PSYC 100 USC Midterm 1
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
Psychological science
the study, through research, of mind, brain, and behavior
Major baises
1. ignoring evidence (confirmation bias)
2. failing to accurately judge source credibility
3. misunderstanding or not using statistics
4. seeing relationships that do not exist
5. using relative comparisons
6. accepting after-the-fact explanations (hindsight bias)
7. taking mental shortcuts (heuristics)
8. failing to see our own inadequacies (self-servicing)
Dualism
the mind and body are separate but intertwined
by René Descartes
Introspection
the systematic examination of subjective mental experiences
people inspect and report on the content of their thoughts
-Wilhelm Wundt, Titchener
Structuralism
1st formal school of psych
the concept that conscious experiences can be broken down into basic components
by Wilhelm Wundt
Q: What is it? What is it made of?
Functionalism
addressed the purpose of behavior
Concerned with how the brain or mind helps humans function or adapt
By William James (mind is adaptive)
What does it do for us?
Gestalt Psychology
- arose in opposition of structuralism
- says the whole of personal experience is more than the sum of perceptions
By Max Wertheimer
Sigmund Freud
neurologist
human behavior is determined by unconscious mental processes
developed psycholanalysis
themes- unconscious influence, early years are formative
Behaviorism
emphasize environmental forces on observable behavior
By John B. Watson then B. F. Skinner, pavlov
Cognitive Psychology
The study of mental functions such as intelligence, thinking, language, memory, and decision making
-mind= information processor
Social Psychology
focuses on situations on how interactions shape people
-attitudes, relations, influence
IRB
does not evaluate scientific merit
2 steps to inform participant-
informed consent- rights as participants
debriefing- after study, offer desensitization help (ie. counseling)
observational methods
naturalistic- unobtrusive
-descriptive notes> can introduce biases
participant observation-covert, not unobtrusive
-going undercover
-high external validity, minimize reactivity
-low internal validity (can not draw cause and effect conclusions)
-observation bias
self reporting method
case studies
