Understanding the Federal Bureaucracy
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Federal Bureaucracy
The administrative system governing federal agencies.
Bureaucrats
Individuals working within the federal bureaucracy.
Civil Servants
Employees hired based on merit for government roles.
Political Appointees
Individuals appointed to positions by elected officials.
Patronage
System of appointing officials based on political support.
Merit System
Hiring based on qualifications and performance.
Pendleton Act
1883 law establishing merit-based civil service.
Hatch Act
1939 law limiting political activities of federal employees.
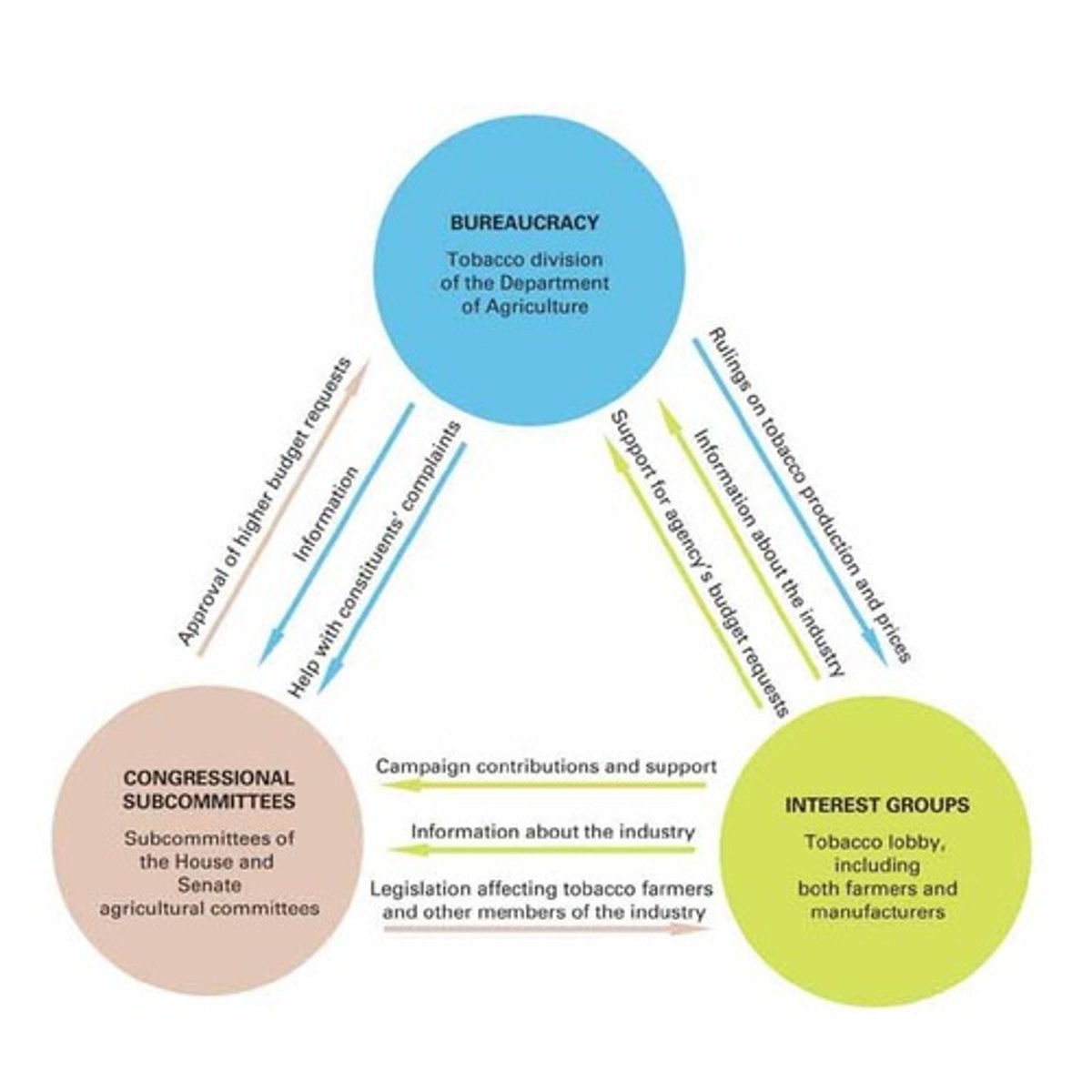
Iron Triangles
Stable relationships among bureaucracies, interest groups, and Congress.
