S1.1 Chemistry
1/19
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Define Elements
substances made from one kind of atom
Define Compounds
made from two or more elements chemically combined
Define Mixtures
elements and compounds are interspersed with each other, but are not chemically combined
How do compounds form from elements?
Elements take part in chemical reactions in which new substances are made in processes that most often involve an energy change
In these reactions, atoms combine together in fixed ratios that will give them full outer shells of electrons, producing compounds
The properties of compounds can be quite different from the elements that form them
Outline the differences between mixtures and compounds
In a mixture, elements and compounds are interspersed with each other, but are not chemically combined
This means the components of a mixture retain the same characteristic properties as when they are in their pure form
In compounds, atoms of different elements are chemically combined together
This means the compounds have different properties as when they are pure
Define homogenus mixtures
mixture has uniform composition and properties throughout
Define heterogenus mixtures
mixture has non-uniform composition, so its properties are not the same throughout
How do you separate a mixture of solids?
For a difference in solubility, a suitable solvent must be chosen to ensure the desired substance only dissolves in it and not other substances or impurities,
Then another suitable separation method must be used
Define and describe the process of filtration
Used to separate an undissolved solid from a mixture of the solid and a liquid / solution
Filter paper is placed in a filter funnel above another beaker
The mixture of insoluble solid and liquid is poured into the filter funnel
Filter paper will only allow small liquid particles to pass through in the filtrate
Solid particles are too large to pass through the filter paper so will stay behind as a residue
Define and describe the process of crystallization
Used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution, when the solid is more soluble in hot solvent than in cold
The solution is heated, allowing the solvent to evaporate and leaving a saturated solution behind
You can test if the solution is saturated by dipping a clean, dry, cold glass rod into the solution
If the solution is saturated, crystals will form on the glass rod when it is removed and allowed to cool
The saturated solution is allowed to cool slowly and solids will come out of the solution as the solubility decreases, and crystals will grow
Crystals are collected by filtering the solution
