AP bio Unit 1 Chemistry of life
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
How do organisms use water to survive
Organisms rely on water because of its unique properties—like polarity, hydrogen bonding, high specific heat, heat of vaporization, cohesion, adhesion, and solvent abilities—which enables essential biological functions such as maintaining temperature, transporting substances, and supporting chemical reactions in the cytoplasm.
We see Polarity & Hydrogen bonds allow water molecules to stick together (cohesion) and to other substances (adhesion) which facilitating transportation (e.g., water moving up plant xylem)
High specific heat ensures stable water temperature, helping maintain internal homeostasis.
High heat of vaporization enables evaporative cooling (e.g., sweating, panting)
Excellent solvent for polar and ionic molecules, enabling transport and biochemical interactions.
Surface Tension
It is the result of cohesion between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding, which creates a “film-like” surface as it has an ability against rupturing when put under tension or stress.
This allows small organism (like insects) to move or rest on water.
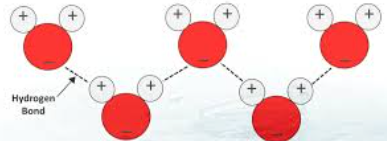
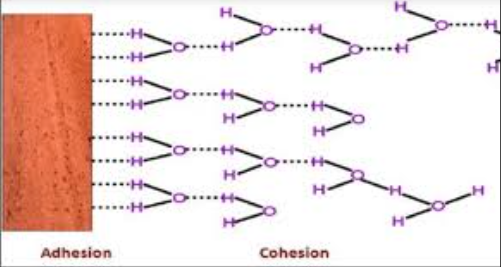
Cohesion
Is the attraction between water molecules causes by hydrogen bonding which allows water molecules to stick together.
This allows for Surface tensions - which lets insects and small organisms move on water
This helps pull water upward in the Xylem during transpiration. Water moves upward in plants through xylem. As water evaporates from leaves, it pull the next water molecules up like a chain. This is because water molecules stick together by hydrogen bonds, when one water molecule is pulled upward, it drags the others with it—allowing continuous after flow from roots to leaves.
Adhesion
Is the attraction between water molecules and other polar surfaces, which helps water stick to things like plant cells walls.
______ helps water molecules stick to the walls of xylem, preventing the water column from sliding back down.
Moreover the _______ + the cohesion together lets water move upward in narrow tubes, which supports transpiration in plants because the _____ makes water molecules stick to the polar walls of the xylem, so gravity doesn't pull the water column straight back down. This “grip” on the walls, combined with ________ allows water to climb upward.
Capillary Actions
Is the ability of water to move upward in the thin tubes because of cohesion (water sticking to water) and adhesion (water sticking to other surfaces)
In plants that water moves upward through the narrow xylem tubes due to capillary action in where the molecules stick together and the water sticks to the xylem walls, which allows water to climb against gravity during transpiration.
In animals they have tiny capillaries, where blood is pulled along partly by capillary action in where the water in blood stays connected and the water in the plasma sticks to capillary walls. This helps blood reach vary narrow vessels where pressure is low.
Solvent
It is a substance, like water, that dissolves other molecules so they can be transported or react in cells. (water is called the universal _____)
This works because water’s polarity causes it to surround and separate ins or polar molecules, allowing them to dissolve.
For example, in blood transport water dissolves salts, sugars, and gases so they can move throughout the body. Or water also dissolves reactants so chemical reactions can occur inside cells.
Specific heat capacity
This is the amount of heat energy needed to to raise the temperature of substance (like water) by 1 degrees Celsius.
Water molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds, when heat is added, much of the energy goes into breaking these hydrogen bonds rather than speeding up the molecules so it takes a longer time for water to heat up.
However when water cools, hydrogen bonds reforms, which releases heat slows as they slow down. (This is why water has a high _____ _____ ______)
This matters causes it causes water to resist rapid temperature changes, keeping cells and environments stable. This further protects organism from overheating or freezing too quickly.
Thermoregulator
Is an organism’s ability to maintain a stable internal temperature despite external temperature changes.