Deregulation
Reduction or elimination of government rules and regulations.
Regulation
Government rules to control or manage activities.
Public Policy Implementation
Execution of government policies by bureaucratic agencies.
Bureaucratic Effectiveness
Ability to efficiently implement public policies.
Federal Employment Statistics
2.7 million federal employees, 2% of civilian jobs.
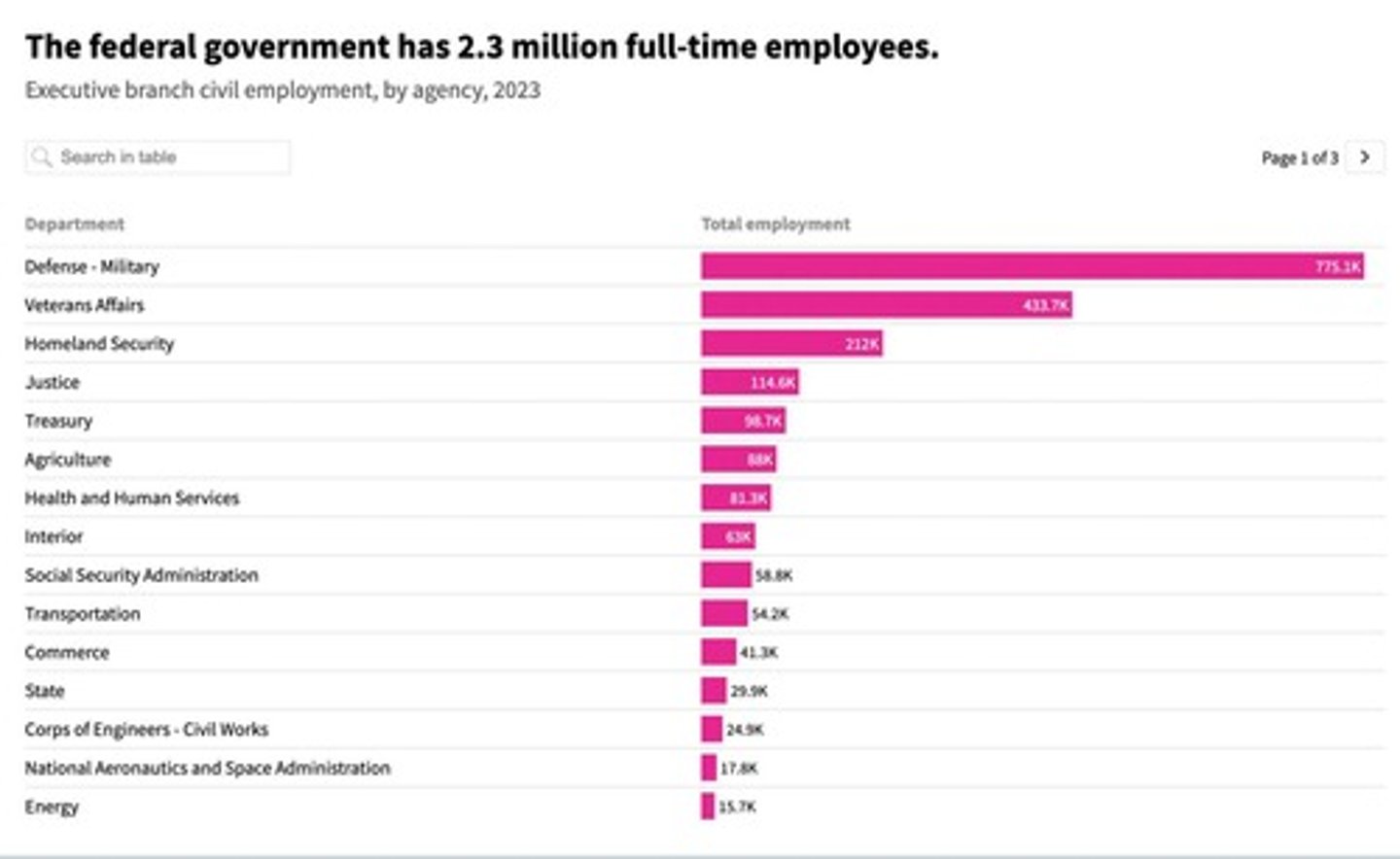
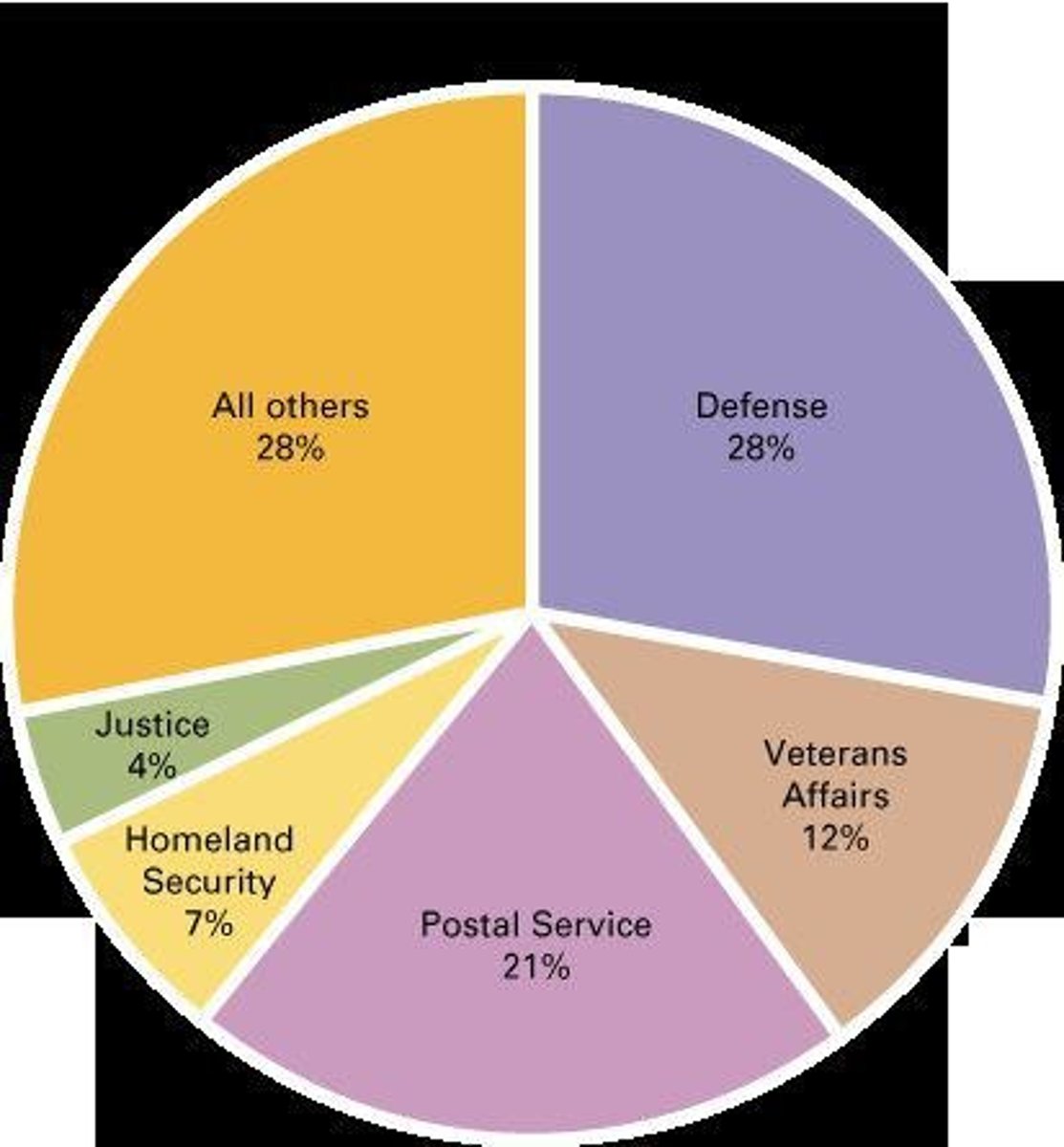
Department of Defense
Largest employer, comprising 28% of federal bureaucrats.
