Chapter 17 - Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and the Ideal Gas Law
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Chapter 16 Recap
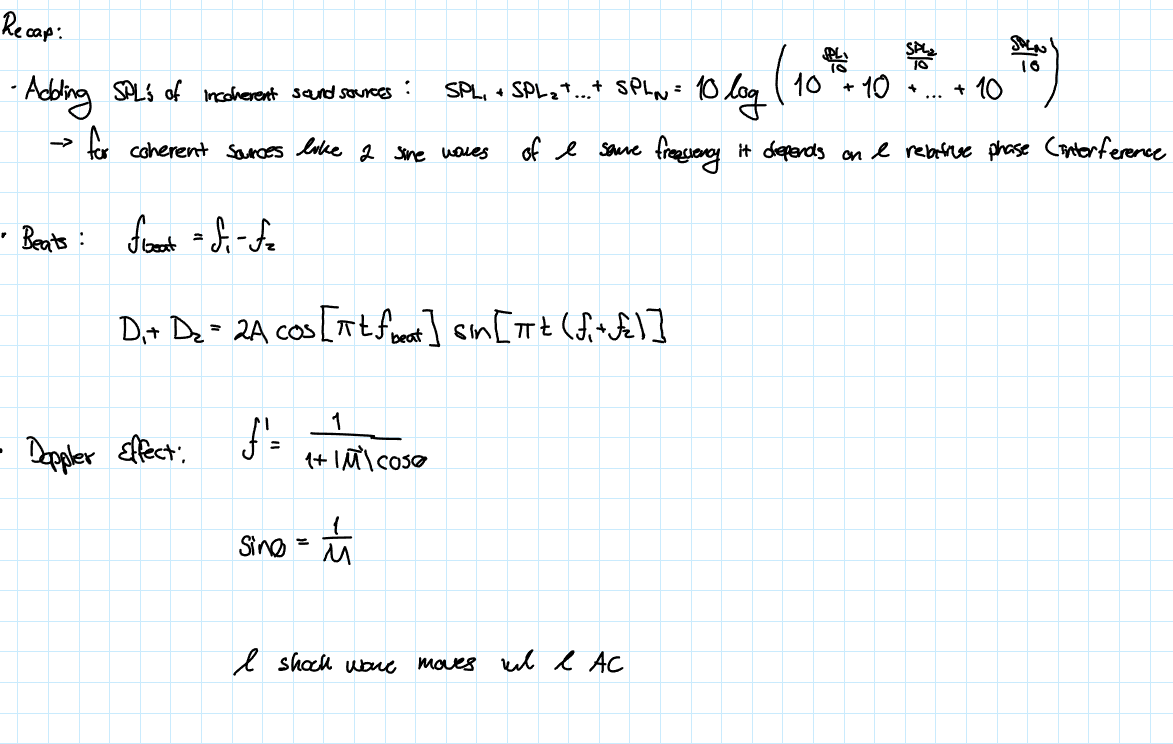
Atomic Theory of Matter
Atoms consist of a nucleus where there are protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons.
Atomic and molecular masses are measured with the unified mass unit [u]. This unit is defined so that the carbon-12 atom has a mass of exactly 12.000 u.
1u = 1.6605E-27 [kg]
The nuclear number of an atom is the amount of protons and neutrons in the atom.
Brownian Motion
As evidence for the atomic theory, Brownian motion is the jittery motion of tiny particles (e.g. pollen grains) suspended in water or any fluids; These are the results of collisions with individual water molecules.
Atomic Theory of Matter
On a microscopic scale, the arrangements of molecules in solids, liquids, and gasses are different and depend on their attractive forces and atom motion
Temperature
Temperature reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating atoms that make up a substance. Many properties of matter change with temperature; ex; electric resistance, radiated color, etc..
Most materials expand when they are heated.