They are then washed with distilled water to remove any impurities and then allowed to dry
Define and describe the process of recrystallization
Recrystallisation is used to purify impure solids
The principle is that a hot solvent is used to dissolve both the organic solid and the impurities and then as the solution cools the solid crystallises out and leaves behind the impurities in the solution
The key is using the minimum amount of solvent to dissolve the solid and avoid loss of the product
If any solid impurities remain in the solution, a hot filtration can be carried out
Once the solution has cooled down to room temperature and crystallised then the product crystals can be recovered by filtration
Define and describe the process of simple distillation
Used to separate a liquid and soluble solid from a solution
The solution is heated and pure water evaporates producing a vapour which rises through the neck of the round-bottomed flask
The vapour passes through the condenser, where it cools and condenses, turning into pure water which is collected in a beaker
After all the water is evaporated from the solution, only the solid solute will be left behind
Define and describe the process of fractional distillation
Used to separate two or more liquids that are miscible with one another (e.g. ethanol and water from a mixture of the two)
The solution is heated to the temperature of the substance with the lowest boiling point
This substance will rise and evaporate first, and vapours will pass through a condenser, where they cool and condense, turning into a liquid that will be collected in a beaker
All of the substance is evaporated and collected, leaving behind the other components(s) of the mixture
For water and ethanol: ethanol has a boiling point of 78 ºC and water of 100 ºC. The mixture is heated until it reaches 78 ºC, at which point the ethanol boils and distills out of the mixture and condenses into the beaker
When the temperature starts to increase to 100 ºC heating should be stopped. Water and ethanol are now separated
Define and describe the process of paper chromatography
This technique is used to separate substances that have different solubilities in a given solvent (e.g. different coloured inks that have been mixed to make black ink)
A pencil line is drawn on chromatography paper and spots of the sample are placed on it. Pencil is used for this as ink would run into the chromatogram along with the samples
The paper is then lowered into the solvent container, making sure that the pencil line sits above the level of the solvent so the samples don´t wash into the solvent container