Bureaucratic Myths
Common misconceptions about bureaucracies and their functions.
Bureaucratic Growth
Trend of increasing size of bureaucratic agencies.
Ambassadorships
Diplomatic positions often awarded to political contributors.
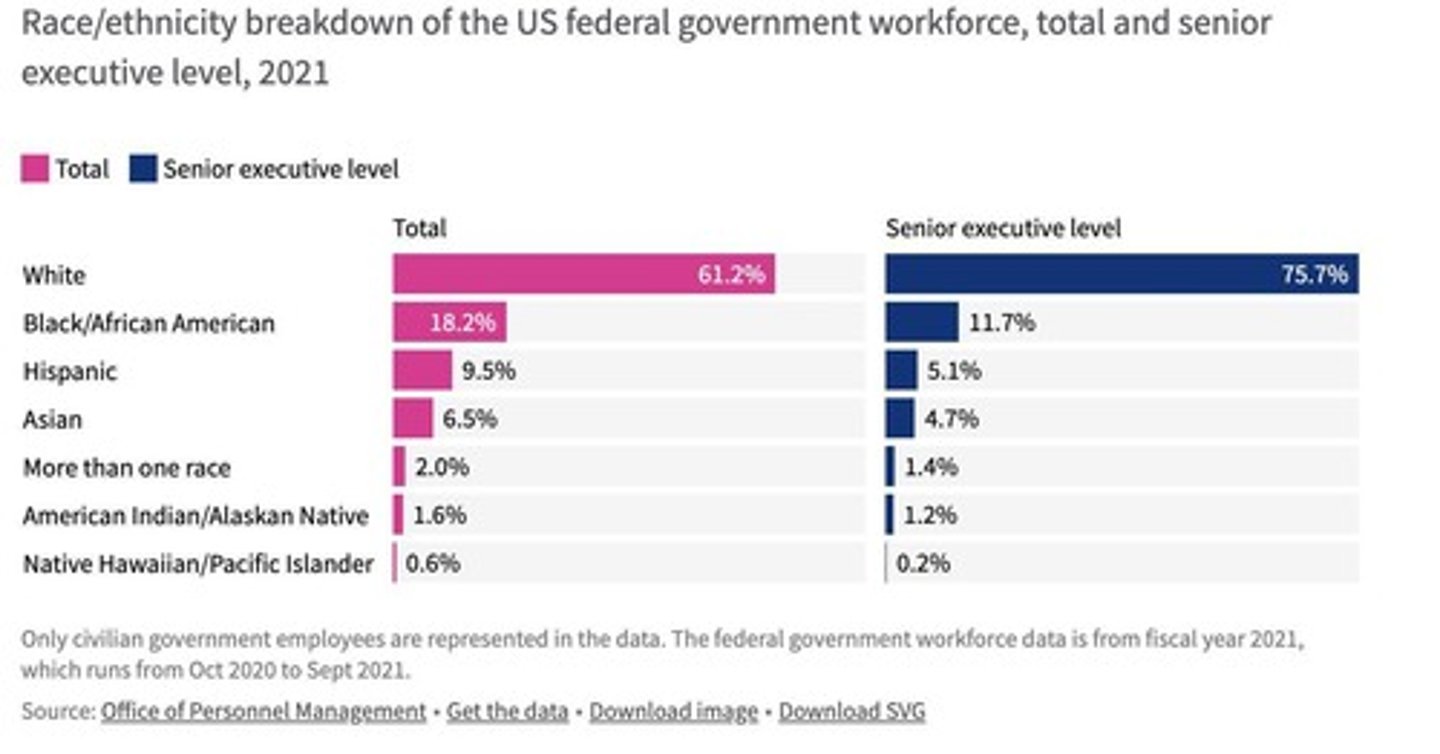
Demographic Balance
Efforts to ensure diversity among appointed officials.