Ex; Hot wire anemometry: For wind-tunnel testing we use the fact that electric resistance changes with temperature to preform hot-wire anemometry (HWA) to measure flow velocity. A current is sent through a thin wire causing it to get hot. As the fluids flow around it, it cools it down, decreasing its electric resistance. The higher the flow velocity, the higher the cooling. Therefore, with some considerations and calculations we can find the flow velocity evolution very rapidly over time to calculate parameters like turbulence intensity.
Thermometers: In order to measure temperature we use advantages of some property of matter that changes with temperature that can be measured.
Temperature Scales
These are normally based on the freezing and boiling point of water
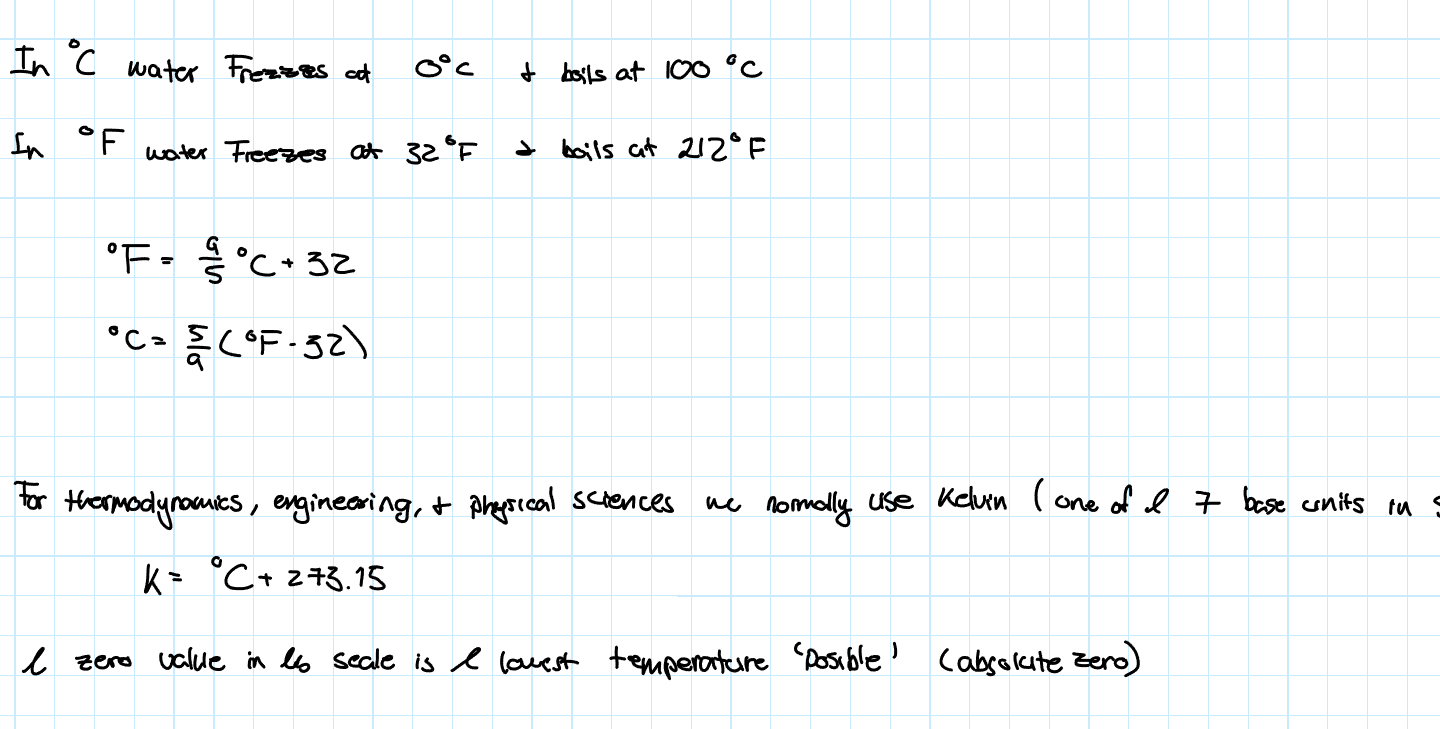
Thermal Equilibrium and the Zerowth Law of Thermodynamics
2 Objects placed in thermal contact will eventually become the same temperature. We say they are in thermal equilibrium when there is NO NET ENERGY FLOW (heat) between them, and the temperature remains the same.