-person or group has something unusual
-pros- lots of info, high external validity, can predict behavior
-limits- social desirability bias, low internal validity, observer bias
experiments
high internal validity
low external validity- artificial setting/task, convneience sampling
observer bias
expectancy effects
longitudinal fissure
runs down center of brain
has corpus callosum (thick bands of fibers that connect hemispheres)
Ventricles
filled with cerebrospinal fluid
schizophrenia- have larger ventircles
hydrocephalus
water on brain
blockage in ventricles causes fluid to accumulate and push on brain tissue
made but not absorbed
temporal lobe
broken into superior, middle, and inferior gyri (wrinkles on brain)
auditory cortex- wernicke's
memory areas
object and face recognition
prefrontal cortex
functions: planning, regulating behavior, directing attention
case studies
1. Phineas Gage- could function but not lead
2. Frontal lobotomy- emotionally flat
amygdala
middle gyrus
fear, facial responses
hippocampus
middle gyrus
processor of new information, makes memories
dementia, amnesia
basal ganglia
connected to frontal lobe and other motor areas
related to voluntary movement and reward related movement
nucleus accumbens
aphasia
deficit
parietal lobe
senses converge, spatial awareness, reading, calculation
devoted to touch
fusaform gyrus
between occipital and temporal
Cross-cutting Research
Frontal lobe - cuts across different research areas
Used to be studying one type of disorder - Realized that same symptoms were showing up in the same research ideas
Interdisiciplinary
Working as a team with people from different backgrounds
Ex. Neurosciences, education, gerontology, music
Primary Goals of Science
description
prediction
control
explanation
Critical thinkers:
1. question claims
2. seek definitions for the parts of the claims
3. evaluate the claims by looking for well-supported evidence
Theory
1. asks questions about how an observable thing works
2. consts of interconnected ideas
Hypothesis
1. is an attempt to answer a theory's questions
2. consists of a testable prediction that should be observed if the theory is correct
six steps of the Scientific method
1. forming a hypothesis
2. conducting a literature review
3. designing a study
4. conducting a study
5. analyzing the data
6. reporting the results
