CMPE 246 Computer Engineering Design Studio
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Embedded System
System composed of hardware AND software to perform a set of pre-programmed functions
Generally includes:
Microprocessor
RAM and ROM
ADC
Firmware
Big Bang Model
No planning or process before development of a system
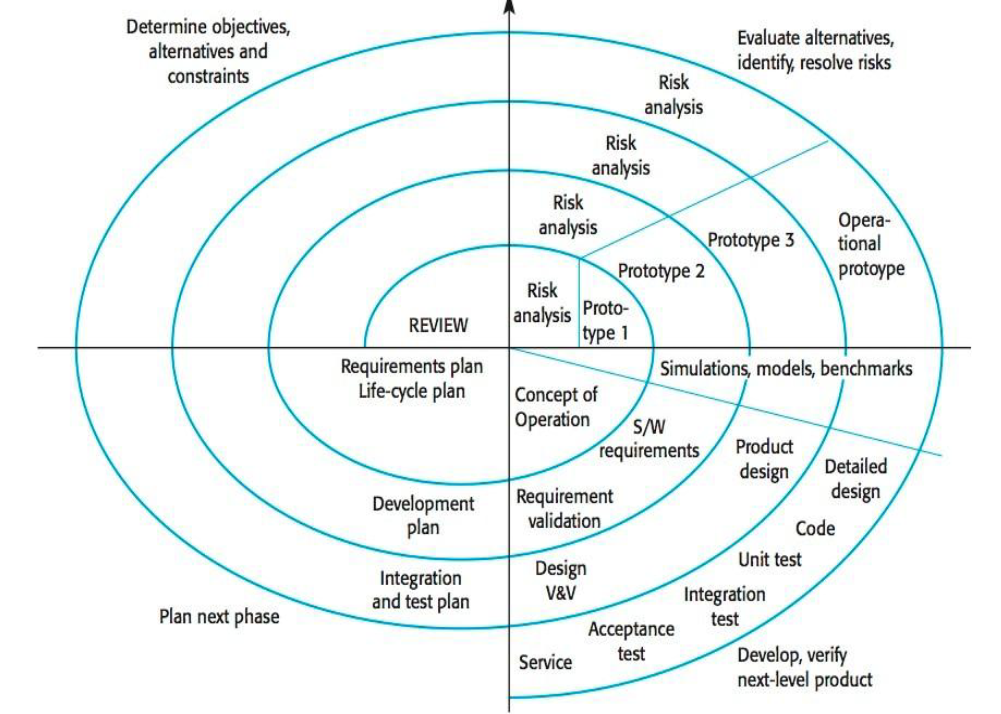
Spiral Model
Loops through a development cycle of 4 phases:
Planning
Risk analysis
Engineering
Evaluation
Waterfall Model
Linear process where the next step cannot start until its previous step is finished.

Code-and-Fix Model
Requirements are defined but no planned processes before development
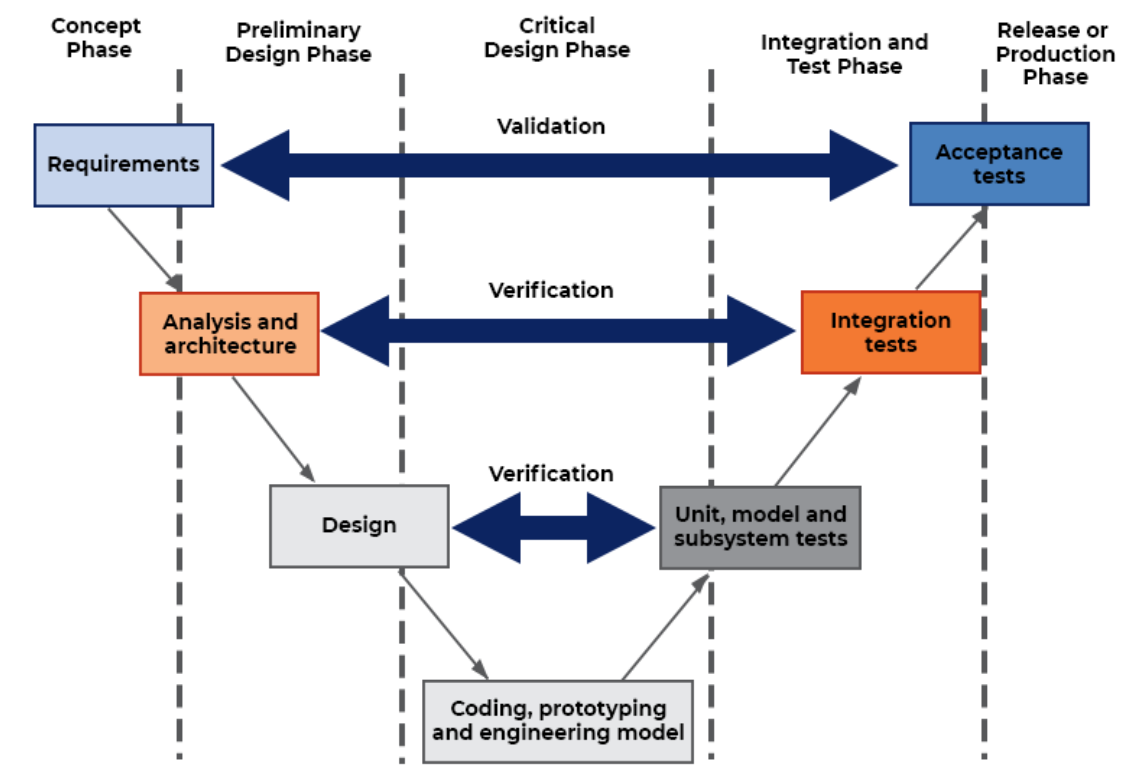
The V-Model
Framework in which development stages are directly tied in with testing stages
ARM processor
Processor of a smaller size in which power efficiency is prioritized
ROM
“Read only memory”
Stores code (AKA instructions) permanently
RAM
“Random Access Memory”
Stores temporary information
PROM
“Programmable ROM”
EPROM
“Erasable and programmable ROM”
Microprocessor
Takes in a task and processes it into instructions for (hardware or software??)