This works as water’ high specific heat helps absorb or release heat slowly, preventing rapid temperature changes in cells and tissues.
For example in humans sweating cools the body via evaporative cooling, and in plants transpiration helps leaves stay at safe temperatures.
Evaporative cooling
Is the process where water absorbs heat as it evaporates, lowering the temperature of a surface or organism.
This works as hydrogen bonds in water require energy to break, so when water evaporates from skin, leaves or other surfaces, it removes the heat that was used to break it.
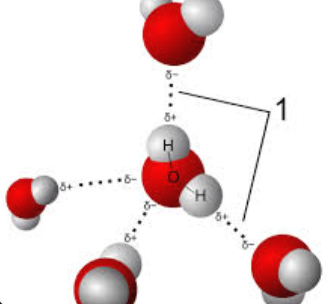
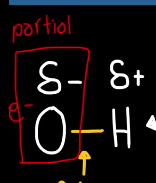
Polarity
Is when a molecules has a slightly postie and slightly negative ends due to uneven sharing of electrons, creating partial negative and positive charges at each end of the molecule and subsequentially an unsymmetrical shape.
This works in water because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, so it “hogs” the shared electrons, making oxygen slightly more negative and hydrogen slightly positive. This creates polar molecules that can form hydrogen bonds with each other and other polar molecules.
Some examples of this would be water being able to dissolve salts, sugars, and other polar molecules. Or Cohesion and adhesion in where it helps water move in plants and maintain surface tension.
Electronegativity
Is the ability of an atom to attract shared electrons in a chemical bonds this is caused from some atoms having more protons in a nucleus which creates a stronger positive pull on the negativity charged electrons.
Hydrogen bonding
The attractive forces between a hydrogen atom covalently (share electrons) bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom, and another very electronegative atom.
Subcomponents, sequence, and properties of molecules influence.
The subcomponents of biological molecules and their sequence determine the properties of that molecules.
For example water is made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom (subcomponents) and the sequence and arrangement (H-O-H angle and polarity) create a polar molecule with slightly positive hydrogen and a slightly negative oxygen.
This causes water to have properties, like cohesion and adhesion, high specific heat, solvent ability, and surface tensions and evaporative cooling.
What do water systems depend on
Water systems depend on properties of water that results from its polarity and hydrogen bonding.
What does the hydrogen bonds in water result in
The hydrogen bonds between water molecules results In cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension.
The structure of molecules determines their what
The structure of molecules determines their function.
How is life maintained
Life is maintained as living cells must take in elements from their environment in order to grow and reproduce.
Anabolic reactions
is one reaction that takes place in the cells in how they use elements to grow and reproduce.
This is where the cell takes the elements to build the cell through reaction that are constructive process where simpler chemical unites (monomers) are joined together to form larger, more complex molecules (polymers).
This reactions require an input of energy, often in the form of ATP, to form new chemical bonds.
These reactions are fundamental to growth, repair, and the maintenance of cells and tissues.
Protein synthesis
This is an example of an anaboilc reaction in where amino acids (monomers) are joined in a chemical reactions to form proteins (polymers)
Photosynthesis
This is an example of an anabolic reaction in which plants use sunlight energy to build glucose (polymers) from carbon dioxide (monomer) and water.
Lipid synthesis
This is an example of an anabolic reaction in which Fatty acids (monomers), are combined to form triglycerides (polymers)
Carbohydrate synthesis
This is an example of an anabolic reaction in which Monosaccharides (monomers), are assembled into polysaccharides (polymers)
Monomer
Is a small molecule that can bond with identical or similar molecules to form polymers.
Think of them as the individual Lego bricks, that, when linked together, build the final structure.
Some Example of common Monomers are:
Amino Acids — the monomers that link together to form proteins
Nucleotides — the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
Monosaccharides — the monomers that combine to form complex carbohydrates

Polymers
A large, complex, molecules made from many smaller, repeating molecular units called monomers.

