Human Genetics Final Exam
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Forward (Hypothesis-Generating)
Random Mutagenesis (Classical genetics) or Chemical Genetics (diverse small molecules) —> Phenotype of Interest —> Gene or Proteins of Interest
Reverse (Hypothesis-Based)
Targeted Mutagenesis/ Targeted Molecules —> Gene/Protein of Interest —> Phenotype of Interest
In situ Hybridization
exposed to a “probe” based on a specific sequence, labeled probe binds to matching sequence, location of bound probe can be seen by microcrope
Antibody staining
immunostaining to detect protein
use adaptive immune system to create custom antibodies to a protein of your choice
Mutagenesis
Mutagenesis screens using “mutagens” to introduce changes in the genome, which might lead to phenotypic changes
Exogenous (older methods)
• Radiation: X-rays, Ionizing radiation, UV,
• Alkylating agents: ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS), ethylnitrosourea (ENU)
Endogenous (newer methods)
• zinc finger nucleases (ZNF)
• transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN)
• clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/Cas proteins (CRISPR)
Transcriptomics
• Bulk RNA-seq provide the average measurement for all the cells
✓It does not provide insights into the stochastic nature of gene expression
• Single-cell RNA-seq allows the measurement of the distribution of expression levels for each gene across a population of cells
zygote
fertilized egg
embryology
traditional name of the study of that phase of an organism that exists between fertilization and birth
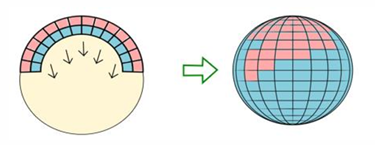
invagination

involution
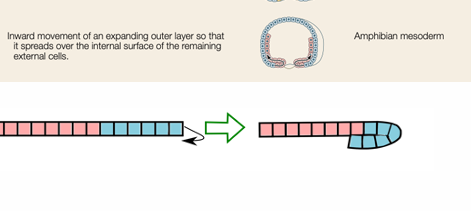
ingression

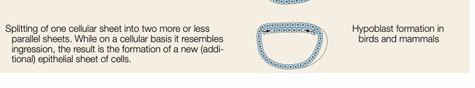
delamination
epiboly
Stages of Developmen
Fertilization • Zygotic genome activation
Cleavage • Lineage segregation • Blastocyst formation & Peri-implantation
Gastrulation
Organogenesis
fertalization