Advantages of Embedded System
Cheap
Portable
Small
Low power consumption
High performance and accuracy
API
“Application Programming Interface"“
Takes instructions from user (picks from API documentation), transfers info to the application of API (info is translated for the software of interest
Drivers
Piece of a software that allows communication between the and hardware
SRAM
“Static Ram”
Retains content as long as electric power is applied to chip
DRAM
“Dynamic Ram”
Retains content for an extremely short amount of time
About 4ms
Masked ROM
Stores data permanently
Typically programmed during the manufacturing stage
EEPROM
“Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM”
Type of hybrid memory
Can be erased with electric power and reprogrammed
Flash Memory
Type of hybrid memory
Retains data without power
NVRAM
“Non-Volatile RAM”
Type of hybrid memory
Fast, persistent data storage for speed
OS Kernel Mode
Has unlimited access to hardware while OS is running
Doing management of which tasks are running
Makes CPU process the higher priority tasks
OS User Mode
Limited access to CPU and memory
Operating System
Copies a program and cuts it down sequentially into tasks that are sent to the processors.
Is split up into user and kernel mode
Process/Task
A singular instruction of a program
Live Code
Code that is actively being run
AKA code currently going through the OS
Prefixes For Storage
Done in 2^n instead of 10^n
Ex:
Gigabyes = 2^30 bytes
Kilo = 2^10 bytes
PROM
“Programmable ROM”
ROM manufactured as blank ROM so user can edit it later.
EPROM
ROM where it’s data can be erased and reprogrammed
Requires strong UV light to erase the data
Dont ever use ts bruh
Buses
System that only transmits information
Ex.
Cables
Wifi
Bluetooth
Lasers
Buffer
Type of memory where one device’s processor will send information into another’s “buffer”
System Bus
AKA memory bus
Connects the CPU and main memory of computer
Actuator
Takes electric signal and blends with energy source to create movement
IDE
“Integrated development environment”
Type sh
Embedded Testing
Literally just Software and hardware verification and validation
AKA V&V
Verification: “yeah this does what we designed it to do”
Validation: “yeah the people and environment say it’s doing what they want it to do”
Firmware
Code embedded into hardware
Ex. Every time washing machine turns on, the firmware ensures it functions the same each time
Bare Metal
Where developers to directly program hardware without OS
Complete control over hardware pieces
ISP
“In-system programming”
Chips of which are already programmed before soldering onto a board
Upgrading Firmware
Two ways:
Flashing
Process of changing the firmware
Erases and replaces the ROM inside microcontroller
Compiler
Converts from high level code into assembly code (AKA binary)
(Optional?) Two types:
Each line is compiled and sent to the processor one at a time for real time changes
Compiles everything and sends to processor, but if changes are made everything will have to compile again (basically translates to .exe files)
(shorten the examples?)
Executable File
.exe file
File that is of compiled code????
Assembly Code
Code of which is in binary form
Used so the processor can understand and complete the tasks
Communication Network
Does three things:
Data exchange: allows devices, sensors, and actuators to transfer/exchange data
System integration: connects multiple devices
Remote and control monitoring: remote supervision. firmware updates, and control commands
Physical Ports
Physical connection points
Ex.
Ethernet ports
Usb ports
Logical Ports
Logical connection point
Routes data
Ex.
TCP/IP
HTTPS
Brewing secure websites
FTP
File transfers
Protocols
Set rules and conventions on how data is formatted, transmitted, processed, and errors detected and corrected
Wireless Communication Protocol
Enables data transmission over air without physical connectors
Key characteristics:
Mobility: data moves without cables
Flexibility: scalable and adaptable to varies environments
Range: range varies: low data rate w/ long range and the opposite
Interference and security: Can be interfered with
BAN
“Body area network”
Literally just network of devices operating in or on a body
WAN
“Wide area network”
Network of devices +-10 meters away from your body
PAN
“Personal area network”
LPWAN
“Low power wide area network”
idfk