BIO PRACTICAL lec2 GIT (coloremitry)
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are the principle plasma proteins in our body
Tinclude Albumin, Globulins, Fibrinogen and Prothrombin.
They are all synthesized in Liver except γ Globulins synthesized in Reticulo Endothelial System (RES).
when does plasma protein levels decreased than normal value ? (below 6 )
Over hydration.
Liver disease (decreased synthesis).
Kidney disease (increased loss in urine as in nephropathy).
Diminished dietary protein intake.
Extensive Burns.
GIT losses (Malabsorption – Protein losing Enteropathy)
Total protein increases in:
dehydration
chronic inflammation (high bacteria = high protein synthesis )
para proteinemia
what is para proteinemia
abnormal Immunoglubuluin or part of it blood or urine
MENTION THE PRINCIPLE OF (colorimetric determination of total plasma proteins )
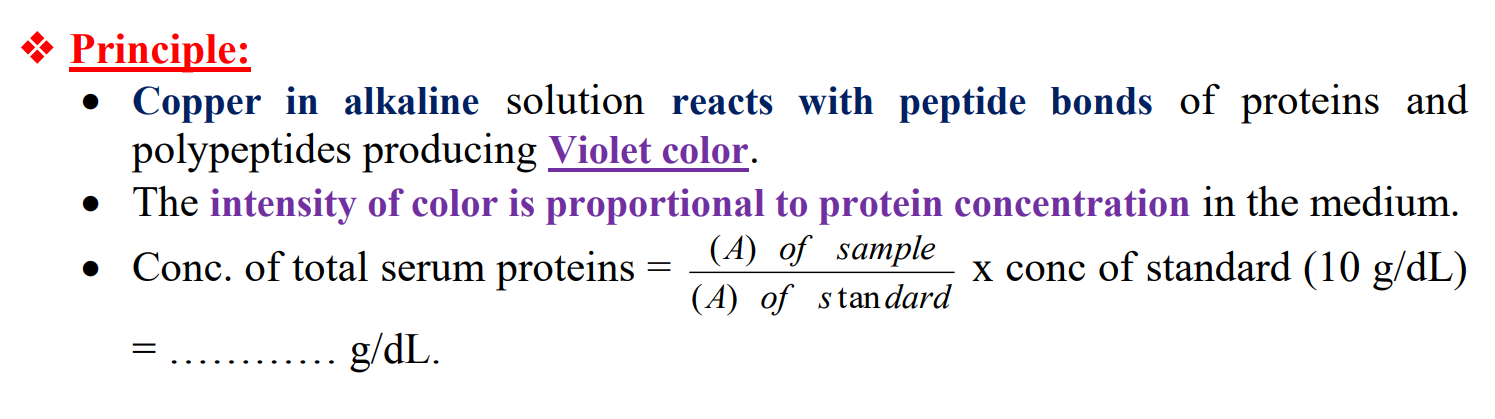
لو عطاك معطيات و قلك جيب تركيز البرروتين شو بتعمل
1) write the formula
2)calculate
3) say if increased or decreased protein level (normal = 6-8g/dl )
4)mention causes of increased or decreased level
what is the reagent used in colorimetry
Biuret reagent (BI=2 , URET=urine)
define newborn screening
panel of laboratory tests performed on newborn to detect genetic diseases
what type of diagnosis does newborn screening focus on
early diagnosis for preventing complications of the genetic diseases
how to perform newborn screening
1) take blood sample (from heel prick)
2) put sample on dry blood spot speicmen (filter paper)
3) it should be taken directly after birth
uses of newborn screening include test for :
1) matabolic problems
2) hormone problems
3) hemoglobin problems
give example of metabolic problem that can be diagnosed by newborn screening
phenylketonuria ( PKU )
give example of hormone problem that can be diagnosed by newborn screening
1) congenital hypothyrodism
2) congenital adrenal hyperplasia
give example of hemoglobin problem that can be diagnosed by newborn screening
1) sickle cell disease
2) thalassemia
define phenylketonuria PKU disease
autosomal recessive genitic disorder
what cause phenylketonuria PKU
decrease in Hepatic Phenylanlanine Hyrdoxylase PAH activity