Catabolic reactions
is one reaction that takes place in the cells and this is a biochemical process that breaks down large, complex molecules (polymers) into smaller, simpler ones, releasing energy in the process.
This energy is captured and stored in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules, which then power essential cellular activities and maintain homeostasis.
A classical example is cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down to generate ATP.
Cellular Respiration
This is an example of an catabolic reaction and this is where it breaks down complex fuel molecules, such as glucose, into simple substances like carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy in the process to create ATP.
Digestion
This is an example of an catabolic reaction and this is where it breaks down large, complex food molecules (like proteins, facts, and carbohydrates) into smaller, simpler ones (like amino acids, fatty acids, and sugars).
This process uses hydrolysis reactions to break the chemical bonds in food, releasing energy that the body can then use.
How anabolic and catabolic reactions interact when you eat food
When you eat food, your body first breaks it down through catbolic reactions, turning carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller molecules like glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids.
This breakdown releases energy in the form of ATP. Your body then uses this energy in anabolic reactions to build new molecules, such as proteins for muscles, DNA for cells, or fats for storage.
Together, these processes allow your body to grow, repair, and maintain itself, linking the energy from food directly to building of your body.
The CHONPS elements
These are the elements that make up 96% of living organisms, and these include: Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), Phosphorus (P), and sulfur (S).
These elements are considered essential building blocks of all biological molecules and are critical for cellular process and the structure and function of all life.
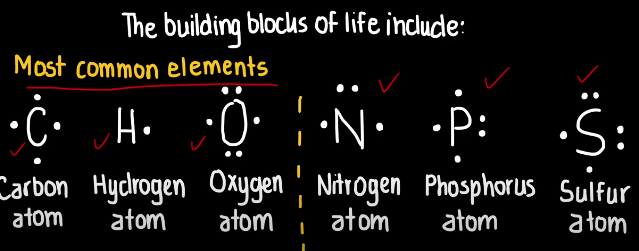
Carbon Atom
Is a atom that has four valence electrons, and in order for it to feel stable it must have 8 valence electrons, so it is able to easily form four strong covalent bonds with other atoms.
Due to this it can bond to other carbon atoms creating long chains, it can create branched chains, and a diversity of molecular shapes. (Due to its rule that it can have four covalent bonds)
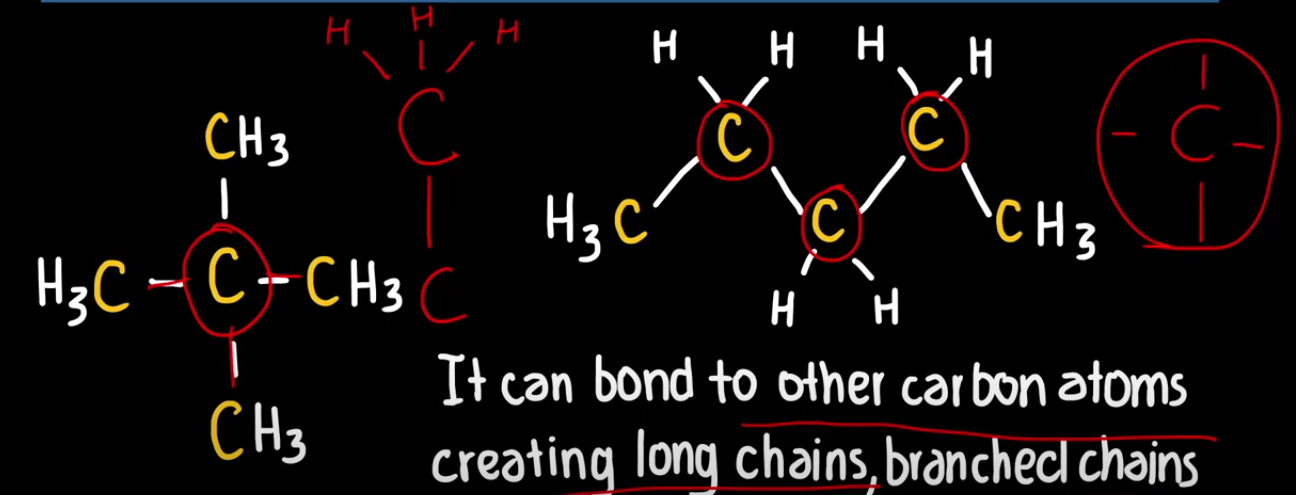
Hydrogen Atom
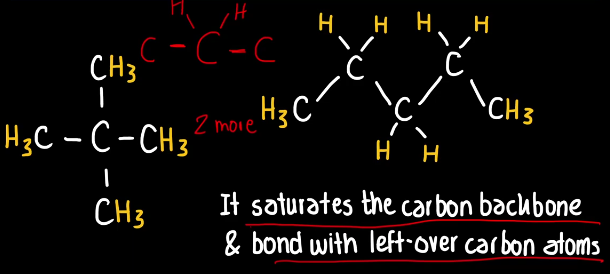
It is an atom that has one valence electron, however it needs two valence electrons to be stable so it can only form one covalent bond with other atoms.