The Zerowth Law of Thermodynamics States that; Two systems A and B, in thermal equilibrium with a third system C are also in thermal equilibrium with each other. Essentially, if some part of the system is in thermal equilibrium then the whole system is in thermal equilibrium?
Thermal Expansion
Most substances expands when heated because their molecules are a bit further apart on average and contracts when cooled. For a 1D approximation, we consider linear expansion
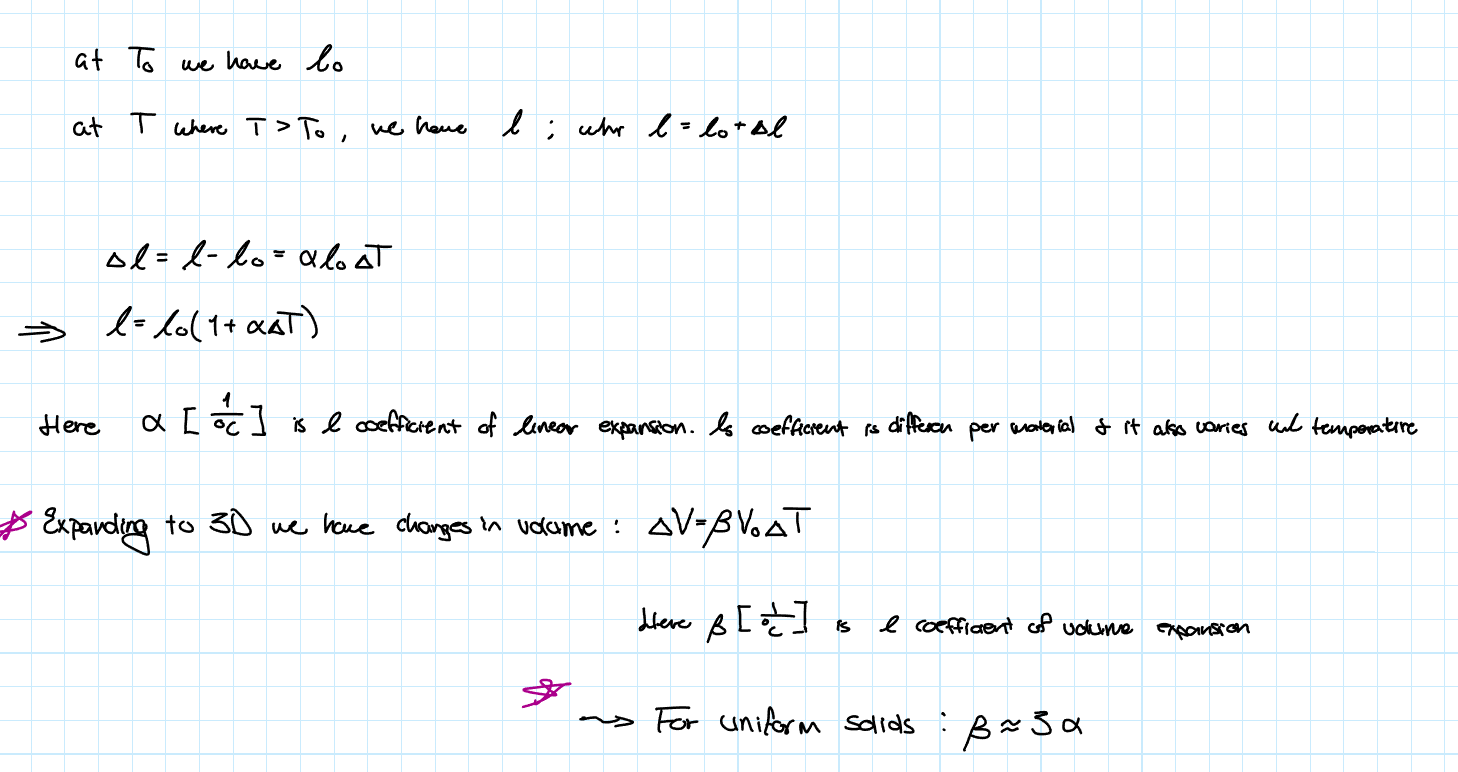
Water and Thermal Expansion
Unlike most substance, water actually expands when it freezes. In fact its minimum volume (max density) occurs at around 4 def C. This fact is crucial for the survival of aquatic life, since water cooled down below 4degC and ice is less dense and will then float. This is due to the hydrogen bonds between water molecules and its restructuring into a larger lattice when it becomes solid (freezing)