Zygotic genome activation
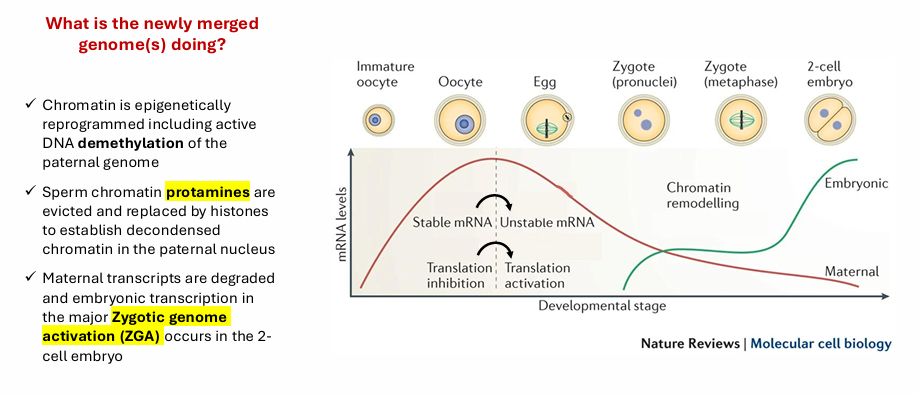
Clevage
is a series of extremely rapid mitotic divisions that immediately follow fertilization
Blastomeres
During cleavage, the enormous volume of zygote cytoplasm is divided into numerous smaller cells called
blastocyst
By the end of cleavage, the blastomeres have usually formed a sphere, known as
Rotational cleavage
What type of cleavage occurs in humans and most mammals?
Late Cleavage / 1st Fate
Hippo Pathway
y is the switch that translates where a cell sits into what lineage it adopts
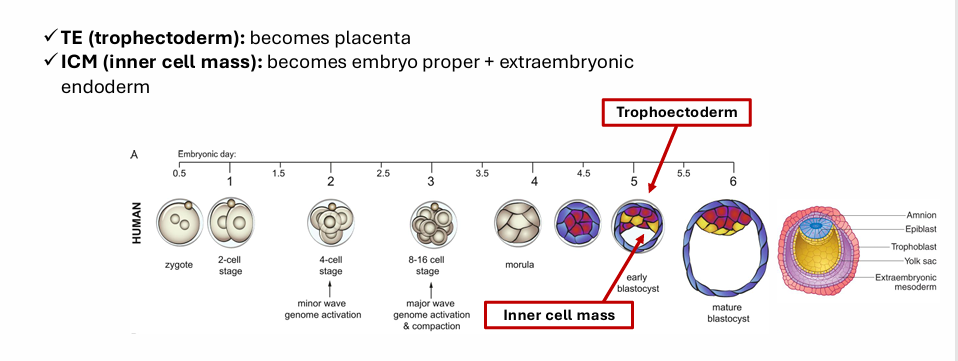
Inner Cell Mass
Hippo Pathway- On
Completely surrounded by neighbors (No apical domain)
Cell–cell contact activates Hippo pathway
Trophoectoderm
Hippo Pathway- OFF
✓Exposed to the outside environment → form anapical domain
✓Apical domain contains a complex that inhibits the Hippo pathway
2nd Fate Decision: Epiblast vs Primitive Endoderm (PrE)
✓ Happens within the ICM, after TE/ICM is already set
✓ FGF4/ERK signaling drives this decision
✓ Epiblast becomes the embryonic tissues; PrE becomes yolk sac derivatives
Totipotent
Can differentiate into all possible cell types
Pluripotent
Can differentiate into any of the three germ layers
Multipotent
Can differentiate into a limited number of cell types within a specific lineage or tissue
Gastrulation

Two cell split
2 chorions, 2 amnions
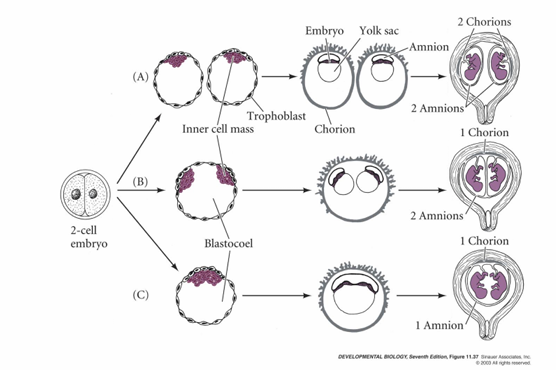
Inner Cell Mass split
2 chorions, 1 amnion
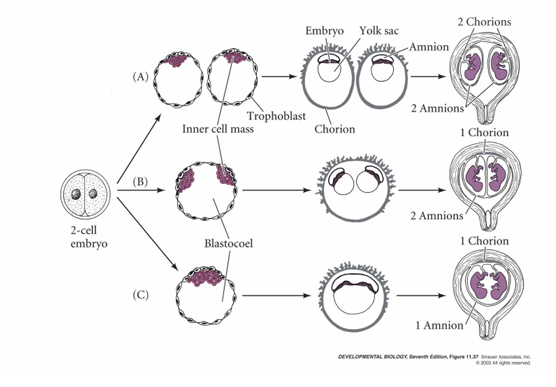
Epiblast split
1 chorion, 1 amnion