Bureaucratic Inefficiency
Perception of bureaucracies as slow and ineffective.
Bureaucratic Representation
Civil servants more diverse than elected officials.
Civil Service System
Framework governing employment and promotion in bureaucracy.
Political Appointees
Transient employees with limited power, under two years.
Civilian Employees
Federal bureaucracy employs 5,100,750 civilians today.
Cabinet Departments
Fifteen departments, each led by a secretary.
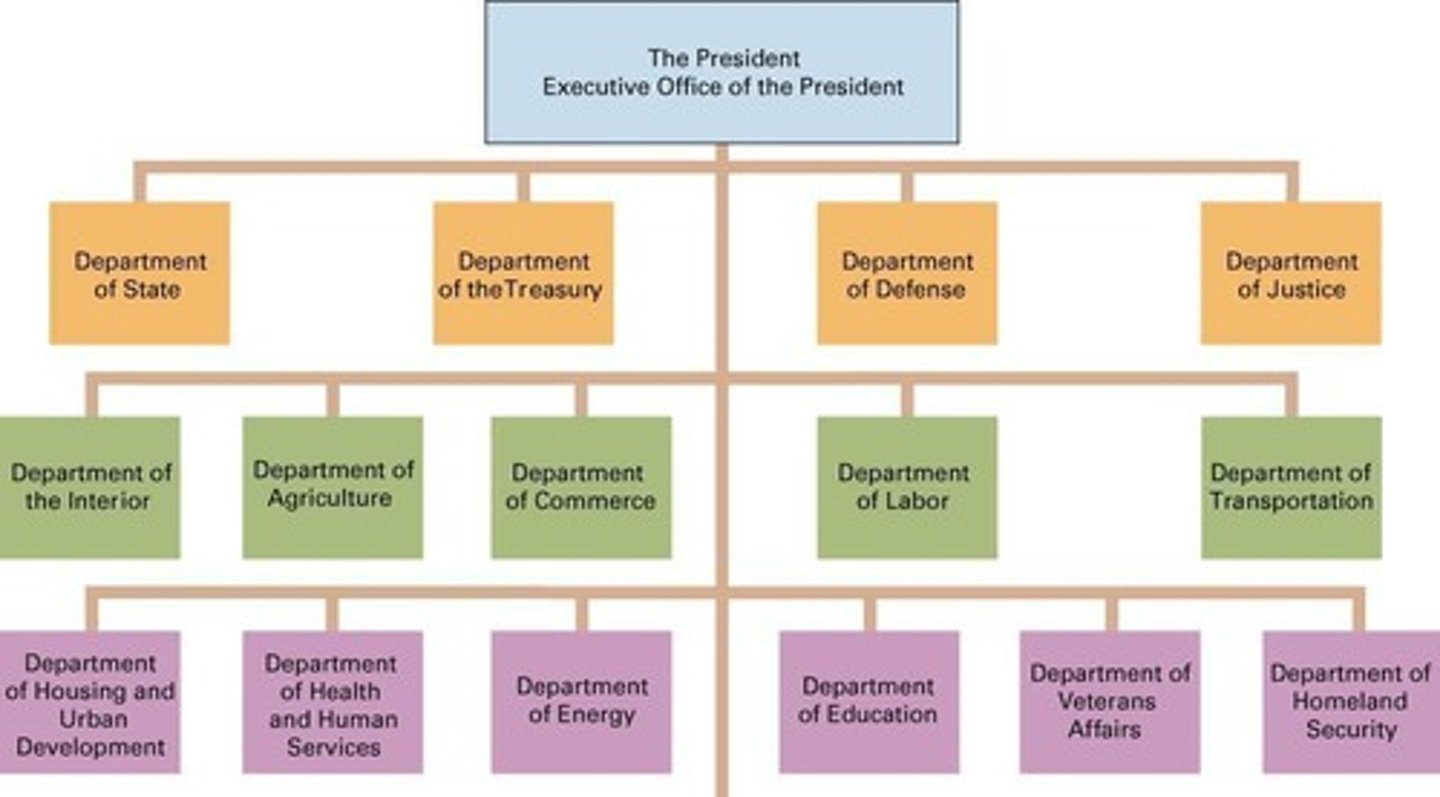
Independent Regulatory Commissions
Enforce rules and resolve disputes, insulated from politics.
