topic 8 - exchange and transport in animals
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
describe the need to transport oxygen into organisms
oxygen is transported INTO organisms
by diffusion
for cells to complete aerobic respiration
describe the need to transport carbon dioxide out of organisms
carbon dioxide is transported OUT OF organisms
by diffusion
as it is a waste product of aerobic respiration
describe the need to transport water into organisms
water is transported into organisms
by osmosis
for osmoregulation
for cell and bodily reactions to occur
describe the need to transport dissolved food molecules into organisms
multicellular organism take in food by eating
food is broken down in the digestive system
dissolved food molecules are transferred INTO the bloodstream at the small intestine
by diffusion
dissolved food molecules in the bloodstream can be transported to all the cells in the body
for cell reactions
describe the need to transport mineral ions into organisms
mineral ions are absorbed into the organism
by active transport
for the activation of enzymes and membrane function
describe the need to transport urea out of organisms
urea is a waste product of the liver
it is toxic to the body
it is transported to the kidneys by the circulatory system
it is ultra filtrated by the blood and ends up in the bladder as urine
state which sub-cellular structure exchange of substances occurs in
cell surface membrane
state the 3 types of transport processes
diffusion
osmosis
active transport
which types of organism has a very large surface area : volume ratio
unicellular organisms
what does a large surface area : volume ratio mean
surface of the organism
to the centre
is very small
what does the large surface area : volume ratio of unicellular organisms mean
they do not need to have specialist exchange surfaces
or transport systems
as diffusion, osmosis and active transport through the cell membrane occur
at a sufficient rate
to meet the needs of the organism
what’s the relative size of the surface area : volume ratio of multicellular organisms
small
state the transport systems in animals
blood and circulatory system
state the transport systems in plants
xylem
phloem
state the function of xylem
moves water and mineral ions
from the roots
to shoots and leaves
state the function of phloem
moves sugars and amino acids
to where they are needed
in the plant
state the function of the circulatory system
blood carries
oxygen
glucose
carbon dioxide
water
waste around the body
state why multicellular organisms need exchange surfaces
they have a small surface area : volume ratio
so exchange surfaces are needed
in order to carry out
diffusion, osmosis and active transport
at a sufficient rate
state exchange surfaces in animals
lungs and alveoli - gas exchange
small intestines and villi - absorption of digested food
state exchange surfaces in plants
roots and root hairs - mineral ions and water are absorbed
leaves - gas exchange
state how multicellular organisms maximise the exchange of materials
have large surface areas
very thin barriers to separate 2 regions
state why having a large surface area maximises the exchange of materials
increase the rate of transport
state why having very thin barriers to separate 2 regions maximises the exchange of materials
provides as short a diffusion path as possible
state how multicellular organisms maximise the exchange of materials
have large surface areas
very thin barriers to separate 2 regions
large network of blood vessels throughout the body
ventilates gas exchange surfaces
state why having a large network of blood vessels maximises the exchange of materials
reduces the distance of exchange of materials between cells and the bloodstream
moves substances towards or away from exchange surfaces to maintain concentration gradients
state why having ventilated gas exchange surfaces maximises the exchange of materials
maintains concentration gradients
explain how the lungs are adapted for gas exchange by diffusion
the lungs are the gas exchange surface in the humans
the lungs contain many rounded alveolar sacs
which act to increase the surface area : volume ratio of the lungs
to increase the rate of gas exchange
explain how the alveoli are adapted for gas exchange by diffusion
thin single layers of cells
to minimise diffusion distance
ventilated
maintains high levels of oxygen and low levels of carbon dioxide in the alveolar air space
good blood supply
ensures constant supply of blood high in carbon dioxide and low in oxygen
layer of moisture on alveolar surface