Anterior-Posterior
important for defining the head/brain
2 signaling centers
A-P split
1. Anterior Visceral Endoderm (AVE) an anterior hypoblast population
2. Henson’s node (“the organizer”)
AVE and node activity set up gradients
BMP, Wnt, FGF
Their antagonists - Dkk 1, Cerberus, lefty-1
BMP, Wnt, FGF
secreted signaling molecules
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs)
Hox gene
helpful in A-P axis formation and creating somites
Zone of Polarizing Activity (ZPA )
is a region of posterior limb bud mesenchyme in the limb field
Shh (sonic hedgehog)
involved in digit formation (based on time and gradient)
Hox regulatory evolution

Left and Right Axis Formation
Cilia on the Henson’s node
Nodal Pathway and nodal flow
Leftward direction (breaking symmetry)
vesicular particles (containing Sonic hedgehog, RA, Ca+)
Neonatal Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia
Hominids
Chimpanzees and Gorillas are also classed as Hominids • Modern humans share a common ancestor with chimps ~8 mya
biped
able to walk on two feet
No major consensus - but overall it likely wasn't a single environment, but rather the instability and variability of the environment over time
Australopithecines
1. adapting to a diet of nuts and seeds by evolving huge teeth and powerful jaw muscles
2. taller and capable of making tools out of stone
Encephalization
big brain
Homo erectus
migrated out of Africa using land bridge
“Denisovan” and “Neanderthal”
Named after cave systems
Out-of-Africa
“Individuals from African ancestry populations harbour the greatest numbers of variant sites, as predicted by the out-of Africa model of human origins
introgression
inbreeding with Neandertals
The Agricultural Revolution
• Starting around 11,000 years ago, Homo sapiens started to select, breed, and domesticate plants and
animals
• The development of agriculture occurred many times independently
Selection Coefficents
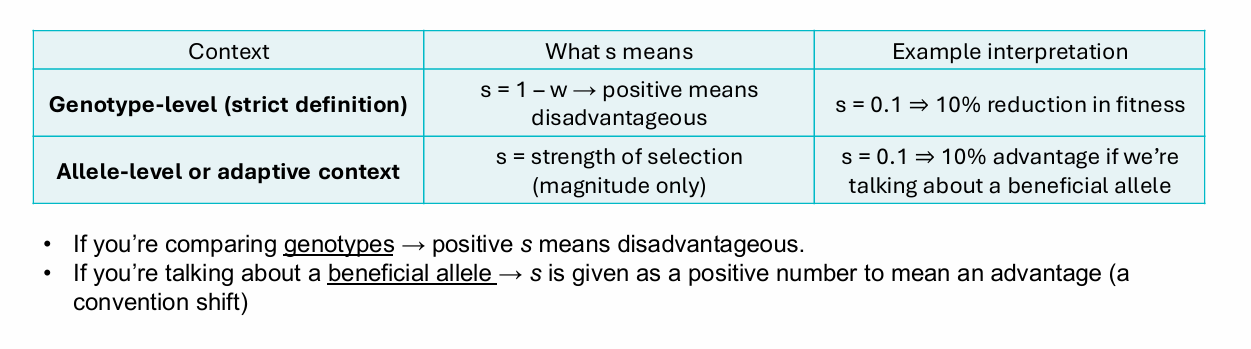
Calculating Relative Fitness
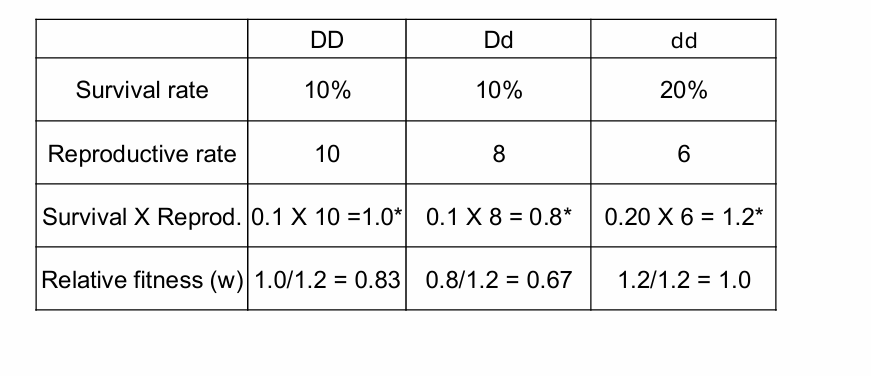
More on selection coefficients

chi-squared
(o-e)2/e
population genetics
is the study of allele and gene frequency distribution and change within populations, driven by fo
modern synthesis

