SPS 10: Electricity & Magnetism
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Wet Cell
a cell that contains 2 different metal bars placed in liquid
Circuit
a complete path for electricity to flow
Closed Circuit
a path for electricity that does not have breaks in it
Series Circuit
a circuit in which the objects are connected in a single path
Open Circuit
a path for electricity that has a break in it
Magnet
Any material that attracts iron, nickel, and colbalt or materials containing the latter
Magnetic Pole
One of 2 points, such as the ends of a magnet, with opposing magnetic qualities
Magnetic Force
The force of attraction or repulsion generated by moving or spinning electrical charges
Electromagnetism
The interaction between electricity and magnetism
Solenoid
A coil of wire with an electric current in it
Electromagnet
A coil that has a soft iron core that acts acts a magnet when an electric current is in the coil
Electric Generator
A device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy
Electromagnetic Induction
The process of creating a current in a circuit by changing a magnetic field
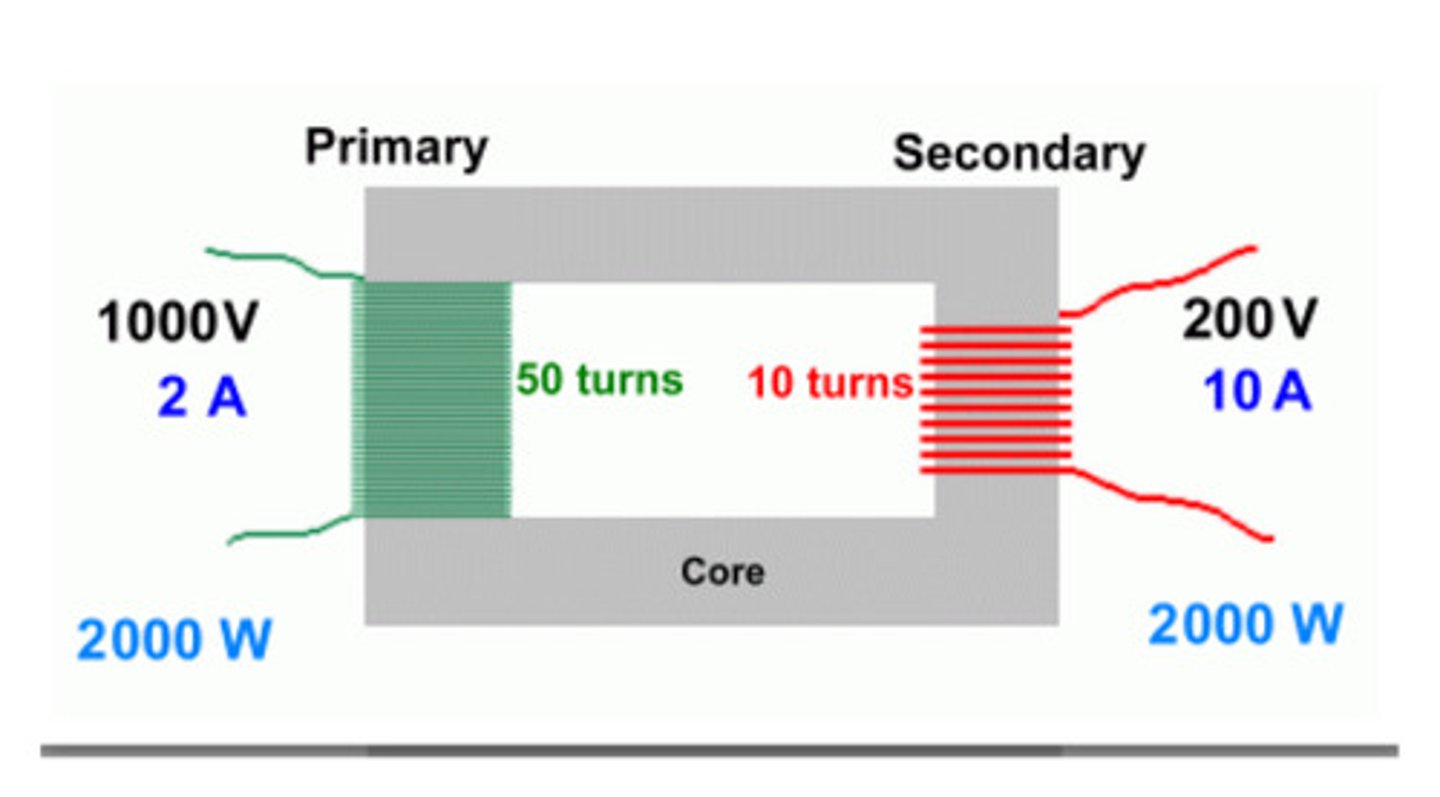
Transformer
A device that increases or decreases the voltage of an alternating current
Repel
To resist attraction
Attract
To draw towards something by physical force
Compass
An instrument for determining direction with a magnetic north
Magnetic Field
Refers to a folce field generated by moving electrical charges
Current
The flow of electrical charges through a conductor; Measured in Amps
Conductor
A material that allows heat and electricity to pass through it.
Voltage
The potential difference that pushes currents through a circuit; Affects the speed of electrons; Measured in Volts
Ohm's Law
Voltage = Current * Resistance
Resistance
"Electrical friction"; The opposition of a material to the flow of electrons through it; Produces heat; Measured in Ohms
What influences resistance?
The material, thickness, length, and temperature of a wire
Direct Current
When electrons flow in the same direction within a wire
Alternating Current
An electric current where the electricity periodically changes direction
Watt
A unit of electrical pressure used to measure how strongly the electrons in a wire are pushed
Load
A device that uses electrical energy to work
Short Circuit
Occurs when charges bypass the loads in a circuit; Sometimes caused by overloading
Static Electricity
The buildup of electrical charges on an object; Leaves the object as electric discharge
Resistor
A device that melts to keep too much electric current from flowing through wires
Parallel Circuit
A circuit where each object is connected to the cell seperately
Fuse
A reusable switch that projects circuits from dangerously high currents
Dry Cell
A battery that has a rod in the center surrounded by a chemical paste
Electrodes
The negative or positive ends of a wet cell
Terminals
The positive and negative ends of the battery
Circuit breakers
A poor conductor or electricity; EX: the filament of a light bulb
Current Electricity
the continuous flow of charge in a complete circuit
Electric Motor
A device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy
Photocell
A device that turns light energy into electrical energy
Electric Discharge
Rapid movement of excess charge from one place to another; EX: Lightning
Cell
A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy
Step-Up Transformer
A transformer that increases voltage and decreases current
Step-Down Transformer
A transformer that decreases voltage and increases current
Potential Difference
The difference in electrical charge between two points in a circuit (expressed in volts)
Galvometer
A device that measures current