helps diffusion as it causes gases to dissolve
explain how surface area affects the rate of diffusion
a bigger cell or structure has a smaller surface area : volume ratio
which slows down the rate at which substances can move across its surface
thus increasing surface area : volume ratio increases the rate of diffusion
state which cells are adapted to increase surface area
root hair cells in plants
cells lining the ileum in animals
explain how concentration gradient affects the rate of diffusion
larger concentration gradient on either side of the membrane
causes faster movement across it
this is because on the side with the higher concentration
more random collisions will occur against the membrane
explain how diffusion distance affects the rate of diffusion
smaller diffusion distance causes faster transport to occur
state which structures are adapted to have smaller diffusion distance
walls of
blood capillaries and alveoli
are only one cell thick
to ensure faster rate of diffusion
explain how temperature affects the rate of diffusion
higher temperature means the molecules move faster
as they have gained more kinetic energy
this results in more collision of molecules against the cell membrane
causing a faster rate of movement/spreading across them
state Fick’s law equation
rate of diffusion ∝ (surface area x concentration difference) / thickness of membrane
explain how the structure of erythrocytes are related to its function
STRUCTURE
biconcave discs
contain no nucleus
contain lots of haemoglobin protein
FUNCTION
erythrocytes are specialised cells that carry oxygen to respiring cells
the haemoglobin binds to oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin
having no nucleus allows more space for more haemoglobin protein
the biconcave disc shape gives erythrocytes a large surface area : volume ratio - maximises diffusion of oxygen in and out
state what erythrocytes are
red blood cells
explain how the structure of lymphocytes are related to their function
STRUCTURE
large cells
contain a big nucleus
highly specific structures
clear, non-granular cytoplasm
FUNCTION
lymphocytes are part of the body’s immune system to defend against pathogenic microorganisms
they produce antibodies to destroy pathogenic cells
they produce antitoxins to neutralise toxins released by pathogens
clear, non-granular cytoplasm allows for lymphocytes to be easily identified using a microscope
explain how the structure of phagocytes are related to their function
STRUCTURE
large cells
contain a big, multi-lobed nucleus
highly specific structures
granular cytoplasm
FUNCTION
carry out phagocytosis by engulfing and digesting pathogens
phagocytes have sensitive cell surface membranes that detect chemicals produced by pathogenic cells
release digestive enzymes when encountering a pathogen
their multi-lobed nucleus and granular cytoplasm makes them easy to distinguish using a microscope
state what lymphocytes and phagocytes are
white blood cells
explain how the structure of plasma is related to its function
STRUCTURE
straw coloured liquid
FUNCTION
suspends the other components of blood within it
transports carbon dioxide
carbon dioxide is dissolved in plasma to form hydrogen carbonate ions
these ions are transported from respiring cells to the lungs
transports digested food and mineral ions
dissolved food molecules absorbed from the small intestine are delivered to the requiring cells around the body by plasma
transports urea
urea is the waste substance produced in the breakdown of proteins into amino acids by the liver
urea is dissolved in the plasma and transported to the kidneys where it exits the body through the bladder
transports hormones
hormones are released into the plasma from the endocrine organs
they’re delivered to target tissues/organs in the body
transports heat energy
heat energy is synthesised in respiration
where it is transferred in plasma to cooler parts of the body or skin
where the heat can be dissipated
explain how the structure of platelets is related to its function
STRUCTURE
fragments of cells
FUNCTION
when the skin is broken, platelets arrive to stop the bleeding
a series of reaction occur within the plasma
platelets release chemicals that cause soluble fibrinogen proteins to convert into insoluble fibrin
which forms an insoluble mesh across the wound
this traps red blood cells at the wound site, forming a clot
this clot eventually dries and develops into a scab which protects the wound from bacteria enetering
explain why blood clotting is important
prevents continued/significant blood loss from wounds