By this valence rule hydrogen usually acts as a filler as it can fill voids in the carbon backbone in where there is a left over covalent bond to be formed and their is no other atom to take the place, it will bond with the left-over carbon atom, as it only needs an additional covalent bond to be fulfilled.
This rule applies to any type of organic molecule.
Hydrocarbons
Are molecules that are formed of Carbon and hydrogen atoms only.
Due to this they are usually non-polar as the bonds between the Carbon and Hydrogen are almost equal in how they share electrons, so there’s no big difference in charge—that makes hydrocarbons no-polar, and ultimately hydrophobic, as they don’t mix well with water.
Moreover they usually store a lot of energy as they are high-energy bonds since the electrons in them are shared almost equally.
An example would be fats as the store energy and they don't dissolve in water.
Oxygen Atom
Is an atom that has 6 valence electrons so it can only form 2 covalent bonds with other atoms.
It has a high electronegativity so it strongly attracts electrons.
When oxygen bonds with hydrogen, and other atoms that have less electronegativity than it, it created partially polar regions withing a molecule a it hogs more electrons, making it hydrophilic (it can be dissolved).
So if you find a molecule that has a OH bond that means its polar and it has the ability to dissolve in water. (so the difference between being polar and no polar can be the presence of oxygen in the molecular structure)
Carbon, Hydrogen & oxygen being the major component used in Macromolecules
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are the most common elements that are used in Building macromolecules (a type of polymer) which include:
Carbohydrates
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic acids
Nitrogen atom
Is an atom that is only able to form three covalent bonds because it has five valence electrons.
It is a key component of proteins and nucleic acids (macromolecules which are a type of polymer)
Phosphor atom
Is an atom that is able to form three or five covalent bonds.
It is a key component of Nucleic acids and phospholipids (macromolecules which are a type of polymer)
Sulfur atom
Is a atom that is able to form two covalent bonds as it has 6 covalent bonds.
It is a key component of some proteins (cysteines) (macromolecules which are a type of polymer)
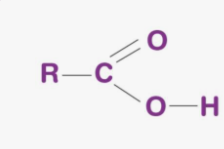
Carboxyl group
Is a functional group in organic molecules with the structure - COOH (a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen and also bonded to a hydroxyl group -OH)
it acts as an acid, easily donating a hydrogen ion (H+) due to oxygen’s strong electronegativity (it takes hydrogen’s electrons —breaking the bonds when in water). When it loses this hydrogen, the group becomes negatively charged, which makes the molecule polar, hydrophilic, and reactive (means it can easily take part in chemical reactions that change or build molecules because when it becomes acidic it allows it to interact with bases or other charged groups in the cell)
This is why molecules like amino acids and fatty acids are acidic and dissolve well in water.
________ groups are also key in chemical reactions such as dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis, allowing larger molecules to form or break apart.
Overall, the ______ group is essential in amino acids (helping proteins form peptide bonds), in fatty acids (giving them their acidic property), and in energy reactions like the citric acid cycle.