3 types of research in Psych
1. Descriptive
2. Correlational
3. experimental
Independent variable
variable that gets manipulated in a research study
Dependent variable
variable that gets measured in a research study
Operational definition
a definition that qualifies (describes) and quantifies (measures) a variable so the variable can be understood objectively
Descriptive Studies
observing and recording the behavior of people/animals
Ex. case study, participant vs naturalistic, surveys
Hawthorne effect
changes in behavior that occur when people know that others are observing them
Correlational Studies
Describe and Predict how variables are related
Ex. postive vs negative correlation, zero correlation
Directionality Problem
uncertain which variable caused the other
Ex. does less sleep cause more stress
or more stress cause less sleep
Third Variable Problem
C actually causes both A and B
Ex. Texting while driving (A) is correlated with driving dangerously (B). Risk taking (C) causes some people to text while driving. (C → A) and Risk taking (C) causes some people to drive dangerously. (C → B)
Experimental Studies (Method)
tests whether a change int he independent variable changes the dependent variable
Confound
anything that affects the dependent variable, a source of error
construct validity
the extent to which variables measure what they are supposed to measure
external validity
the degree to which the findings of a study can be generalized to other people, settings, or situations
internal validity
the degree to which the effects observed in an experiment are due to the independent variable and not confounds
reliability
consistency
Central tendency
represents typical response or behavior of group as whole
Central Nervous system
brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
all the nerves not part of CNS
Somatic nervous system
controls skeletal muscles, skin input
sensory system: afferent (to brain)
motor system: efferent (away from brain)
Automatic Nervous system
regulates glands, blood, internal organs
Sympathetic Nervous system
energy output, excites you
Parasympathetic Nervous system
conserves energy, maintains quiet state
Types of neurons
Sensory (afferent): detect info from physical world (goes from skinto primary cortex)
