
single strand of ribonucleotides (ribose, phosphate group and base)
36
New cards
what does RNA stand for?
ribonucleic acid
37
New cards
what does a codon code for?
one amino acid
38
New cards
what are key features of tRNA?
has an anticodon which is complementary to the mRNA codon
39
New cards
what type of nucelotide is uracil? (RNA)
pyrimidine