Conditions for Hardy Weinberg Principle

Inbreeding depression
This inbreeding may lower the population’s ability to survive and reproduce, a phenomenon called inbreeding depressio
Genetic Hitchhiking
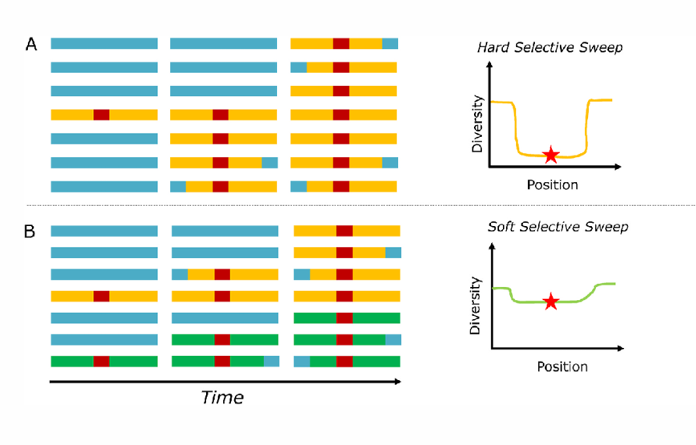
Gene flow
homogenizing force
ex. adaptive introgression
Pharmacogenetics
The field of research that studies how a person’s genetic makeup impacts how they respond to drugs
precision medicine
What can effect a drug response?
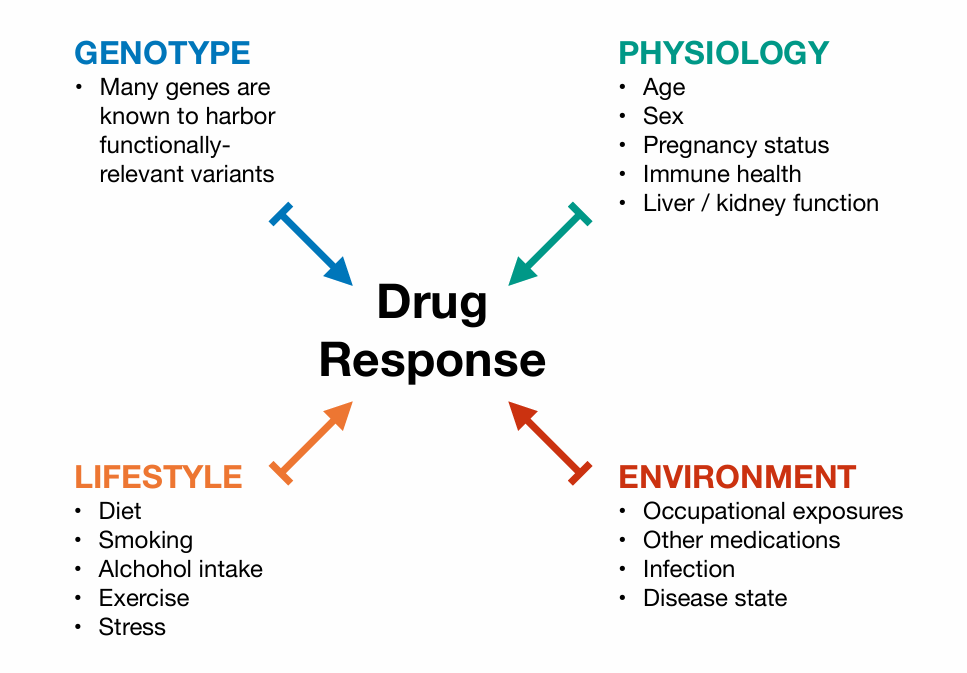
Pharmacokinetics
What the body does to the drug