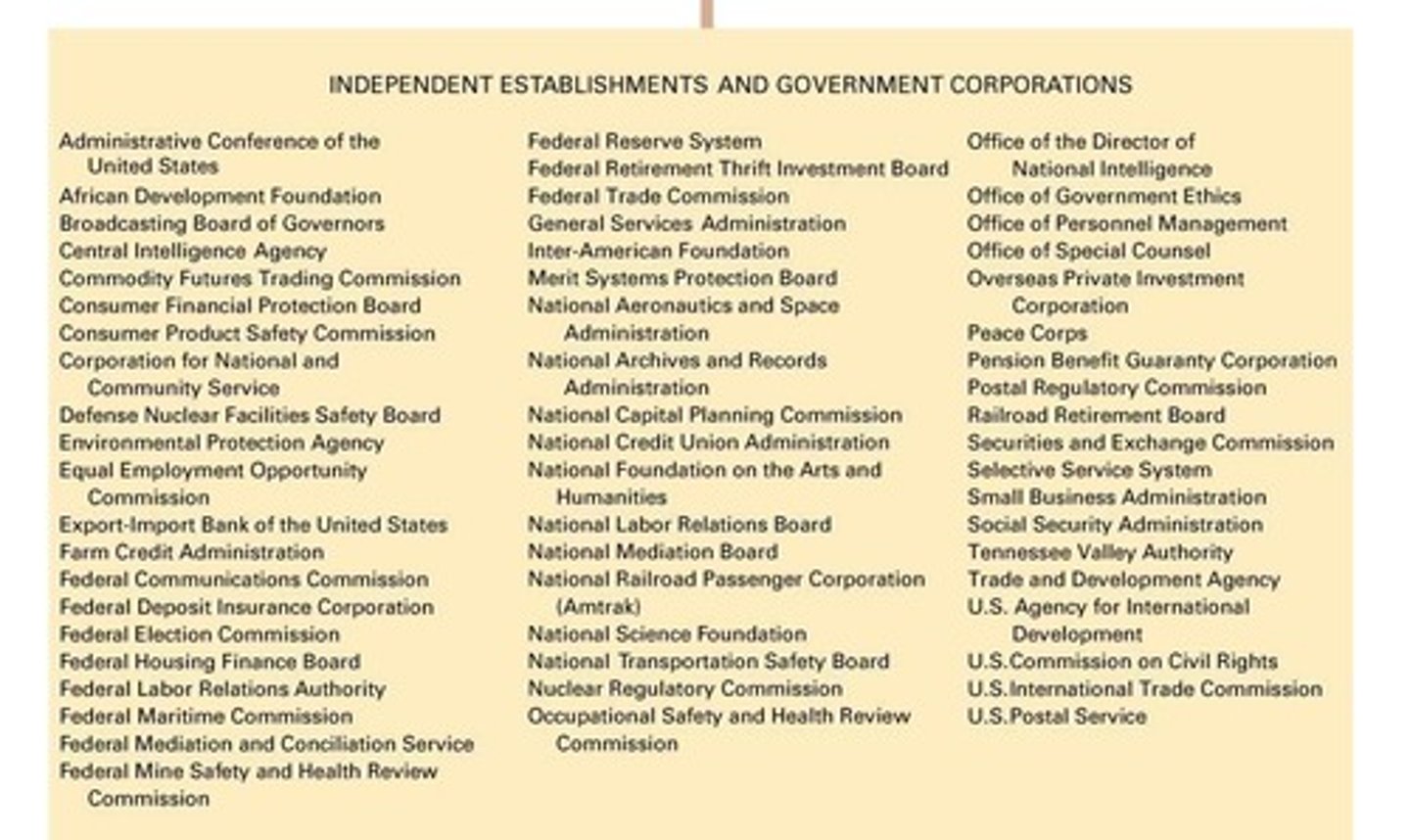
Government Corporations
Provide services at lower costs than private sector.