Amine group
The _______ group (-NH2) is a function group made of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen’s, and it is important in biology because it acts as a base.
The nitrogen atom has a high tendency to attract another hydrogen ion (H+), which gives the group a positive charge and makes the molecule polar, hydrophilic, and reactive (means it can easily take part in chemical reactions that change or build molecules because it is basic, allowing it to interact with acidic or other charged groups in the cell).
This property allows amino groups to play a central role in building biological molecules. For example, every amino acid contains an amino group, and during protein synthesis, it react with carboxyl group of another amino acid to form peptide bonds, which links amino acids together into proteins.
The ability of amino groups to accept H+ and to form strong covalent bonds (the nitrogen in the amino group has a lone pair of electrons that lets it bond tightly to the carbon in a carboxyl group. in Dehydration synthesis, the -OH from the carboxyl group and the -H from the amino group combine and leave as water. The leftover nitrogen and carbon form a new covalent bond—the peptide bond—which is very strong and stable) makes them essential in the structure and function of proteins, as well as in regulating pH balance inside cells
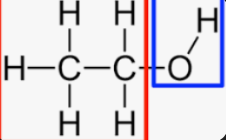
Hydroxyl group
Is a function group made of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (-OH). It is important in biology because it makes molecules polar and hydrophilic due to oxygen’s strong electronegativity, which causes the group to form hydrogen bonds with water.
This polarity helps molecules with ______ groups dissolve in aqueous environment like the cytoplasm.
_______ groups are common in many biological molecules, including sugars, alcohols, and some amino acids, where they increases solubility and allow chemical reactions (due to their polar nature).
They are also reactive because they can participate in dehydration synthesis, where a _______ group and a hydrogen form another molecule combine to form water, allowing larger polymers like carbohydrates and proteins to form.
Overall, _______ groups are crucial for making molecules soluble, interactive, and able to join in the reactions that build life’s macromolecules.
Methyl group
Is a function group made of one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen’s (-CH3).
Unlike many other function groups, it is nonpolar and hydrophobic. Meaning it does not mix well with water and does not donate or accept hydrogen ions.
Because of this, the _____ group is not chemically reactive in the same way that carboxyl and hydroxyl groups are, but it is still biologically important.
______ groups often act as “tags” that can turn genes on or off through a process called DNA methylation, which plays a major role in regulating gene expression.
They also appear in fatty acids chains, where their nopolar nature helps make lipids insoluble in water, contribution to the structure of cell membranes.
Overall, the ______ group is important because, even though it is not very reactive, its nonpolarity and role in gene regulation make it essential for biological function.
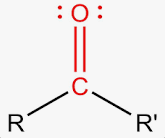
Carbonyl group
Is a functional group made of a carbon atom atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O).
It is important in biology because the oxygen is highly electronegative, which makes the group polar and gives the carbon a slight positive charge.
This polarity allows the carbonly group to be very reactive and to interact with many other molecules in water-based environments.
Phosphate group
Is a functional group Mae of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms (-PO4), one of which is usually bonded to the rest of the molecule.
it is highly reactive and negative charges, which makes molecules containing it polar and hydrophilic.
_______ groups are important in biology because they can store and transfer energy, as seen in ATP (adenosine triphosphate), where breaking the bonds between _______ releases energy for cellular process.
They also play key roles in nucleic acids, forming part of the backbone of DNA and RNA by linking nucleotides together.
Additionally, _________ groups can participate in phosphorylation reactions, where adding a _________ to a molecules changes its activity or function, which is critical in regulating proteins and metabolism.
The reactivity of _______ comes from the high-energy bonds between its oxygen atoms, making it a central player in energy transfer and signaling in cells.
Carbohydrates
Is an organic macromolecules (type of polymer) and it is always made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in ration of 1 (carbon): 2(hydrogen): 1 (oxygen).
The main function groups that make this up are Hydroxyl groups (-OH) and Carbony groups (C=O), the hydroxly group gives _________ water solubility and reactivity, while the carbonly groups allows them to form rings (as it reacts with one of its own hydroxyl groups, which forms a covalent bonds turing the straight chain into a ring structure, which is how sugars mostly exist in cells), link into polysaccharides, and participate in energy-related reactions.