motor (efferent): direct muscles to contract or relax (goes from brain to muscles)
interneurons: communicate within local or short-distance circuits
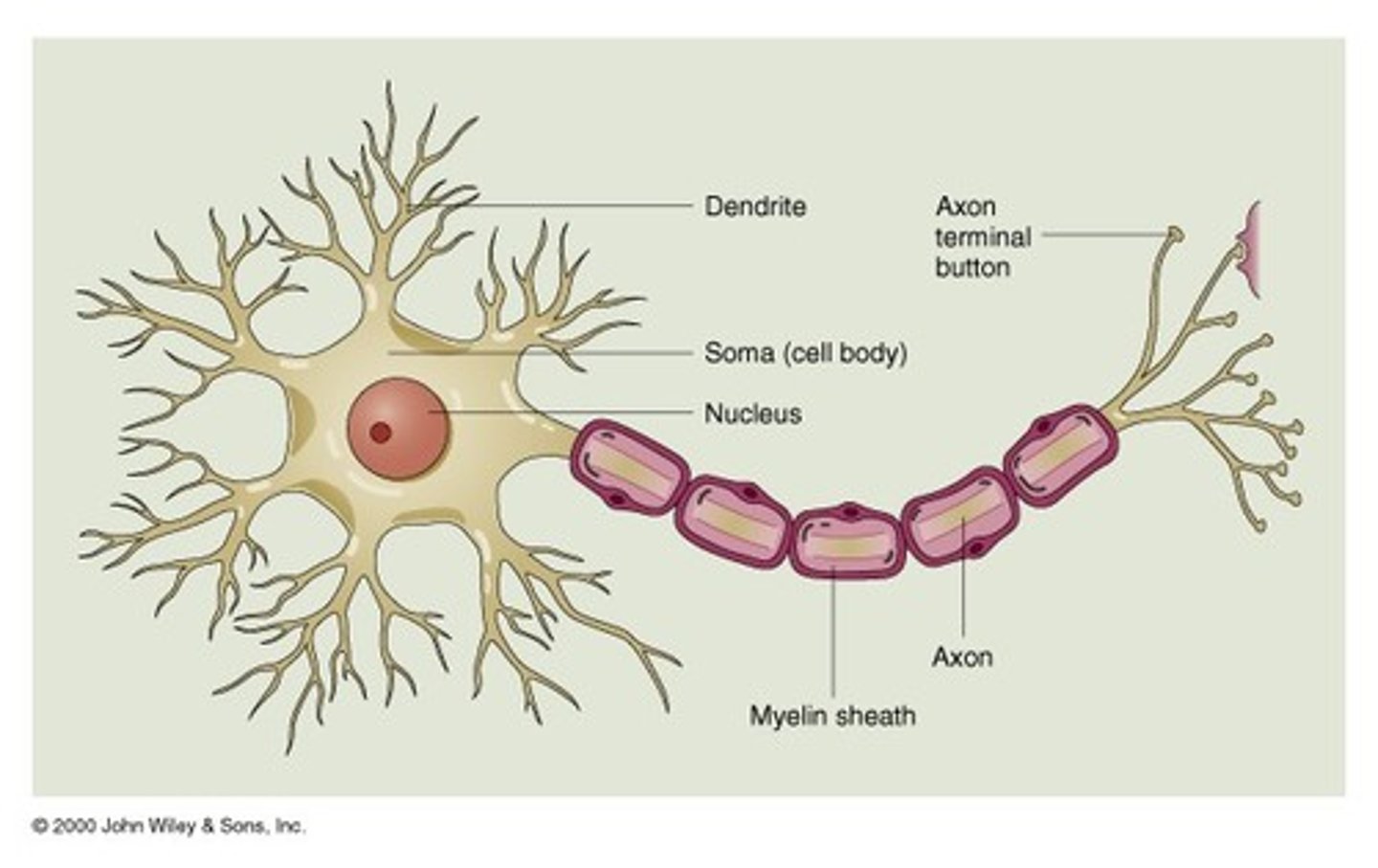
dendrite
cell body
axon
terminal buttons
synapse (synaptic cleft)
vi. myelin sheath
nodes of Ranvier
resting membrane potential
electrical change (difference): negative on the inside vs outside
Excitatory signals
reduce polarization, increase action potential
Inhibitory signals
increase polarization, decrease action potential
Agonist
mimics action of a neurotransmitter, increases reaction
Antagonist
dug that blocks action of a neurotransmitter, decreases reaction
Polarity of neuron inside compared to outside
-70mv
Action Potential Process
- ligand channels open due to the receptor-binding, sodium comes in
- threshold is reached at axon hillock
- sodium rushes into the axon
- trigger, trigger all the voltage gated sodium channels
- Propagatgion down axon "rush"
- Neurotransmitter is released at the end
Ca 2+
facilitates release of neurotransmitters
Cerebral Cortex
4 Lobes:
- Frontal
- Parietal
- Occipital
- Temporal
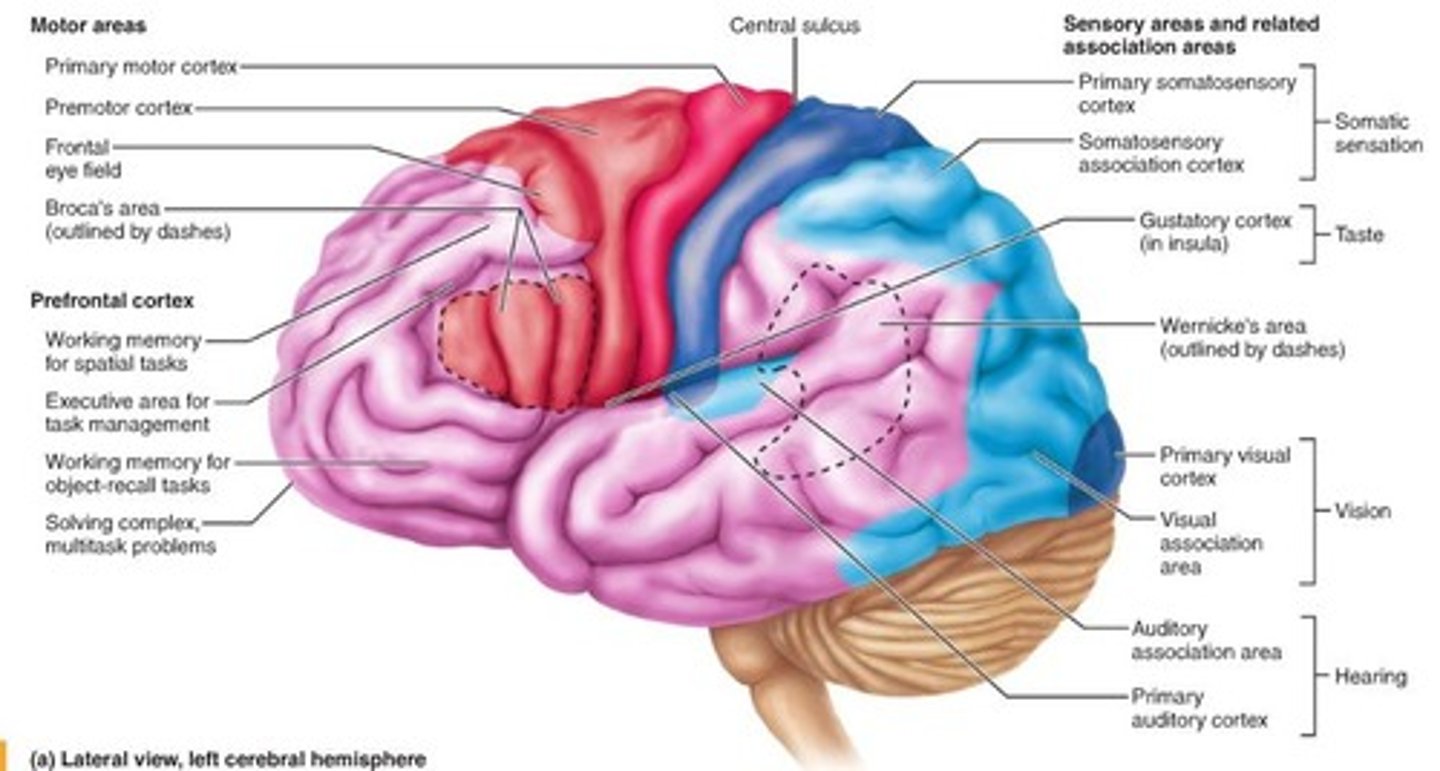
Frontal Lobe
attention, inhibition, decision making, movement
- prefrontal cortex: planning, regulating behavior, directing attention, emotions
- primary motor cortex:
- Broca's Area: speech
Temporal Lobe
hearing, face and objection recognition
- Superior, middle and inferior gyri
- Primary auditory cortex
- Wernicke's area: speech comprehension
Limbic system
feeling
- Thalamus: sensory relay station
- Amygdala: fear and emotion, facial recognition
- Hippocampus: memory
-basal ganglia: planning/producing movement
Basal Ganglia
circuit connected to frontal lobe and otrher motor areas
- voluntary movement, plannign movemen
- uses dopamine, ex. parkinson's
Occipital Lobe
Vision
largest area= primary visual cortex
Parietal Lobe
sense converge area, spatial awareness, sight+sound = meaning (reading)
- somatosensory cortex: touch input
attention
Dorsal stream
Where
spactial awareness
parietal -> frontal
Ventral stream
What
object recognition
parietal -> temporal
Cerebellum
posture, balance, visual tracking
highly practiced body movements (muscle memory)
- Medulla and Pons : regualte heart rate, breathing
Excitatory
Na+
Inhibitory
Cl-
Acetylocholine
Motor control over muscles