scab formation prevents entry of pathogenic microorganisms
remains in place to allow new skin to grow unharmed
state the 3 types of blood vessel
arteries
arterioles - small arteries that branch into venules
veins
venules - small veins
capillaries
explain how the structure of arteries are adapted to their function
STRUCTURE
thick, muscular walls containing elastic fibres
narrow lumen
FUNCTION
carries blood at high pressure and rapid speed away from the heart
thick, muscular walls allow the artery to withstand and maintain the high blood pressure as it recoils after the blood has passed through
narrow lumen helps to maintain high blood pressure
carries oxygenated blood (except the pulmonary artery)
explain how the structure of veins are adapted to their function
STRUCTURE
thin walls
large lumen
contain valve
FUNCTION
carries blood at low pressure towards the heart
large lumen reduces resistance to blood flow under low pressure
valves prevent backflow of blood as it is under low pressure
carries deoxygenated blood (except the pulmonary vein)
explain how the structure of capillaries are adapted to their function
STRUCTURE
thin walls - one cell thick
‘leaky’ walls
FUNCTION
carries blood at low pressure within tissues
capillaries walls are thin and ‘leaky’ to allow substances to easily diffuse in and out of them
‘leaky’ walls allows blood plasma to leak out and form tissue fluid surrounding cells
carries both oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
carries blood at low speed
explain how the structure of heart is related to its function
STRUCTURE
double pump
2 ventricles
septum
coronary arteries
cardiac muscle tissue
valves
FUNCTION
oxygenated blood enters from the left side of the heart and is pumped to the rest of the body
left ventricle has a thicker muscle wall than the right ventricle as it pumps blood at high pressure around the entire body
deoxygenated blood enters from the right side of the heart and is pumped to the lungs
right ventricle has a thinner muscle wall than the left ventricle as it pumps blood at low pressure to the lungs
septum separates the two sides of the heart to prevent the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
coronary arteries supply the cardiac muscle tissues of the heart with oxygenated blood
this happens as the heart is a muscle that needs a constant supply of oxygen and glucose for aerobic respiration to allow for continued muscle contraction
valves prevent blood flowing backwards
describe the pathway of blood through the heart
deoxygenated blood coming from the body flows through the vena cava into the right atrium
the atrium contracts, forcing the blood through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle
the right ventricle contracts to push blood through the semilunar valve into the pulmonary artery
blood travels to the lungs and moves through capillaries past the alveoli where gas exchange takes place
low blood pressure on the right side of the heart prevents damage to the pulmonary capillaries
oxygenated blood returns to the heart via the pulmonary vein to the left atrium
the atrium contracts and forces the blood through bicuspid valve into the left ventricle
the left ventricle contracts and blood is forced through the semilunar value and out through the aorta
thicker muscles walls of the left ventricle produce a high enough blood pressure to allow the blood to travel through the whole body
describe the circulatory system
circulatory system consists of closed network of blood vessels connected to the heart
oxygenated blood is carried away from the heart and towards organs in arteries
arteries narrow to arterioles and then further to capillaries as they pass through organs
in the organs, the respiring cells use up the oxygen bound to haemoglobin on red blood cells
the capillaries then widen to venules then further to veins as they move away from organs
veins carry deoxygenated blood back towards the heart
state the function of lymphatic vessels
network of vessels
that collects all excessive tissue fluid
that leaks out the ‘leaky’ capillary walls
and delivers this fluid back to the circulatory system
state the blood vessels that direct blood TOWARDS the HEART
vena cava
pulmonary vein
state the blood vessels that direct blood TOWARDS the LUNGS
pulmonary artery
state the blood vessels that direct blood TOWARDS the KIDNEY
renal artery
state the blood vessels that direct blood AWAY FROM the HEART
aorta
pulmonary artery
state the blood vessels that direct blood AWAY FROM the LUNGS
pulmonary vein