They serve as the primary source of energy for cells and also provide structural support in platns and some animals (as some of them form strong, long chains that cells can’t easily break. In plants, cellulose chains (a _________) make cell walls rigid, giving the plant shape. In some animals, like insects, chitin (a ___________) form hard exoskeletons for protection and support)
A simple monosaccharides like glucose, are quick energy sources, while complex ________ or polysaccharides like starch, glycogen, and cellulose, store energy or give structural strength.
___________ are hydrophilic because of their many hydroxyl (-OH) groups, which allows them to dissolve in water and interact with other molecules.
They are also reactive in the sense that their bonds can be broken during cellular respiration to release energy or joined through dehydration synthesis to build larger molecules.
Overall, __________ are essential for energy storage, supply, and structural roles in living organisms.
MADE OF CHO
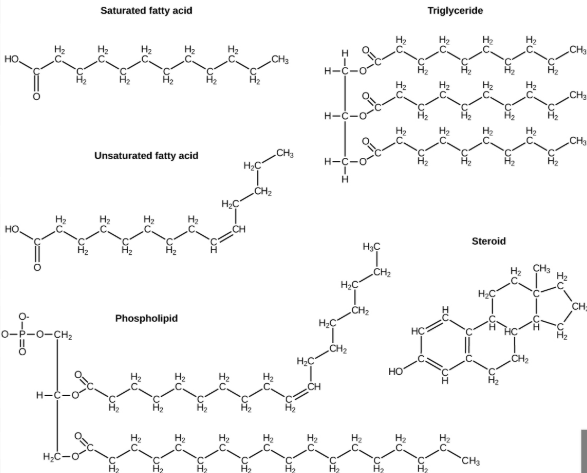
Lipids
Is a macromolecule (a type of polymer) and they are a diverse group of hydrophobic biological molecules and they are made mostly of carbon and hydrogen (Methyl), with very few oxygen atoms (high electronegativity, so less to prevent it from being polar).
They include fats, oils, and phospholipids, and steroids, and their primary function is to store long-term energy, provide insulation and protection, and form cell membranes.
_______ are hydrophobic because they hydrocarbon chains are nonpolar, which means they do not mix well with water.
In fats and oils, fatty acids are linked to glycerol through dehydration synthesis, forming triglycerides, which efficiently store energy due to the high number of C-H bonds.
Phospholipids, which make up cell membranes, have a polar head (hydrophilic) and a nonpolar tail (hydrophobic), allowing them to form the lipid biayler.
Steroids, like cholesterol, are lipids with a ring structure (as the carbon atoms bond in a way that form stable rings rather than chains) that help maintain membrane fluidity and acts as signaling molecules (as they slip through cell membranes because they are lipid-soluble, and bind to a specific receptor proteins inside cells. Once bound, they can turn genes on or off, which changes how the cell works).
Overall, lipids are essential for energy storage, membrane structure, and cell signaling in biological systems.
MADE of CHO—less O
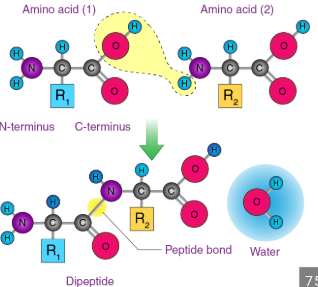
Proteins
These are large, complex molecules (macromolecules— a type of polymer), made of chains of amino acids (molecules that contain both an amino group -NH2 and a Carboxyl group -COOH, also with a side chain (R), however a loss of H20 due to dehydration synthesis—the -OH from the carboxyl group and the H from the amino group combine to form water) linked by peptide bonds.
They are essential for nearly every function in living organisms, including structural supports, transport (by binding to molecules and moving them where they’re needed) signaling (by detecting signals and passing them along to make the cell respond), movement (Actin and myosin proteins in muscle cells slide past each other to make muscles contract, and _______ also help move organelles or vesicles inside cells along cytoskeleton tracks), an catalyzing reactions as enzymes.