Pharmacodynamics
What the drug does to the body
Drugs generally produce their effects by interacting with specific proteins, primarily receptorsDetoxification
Detoxification

Phase I
modification
e.g. hydroxylation by cytochrome P450 enzymes
‣ Modifies drug molecule by adding/exposing functional groups ‣ Typically makes drug polar and more water soluble
Phase II
conjugation
e.g. glutathione group added by a glutathione S-transferasP
‣ Drug molecule is coupled to a large chemical group ‣ This further increases water solubility and polarity, often making the metabolite unable to pass through cell membranes
Glutathione S-transferases and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases
Phase III
excretion
e.g. removal from the body via ABC transporters
‣ Transporters move metabolites from cells into urine, bile, intestine
Predicting Metabolizing Types
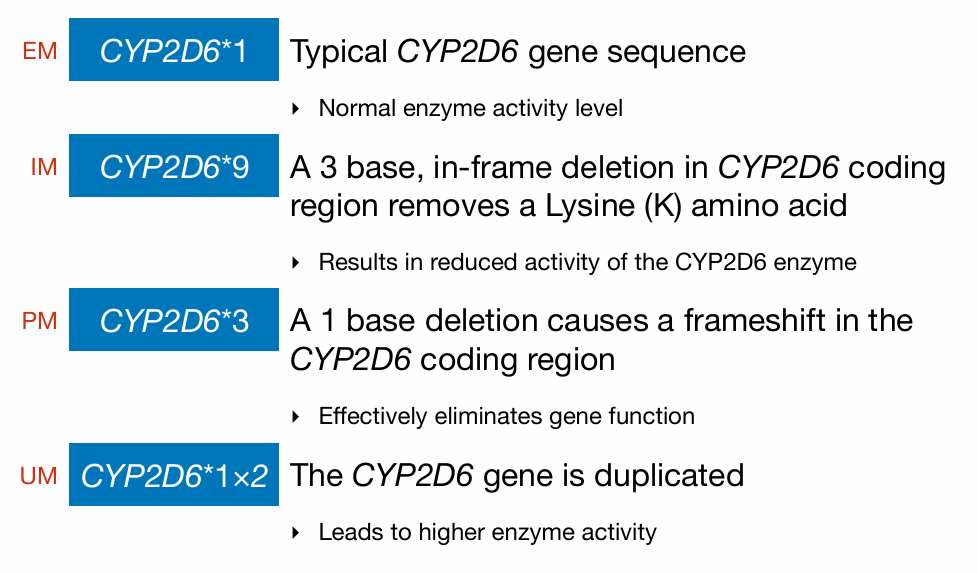
Metabolizer Phenotypes