state the blood vessels that direct blood AWAY FROM the KIDNEYS
renal vein
describe cellular respiration
exothermic reaction
that occurs continuously
in living cells
to release energy
for metabolic processes
describe the process of aerobic respiration
aerobic respiration requires oxygen
it is the complete breakdown of glucose
to release a relatively large amount of energy
for use in cell processes and reactions
carbon dioxide and water are produced as waste products
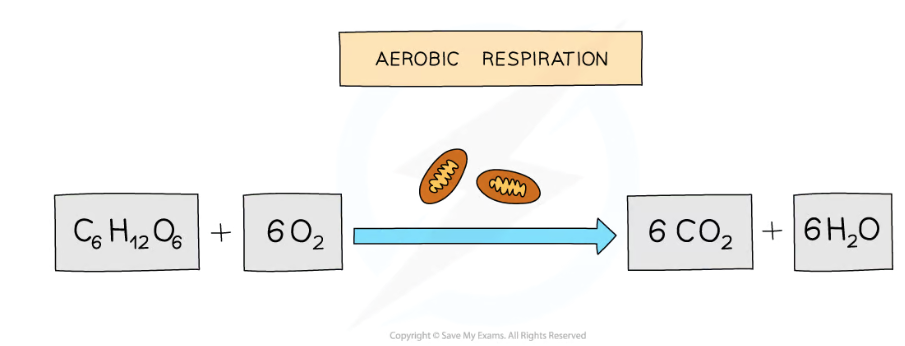
state aerobic respiration definition
chemical reaction in cells
that uses oxygen
to break down nutrient molecules
to release energy
describe the process of anaerobic respiration
anaerobic respiration doesn’t require oxygen
it involves the incomplete breakdown of glucose
so it releases a relatively small amount of energy
to use in cell processes
different breakdown products are formed based on the organism
state anaerobic respiration definition
chemical reaction in cells
that breaks down
nutrient molecules
to release energy
without oxygen
describe anaerobic respiration in animals
anaerobic respiration takes place in muscle cells during vigorous exercise
during vigorous exercise, animal muscles have a higher demand for energy
when oxygen runs out for aerobic respiration, glucose is broken down without it
producing lactic acid instead
glucose has not been fully broken down meaning there is still energy stored within the bonds of lactic acid molecules
anaerobic respiration releases less energy than aerobic respiration
state the word and symbol equation for anaerobic respiration in animals

describe lactic acid and oxygen debt
lactic acid builds up in muscles cells and lowers the pH of muscle tissues
acidic conditions can denature the enzymes in cells
lactic acid will eventually be metabolised using oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products
the amount of energy required to metabolise the lactic acid is ‘oxygen debt’
the process of metabolising the lactic acid is ‘repaying the oxygen debt’
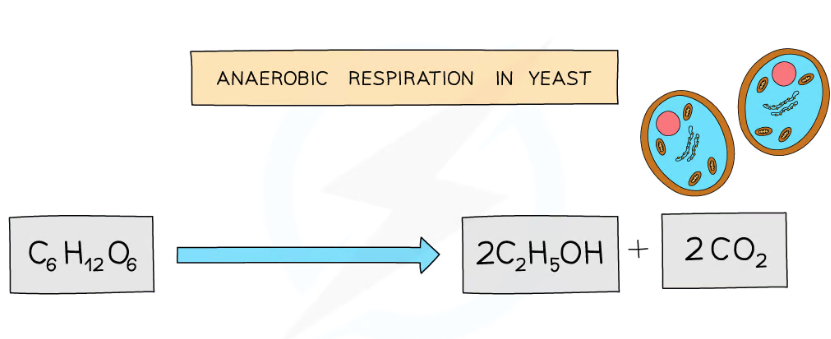
describe anaerobic respiration in plants and fungi
plants and yeast can respire without oxygen
breaking down glucose in the the absence of oxygen
to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide
anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is fermentation
state the symbol equation for anaerobic respiration in fungi
describe the method to investigate the production of carbon dioxide in respiration
measure out 10cm³ of hydrogen carbonate indicator into 3 boiling tubes
put a layer of cotton wool into each boiling tube
place 10 germinating seeds in tube A
place 10 dead seeds in tube B
place 10 glass beads in tube C
seal each tube with a rubber bung
after 3 hours, observe the colour of the indicator
tube A should turn yellow as the seeds are respiring and producing carbon dioxide
tube B should remain orange as the dead seeds produce no carbon dioxide
tube C should remain orange as there is no living material in the tube
state the results of hydrogen carbonate indicator
low carbon dioxide levels - purple
atmospheric carbon dioxide levels - orange
high carbon dioxide levels - yellow
describe the method to investigate the production of heat in respiration
set up 2 flasks, one containing dead seeds, one containing germinating seeds
ensure the cotton wool is plugging the top of each flask
hold the thermometer in place with the cotton wool
invert the flasks
record the initial temperature of both flasks
after 4 days, record the final temperature
the thermometer in the flask with the germinating seeds should show an increase in temperature
because the seeds in this flask are respiring and producing heat energy in the process
showing that respiration is an exothermic reaction
the flask with the dead seeds should remain at room temperature
because the seeds are not respiring as they were dead, meaning temperature will remain the same as the exothermic reaction isn’t occurring
state the equation for cardiac output
cardiac output = stroke volume x heart rate
state the width of a whole capillary
only 5-10 micrometres
state what a constant flow of blood in the capillary does to concentration gradients between capillaries and cells
maintains a steep concentration gradient
stroke volume definition
volume of blood pushed out of a ventricle into an artery
cardiac output definition
volume of blood pushed into the aorta per minute
heart rate definition
number of beats per minute
state what factors cause cardiac output to change
exercise
fight or flight
anticipating exercise