Thermal Stresses
If a material is fixed and the temperature changes it will experience thermal stresses

The Gas Laws and Absolute Temperature
A relationship between the volume, pressure, temperature, and mass of a gas is called an equation of state. For now we consider gasses that are not too dense, not too close to the liquefaction point, and with pressure below 1 atm
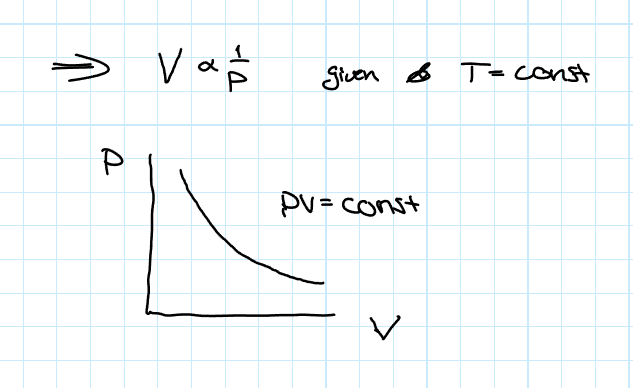
Boyle-Mariotte’s Law
This law states that the volume of a given amount of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure as long as the temperature is constant
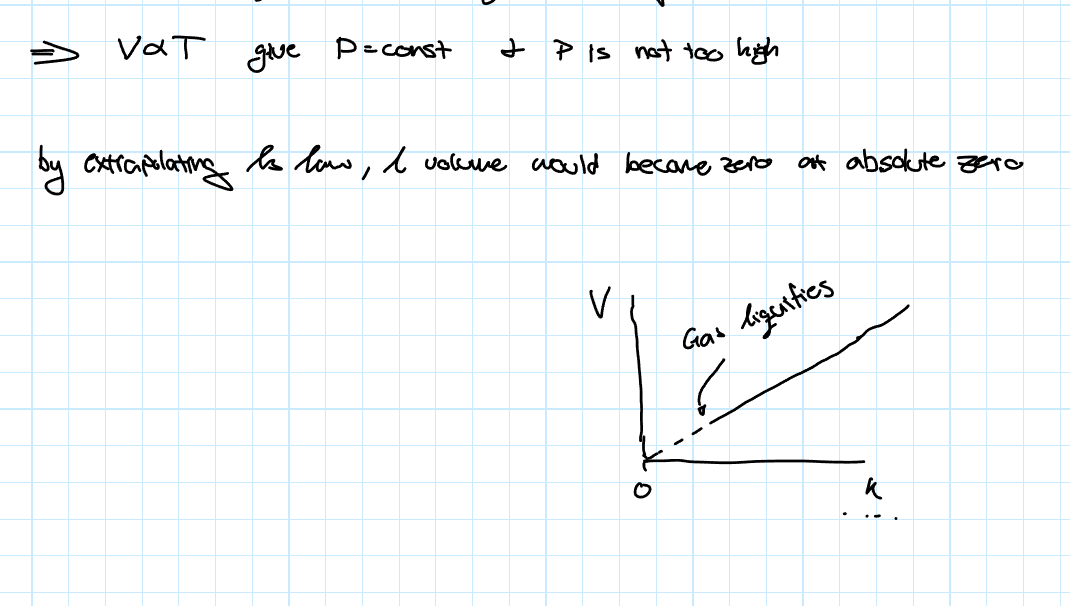
Charles’ Law
This law states that the volume of a given amount of gas is linearly proportional to the temperature as long as the pressure is constant and not too high
Gay-Lussac’s Law
This law sates that the volume of a given amount of gas is linearly proportional to the temperature as long as the volume is constant and not too high