what happen of HPH decrease
phenylalanine will not be converted to tyrosine —→ accumulation of phenyl alanine which is toxic for brain ,blood and urine
what if the phenyl alanine is acuumulated in brain
it will cause chemical imbalance (mental retardation)
how is the level of Tyrosine is phenylketonuria PKU disease
abnormally low particularly of dietery tyrosine is difficient
so what will happen if tyrosine levels are low
compounds derived from tyrosine will also be low
what are aslan the compounds derived from tyrosine
1) melanin pigment (hair,skin,eye color)
2)Neurotransmitters (domapine & noradrenaline & adrenaline )
give a treatment that can reduce the mental impairment caused by PKU
diet rich in tyrosine and low in phenylalanine
mention the DIAGNOSIS of phenylketonuria
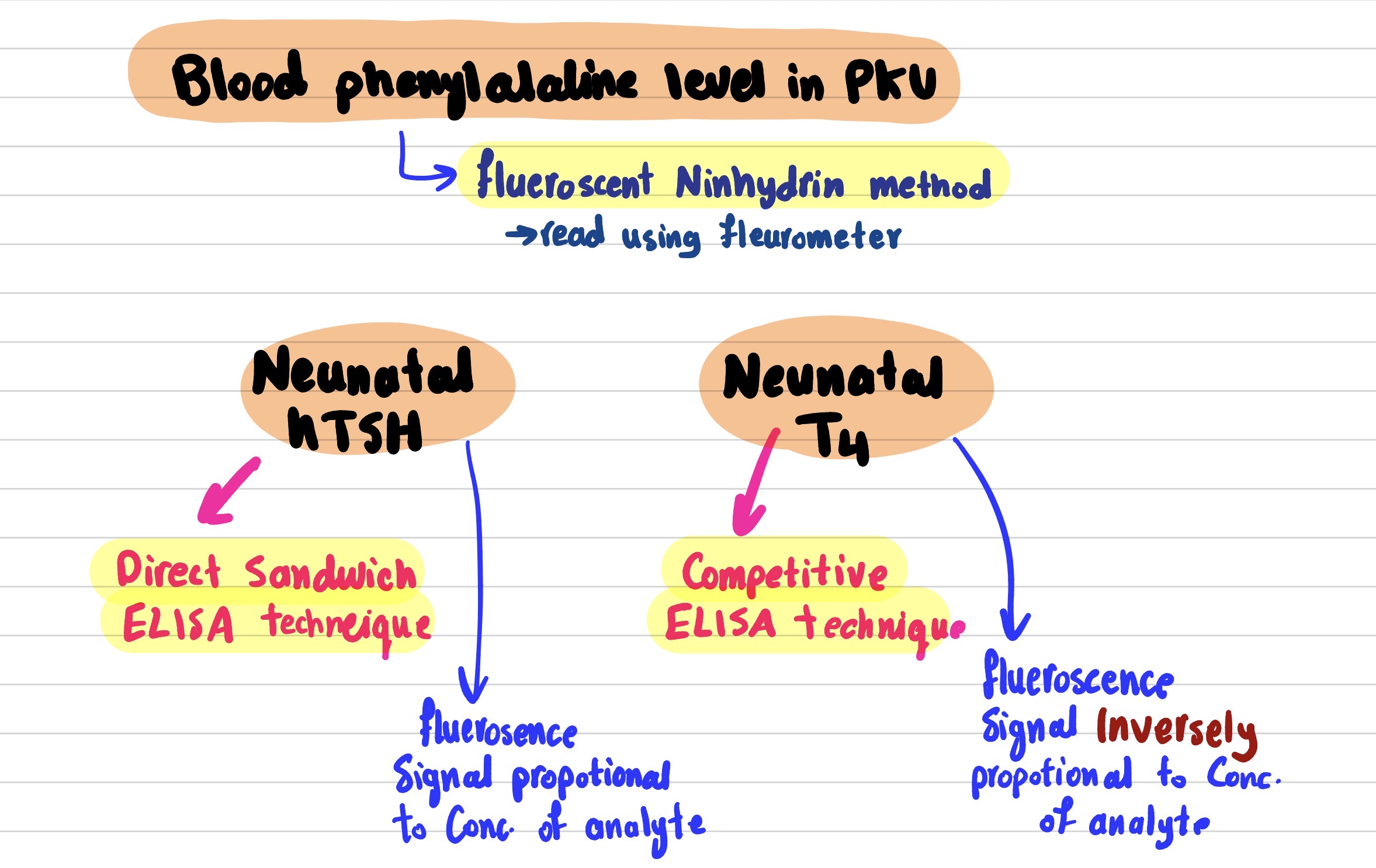
1) newborn screening is done in 1st week of life by measuring the blood phenylalanine twice:
1st time directly after birth
2nd time 48 hours after feeding milk
what method is used to diagnose PKU
fluorescent Ninhydrin method
what device read the fluorescent od ninhydrin
fluorometer
tell me the hormone problems that can be detected by newborn screening
1) congenital hypothyrodism
2) congential adrenal hyperplasia
define congenital hyperthyrdosim
Congenital Hyperthyrodism {CH) , result from a failure of the thyroid glans to produce thyroid hormones is good amounts
treatment of congenital hyperthyrodism
easily treated by daily doses of thyroxin
what are the diagnosis of congenital hyperthyrodsim
1) clinical diagnosis {difficult to establish } disease may continue unrecognized for a long time causing
irreversible brain damage
mental retardation
2) laboratory diagnosis { increased TSH and decreased T4 are clear sign of CH}
mention the method used for screening of Neonatal hTSH
Direct sandwich ELISA teqnique
what fluorescence signal tell us in determination of neonatal hTSH
Flueroscence signal is proprtional to analyte concentration
mention the method used for screening of Neonatal T4
competitive ELISA technique
what fluorescence signal tell us in determination of neonatal T4
Fluoroscence signal is INVERSELY proportional to analyte concentration