Presence / Absence PCR-based Tests
PCR than gel visualization or not
PCR Repeat Length
PCR and visualize size fragments
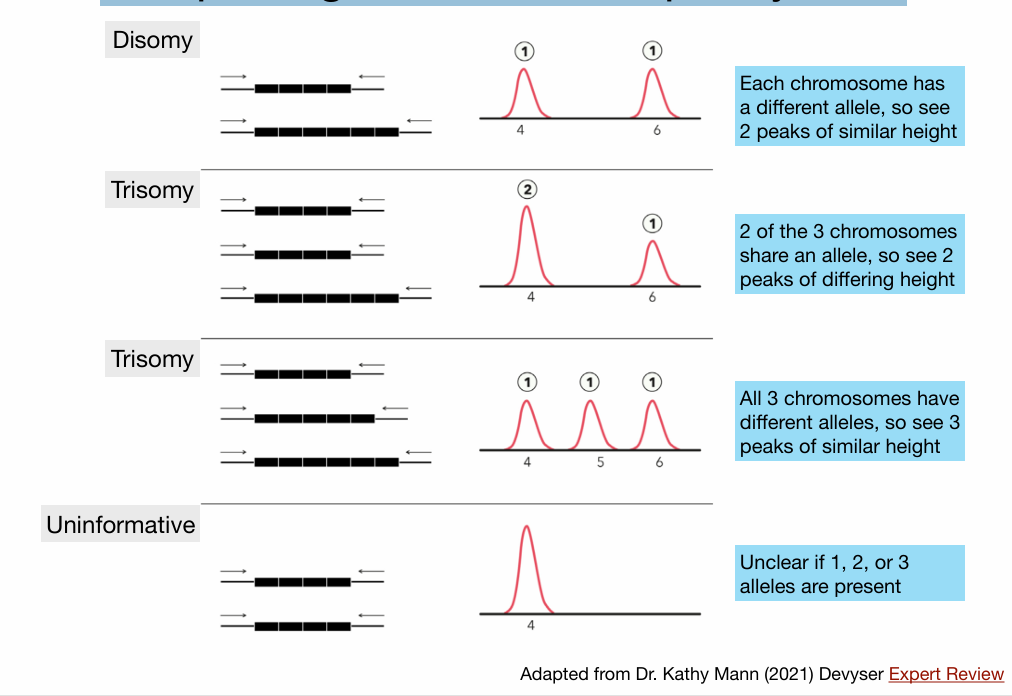
Quantitative PCR
does allow copy number to be assessed
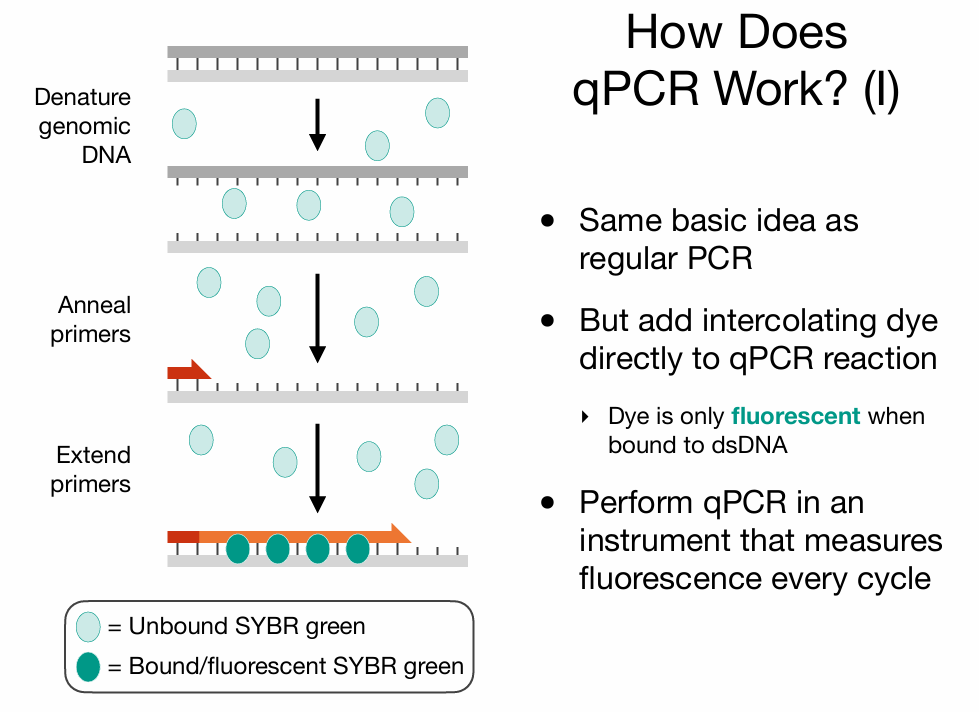
Quantitative Fluorescent PCR

Interpreting QF-PCR Aneuploidy Data