Each protein’s structure— primary (sequence of amino acids), secondary (alpha-helices and beta-sheets), tertiary (3D folding), and quaternary (multiple polypeptide chains)— determines its function, and even small changes in structure can affect activity.
Proteins are polar and nonpolar depending on the side chains of their amino acids, which affects how they interact with water and other molecules.
They are formed through dehydration synthesis and broken down by hydrolysis, allowing cells to build or recycle them as needed.
Overall, proteins are vital because their structure and chemical properties enable them to perform the wide range of tasks required for life.
MADE OF CHON sometimes S
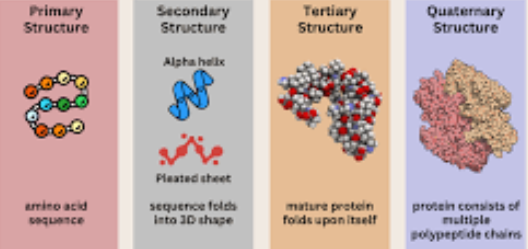
Nucleic Acids
These are macromolecules made of long chains of nucleotides, each consisting of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
They store and transmit genetic information (DNA) and help make proteins (RNA).
They phosphate group makes nucleic acidic and polar, allowing them to interact with water, while the sequence of nitrogenous bases sequence of nitrogenous bases encodes instructions for building proteins.
Nucleotdies are linked by phosphodiesterase bonds, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA or RNA.
DNA is a double-stranded and stores long-term genetic information, whereas RNA is usually single-stranded and translates DNA instrction into proteins.
Nucleic acids are essential for inhetiance, protein syntehsis, and cell regulation, meaking them criticla moelculesi in all living organimis.
Where do nutrients originate from
They originate from elements in the environment, and these elements are rearranged to form carbohydrates, proteins, facts, vitamins, minerals and waters. (all macromolecules)
What are the main elements of lie referred to.
The main elements of life are often referred to as CHONPS, and they are combined in a multitude of ways and every different structure posses a different function.
For example Methyl (CH3 linked with R) structure causes it to be nonpolary, hydrophobic, and stable.
How can two organisms eat the same thing, Or “start with the same pieces,” but end with a different stricture.
Two organisms can eat the same for or start with the same elements (like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) but end up with different structures because their genes dictate how their cells assemble these building blocks.
For example, both a plant and animal may use glucose, but a plant’s genes dictate it to make cellulose for structure, while and animal’s genes direct it to make glycogen for energy storage.
The same starting molecules can be rearranged in different ways according to genetic instructions, producing the unique molecules and structure that define each organism.
What does it mean to “digest food?” What does it mean to “build muscle?” What do you eat to “build muscle?” Explain: You are what you eat!”
Digesting food means breaking down the molecules in the food you eat (like carbohydrates, proteins, and facts) into their smaller building blocks—sugars, amino acids, and fatty acids— so your body can absorb and use them.
Building muscle means taking those small molecules, especially amino acids, and reassembling them into proteins according to your body’s genetic instructions to make muscles fibers.
To build muscle, you need protein-rich food because they provide the amino acids your body uses as raw material to reassemble to build muscle.
The phrase, “you are what you eat” means that your body literally uses the atoms and molecules from your food to construct your cells, tissues, and organs. Essentially, the molecules you consume become part of you.
Essential knowledge
Organisms must exchange matter with the environment to grow, reproduce, and maintain organization.
Atoms and molecules from the Environment are necessary to Build new molecules.
For example Carbon is used to build biological molecules like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Carbon is used in storage compounds and cell formation in all organisms.
Nitrogen is used to build proteins and nucleic acids, and Phosphorus is used to build nucleic acids and certain lipids.
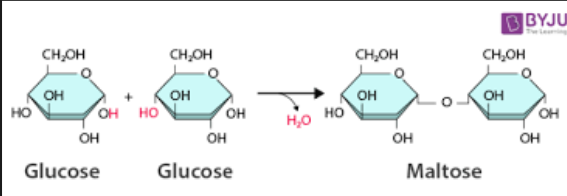
Dehydration synthesis
is a chemical reaction that join two monomers to make a polymer by removing water (H2O).