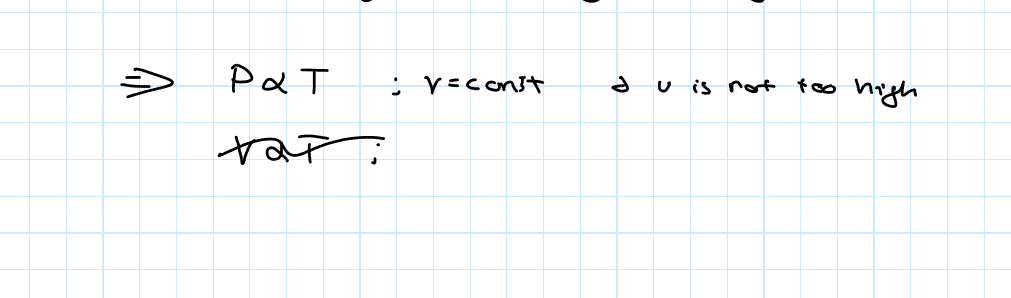
Ideal Gas Law
By combining all the other laws…
If Pressure and temperature are constant, then the volume is proportional to the mass of the gas

Moles
When discussing mass at a molecular lever we use the mole [mol]
1 mol is defined as the number of atoms of substance that is numerically equal to the atomic/molecular mass of a substance
![<p>When discussing mass at a molecular lever we use the mole [mol]</p><p>1 mol is defined as the number of atoms of substance that is numerically equal to the atomic/molecular mass of a substance </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c9029005-7b6d-434a-a35d-b5af0fd7194f.png)
Number of Moles in a Certain Mass of a Substence
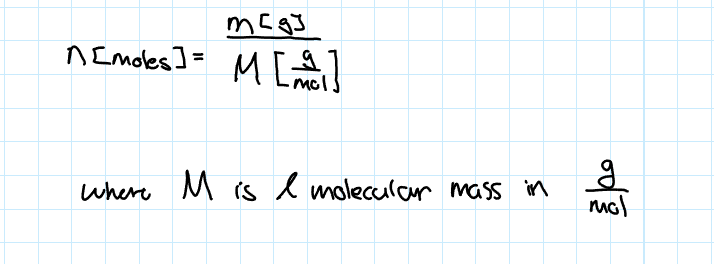
Avogardo’s Number
This number is the amount of atoms in 1 mol
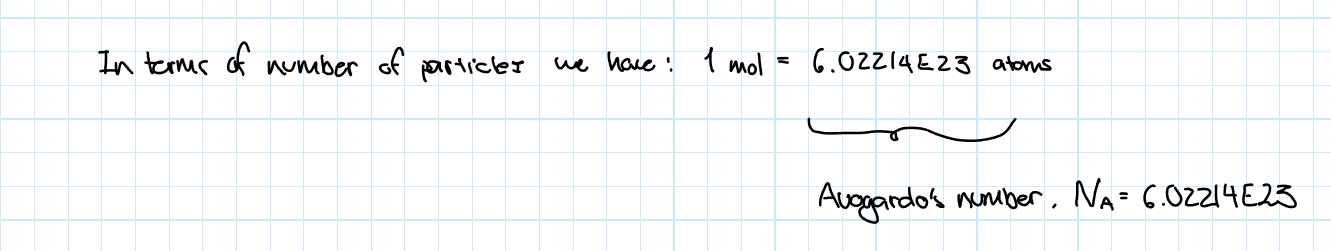
Ideal Gas Law Overview

Another way to Write the Ideal Gas Law