learning, memory, sleeping and dreaming
alzheimer's
Epinephrine
Energy
Norepinephrine
Arousal, vigilance, and attention
pons-> brain
pons -> sympathetic NS
anti-depressants
Serotonin
emotional states, impulsiveness
dreaming
LSD, mushrooms
dopamine
reward and motivation
parkinson's: substantia nigra -> basal ganglia
reward: nucleus accumbens
attention: prefrontal cortex
GABA
motor control for voluntary
inhibition of action potentials
anxiety reduction, results in seizure if not enough
Glutamate
enhancement of action potentials
learning and memory
excitatory
need to be equal to GABA
endorphin
pain reduction
reward
natural pain killers, heroin, morphine bind to these receptors
Agonist neurotransmitters
Benxodiazepines (Xanax, Ambien)
Barbiturates (phenobarbital)
Alcohol
Anti-convulsant medication
Change blindness
a failure to notice large changes in one's environment
Subliminal Perception
the processing of information by sensory systems without conscious awareness
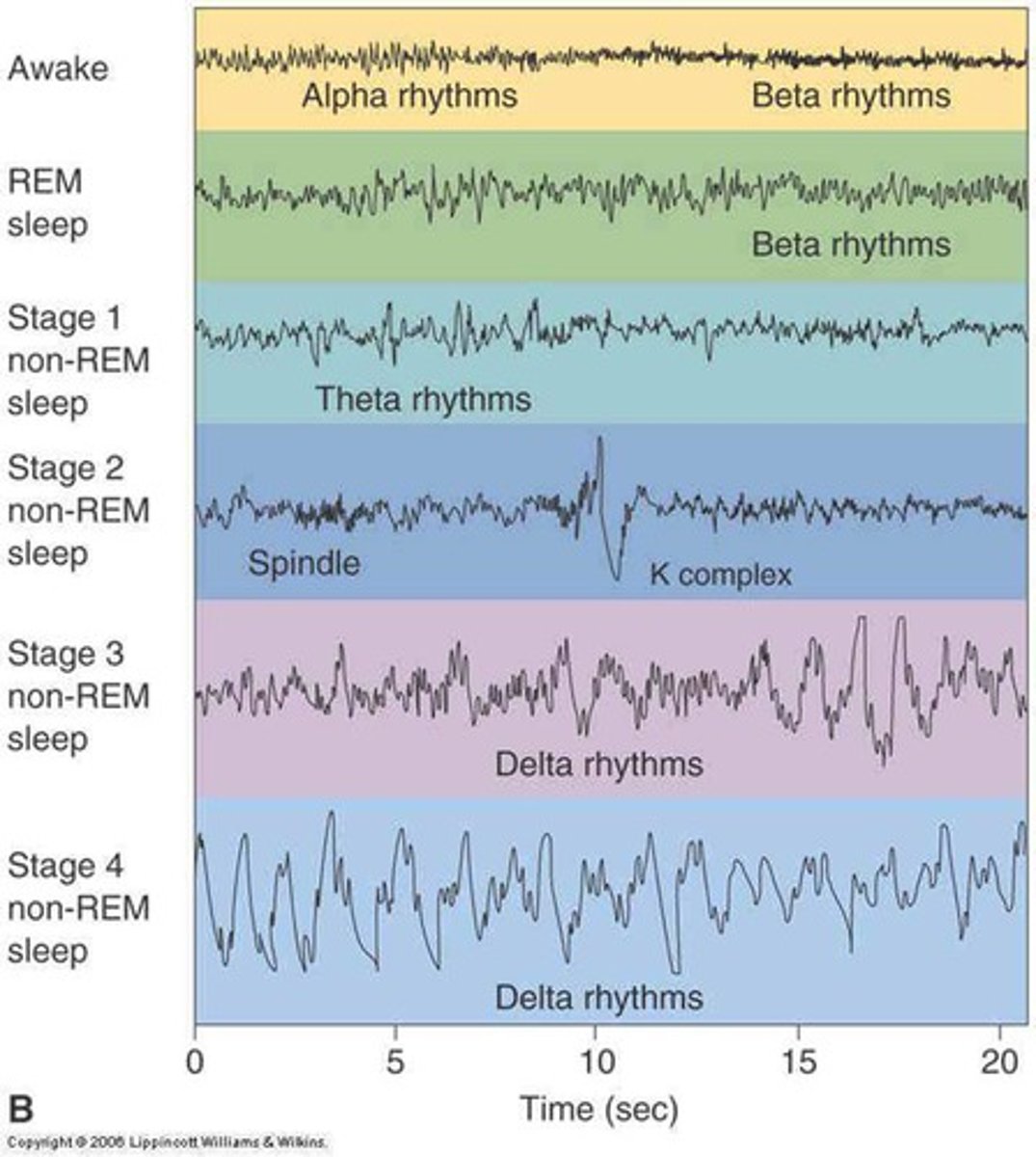
SWS
Slow wave sleep
deep sleep
stage 3-4
REM
rapid eye movement
occipital + brain stem is active
paralyzed
dreaming
deepest stage
Narcolepsy
- Affects the awake state
- Extreme daytime sleepiness, falling asleep
- Too much REM sleep
○ No deep sleep
- Linked to low hypocretin
○ Help Excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain
- May occur with cataplexy
○ Go into random sleep cycles
○ Lose muscle tone
REM behavior disorder
- Happens more in men
- During REM don't have muscle inhibition
- Higher risk of Parkinson's disease
- hits people (LOL)
Sleep paralysis
- 3/4 REM cycle
- Continued muscle inhibition
Cannot move even when conscious
PHD vs PsyD
PsyD no research training
cant be educators
at professional schools
psychiatrist
MD
medial perspective- can prescribe medication
Master Level Training
individual practive
talking/communication support
Why is psych misunderstood?
considered common sense
behavior is easy to theorize about
therapy is not specific or regulated
crisis debriefing, rebirthing
2 historic debates
nature vs. nurture (2/3 genetics driven, 1/3 other)
mind body problem- connected
glial cells
support- blood vessels to cell
clean up
support neural migration (only in prenatal)
facilitate nerual communication
form myelin
myelin in PNS
somatosensory, schwann cells