The solvent travels up the paper by capillary action, taking some of the coloured substances with it
This will show the different components of the ink / dye
Define Solids and their properties
Solids have a fixed volume and shape and they have a high density
The atoms vibrate in position but can’t change location
The particles are packed very closely together in a fixed and regular pattern
Define Liquids and their properties
Liquids also have a fixed volume but adopt the shape of the container
They are generally less dense than solids (an exception is water), but much denser than gases
The particles move and slide past each other which is why liquids adopt the shape of the container and also why they are able to flow freely
Define Gasses and their properties
Gases do not have a fixed volume, and, like liquids, take up the shape of the container, but they fill the whole container
Gases have a very low density
Since there is a lot of space between the particles, gases can be compressed into a much smaller volume
The particles are far apart and move randomly and quickly (around 500 m/s) in all directions
They collide with each other and with the sides of the container (this is how pressure is created inside a can of gas)
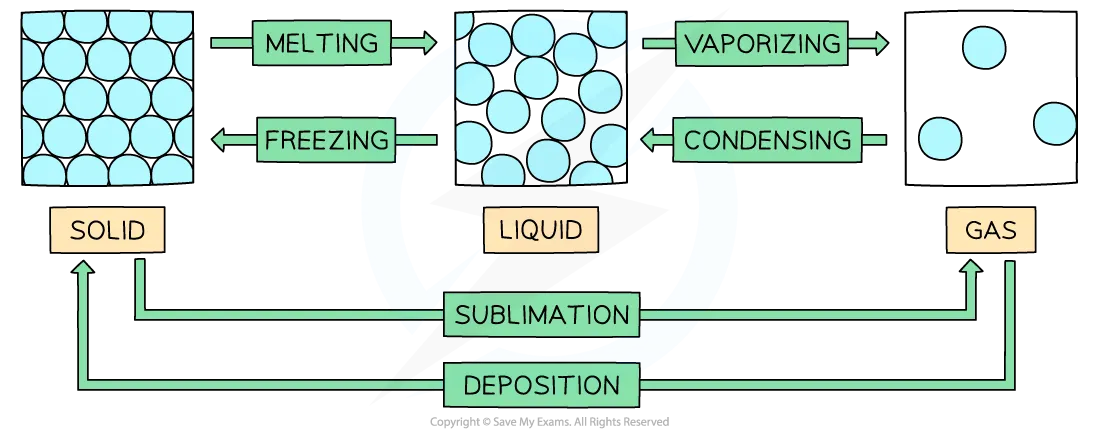
Define changes of state and how they occur
Changes of state are physical changes that are reversible
These changes do not change the chemical properties or chemical makeup of the substances involved
Vaporisation includes evaporation and boiling
Evaporation involves the change of liquid to gas, but unlike boiling, evaporation occurs only at the surface and takes place at temperatures below the boiling point
Boiling occurs at a specific temperature and takes place when the vapour pressure reaches the external atmospheric pressure
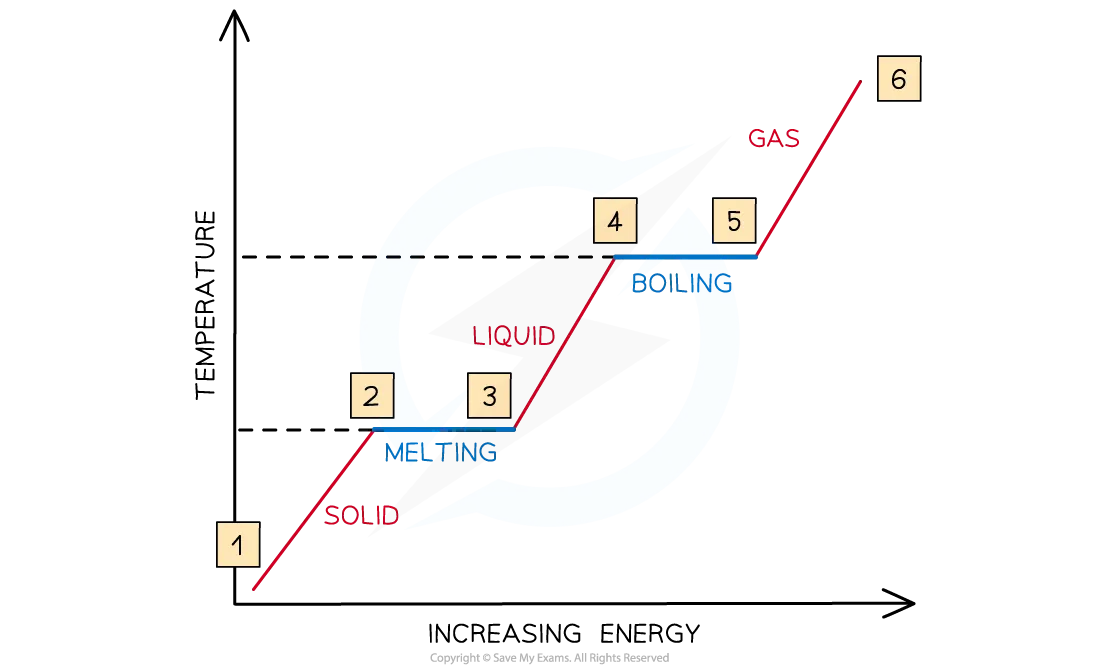
Describe the relationship between temperature and kinetic energy
Between 1 & 2, the particles are vibrating and gaining kinetic energy and the temperature rises
Between 2 & 3, all the energy goes into breaking bonds – there is no increase in kinetic energy or temperature
Between 3 & 4, the particles are moving around and gaining in kinetic energy
Between 4 & 5, the substance is boiling, so bonds are breaking and there is no increase in kinetic energy or temperature
From 5 & 6, the particles are moving around rapidly and increasing in kinetic energy
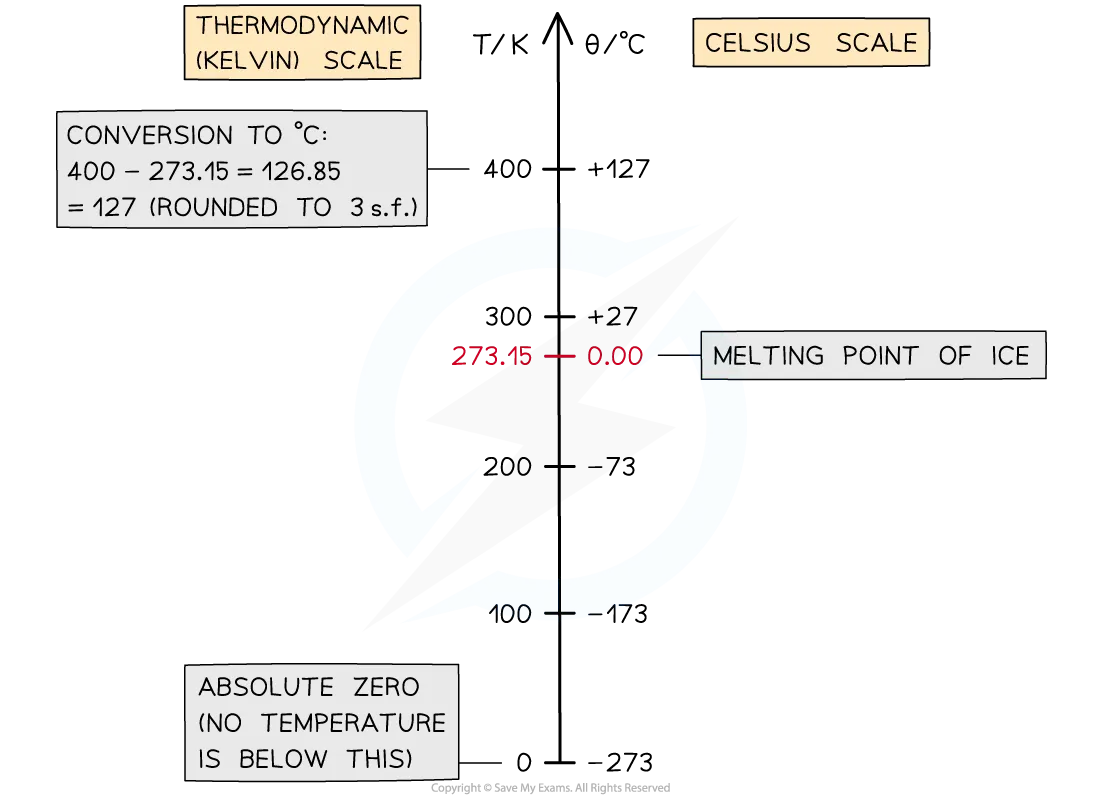
How do you convert between Kelvin and Clesius?
Temperature can be converted from Celsius to kelvin by adding 273:
Temperature in K = Temperature in °C + 273
Temperature in °C = Temperature in K - 273