Tennessee Valley Authority
A government corporation providing electricity and services.
U.S. Postal Service
Government corporation handling mail delivery services.
Amtrak
Government corporation providing intercity passenger rail services.
Independent Executive Agencies
45-50 agencies not categorized as departments or corporations.
Regulatory Capture
When regulatory agencies favor industry over public interest.
Bureaus
Subdivisions within departments managing specific functions.
Fixed Terms
Commissioners serve set terms to ensure stability.
Alphabet Soup
A term for various regulatory commission acronyms.
Implementation
The process of executing government policies and plans.
Voting Rights Act of 1965
Case study of successful bureaucratic implementation.
Privatization
Transfer of public services to private sector management.
Senior Civil Servants
Experienced officials guiding political appointees.
Undersecretaries
Assist secretaries in managing cabinet departments.
Assistant Secretaries
Support undersecretaries in departmental operations.
Dispute Resolution
Process of settling conflicts over regulatory rules.
Consumer Charges
Fees for services provided by government corporations.
Implementation
Process of executing policies through actions.
Policies
Guidelines that govern actions and decisions.
Bureaucracies
Organizations that manage and implement policies.
Program Design
Structure and strategy for policy execution.
Clarity
Clear understanding of policy goals and processes.
Resources
Assets required for effective policy implementation.
Funding
Financial support necessary for program execution.
Personnel
Staff needed to carry out policy tasks.
Authority
Legal power to enforce and implement policies.
Administrative Routine
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for operations.
Dispositions
Attitudes and behaviors of administrators affecting implementation.
Fragmentation
Division of responsibilities leading to implementation challenges.
Voting Rights Act of 1965
Legislation aimed at protecting African American voting rights.
Federal Registrars
Officials responsible for overseeing voter registration.
U.S. Marshals
Federal law enforcement protecting voter registration efforts.
Penalties for Obstruction
Consequences for hindering voter registration processes.
Privatization
Shifting government functions to private sector entities.
Decentralization
Distributing authority away from central government.
Performance Incentives
Motivations for improved efficiency and effectiveness.
Contractors
Private companies hired to perform government tasks.
Regulation History
Evolution of government oversight from minimal to extensive.
Deregulation
Reduction or elimination of government rules.
Motivation for Deregulation
Cost savings and efficiency improvements.
Iron Triangle
Relationship between industry, Congress, and agencies.
Agency Heads
Leaders appointed to manage government agencies.
Executive Orders
Directives from the president with legal force.
Congressional Control
Methods Congress uses to oversee bureaucracy.
Oversight Hearings
Congressional sessions to monitor agency actions.
Bureaucracy
Administrative system managing government functions.
Unelected Policymaking Institutions
Bureaucracy and courts making policy decisions.
Regulated Industry's Interest Groups
Organizations advocating for specific industry interests.
Congressional Committees
Groups in Congress overseeing specific policy areas.
Responsive to Public Interest
Bureaucracy's obligation to serve citizen needs.
Bureaucracy and Democracy
Bureaucracy's role in a democratic government.
Acquisitive Bureaucracy
Bureaucracy seeking to expand its power.
Federal Bureaucracy Growth
Federal bureaucracy has shrunk over 40 years.
Deregulation Consequences
Potential risks of reducing regulatory oversight.
Reorganize Agencies
Changing structure or function of government departments.
Alter Agency Budgets
Changing financial allocations for government agencies.
Paradoxical Relationship
Congress's conflicting roles in bureaucracy management.
Industry Lobbyists
Individuals advocating for industry interests in government.
Scope of Government
Extent of government involvement in society.
Bureaucracy's Role
Addressing social and economic challenges.
Death of an Iron Triangle
Collapse of established regulatory relationships.