The H and OH from the two monomers combine to form water, and the reaming parts of the monomers bond together. This is how cell build carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids (macromolecules) from their smaller building blocks.
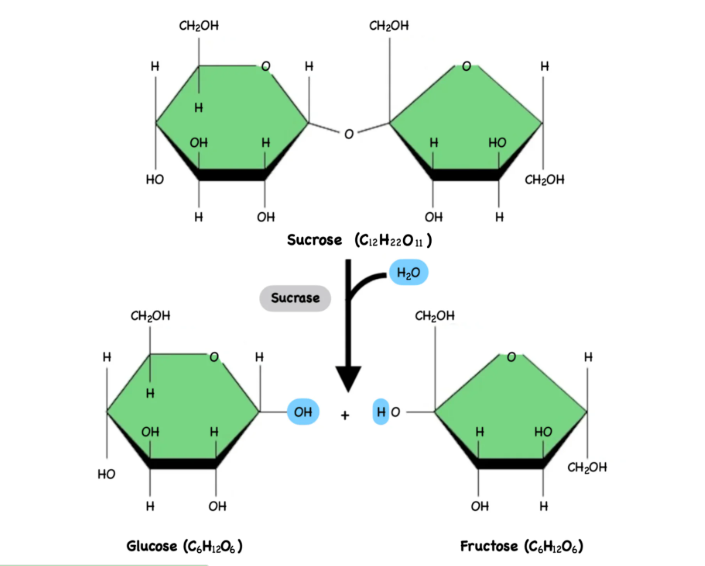
Hydrolosis
is a chemical reaction that breaks a polymer into monomers by adding a water molecule (H2O). The reaction requires energy to break the weak bonds in the polymer.
The water molecules splits into H and OH, which attach to the ends of the broken bond, allowing the polymer to separate.
Essentially, the energy from the cell “attacks” the weak points of the polymer (usually the O bonds) helping to break the bonds so the monomers can be released for energy use or to build new molecules.
What are Hydrolysis and Dehydration synthesis are used to do?
They are used to break and form covalent bonds between monomers, allowing cell to build or break down polymers.
What are polymers built from
Polymer share built through dehydration synthesis, from two or more monomers in order to form more complex carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is needed in order or organisms to use energy from polymers.
In order or organisms to use the energy from polymers, the polymers must break down. This is done through the process of hydrolysis
Simple Sugar
Is a carbohydrate made of a single sugar molecule (monomer) that servers as the basic building blocks for more complex carbohydrates and a quick source of energy for cells.
Complex Carbohydrate
It is a long-chain molecules made of many sugar (monosaccharide/ monomers) sub units linked together.
Why type of bonds are prevalence in Carbohydrates
They type of bonds that are prevalent in Carbohydrates and Covalent bonds, that are single bonds.
What different structures does a Carbohydrate bond use
It uses a linear structure, it can also use ring structures that are categorized as things like pentagons, hexagon, octagon, …. man geometric based shape. They can also come in the form of Hexagons.
Some reasons for ring and Hexagons is because of intramolecular reaction in where their is a reaction between two functional groups already present withing the same carbohydrate molecule; a carbonly group and a hydroxyl group.
Why are carbohydrates easily broken down for energy and are considered to primary energy source for organisms
They are primary energy sources because their sugar-based chemical structure is easily broken down by enzymes into glucose, which cells then readily use to generate energy. And in comparison to the other macromolecules carbohydrates have the less energy so the body utilizes the least energetic molecules in order to preserve the high-energy for more intensive uses.
How does food humans eat eventually ends up in the bloodstream as glucose
The process primary included the digestion of carbohydrates through hydrolysis, the absorption of the simple sugars in the small intestine, and the regulation of these levels by the liver and pancreas in order to be distributed across the body so the cells can utilize these for energy.